Professional Documents
Culture Documents
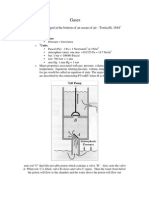
State 1 Millibar
State 1 Millibar
Uploaded by
sibi Raj0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageOriginal Title
7. State 1 millibar
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageState 1 Millibar
State 1 Millibar
Uploaded by
sibi RajCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
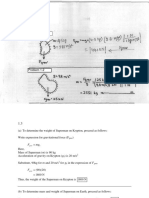
1.
nderstanding Millibar and Bar:
The millibar (mb) and the bar are units of pressure commonly used in
meteorology and other scientific fields.
The bar is a larger unit of pressure, while the millibar is a smaller unit.
2. Definition of Millibar:
The millibar is defined as one one-thousandth of a bar. This means that
1 millibar is equal to 1100010001 bar.
3. Conversion to Pascals:
To further understand the value of a millibar, it's helpful to convert it to
pascals, which is the SI unit of pressure.
1 bar is equal to 100,000 pascals. Therefore, 1 millibar is equal to
1100010001 of 100,000 pascals, which simplifies to 100 pascals.
So, 1 millibar is equivalent to 100 pascals.
4. Relationship to Newton per Square Meter:
Now, to relate this to newtons per square meter (N/m²), which is
another unit of pressure:
1 pascal (Pa) is defined as 1 newton per square meter (N/m²).
Since 1 millibar is equal to 100 pascals, it can also be expressed as 100
N/m².
Therefore, 1 millibar is equivalent to 100 N/m².
5. Practical Application in Meteorology:
In meteorology, atmospheric pressure is often measured in millibars.
For example, standard atmospheric pressure at sea level is
approximately 1013.25 millibars, which is equivalent to 101,325 pascals
or 101,325 N/m².
Therefore, 1 millibar is equal to 1100010001 of a bar, which is equivalent to 100
pascals or 100 newtons per square meter (N/m²). This relationship is important in
meteorology for measuring atmospheric pressure and understanding weather
patterns.
You might also like
- MSL Technical Guide 19 Measuring Atmospheric Pressure With A BarometerDocument4 pagesMSL Technical Guide 19 Measuring Atmospheric Pressure With A BarometerkumarNo ratings yet
- KhalidDocument3 pagesKhalidSyed Adnan AqibNo ratings yet
- Orals MetDocument1 pageOrals MetcaptyashpalNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Lecture Notes - SCI 3114Document84 pagesFluid Mechanics - Lecture Notes - SCI 3114Sharlene Cecil PagoboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1a GasesDocument12 pagesChapter 1a GasesKarunakarNo ratings yet
- SCH 103 Physical Chemistry 1 Lecture Notes 1 of 2020.Document16 pagesSCH 103 Physical Chemistry 1 Lecture Notes 1 of 2020.Samwel Ochok100% (1)
- 7 1 Power in The WindDocument1 page7 1 Power in The WindDennis Dale FanogaNo ratings yet
- Pressure: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesPressure: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadarla999No ratings yet
- SCH 103 Lecture Notes 2020 Part 1 Dec 11th.Document58 pagesSCH 103 Lecture Notes 2020 Part 1 Dec 11th.Samwel Ochok100% (2)
- atmospheric pressureDocument9 pagesatmospheric pressureFizza FatimaNo ratings yet
- Units of PressureDocument3 pagesUnits of PressureEric PierceNo ratings yet
- Orals MetDocument3 pagesOrals MetcaptyashpalNo ratings yet
- PRESSUREDocument2 pagesPRESSUREZoteloNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 PressureDocument5 pagesTopic 4 PressureRaymund SuaybaguioNo ratings yet
- Units of MeasurementDocument18 pagesUnits of MeasurementJohn PhilippNo ratings yet
- SIALANA Pressure of GasDocument14 pagesSIALANA Pressure of GasTito V. Bautista Jr.No ratings yet
- PressureDocument228 pagesPressureDhirajMadanNo ratings yet
- AP Unit8Document15 pagesAP Unit8Abhay Shankar BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Mechanism For DiffractionDocument13 pagesMechanism For DiffractionraghvendrmNo ratings yet
- Vikash Babu Fundamentals of Gas Dynamic-15-24Document10 pagesVikash Babu Fundamentals of Gas Dynamic-15-24عمر ربيع المحلاوىNo ratings yet
- Konversi TekananDocument4 pagesKonversi TekananHuyuth HuyNo ratings yet
- Units - MDocument26 pagesUnits - MApurva ChoukseyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 M3Document3 pagesChemistry 2 M3Rain AlmsNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Chemical Analysis: Edition 8Document34 pagesQuantitative Chemical Analysis: Edition 8Louay MohsenNo ratings yet
- PRESSUREDocument2 pagesPRESSUREannmarieNo ratings yet
- Pressure MeasurementDocument18 pagesPressure Measurementhadeed shaikhNo ratings yet
- Steam Engineering Principles and Heat TransferDocument99 pagesSteam Engineering Principles and Heat Transferalex mobileNo ratings yet
- CH 4 States of Matter I (Gases)Document30 pagesCH 4 States of Matter I (Gases)batazaiNo ratings yet
- AltimeterAppNote1Document12 pagesAltimeterAppNote1Ezza Yang Mana LagiNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Pressure - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesAtmospheric Pressure - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Environment - AtmosphereDocument26 pagesEnvironment - AtmosphereColeen RamosNo ratings yet
- General Science 4Document44 pagesGeneral Science 4dayakar100% (1)
- Lec 1Document23 pagesLec 1Sourya VarenyaNo ratings yet
- What Are The PrefixesDocument17 pagesWhat Are The PrefixesAmeer AzharNo ratings yet
- Pressure Units ConversionsDocument3 pagesPressure Units ConversionsK S RaoNo ratings yet
- Problem 1.1Document32 pagesProblem 1.1리재준No ratings yet
- Fluid PressureDocument28 pagesFluid PressureHASSAN ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Naval Weapons EngineeringDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Naval Weapons Engineeringsaravanaraj4uNo ratings yet
- Met1 PDFDocument6 pagesMet1 PDFRaveena SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assosa University: Compressible FlowDocument74 pagesAssosa University: Compressible FlowWillky FrezerNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanical Engineering PrinciplesDocument40 pagesBasic Mechanical Engineering PrinciplesjoelNo ratings yet
- Units and Conversion FactorsDocument1 pageUnits and Conversion FactorsdpkNo ratings yet
- Inherent NoiseDocument1 pageInherent NoiseSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- Gauge Pressure AbsoluteDocument3 pagesGauge Pressure AbsoluteWin AlcaideNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Compressible FlowDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Compressible Flowram kishor singhNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals OF Fluid MechanicsDocument7 pagesFundamentals OF Fluid MechanicsMike Adrian CerbitoNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Aerodynamics: Iiae 2016Document31 pagesAircraft Aerodynamics: Iiae 2016Pushkar KolharNo ratings yet
- Properties of GasesDocument61 pagesProperties of GasesHye Rin KangNo ratings yet
- Bernoullis Equation and Fluids Statics 2021Document17 pagesBernoullis Equation and Fluids Statics 2021Faizan RehmanNo ratings yet
- One Volt Representing 54435Document1 pageOne Volt Representing 54435Siva GuruNo ratings yet
- 15 08 14 15 46 55 2808 Ccet0280 PDFDocument103 pages15 08 14 15 46 55 2808 Ccet0280 PDFGaurav RajputNo ratings yet
- GP6 PressureDocument5 pagesGP6 Pressuredinakempho3No ratings yet
- METEOROLOGYDocument132 pagesMETEOROLOGYMariaEnache23No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - ReviewerDocument72 pagesFluid Mechanics - ReviewerDominic DominguezNo ratings yet
- One Volt Representing CFHHHDocument1 pageOne Volt Representing CFHHHSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- Boyles Law Powerpoint Presentation MELCS 1 QUARTER 4 Prosperity and IndustryDocument15 pagesBoyles Law Powerpoint Presentation MELCS 1 QUARTER 4 Prosperity and IndustryJeo ShinNo ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument47 pagesAtmosphereRocker HuzzNo ratings yet
- Units, Trigonometry, and Vectors: Spec 11-3 General Physics 1Document13 pagesUnits, Trigonometry, and Vectors: Spec 11-3 General Physics 1Leonard Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations and the Principles of Electromagnetic PhenomenaFrom EverandMaxwell's Equations and the Principles of Electromagnetic PhenomenaNo ratings yet