Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarense - Sample Questions
Unit 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarense - Sample Questions
Uploaded by
mariyamfathima7670 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Unit 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarense - Sample questions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesUnit 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarense - Sample Questions
Unit 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarense - Sample Questions
Uploaded by
mariyamfathima767Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
UNIT – 10 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
SAMPLE QUESTIONS
1. Give reasons for the following:
i) Chloroethane is insoluble in water.
ii) Thionyl chloride method is preferred for preparing alkyl chlorides from alcohols.
iii) Chloroform is stored in closed dark coloured bottles completely filled so that air
is kept out.
iv) C – Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than C – Cl bond length in CH 3 – Cl
v) SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemisation in optically active alkylhalides.
vi) Benzyl chloride is highly reactive towards the SN1 reaction.
vii) 2-bromobutane is optically active but 1-bromobutane is optically inactive.
viii) Electrophilic reactions in haloarenes occur slowly.
ix) The treatment of alkyl chloride with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of
alcohol but in the presence of alcoholic KOH , alkene is the major product.
x) The presence of NO2 group at o/p position increases the reactivity of haloarenes
towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
xi) N-Butyl bromide has higher boiling point than t-butyl bromide.
xii) Racemic mixture is optically inactive.
xiii) P-dichlorobenzene has higher melting point than those of o- and m- isomers.
2. Out of SN1 and SN2 , which reaction occurs with
a) Inversion of configuration
b) Racemisation
3. What happens when bromine attacks CH2 = CH - CH2-C ≡ CH
4. Out of chlorobenzene and cyclohexyl chloride, which one is more reactive towards
nucleophilic substitution reaction and why?
5. Why is t-butyl bromide more reactive towards SN1 reactions as compared to n-butyl
bromide?
6. Explain why:
1. the dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride?
2. Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions?
7. An optically active compound having molecular formula C 7H15Br reacts with aqueous KOH
to give a racemic mixture of products. Write the mechanism involved in this reaction.
8. Following compounds are given to you:
2-bromopentane, 2-bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-bromopentane
i) Write the compound which is most reactive towards SN2 reaction.
ii) Write the compound which is optically active.
iii) Write the compound which is most reactive towards beta elimination reaction.
9. Among all the isomers of molecular formula C 4H9Br, identify
a) the one isomer which is optically active.
b) the one isomer which is highly reactive towards SN2
c) the two isomers which give same product on dehydrohalogenation with
alcoholic KOH.
10. Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C 5H12, Identify the one that on
photochemical chlorination yields
a) A single monochloride
b) Three isomeric monochlorides
c) Four isomeric monochlorides
11. Which one of the following compounds is more easily hydrolysed by KOH and why?
CH3CHClCH2CH3 or CH3CH2CH2Cl
12. Although chlorine is an electron withdrawing group, yet it is ortho, para directing in
electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Why?
You might also like
- A Practical Total Synthesis of CocaineDocument13 pagesA Practical Total Synthesis of CocaineRodrigo Fernanda100% (4)
- Class 12 Org Che CHAPTER 10Document10 pagesClass 12 Org Che CHAPTER 10DeekshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes: Subject: Chemistry Class: XII Worksheet: IDocument3 pagesChapter - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes: Subject: Chemistry Class: XII Worksheet: IPathan MohsinNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class Xii - Chemistry Chapter - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument3 pagesWorksheet Class Xii - Chemistry Chapter - Haloalkanes and Haloarenesjiya jainNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class Xii - Chemistry Chapter - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument3 pagesWorksheet Class Xii - Chemistry Chapter - Haloalkanes and Haloarenesjiya jainNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class Xii - Chemistry Chapter - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument3 pagesWorksheet Class Xii - Chemistry Chapter - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesApratim NagNo ratings yet
- Ws of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes XiiDocument3 pagesWs of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes XiiRitikNo ratings yet
- Ws of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes XiiDocument3 pagesWs of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes XiiGaurav SarohaNo ratings yet
- The Reaction Gives Pure Alkyl HalidesDocument8 pagesThe Reaction Gives Pure Alkyl HalidesMohammed IliasNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Based Questions (6 Marks) Section-ADocument4 pagesReasoning Based Questions (6 Marks) Section-ARishi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet HaloalkaneDocument3 pagesRevision Sheet HaloalkaneSahil PandeyNo ratings yet
- Important Questions On Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12Document3 pagesImportant Questions On Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12justtryingtoghostNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument5 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenessaumya dhayalNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes-Imp QNSDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes-Imp QNSjamesNo ratings yet
- Revision - HaloalkanesDocument4 pagesRevision - HaloalkanessafaaNo ratings yet
- CH-10 Halogen DerivativeDocument9 pagesCH-10 Halogen DerivativeKirtan Singh RaoNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesRAUNAK DEYNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Worksheet 16 With SolutionsDocument13 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Worksheet 16 With Solutionsvircritharun718No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledAnurag DubeyNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument14 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesHarshitha GowdaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 of Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument5 pagesWorksheet 2 of Haloalkanes and HaloarenesaydenjayasinghNo ratings yet
- Give ReasonsDocument1 pageGive Reasonsp2109760No ratings yet
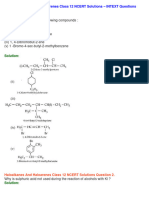
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 NCERT SolutionsDocument32 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 NCERT Solutionschithiraikumar83No ratings yet
- Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)Document10 pagesVery Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)Ꮢupesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Halo AlkanesDocument11 pagesHalo AlkanesshNo ratings yet
- HaloalkanesDocument2 pagesHaloalkanesSameer DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument5 pagesWorksheet-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesAslamNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes SOLUTIONSDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes SOLUTIONSDr. Rupy dhirNo ratings yet
- Holiday Work Class 12Document14 pagesHoliday Work Class 12bighneshrath07No ratings yet
- Ch6 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES HHW WORKSHEETDocument4 pagesCh6 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES HHW WORKSHEETAaditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument2 pagesCHEMISTRYVaibhavMittalNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Revision Paper On Chapter 2Document3 pagesClass 12 Revision Paper On Chapter 2JeevanNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 10 PDFDocument13 pages12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 10 PDFSahil Kalra100% (1)
- Reasoning Questions in Organic Chemistry Text ExerciseDocument14 pagesReasoning Questions in Organic Chemistry Text ExerciseEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument1 pageHaloalkanes and HaloarenesPES 21No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes Q BankDocument7 pagesHaloalkanes Q BankVishnuNo ratings yet
- Reasoning OrganicDocument31 pagesReasoning OrganicBlack IceNo ratings yet
- CH - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes AssignmentDocument6 pagesCH - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes AssignmentHarshtej Singh MakkarNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes NewDocument6 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes NewPuceNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Bank 1690183665Document26 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Bank 1690183665Pratibaa LNo ratings yet
- Class 12th Chemistry Haloalkenes and HaloarenesDocument1 pageClass 12th Chemistry Haloalkenes and Haloarenes10A / 33 / Soham DwivediNo ratings yet
- A RX and ArXDocument2 pagesA RX and ArXKeep Smiling with SanidhyaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes Ws-2Document2 pagesClass 12 Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes Ws-2Chintu RajNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDocument11 pagesHand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesLuisgarciaBerlangaNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Theory QDocument14 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Theory QSenjuti ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes. Set 1Document7 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes. Set 1Achyuta GajurelNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes QNADocument1 pageHaloalkanes and Haloarenes QNAtanishasainits2No ratings yet
- Chemistry HOLIDAYS Assignment Questions (Class 12th)Document9 pagesChemistry HOLIDAYS Assignment Questions (Class 12th)Aayush SahuNo ratings yet
- Acfrogbyyb W54zpzfswkn8k3vq0clq6et8mk Ne Px62hvrlk5chrlql9xx83xtq2sr0dqcuhrswcoglr Ueky068cras4ph7jxkmy 143kq0wnhekbynbh 4 Eq1p0kvslajoriecir6ikqqswDocument8 pagesAcfrogbyyb W54zpzfswkn8k3vq0clq6et8mk Ne Px62hvrlk5chrlql9xx83xtq2sr0dqcuhrswcoglr Ueky068cras4ph7jxkmy 143kq0wnhekbynbh 4 Eq1p0kvslajoriecir6ikqqswThanh Hằng NgôNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Class XII - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument8 pagesAssignment - Class XII - Haloalkanes and Haloarenesgarv khoslaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument14 pagesNCERT Solutions For Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesPrithvi AryaNo ratings yet
- DAz I0 XACIl 8 y RGFmy FNTDocument5 pagesDAz I0 XACIl 8 y RGFmy FNTAditya YadavNo ratings yet
- JF PVQQ FRFFNC Eu HCMGAMDocument67 pagesJF PVQQ FRFFNC Eu HCMGAMelonmuskonmoonNo ratings yet
- Halo Alkanes 24-25Document2 pagesHalo Alkanes 24-25asdaDQDNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes AssignmentDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes AssignmentManaswini JhaNo ratings yet
- Halo NewDocument10 pagesHalo NewMohammed IliasNo ratings yet
- CLASS - 12th CAMPION SCHOOL, BHOURI, BHOPAL PT-2 EXAMINATION SUBJECT - CHEMISTRY MM - 50Document22 pagesCLASS - 12th CAMPION SCHOOL, BHOURI, BHOPAL PT-2 EXAMINATION SUBJECT - CHEMISTRY MM - 50Harshil NagwaniNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Questions in Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesReasoning Questions in Organic ChemistryPavankumar SNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes QDocument35 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes QAbhinav BishtNo ratings yet
- Progress in Reaction Kinetics: Volume 6From EverandProgress in Reaction Kinetics: Volume 6K. R. JenningsNo ratings yet
- MC Chapter 5 TestDocument13 pagesMC Chapter 5 TestGyu Tae JinNo ratings yet
- Genbio (Tests)Document5 pagesGenbio (Tests)Alecz zzNo ratings yet
- Csir Net Gate Advanced Organic Chemistry PDFDocument15 pagesCsir Net Gate Advanced Organic Chemistry PDFdhanapalNo ratings yet
- Naming of Organic Compounds PDFDocument6 pagesNaming of Organic Compounds PDFjj thomosnNo ratings yet
- Polymers NotesDocument10 pagesPolymers NotesThaarvena RetinaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document9 pagesLab 2NelvianaNo ratings yet
- Anaheim Abstracts Spring 2011Document725 pagesAnaheim Abstracts Spring 2011Manoj Kumar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Srinath SanthanamDocument5 pagesSrinath SanthanamTamil NSKNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Carboxylic Acids Lab Report Organic Chemistry 2 LabDocument7 pagesReactions of Carboxylic Acids Lab Report Organic Chemistry 2 LabMarylyn AyoubNo ratings yet
- Derivatization Methods in GC and GCDocument32 pagesDerivatization Methods in GC and GCLorena De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Extra Tutorial FIS 2054 (1-5)Document4 pagesExtra Tutorial FIS 2054 (1-5)Na'im SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Acetic Acid Industrial ChemistryDocument12 pagesAcetic Acid Industrial ChemistryPragadeeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter05 StereochemistryDocument106 pagesChapter05 StereochemistryJoemer Absalon Adorna100% (1)
- 2) Type of Catalyst (Ebook)Document4 pages2) Type of Catalyst (Ebook)mirdza94No ratings yet
- Stereoisomerism Pyqs NsecDocument8 pagesStereoisomerism Pyqs Nsecmanol sahooNo ratings yet
- Alcohols+,+Phenols+,+Ether+ +Best+PYQDocument128 pagesAlcohols+,+Phenols+,+Ether+ +Best+PYQArpit ShirbhateNo ratings yet
- Frustrated Lewis Pairs: Tutorial 3 Sophia KyriakidiDocument17 pagesFrustrated Lewis Pairs: Tutorial 3 Sophia KyriakidiSoFia RiakidikiNo ratings yet
- Cyclohexanone ApplicationDocument2 pagesCyclohexanone ApplicationAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- 2-Benzopyrylium Salts. 25. Reaction of 2-Benzopyrylium Salts With Some NucleophilesDocument4 pages2-Benzopyrylium Salts. 25. Reaction of 2-Benzopyrylium Salts With Some NucleophilesNaresh kumarNo ratings yet
- J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1997 1Document6 pagesJ. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1997 1Sulagna DasNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument14 pagesIsomerismAruna SriNo ratings yet
- SA Unit 5 POLYMER AND ORGANOMETALLIC COMPOUNDSDocument34 pagesSA Unit 5 POLYMER AND ORGANOMETALLIC COMPOUNDSguptaneha8700003783No ratings yet
- What Is Organic Chemistry?Document5 pagesWhat Is Organic Chemistry?Topuls ItigiNo ratings yet
- United States Patent: Benzene From Pyrolysis Naphtha Produced by High-TemperaDocument8 pagesUnited States Patent: Benzene From Pyrolysis Naphtha Produced by High-TemperalandagoNo ratings yet
- Stereoisomerism Theory PDFDocument24 pagesStereoisomerism Theory PDFGOURISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds 2010Document52 pagesOrganic Compounds 2010Judy MelegritoNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions PDFDocument13 pagesNucleophilic Substitution Reactions PDFBhushan Dravyakar100% (6)
- Chemistry of Epoxies - Epoxy Resin, Novolacs, and PolyurethanesDocument9 pagesChemistry of Epoxies - Epoxy Resin, Novolacs, and Polyurethanesdas.soumyabrata50% (2)
- Laboratory Test For HydrocarbonsDocument2 pagesLaboratory Test For HydrocarbonsdhonaNo ratings yet