Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 11
Chapter 11
Uploaded by
duyennthds170525Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 11
Chapter 11
Uploaded by
duyennthds170525Copyright:
Available Formats
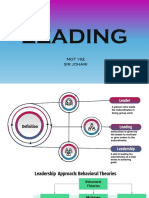
As a process, the use of noncoercive
influence to shape the group’s or
organization’s goals, motivate behavior
toward the achievement of those goals, and
help define group or organizational culture
The meaning of Leadership
As a property, the set of characteristics
attributed to individuals who are perceived
to be leaders
Distinctions between Management and
The Nature of Leadership Leadership
Legitimate power - authority
Power: The ability to affect the behavior of
Reward power
others
Coercive power
Leadership and Power
Referent power
Power: The ability to affect the behavior of
others
Expert power
Leadership Traits
Generic Approaches to Job-centered leader behavior
Michigan Studies (Rensis Likert)
Leadership (universal Employee-centered leader behavior
perspective)
Initiating-structure behavior
Leadership Behaviors Ohio State Studies
Consideration behavior
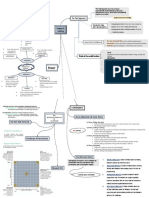
Concern for production
Managerial Grid
Concern for people
Leader-member relations
Least preferred coworker Theory (LPC
Task structure
Theory)
Position power
Directive
Supportive
Path-Goal Theory Leader behavior
Participative
The Nature of Situational Approaches to
Achievement-oriented
Leadership
Leadership Decision significance
Decision timeliness
Decide
Consult (individually)
Vroom’s Decision Tree Approach
Decision-making styles Consult (group)
Facilitate
Delegate
out-group
The Leader-member exchange Approach
in-group
Substitutes for leadership
Related Approaches to
Charismatic Leadership
Leadership
Transformational Leadership
Strategic Leadership
Emerging Approaches to
Cross-Cultural Leadership
Leadership
Ethical Leadership
Inducement
Common Political Behaviors Persuasion
Political Behavior in Coercion
Organizations Impression management
Managing Political Behavior
You might also like
- Leadership Theory and Practice - Chap1 Northouse 8th Ed.Document9 pagesLeadership Theory and Practice - Chap1 Northouse 8th Ed.Amade Sene100% (1)
- Cockney MonologuesDocument2 pagesCockney MonologuesLaReceHawkins86% (7)
- Isimba - A Church Management System For STDocument22 pagesIsimba - A Church Management System For STAllan Credo100% (3)
- Chapter 9 TestbankDocument34 pagesChapter 9 Testbankvx8550_373384312100% (5)
- IFA Coaching Session PlannerDocument2 pagesIFA Coaching Session Plannerabdesslam chamamiNo ratings yet
- Leadership and Styles of Leadership - Change ManagementDocument19 pagesLeadership and Styles of Leadership - Change Managementphamhuynh nhulyNo ratings yet
- Ch6 - LeadingDocument12 pagesCh6 - LeadingAris HushainiNo ratings yet
- Rebyuwer Siguro Sa Orgbev Chapter 11Document4 pagesRebyuwer Siguro Sa Orgbev Chapter 11Jerico DungcaNo ratings yet
- Leader SHIP vs. Manag EmentDocument1 pageLeader SHIP vs. Manag EmentMuhammad Mubeen Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Leadershipand The Art of DiscretionDocument6 pagesLeadershipand The Art of DiscretionJovanie BeñolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 LeadershipDocument1 pageChapter 12 LeadershipHong Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter Fourteen: LeadershipDocument22 pagesChapter Fourteen: LeadershipTanmay PednekarNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Development of Leadership TheoryDocument22 pagesWeek 1 Development of Leadership Theoryagung prawiraNo ratings yet
- Leadership Defined Trait Theory: Student Name: Oana Chiriac Student Number:179160789Document1 pageLeadership Defined Trait Theory: Student Name: Oana Chiriac Student Number:179160789Oana ChiriacNo ratings yet
- UGB 164final-1Document1 pageUGB 164final-1Oana ChiriacNo ratings yet
- Leadership Defined Trait Theory: Student Name: Oana Chiriac Student Number:179160789Document1 pageLeadership Defined Trait Theory: Student Name: Oana Chiriac Student Number:179160789Oana ChiriacNo ratings yet
- Leadership ManagementDocument3 pagesLeadership ManagementElla SugayNo ratings yet
- HBO SemiFinalsDocument6 pagesHBO SemiFinalsgracezyl18No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 LeadershipDocument26 pagesChapter 7 Leadershipmukesh paridaNo ratings yet
- Leading (Slide)Document7 pagesLeading (Slide)AldrinNyandangNo ratings yet
- 6 Lecture UpdatedDocument20 pages6 Lecture Updatedlonghtgbh200181No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Managers & Managing (JG) : Management Efficiency EffectivenessDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - Managers & Managing (JG) : Management Efficiency EffectivenessDiva Tertia AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Leadership: Presented By: Debasish SahaDocument21 pagesLeadership: Presented By: Debasish Sahadebasish_saha87No ratings yet
- Leadership and Styles of Leadership - Change ManagementDocument19 pagesLeadership and Styles of Leadership - Change ManagementDuyên PhúNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument3 pagesAnxiety DisorderElla SugayNo ratings yet
- Organisational Behavior OVERALL PPT PPTDocument221 pagesOrganisational Behavior OVERALL PPT PPTHailemariam KibretNo ratings yet
- Leadership by Milkyas SolomonDocument17 pagesLeadership by Milkyas SolomonVerity SplendourNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document10 pagesTopic 1eida5982No ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Nature of LeadershipDocument10 pagesTopic 1 The Nature of LeadershipNg Lee LeeNo ratings yet
- POM FinalDocument15 pagesPOM FinalAnu SinhaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Organization DesignDocument5 pages2 - Organization DesigngülraNo ratings yet
- Presentation1.Pptx HospiDocument8 pagesPresentation1.Pptx HospiJant Joyce U. UlepNo ratings yet
- 10.25.2021 Organizational Systems Part 2Document17 pages10.25.2021 Organizational Systems Part 2anitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6yasmeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - IntroductionAndrew NagehNo ratings yet
- Leadership Agility: A Business Imperative For A VUCA WorldDocument1 pageLeadership Agility: A Business Imperative For A VUCA WorldMuhamad AbdiNo ratings yet
- HM003 - Sahil Kumar - Assignmant 3 - An E-Poster PresentationDocument3 pagesHM003 - Sahil Kumar - Assignmant 3 - An E-Poster PresentationjdncwefdfnNo ratings yet
- MGT 400 Behavioral Management TheoryDocument5 pagesMGT 400 Behavioral Management TheoryALIA MAISARAH ABDUL RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: 1. Conceptions (P) 4. Functions & Roles (P, M, D)Document1 pageAssignment 1: 1. Conceptions (P) 4. Functions & Roles (P, M, D)Long NguyễnNo ratings yet
- OCD Chapter 3 Group 3Document10 pagesOCD Chapter 3 Group 3Akshay TyagiNo ratings yet
- CBR-Leadership-W6-L26 to L30(1)-38Document1 pageCBR-Leadership-W6-L26 to L30(1)-38lnarashimman76No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 LeadershipDocument3 pagesChapter 9 LeadershipKatleen DugenioNo ratings yet
- Northouse8e PPT 04Document21 pagesNorthouse8e PPT 04ARSLAN MEHMOODNo ratings yet
- Mpu 323Document12 pagesMpu 323Cải NgồngNo ratings yet
- Orgbev CH 11Document4 pagesOrgbev CH 11xoxo.guapa08No ratings yet
- Session 4Document29 pagesSession 4ahmadNo ratings yet
- Leadership and ManagementDocument5 pagesLeadership and ManagementElizabella Henrietta TanaquilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LeadershipDocument20 pagesIntroduction To LeadershipFayazul Hasan100% (2)
- Lecture 3 - LeadershipDocument34 pagesLecture 3 - LeadershipLavan SathaNo ratings yet
- CORP2165D Lecture 04Document26 pagesCORP2165D Lecture 04kinzi chesterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Basic Approaches To LeadershipDocument21 pagesChapter 11: Basic Approaches To LeadershipAnna MahmudNo ratings yet
- Part One Leadership Is A Process, Not A Position: PrefaceDocument1 pagePart One Leadership Is A Process, Not A Position: PrefaceLI WilliamNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument29 pagesLeadershipcaptainrashid89No ratings yet
- 20220729175037MOHAMED014Block 11 Summary LeadershipDocument29 pages20220729175037MOHAMED014Block 11 Summary Leadershipnicholas wijayaNo ratings yet
- Leading 3 PDFDocument29 pagesLeading 3 PDFLeiden Jane Toledano100% (1)
- Sharing Power: EmpowermentDocument17 pagesSharing Power: EmpowermentEshu NarangNo ratings yet
- A Review of New Leadership Theories and Its ComponentsDocument12 pagesA Review of New Leadership Theories and Its ComponentsEmdad YusufNo ratings yet
- Leadership SkillsDocument106 pagesLeadership SkillsRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives Learning Objectives: Reflection Question Reflection QuestionDocument6 pagesLearning Objectives Learning Objectives: Reflection Question Reflection QuestionRona TuburanNo ratings yet
- Journal of Leadership Organizational Studies-2013-Simonet-199-213Document15 pagesJournal of Leadership Organizational Studies-2013-Simonet-199-213oyetunde ogundiwinNo ratings yet
- 4 Business Leadership Skills SlidesDocument23 pages4 Business Leadership Skills Slidesshaikha alrazooqiNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument16 pagesLeadershipPK SNo ratings yet
- Strategy-Driven Talent Management: A Leadership ImperativeFrom EverandStrategy-Driven Talent Management: A Leadership ImperativeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Sworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net WorthDocument2 pagesSworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net WorthKal El DadiNo ratings yet
- Rev JSRR 45765Document2 pagesRev JSRR 45765Amit BNo ratings yet
- TJC History 2021 BrochureDocument27 pagesTJC History 2021 BrochureMelissa TeoNo ratings yet
- Nemesis - TipsDocument2 pagesNemesis - TipsZoran StrajinNo ratings yet
- Fuller Factory#PricingDocument39 pagesFuller Factory#PricingkkkhattabbbNo ratings yet
- Esoteric Christianity 06 Being Born AgainDocument15 pagesEsoteric Christianity 06 Being Born AgainTortura ChinaNo ratings yet
- Philips+22PFL3403-10+Chassis+TPS1 4E+LA+LCD PDFDocument53 pagesPhilips+22PFL3403-10+Chassis+TPS1 4E+LA+LCD PDFparutzu0% (1)
- (Download PDF) Deviance and Social Control A Sociological Perspective 2Nd Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument53 pages(Download PDF) Deviance and Social Control A Sociological Perspective 2Nd Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFyoichiolanzo100% (9)
- Sankaran, Mahesh - Scogings, Peter F - Savanna Woody Plants and Large Herbivores (2020, John Wiley & Sons LTD)Document781 pagesSankaran, Mahesh - Scogings, Peter F - Savanna Woody Plants and Large Herbivores (2020, John Wiley & Sons LTD)Ariadne Cristina De AntonioNo ratings yet
- Explore (As) : Types of Commission and InterestsDocument4 pagesExplore (As) : Types of Commission and InterestsTiffany Joy Lencioco GambalanNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing - S. Jayaraman, S. Esakkirajan and T. VeerakumarDocument4 pagesDigital Image Processing - S. Jayaraman, S. Esakkirajan and T. VeerakumarBenedict IsaacNo ratings yet
- Licensure Examination For TeachersDocument14 pagesLicensure Examination For Teachersonin saspaNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionDocument32 pagesConstitutionAbhisht HelaNo ratings yet
- Audio Phile 2496Document5 pagesAudio Phile 2496Antonio FernandesNo ratings yet
- TL-WN722N (UN) (US) V2 Datasheet PDFDocument4 pagesTL-WN722N (UN) (US) V2 Datasheet PDFBender :DNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 The History of The Maritime IndustryDocument11 pagesLesson 3 The History of The Maritime IndustryMELİH KUTLUNo ratings yet
- Student Assesment PDFDocument1 pageStudent Assesment PDFBelaNo ratings yet
- Hanson Uk Cracked ConcreteDocument1 pageHanson Uk Cracked ConcreteAhmed Daahir AdenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Group 3 - Behavioral Processes in Marketing ChannelsDocument26 pagesChapter 4 - Group 3 - Behavioral Processes in Marketing ChannelsJanine Mariel LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Architecture in EthDocument4 pagesArchitecture in Ethmelakumikias2No ratings yet
- Assessment of Digestive and GI FunctionDocument23 pagesAssessment of Digestive and GI FunctionSandeepNo ratings yet
- MLR LLRDocument41 pagesMLR LLRKUNNAMPALLIL GEJO JOHNNo ratings yet
- Testable Concepts in MCQDocument188 pagesTestable Concepts in MCQrami100% (1)
- Report of Micro Project (2) - 1Document8 pagesReport of Micro Project (2) - 1ythNo ratings yet
- LEGAL REASONING SKILLS ProjectDocument19 pagesLEGAL REASONING SKILLS ProjectShreya Ghosh DastidarNo ratings yet
- BE1 Final Without Recheckreassessment - 453112Document1 pageBE1 Final Without Recheckreassessment - 453112MoloNo ratings yet