Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Info Sheet
Info Sheet
Uploaded by
sheiiiiiiii0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageOriginal Title
info sheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageInfo Sheet
Info Sheet
Uploaded by
sheiiiiiiiiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Acute Promyelocytic
Leukemia
HematulogZzz
What is APL?
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL), a fast-growing subtype of Acute Myeloid
Leukemia (AML) that develops from abnormal promyelocytes, can cause serious bleeding
and infection due to its disruption of normal blood cell production. However, APL is one of
the most curable forms of leukemia with early diagnosis and proper treatment.
This can crowd out normal cells in the bone marrow and cause hypercellularity. This
will the lead to disruption of production of all types of blood cells. This type of leukemia
accounts to 5-15% of all adults a year and approximately 600-800 new cases anually.
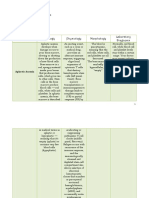
Signs and Symptoms Causes and Treatment
Risk Factors
Bleeding Issues: All-trans retinoic acid
Specific genetic
Easy bruising or unexplained (ATRA): The cornerstone of
abnormality
bleeding from gums, nose, or other APL treatment. It helps
involving the
sites. abnormal promyelocytes
translocation
Heavy menstrual bleeding. mature and die off.
between
Blood in stool or vomit (may appear Arsenic trioxide (ATO):
chromosomes 15
black or tarry). Often used in combination
and 17.
Bone Marrow Problems: with ATRA or for patients
Fatigue and weakness from anemia who don't respond well to
Creates a fusion
Increased susceptibility to infections ATRA alone.
protein that
due to low white blood cells. Chemotherapy
disrupts the
Other Potential Symptoms: Supportive care to manage
normal
Shortness of breath due to low red side effects, prevent
development of
blood cells or bleeding in the lungs. infections, and support
promyelocytes
Fever overall well-being.
Headaches, confusion, or vision
problems (rare, but can occur due to Course:BSMT3
bleeding in the brain Date:04/26/2024
Bone or joint pain
You might also like
- Bruising OSCE History Taking PaediatricsDocument6 pagesBruising OSCE History Taking PaediatricsJJ LimNo ratings yet
- SAP Dictionary FrenchDocument747 pagesSAP Dictionary FrenchClaudio Di FrancescoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 and 2 Obl IconDocument10 pagesChapter 1 and 2 Obl IconPia ValdezNo ratings yet
- Research Source Map Education Infographic in Violet Yellow Semi-Realistic Flat Graphic StyleDocument1 pageResearch Source Map Education Infographic in Violet Yellow Semi-Realistic Flat Graphic StylesheiiiiiiiiNo ratings yet
- AZATHIOPRINE Drug StudyDocument4 pagesAZATHIOPRINE Drug StudyAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AzathioprineDocument3 pagesDrug Study AzathioprineBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology:: in The Absence of Abnormal Infiltrate and With No Increase in ReticulinDocument6 pagesEpidemiology:: in The Absence of Abnormal Infiltrate and With No Increase in ReticulinSandeep m rNo ratings yet
- Hematology Topics 16-20Document20 pagesHematology Topics 16-20Angelo Jude CobachaNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (Drug Study)Document3 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia (Drug Study)Krisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Types of Anemia Etiology Physiology Morphology Laboratory DiagnosisDocument19 pagesTypes of Anemia Etiology Physiology Morphology Laboratory DiagnosisEG OngtecoNo ratings yet
- Pink Modern Breast Cancer Awareness InfographicDocument1 pagePink Modern Breast Cancer Awareness InfographicsheiiiiiiiiNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia For Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Anton Leonard Frca Mrcpi Jonathan Thompson BSC (Hons) MD FrcaDocument5 pagesAnaesthesia For Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Anton Leonard Frca Mrcpi Jonathan Thompson BSC (Hons) MD FrcaMinaz PatelNo ratings yet
- The Specialist: Consultation WithDocument8 pagesThe Specialist: Consultation WithsarabisimonaNo ratings yet
- Natural Remedies To Increase Platelet Count: Swati BurungaleDocument5 pagesNatural Remedies To Increase Platelet Count: Swati BurungaleraamNo ratings yet
- 4 PEDIA 8 - Bleeding DisordersDocument5 pages4 PEDIA 8 - Bleeding DisordersRainy Liony DuhNo ratings yet
- Study Guide in MCNDocument29 pagesStudy Guide in MCNEden RelacionNo ratings yet
- Trombositopenia AfpDocument5 pagesTrombositopenia AfpFadhila RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Aplastic Hemolitic 2021 OlgaDocument43 pagesAplastic Hemolitic 2021 OlgalaibaNo ratings yet
- Care of Preschoolers With Health ProblemsDocument5 pagesCare of Preschoolers With Health ProblemsmajoodhNo ratings yet
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument11 pagesAplastic Anemiaquidditch07No ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec IiiDocument4 pagesAnaphy Lec IiiKrishna LibrodoNo ratings yet
- Acute Biologic Crisis Quizlet 1Document4 pagesAcute Biologic Crisis Quizlet 1krissereiNo ratings yet
- Anemia AplasticaDocument14 pagesAnemia Aplasticajesus.alfonso.sanchez.herreraNo ratings yet
- Alteplase: Effects Your Health byDocument2 pagesAlteplase: Effects Your Health byMohit MokalNo ratings yet
- Adult Evans' SyndromeDocument12 pagesAdult Evans' SyndromeLilasNo ratings yet
- Atraumatic Acute Limb Ischemia: Clinical Presentation, Classification, Assessment and Management - A ReviewDocument7 pagesAtraumatic Acute Limb Ischemia: Clinical Presentation, Classification, Assessment and Management - A ReviewPeertechz Publications Inc.No ratings yet
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument14 pagesAplastic AnemiaAna Lilia CalvilloNo ratings yet
- ALSANGEDY BULLETS FOR PACES Behcet DiseaseDocument2 pagesALSANGEDY BULLETS FOR PACES Behcet Diseaseqayyum consultantfpscNo ratings yet
- What Is Anemia?Document3 pagesWhat Is Anemia?Puspa AntikaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test Day 1: Male: 13.5-17.5 G/DLDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test Day 1: Male: 13.5-17.5 G/DLRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis Paper PresentationDocument52 pagesLiver Cirrhosis Paper PresentationNagabharana Hm HollattiNo ratings yet
- Anemia AplásicaDocument11 pagesAnemia AplásicaStefanyNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Aplastic Anemia 212 1Document1 pageConcept Map Aplastic Anemia 212 1S AustinNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Hemopoietic SystemDocument29 pagesDiseases of Hemopoietic SystemRupak PandeyNo ratings yet
- Essential Thrombocytemia: Rahmawati Minhajat A. Fachruddin BenyaminDocument12 pagesEssential Thrombocytemia: Rahmawati Minhajat A. Fachruddin BenyaminMJ PutraNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia: in This PageDocument6 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia: in This Pagebabbajee4uNo ratings yet
- MielomaDocument4 pagesMielomaJefferson MorenoNo ratings yet
- Tromboembolismo FelimoDocument13 pagesTromboembolismo FelimoMicaela AlvarezNo ratings yet
- ThrombosisDocument9 pagesThrombosisLinmayee SamalNo ratings yet
- Osmosis 41Document1 pageOsmosis 41Sarawini KosolsombatNo ratings yet
- Acute Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument27 pagesAcute Ischemic Heart DiseaseJaymee CachoNo ratings yet
- Mr. Jones Case StudyDocument4 pagesMr. Jones Case StudyDiane JaravataNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1357303921000050 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S1357303921000050 MainKarla MonsalvoNo ratings yet
- Updates in Cardiac Amyloidosis. A ReviewDocument14 pagesUpdates in Cardiac Amyloidosis. A ReviewPuig CozarNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Case: Pathogenisis:: NmcastroDocument5 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Case: Pathogenisis:: NmcastroAngelo ErispeNo ratings yet
- III. FINAL Nursing Care of Clients With Disturbances in Male Female Reproduction Sexuality EditedVersionDocument26 pagesIII. FINAL Nursing Care of Clients With Disturbances in Male Female Reproduction Sexuality EditedVersionKurt PepitoNo ratings yet
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument2 pagesAplastic AnemiaDawnmurph Dharlene Wag-eNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders - SarahDocument17 pagesBleeding Disorders - SarahkhaledNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Clopidogrel)Document7 pagesDRUG STUDY (Clopidogrel)Fatima MohammedNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of The Full Blood Count in Systemic Disease - A Guide For The PhysicianDocument6 pagesInterpretation of The Full Blood Count in Systemic Disease - A Guide For The PhysicianKarthik SNo ratings yet
- ANEMIADocument28 pagesANEMIAwanda0% (1)
- 3 Inflammation Repair & Blood Disorder - Group 3Document6 pages3 Inflammation Repair & Blood Disorder - Group 3Denvic Nove G. BarberoNo ratings yet
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument19 pagesAplastic AnemiaShara SampangNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Arteri - VenaDocument44 pagesPenyakit Arteri - VenaAzkiaNo ratings yet
- Amiloidosis Cardiaca 2021Document10 pagesAmiloidosis Cardiaca 2021gragerinNo ratings yet
- Clinical Liver Disease - 2021 - Sharma - Liver Abscess Complications and TreatmentDocument5 pagesClinical Liver Disease - 2021 - Sharma - Liver Abscess Complications and TreatmentNaldo NathanNo ratings yet
- roDAKS Chapter 37Document3 pagesroDAKS Chapter 37John DavidNo ratings yet
- Hema - PointersDocument5 pagesHema - PointersLUALHATI VILLASNo ratings yet
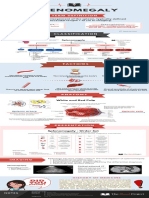
- Splenomegaly PDFDocument1 pageSplenomegaly PDFlakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis - Hematology BlockDocument40 pagesHemostasis - Hematology BlockamandaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyRea LynNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts for Patients: Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: Prompt action saves livesFrom EverandFast Facts for Patients: Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: Prompt action saves livesNo ratings yet
- Law On Treaties Group 4Document51 pagesLaw On Treaties Group 4Seyre Eser ArymNo ratings yet
- Sample Offer LettersDocument4 pagesSample Offer LettersAvinash KumarNo ratings yet
- A General Framework For The Integration of Computational Fluid Dynamics and Process Simulation - 2000 - F - Bezzo PDFDocument6 pagesA General Framework For The Integration of Computational Fluid Dynamics and Process Simulation - 2000 - F - Bezzo PDFRaúl RivasNo ratings yet
- Patricia Eldridge 4.19.23Document3 pagesPatricia Eldridge 4.19.23abhi kumarNo ratings yet
- Uv VarnishDocument4 pagesUv VarnishditronzNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Design Flow Using Altera's FPGA Development Board (DE2-115 T-Pad)Document107 pagesEmbedded Systems Design Flow Using Altera's FPGA Development Board (DE2-115 T-Pad)john smithNo ratings yet
- PandorasBoxv55EN 7824Document9 pagesPandorasBoxv55EN 7824jimNo ratings yet
- BRM Case StudyDocument2 pagesBRM Case StudyNaina lalwaniNo ratings yet
- Webdriver CodeDocument3 pagesWebdriver CodejailaxmieceNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument5 pagesHyperthermiaRapunzel Leanne100% (1)
- MBBN 750Document183 pagesMBBN 750Lamber LiNo ratings yet
- 129 Bba-206Document3 pages129 Bba-206Ghanshyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- 97 f150 PinoutDocument4 pages97 f150 PinoutUlises AlfaroNo ratings yet
- 8&9-High Voltage KitDocument7 pages8&9-High Voltage KitMinh VienNo ratings yet
- Food Beliefs and Food Supply Chains The Impact of Religion and Religiosity in IsraelDocument7 pagesFood Beliefs and Food Supply Chains The Impact of Religion and Religiosity in IsraelyssifzakiatuNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan-Biology Grade 8Document9 pagesDaily Lesson Plan-Biology Grade 8Zhaine MendozaNo ratings yet
- 11 Spring Security Registration Rememberme EmailverificationDocument5 pages11 Spring Security Registration Rememberme EmailverificationvigneshNo ratings yet
- BCI Moves Plea Urging SC To Direct Govt To Provide Interest-Free Loans Up To Rs 3 Lakhs Each For Lawyers in Need Due To COVID-19Document36 pagesBCI Moves Plea Urging SC To Direct Govt To Provide Interest-Free Loans Up To Rs 3 Lakhs Each For Lawyers in Need Due To COVID-19JAGDISH GIANCHANDANINo ratings yet
- Curriculum VitaeDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitaech MuzammalNo ratings yet
- Bacolod Brewery: Additive and Deductive Works: Material Diameter LengthDocument1 pageBacolod Brewery: Additive and Deductive Works: Material Diameter LengthWilliam Jefferson RañadaNo ratings yet
- Infoplc Net Technical Note Rlxib Ihw Wireless Modbus TCP m340Document39 pagesInfoplc Net Technical Note Rlxib Ihw Wireless Modbus TCP m340Jose LunaNo ratings yet
- Customer Is Always RightDocument5 pagesCustomer Is Always RightNikhil CoolNo ratings yet
- Kel IV ReportDocument18 pagesKel IV ReportAnoopAsokan0% (1)
- 2.2 Smaller Version of The Complete Personal Finance DashboardDocument823 pages2.2 Smaller Version of The Complete Personal Finance DashboardVijay YadavNo ratings yet
- Ch.3 ResDes Exp DescDocument12 pagesCh.3 ResDes Exp DescSangamesh BagaliNo ratings yet
- Land LawDocument19 pagesLand LawRitesh KumaiNo ratings yet
- Comix 35Document6 pagesComix 35oriol.berges.bergadaNo ratings yet
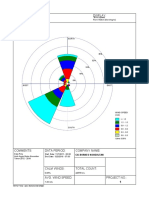
- Wind Rose Plot: DisplayDocument1 pageWind Rose Plot: Displaydhiecha309No ratings yet