Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hand Pe
Hand Pe
Uploaded by
Iffah Nabiha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views2 pagesOriginal Title
HAND PE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views2 pagesHand Pe
Hand Pe
Uploaded by
Iffah NabihaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
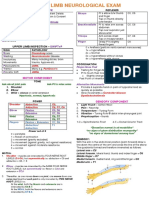
Hand examination
LOOK NEUROVASCULAR TEST 7 functions of the hand:
Skin ● discoloration ● Sensation Sensory territories and innervations of the hand 1) Power Grip – squeeze my fingers
-erythema (cellulitis) two-point discrimination 2) Hook Grip – hook my hand
-white (arterial insufficiency) ● Motor 3) Precision Grip hold pen
-blue/purple (venous congestion) radial nerve: test thumb IP joint extension against resistence 4) Lateral Pinch Grip – key grip
-black spots (melanoma) median nerve 5) Tip Pinch – pick up coin
-trophic changes recurrent motor branch: palmar abduction of thumb 6) Hand grasp
● scars/wounds anterior interosseous branch: flexion of thumb IP and index DIP ("A-OK sign") 7) Paperweight
Swelling ulnar nerve: cross-fingers or abduct fingers against resistence
Muscle ● thenar atrophy ● Vascular
atrophy median nerve involvement radial pulse
caused by carpal tunnel syndrome ulnar pulse
● interossei atrophy Allen's test
ulnar nerve involvement capillary refil
caused by cubital tunnel or cervical
radiculopathy NERVE ASSESSMENT
● subcutaneous atrophy Tinel's -tests for carpal tunnel syndrome
locally post-steroid injection -examiner percusses with two fingers over distal palmar
Deformity ●asymmetry crease in the midline
●angulation -positive if patient reports paresthesias in median nerve
●rotation distribution
●absence of normal anatomy (previous - also to test for nerve regeneration-look for pain for site
amputation) of raw nerve ending
●cascade sign Phalen's -tests for carpal tunnel syndrome
Fingers converge toward the scaphoid with the hands pointed up, the patient's wrist is allowed to
tubercle when flexed at the MCPJ and PIPJ flex by gravity in palmar flexion for 1 minutes maximum
if one or more fingers do not converge, then -positive if patient reports paresthesias in median nerve
trauma to the digits has likely altered normal distribution
alignment Carpal -For carpal tunnel
FEEL compression - pressure on transverse carpal ligament
● Masses (ganglions, nodules) Wrist masses (ganglions, nodules) test -positive if numbness
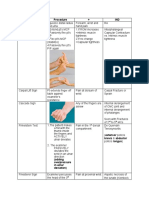
● Temperature Froment's tests for ulnar nerve motor weakness
warm: infection, inflammation sign patient asked to hold a piece of paper between thumb and
cool: vascular pathology radial side of index
● Tenderness positive if as the paper is pulled away by the examiner the
● Crepitus (fracture) patient flexes the thumb IP joint(FPL) in an attempt to
● Clicking or snapping (tendonitis) hold on to paper
● Joint effusion (infection, inflammation, trauma) Wartenberg's tests ulnar nerve motor weakness
sign patient asked to hold fingers fully adducted with MCP, PIP,
MOVE and DIP joints fully extended
Screen by positive if small finger drifts away from others into
-grip & open hand abduction
-make OK sign Jeanne's sign tests for ulnar nerve motor weakness
-prone & extend (claw) ask patient to demosntrate key pinch
-gong xi fa cai hand-HOB positive finding if patients first MCP joint is hyperextended
Hand examination
LOOK NEUROVASCULAR TEST 7 functions of the hand:
Skin ● discoloration ● Sensation Sensory territories and innervations of the hand 1) Power Grip – squeeze my fingers
-erythema (cellulitis) two-point discrimination 2) Hook Grip – hook my hand
-white (arterial insufficiency) ● Motor 3) Precision Grip hold pen
-blue/purple (venous congestion) radial nerve: test thumb IP joint extension against resistence 4) Lateral Pinch Grip – key grip
-black spots (melanoma) median nerve 5) Tip Pinch – pick up coin
-trophic changes recurrent motor branch: palmar abduction of thumb 6) Hand grasp
● scars/wounds anterior interosseous branch: flexion of thumb IP and index DIP ("A-OK sign") 7) Paperweight
Swelling ulnar nerve: cross-fingers or abduct fingers against resistence
Muscle ● thenar atrophy ● Vascular
atrophy median nerve involvement radial pulse
caused by carpal tunnel syndrome ulnar pulse
● interossei atrophy Allen's test
ulnar nerve involvement capillary refil
caused by cubital tunnel or cervical
radiculopathy NERVE ASSESSMENT
● subcutaneous atrophy Tinel's -tests for carpal tunnel syndrome
locally post-steroid injection -examiner percusses with two fingers over distal palmar
Deformity ●asymmetry crease in the midline
●angulation -positive if patient reports paresthesias in median nerve
●rotation distribution
●absence of normal anatomy (previous - also to test for nerve regeneration-look for pain for site
amputation) of raw nerve ending
●cascade sign Phalen's -tests for carpal tunnel syndrome
Fingers converge toward the scaphoid with the hands pointed up, the patient's wrist is allowed to
tubercle when flexed at the MCPJ and PIPJ flex by gravity in palmar flexion for 1 minutes maximum
if one or more fingers do not converge, then -positive if patient reports paresthesias in median nerve
trauma to the digits has likely altered normal distribution
alignment Carpal -For carpal tunnel
FEEL compression - pressure on transverse carpal ligament
● Masses (ganglions, nodules) Wrist masses (ganglions, nodules) test -positive if numbness
● Temperature Froment's tests for ulnar nerve motor weakness
warm: infection, inflammation sign patient asked to hold a piece of paper between thumb and
cool: vascular pathology radial side of index
● Tenderness positive if as the paper is pulled away by the examiner the
● Crepitus (fracture) patient flexes the thumb IP joint(FPL) in an attempt to
● Clicking or snapping (tendonitis) hold on to paper
● Joint effusion (infection, inflammation, trauma) Wartenberg's tests ulnar nerve motor weakness
sign patient asked to hold fingers fully adducted with MCP, PIP,
MOVE and DIP joints fully extended
Screen by positive if small finger drifts away from others into
-grip & open hand abduction
-make OK sign Jeanne's sign tests for ulnar nerve motor weakness
-prone & extend (claw) ask patient to demosntrate key pinch
-gong xi fa cai hand-HOB positive finding if patients first MCP joint is hyperextended
You might also like
- Shoulder Dislocation and Reduction - UpToDateDocument64 pagesShoulder Dislocation and Reduction - UpToDateCatedra 2018No ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve AssessmentDocument42 pagesCranial Nerve AssessmentValeryn Quiman100% (8)
- Karen - S Notes-Clinical ExaminationDocument11 pagesKaren - S Notes-Clinical ExaminationGanesh Namasivayam100% (3)
- DR Karen Short NotesDocument412 pagesDR Karen Short NotesNayantara Nair100% (2)
- Illustrated Rheumatology ExaminationDocument4 pagesIllustrated Rheumatology ExaminationHashraf Affendi50% (2)
- HAND ExaminationDocument11 pagesHAND ExaminationEbtesamNo ratings yet
- Test Name Procedure + IND: ND TH STDocument3 pagesTest Name Procedure + IND: ND TH STDesi SmithNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve-1Document35 pagesPeripheral Nerve-1Manirarora EtienneNo ratings yet
- O - Hand ExaminationDocument2 pagesO - Hand ExaminationTham Yuen SinNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument33 pagesCarpal Tunnel SyndromeRasYa DINo ratings yet
- Ingles Resumen FinalDocument26 pagesIngles Resumen FinalKarli ValentineNo ratings yet
- CasesDocument15 pagesCasesoha37229No ratings yet
- All Clinical Examinations GuideDocument29 pagesAll Clinical Examinations Guideasalizwa ludlalaNo ratings yet
- Iontophoresis Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument2 pagesIontophoresis Carpal Tunnel SyndromeIkre19No ratings yet
- Wrist and Hand Disease Description Pathophysiology Sign and Symptoms Management Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument4 pagesWrist and Hand Disease Description Pathophysiology Sign and Symptoms Management Carpal Tunnel SyndromeMei BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument22 pagesCarpal Tunnel SyndromePinimNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Exam LectureDocument30 pagesNeurologic Exam LectureJenro De MesaNo ratings yet
- US Spine ExtremitiesDocument3 pagesUS Spine ExtremitiesBrent DizonNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve AssessmentDocument42 pagesCranial Nerve Assessmentmalik003100% (1)
- Cranialnerveassessmentfinal 140501113414 Phpapp01 PDFDocument42 pagesCranialnerveassessmentfinal 140501113414 Phpapp01 PDFAlma Baterina100% (1)
- Diabetic Foot UlcerDocument6 pagesDiabetic Foot UlcerHengkai NeoNo ratings yet
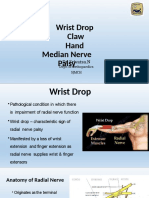
- Wrist Drop Claw Hand Median Nerve Palsy: Dr. Srivatsa.NDocument46 pagesWrist Drop Claw Hand Median Nerve Palsy: Dr. Srivatsa.NMurali KarthikkNo ratings yet
- OSCEstop Neurological Hand ExaminationDocument1 pageOSCEstop Neurological Hand Examinationtaek123No ratings yet
- Week 6 Cad Question TablesDocument4 pagesWeek 6 Cad Question Tablesapi-479499469No ratings yet
- REFERAT Koass Neurologi - Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument34 pagesREFERAT Koass Neurologi - Carpal Tunnel SyndromeVindhita RatiputriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17-Hand InjuriesDocument20 pagesLecture 17-Hand InjuriesIbrahim QariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 36Document3 pagesChapter 36Samantha QuintoNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System Examination: Overview & PurposeDocument5 pagesCentral Nervous System Examination: Overview & PurposebismahNo ratings yet
- Allll Exams Combinedd FinalDocument14 pagesAllll Exams Combinedd FinalAnshuNo ratings yet
- Rhumato5an Poly-Sd Canalaires2017Document3 pagesRhumato5an Poly-Sd Canalaires2017Amine OuanayaNo ratings yet
- Hand ExaminationDocument39 pagesHand ExaminationAhlam AliNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Hand: o o o oDocument5 pagesExamination of The Hand: o o o oGurunadh OrthoNo ratings yet
- UL Neuro ExamDocument1 pageUL Neuro ExamNayerShammaaNo ratings yet
- NEURO - Retdem: A. Testing For Corneal Reflex (CN5 & CN7 Test)Document1 pageNEURO - Retdem: A. Testing For Corneal Reflex (CN5 & CN7 Test)Peter GirasolNo ratings yet
- Neuromusculosklatal Disorders FK UnayaDocument62 pagesNeuromusculosklatal Disorders FK UnayaSuci MayveraNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Peripheral Nerve CompressionDocument4 pagesLec 2 Peripheral Nerve CompressionEmily MurrayNo ratings yet
- Locomotor - Hand Clinical Mark SheetDocument7 pagesLocomotor - Hand Clinical Mark SheetDrShamshad KhanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination - Karen Notes - SHIRI For BD DoctorsDocument11 pagesClinical Examination - Karen Notes - SHIRI For BD DoctorsHelp LineNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Peripheral Nerve CompressionDocument4 pagesLec 2 Peripheral Nerve CompressionEmily MurrayNo ratings yet
- AG 8th TermDocument50 pagesAG 8th TermNeelesh PatilNo ratings yet
- MED 201 Somatic Sensory System Examination IBDDocument5 pagesMED 201 Somatic Sensory System Examination IBDAnnika Ysabelle S. LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve Disorders (Dr. Ken)Document72 pagesPeripheral Nerve Disorders (Dr. Ken)Nurindha Shimelia M ZNo ratings yet
- Forearm, Wrist & Hand Special TestDocument17 pagesForearm, Wrist & Hand Special TestelinelisaNo ratings yet
- Clinical ExaminationDocument11 pagesClinical ExaminationLaura GranadosNo ratings yet
- Examination of The HandDocument20 pagesExamination of The HandOtnil DNo ratings yet
- W7 CTSDocument4 pagesW7 CTSStevanie SesiliaNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve Examination (Final)Document2 pagesPeripheral Nerve Examination (Final)Nurul Amalina OsmanNo ratings yet
- Hand Injuries Guidelines 2020Document64 pagesHand Injuries Guidelines 2020Andrew WongNo ratings yet
- Wrist&HandDocument31 pagesWrist&HandkjunhunNo ratings yet
- Conditions Peculiar To The HandsDocument22 pagesConditions Peculiar To The HandsAndrew WongkarNo ratings yet
- Obaid Hand ExaminationDocument2 pagesObaid Hand ExaminationAlaa ElbulukNo ratings yet
- Neuro 1 and 2 LabDocument3 pagesNeuro 1 and 2 LabHardikPatelNo ratings yet
- Week 8 PCP Workbook QuestionsDocument4 pagesWeek 8 PCP Workbook Questionsapi-479717740No ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Quick Recertific Ation SeriesDocument2 pagesCarpal Tunnel Syndrome: Quick Recertific Ation SeriesevaNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: BackgroundDocument2 pagesCarpal Tunnel Syndrome: Backgroundyoyo06chillinNo ratings yet
- (SEMINAR) Median Nerve Injury + Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument25 pages(SEMINAR) Median Nerve Injury + Carpal Tunnel SyndromeAda JoraimiNo ratings yet
- How Training Session 2b2Document1 pageHow Training Session 2b2Rhomizal MazaliNo ratings yet
- 3 Wrist EXDocument11 pages3 Wrist EXHarris TaheryNo ratings yet
- Neuro and Cranial Nerve Assessment GuideDocument1 pageNeuro and Cranial Nerve Assessment GuidepriyaNo ratings yet
- Role of Fascial Connectivity in Musculoskeletal Dysfunctions PDFDocument9 pagesRole of Fascial Connectivity in Musculoskeletal Dysfunctions PDFErika DiazNo ratings yet
- Free Review - June - Haag - enDocument5 pagesFree Review - June - Haag - enmaryloop1917No ratings yet
- A Singular Case Study: Acupuncture Treatment With GB20, GB21, UB11, LI4, LI16 For Acute Pain Management in Cervical SpondylosisDocument4 pagesA Singular Case Study: Acupuncture Treatment With GB20, GB21, UB11, LI4, LI16 For Acute Pain Management in Cervical SpondylosisSyam ChandrasekharanNo ratings yet
- 2023 Sensoriedade Interocepção AutismoDocument11 pages2023 Sensoriedade Interocepção AutismoGisella Mouta FaddaNo ratings yet
- PTJ/PZZ 182Document24 pagesPTJ/PZZ 182leticia coutinhoNo ratings yet
- Total Hip Replacement Rehab ProtocolDocument11 pagesTotal Hip Replacement Rehab ProtocolnurulishtimalNo ratings yet
- Wrist Joint and Carpal TunnelDocument30 pagesWrist Joint and Carpal TunnelWendysilakoNo ratings yet
- Tiktinsky Et Al - Electrotherapy, Yesterday, Today and TomorrowDocument6 pagesTiktinsky Et Al - Electrotherapy, Yesterday, Today and TomorrowCRISTOBAL JAVIER LOPEZ ALISTENo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Exercise Program Improves Foot Alignment in People With Flexible Flat Foot: A Randomised TrialDocument5 pagesA Comprehensive Exercise Program Improves Foot Alignment in People With Flexible Flat Foot: A Randomised Trial黃子庭No ratings yet
- Orthotics - Ul & LLDocument48 pagesOrthotics - Ul & LLReena PremNo ratings yet
- Industrial RehabDocument54 pagesIndustrial RehabMiti ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Short Wave DiathermyDocument73 pagesShort Wave DiathermySabarie PNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Exercise TherapyDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Exercise TherapyThopu UmamaheswariNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb, Abdomen & Pelvis Questions I MbbsDocument11 pagesLower Limb, Abdomen & Pelvis Questions I MbbsDarshan AcharyaNo ratings yet
- History of PTDocument1 pageHistory of PTJoserie HernaneNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPYESSAMIN GUADIZNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Topic 26 HealthDocument7 pagesUcsp Topic 26 HealthLiza EmmanuelleNo ratings yet
- Ask The Experts: Evidence-Based Practice: Percussion and Vibration TherapyDocument3 pagesAsk The Experts: Evidence-Based Practice: Percussion and Vibration Therapysebastian arayaNo ratings yet
- TannenbaumDocument12 pagesTannenbaumayunda sherinaNo ratings yet
- AHP - Blueprint and Reference (Arb)Document8 pagesAHP - Blueprint and Reference (Arb)arian tejaratNo ratings yet
- Dsusjrc04140026 Rev 3 Pinnacle STDocument32 pagesDsusjrc04140026 Rev 3 Pinnacle STXeniaNo ratings yet
- Comparing Craniosacral Therapy To Osteopathic and Sacro Occipital Technique Chiropractic Cranial Practitioners.Document4 pagesComparing Craniosacral Therapy To Osteopathic and Sacro Occipital Technique Chiropractic Cranial Practitioners.MitchellSNo ratings yet
- Sarhad University of Science & Information Technology, PeshawarDocument3 pagesSarhad University of Science & Information Technology, Peshawarkhan khanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Name: Cintia KrajnyákDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Name: Cintia Krajnyáklambda-7607ffNo ratings yet
- Somatics Exercises - Learn Thomas Hanna's Somatics ExercisesDocument12 pagesSomatics Exercises - Learn Thomas Hanna's Somatics ExercisesNicholas Featherston0% (1)
- Internal Fixation of Distal Fibula Fractures JFAS 1995Document9 pagesInternal Fixation of Distal Fibula Fractures JFAS 1995Evan BowlesNo ratings yet
- Final PPRDocument24 pagesFinal PPRAman hussainNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Physiotherapy Intervention by Using Ultrasound and Piriformis Stretching in Management To Reduce Pain in Piriformis SyndromeDocument3 pagesThe Effect of Physiotherapy Intervention by Using Ultrasound and Piriformis Stretching in Management To Reduce Pain in Piriformis SyndromeInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Muscle GroupsDocument25 pagesMuscle GroupsRoxana LorenteNo ratings yet