Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atrial Fibrillation: Epidemiology
Atrial Fibrillation: Epidemiology
Uploaded by
dacc1337Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ACLS PharmacologyDocument6 pagesACLS PharmacologyEunice Angela Fulgueras86% (7)
- Queensland RMO Application GuideDocument18 pagesQueensland RMO Application GuideSOMANATHAN UMAHSUTHANNo ratings yet
- Stroke Topic DiscussionDocument19 pagesStroke Topic Discussionapi-648714317No ratings yet
- CVS MCQsDocument36 pagesCVS MCQssk100% (1)
- Antiarrhythmic Drug Classes MnemonicDocument6 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drug Classes MnemonicMcat NotensionNo ratings yet
- Q. Write Down The ECG Criteria of AF?: Atrial Fibrillation (D-470)Document5 pagesQ. Write Down The ECG Criteria of AF?: Atrial Fibrillation (D-470)DR.SANJOY GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation: Dr. Zirath + Dr. MehtaDocument29 pagesAtrial Fibrillation: Dr. Zirath + Dr. MehtaAjayNo ratings yet
- AF Update May2020 IVDocument71 pagesAF Update May2020 IVThanc FishNo ratings yet
- Atrial FibrillationDocument47 pagesAtrial Fibrillationvikrannth vNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To AFDocument32 pagesClinical Approach To AFEmdan SengadjiNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation Management: Mini-LectureDocument21 pagesAtrial Fibrillation Management: Mini-LectureFahmi RaziNo ratings yet
- Topic - ADocument4 pagesTopic - Aapi-549451092No ratings yet
- Anti Coagulation For Surgery GuidelineDocument3 pagesAnti Coagulation For Surgery GuidelineNur SusiawantyNo ratings yet
- ATrial FibrillationDocument21 pagesATrial FibrillationMohammad Farouq OmarNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation FinalDocument67 pagesAtrial Fibrillation FinalHafiz Wajid SadiqNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Flash CardsDocument5 pagesCardiology Flash CardsRodrigo FonsecaNo ratings yet
- 8.hypertension 2019Document92 pages8.hypertension 2019Taima FayezNo ratings yet
- TD Hypertensive Crises 1Document3 pagesTD Hypertensive Crises 1api-539267574No ratings yet
- Glomerular Diseases - Natural HistoryDocument14 pagesGlomerular Diseases - Natural HistoryAnand ChellappanNo ratings yet
- Betablockers FinallyDocument51 pagesBetablockers FinallyAlaa MahdiNo ratings yet
- Management of Stroke: in The Name of God The Most Gracious The Most MercifulDocument29 pagesManagement of Stroke: in The Name of God The Most Gracious The Most MercifulHaider Nadhem AL-rubaiNo ratings yet
- Atrial FibrillationDocument3 pagesAtrial FibrillationececasselNo ratings yet
- Afib For JCU 2Document33 pagesAfib For JCU 2Sofia KusumadewiNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation TDDocument6 pagesAtrial Fibrillation TDapi-594366475No ratings yet
- Af IndigoDocument60 pagesAf IndigoLalrin ChhanaNo ratings yet
- AntiarrhythmicsDocument2 pagesAntiarrhythmicsdacc1337No ratings yet
- City Hospitals Sunderland A&E Department: Information Card PackDocument47 pagesCity Hospitals Sunderland A&E Department: Information Card PackMulki HakamNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation 2021 - YCDocument24 pagesAtrial Fibrillation 2021 - YCHamza AldiriNo ratings yet
- Risk Stratification Flowchart - 1Document4 pagesRisk Stratification Flowchart - 1wuddafrenNo ratings yet
- HTN CDocument26 pagesHTN CharviliaNo ratings yet
- Arrythmia Management in Primary CareDocument51 pagesArrythmia Management in Primary CarecelinamannaNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Crises - Current ApproachDocument35 pagesHypertensive Crises - Current ApproachShre RanjithamNo ratings yet
- Recitation Final 2022Document11 pagesRecitation Final 2022api-662601291No ratings yet
- Acls-Bradycardia (Case Illustartion: Atrioventricular Block)Document40 pagesAcls-Bradycardia (Case Illustartion: Atrioventricular Block)Narisa Felinka KusumaNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation in Atrial FibrillationDocument22 pagesAnticoagulation in Atrial FibrillationprobowurNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier: Episode 6 - Transient Ischemic AttacksDocument5 pagesPrepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier: Episode 6 - Transient Ischemic AttacksJesily JoyNo ratings yet
- Empagliflozin The Foundation Therapy in Heart FailureDocument48 pagesEmpagliflozin The Foundation Therapy in Heart FailureAkhil SharmaNo ratings yet
- HPN in CKDDocument27 pagesHPN in CKDLeigh Picardal Caragos-MerinNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disease: DR - Ahsan AyubDocument52 pagesCardiovascular Disease: DR - Ahsan AyubarshmeentariqNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Withdrawal: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument30 pagesAlcohol Withdrawal: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and TreatmentNab ShaayaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Diseasea and The ElderlyDocument31 pagesCardiovascular Diseasea and The ElderlyArifin SiregarNo ratings yet
- Hipertensi - SMT 6 2017 - 1Document101 pagesHipertensi - SMT 6 2017 - 1yussikafernandaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Withdrawal Management: Recognition and Management of DTS, Seizures and Wernicke'S EncephalopathyDocument32 pagesAlcohol Withdrawal Management: Recognition and Management of DTS, Seizures and Wernicke'S EncephalopathySangkaran KumarNo ratings yet
- nsg-432 Careplan 2Document11 pagesnsg-432 Careplan 2api-521003884No ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyDocument1 pageCollege of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Shock and Inotropes With DR Sumesh AroraDocument54 pagesShock and Inotropes With DR Sumesh AroraAhmed AhmedNo ratings yet
- QR HypertensionDocument8 pagesQR Hypertensionwaniaqilah workNo ratings yet
- Final NWCN AF Guidelines (Issue 3 - Jun2011)Document2 pagesFinal NWCN AF Guidelines (Issue 3 - Jun2011)herlinNo ratings yet
- Blood Sample Normal Panic Values For Abgs: Clinical SignificanceDocument7 pagesBlood Sample Normal Panic Values For Abgs: Clinical SignificanceJennifer KanouffNo ratings yet
- PolycythemiaDocument26 pagesPolycythemiaFuad Aman AbjNo ratings yet
- Acute Heart Failure in Acute Coronary Syndrome: Buying Time To RevascularizationDocument43 pagesAcute Heart Failure in Acute Coronary Syndrome: Buying Time To RevascularizationMunasir BahriNo ratings yet
- Astra End HipDocument47 pagesAstra End HipIlze KonrādeNo ratings yet
- PHC 550 Case-Based Learning 1Document24 pagesPHC 550 Case-Based Learning 1Atiqah AzmiNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Salimbagat, Christine. P Section: 262Document2 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Salimbagat, Christine. P Section: 262Christine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- 09.5 Hard Cases of NSTEMI Achmad Lefi MD FIHADocument29 pages09.5 Hard Cases of NSTEMI Achmad Lefi MD FIHAEmdan SengadjiNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive EmergencyDocument51 pagesHypertensive EmergencyRaudzah RamliNo ratings yet
- Hypertension PPPT Kcotc Dec 2012Document32 pagesHypertension PPPT Kcotc Dec 2012simonchabili123No ratings yet
- Curs Urg HtaDocument45 pagesCurs Urg HtaMada DobosNo ratings yet
- Approach To ThrombophiliaDocument58 pagesApproach To ThrombophiliaVanessa EdizaNo ratings yet
- Infective eDocument29 pagesInfective eFuad Aman AbjNo ratings yet
- Blood Sample Normal Panic Values For Abgs: Clinical SignificanceDocument7 pagesBlood Sample Normal Panic Values For Abgs: Clinical SignificancegeonarcisoNo ratings yet
- Stroke Conference PDFDocument729 pagesStroke Conference PDFgelvin27No ratings yet
- "Pulmonary Hypertension": Jimmy Ford, MD Pulmonary and Critical CareDocument51 pages"Pulmonary Hypertension": Jimmy Ford, MD Pulmonary and Critical CareSohil ElfarNo ratings yet
- Cath PCI EdukasiDocument7 pagesCath PCI EdukasiAgnesthesiaNo ratings yet
- Basic Sciences QN PaperDocument29 pagesBasic Sciences QN PapermanorasmanthewNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Disease IM 8-12 NewDocument80 pagesValvular Heart Disease IM 8-12 NewRachilla Arandita SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Esc PPCMDocument17 pages2019 Esc PPCMJayden WaveNo ratings yet
- Chronic Stable Angina NEJM 2005Document10 pagesChronic Stable Angina NEJM 2005RebeccaNo ratings yet
- DeVega TV RepairDocument8 pagesDeVega TV Repairndang01No ratings yet
- DR Amao Core Principles of Interpreting Ecg TracingDocument39 pagesDR Amao Core Principles of Interpreting Ecg Tracingdan ekelemeNo ratings yet
- First Aid of Heart AttackDocument3 pagesFirst Aid of Heart Attackarram madhaviNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cath LabDocument2 pagesCardiac Cath Labapi-542649907No ratings yet
- Full Download Book Diagnosis and Treatment of Mitral Valve Disease A Multidisciplinary Approach PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Diagnosis and Treatment of Mitral Valve Disease A Multidisciplinary Approach PDFviolette.craig390100% (27)
- Post Transplant Proteinuria Clinical AuditDocument20 pagesPost Transplant Proteinuria Clinical AuditOmkar NilangiNo ratings yet
- Congenital Cardiac Defects PPT PDF 211Document47 pagesCongenital Cardiac Defects PPT PDF 211Ahmed YasserNo ratings yet
- 2nd Announcement PIT XXIIDocument12 pages2nd Announcement PIT XXIIdr sutjiNo ratings yet
- Report Gisenyi DHDocument17 pagesReport Gisenyi DHjean uwakijijweNo ratings yet
- Multivessel Pci Nejm - AppendixDocument47 pagesMultivessel Pci Nejm - Appendixmajeid saidNo ratings yet
- Research Essay 1Document12 pagesResearch Essay 1api-432883682No ratings yet
- Acute Heart FailureDocument24 pagesAcute Heart FailureTeddy MauriceNo ratings yet
- 2013 ESC Stabilna Koronarna BolestDocument66 pages2013 ESC Stabilna Koronarna BolestМилан ЛабудовићNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine - Nephrology: Topic: Cystic Kidney Diseases Lecturer: Dra. Myrna NgoDocument3 pagesInternal Medicine - Nephrology: Topic: Cystic Kidney Diseases Lecturer: Dra. Myrna NgoVon HippoNo ratings yet
- A Case of Myocardial Bridging: Marco Guglielmo, MD, Feacvi, FSCCTDocument23 pagesA Case of Myocardial Bridging: Marco Guglielmo, MD, Feacvi, FSCCTRaul CincaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Assessment Algorithm: Is Patient at Risk For CKD?Document1 pageChronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Assessment Algorithm: Is Patient at Risk For CKD?Sirsefti AnggiNo ratings yet
- Books For Cardiology FellowshipDocument4 pagesBooks For Cardiology FellowshipRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease Presentation and ManagementDocument4 pagesCongenital Heart Disease Presentation and ManagementCh RajeshNo ratings yet
- What Causes An Enlarged HeartDocument5 pagesWhat Causes An Enlarged HeartmosesNo ratings yet
- Definition and Criteria For Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pagesDefinition and Criteria For Chronic Kidney DiseaseImelda Nicolas GarciaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Review: Brash Syndrome: Bradycardia, Renal Failure, Av Blockade, Shock, and HyperkalemiaDocument8 pagesClinical Review: Brash Syndrome: Bradycardia, Renal Failure, Av Blockade, Shock, and HyperkalemiaSyed Shahrul Naz SyedNo ratings yet
Atrial Fibrillation: Epidemiology
Atrial Fibrillation: Epidemiology
Uploaded by
dacc1337Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atrial Fibrillation: Epidemiology
Atrial Fibrillation: Epidemiology
Uploaded by
dacc1337Copyright:
Available Formats
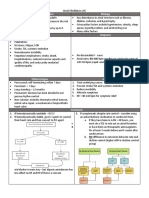
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
0.4-2% prevalence; 4% in >60yrs; >10% in >85yrs; 2x risk of death compared to sinus rhythm; recurrence
Epidemiology most common in 1st 3 months, usually due to failure of drug or dosage; 2/3 spontaneously revert in 24hrs
IHD 40%; valve disease; HTN; hypoK/Mg; thyrotoxicosis (1%); HOCM; sick sinus syndrome; ETOH
Aetiology intoxication; no cause in 5%
CVA: causes 25% CVA’s >80yrs; risk of CVA increases with age; overall 4.5% risk of stroke if uncoagulated
Incidence/yr: 0.1% if lone AF <60yrs with normal echo (no incr risk of stroke or death)
1.5% if low risk and anticoagulated (warfarin/aspirin)
Complications 5% if AF and no structural heart disease, not anticoagulated
10% if AF and RHD
Other: Syncope, hypotension, ischaemia, CCF
Use: to determine anticoagulation choice
1 for: CCF / HTN / >75yrs / diabetes 2 for: previous CVA / TIA / thromboembolism
CHADS2 Score 0 = 2%/yr risk of CVA = aspirin only
Score 1 = 3%/yr risk of CVA = aspirin / warfarin
Score 2 = 4%/yr risk of CVA = warfarin Other scores: 3=6% / 4=8.5% / 5=12.5% / 6=18%
History: palpitations often absent in elderly; ?cause; ?complications
Examination: no a wave on JVP; absent S4
Investigations: CXR, U+E, FBC, cardiac biomarkers
Assessment Echo: L atrium size, LA thrombus, structural abnormalities; TOE 100% sensitive, 99% specific for intra
cardiac thrombus
ECG: Irregularily irregular RR; no P waves (may be course fibrillation early after onset with rate 350-
600); V rate very rapid if accessory tract (eg. AF with WPW)
Indications: Symptomatic / CCF
Young (<65yrs) + no significant PMH
Lone AF
Corrected cause and <48hrs duration
Effect: 55% remain in SR at 1yr (compared to 30% without treatment); <50% in SR at
Management Cardioversion 5yrs
Pros: improved QOL compared to rate control; 90% success if <48hrs
Cons: 1-5% risk of embolism on cardioversion; no survival benefit over rate control in
older/high risk patients; less likely successful if >65yrs / in CCF / late presentation
(50% success if >48hrs) / previous AF / recurrence while on anti-arrhythmics /
structural cardiac lesion, large LA
Indications: if CV instability / ischaemia
Electrical Failed pharmacological
Dose: sedation → start at 70J (requires higher dose than atrial flutter)
Cardioversion Effect: 70J=50% success / 100J=85% / 140J=90% / 210J=>95%
AP more effective than standard apex/base
Flecainide: 2mg/kg IV over 30mins → 200-300mg PO
Indication: use if <55yrs, no IHD, no structural heart disease
Effect: 60% reversion in 3hrs, 80% in 8hrs
CI: IHD, structurally abnormal heart
Amiodarone: 2-5mg/kg IV over 5-10mins
Indication: use if not for flecainide and SBP >90 (otherwise, electrical)
Effect: 50% reversion in 24hrs, 90% in 48hrs; in maintenance, 65% in SR at 1yr
Pros: little negative inotropy, OK if structural heart disease
Pharmaco- Cons: significant long term toxicity
logical
Sotalol: 80-160mg IV
Cardioversion Effect: low reversion rate, so don’t use if cardioversion important; in maintenance,
40% in SR at 1yr
Pros: good if HTN; has rate control properties
CI: CV instability, poor LV function
Dofetilide / ibutilide:
Effect: 90% reversion rate
Cons: TdP occurs in 5%; incr risk of impaired LV function; requires admission to
monitored bed; no maintenance available
Indication: if >65yrs / CAD / mitral stenosis / structural heart disease
CI to anti-arrhythmics
Management LA diameter >5.5cm
Cardioversion failed / unlikely to be successful / unlikely to be retained
...and HR >90
Aim: HR 70-80 if normal / 60-70 if AS, MS, LVH, IHD / 80-90 if AR, MR
Digoxin: 500mcg IV → 250mcg Q4-6hrly to total 1500mg → 62.5– 250mcg/day
Rate Control Indication: in sedentary patient
Cons: ineffective if shock, sepsis, hypoxia; may be no better than placebo
Verapamil: 1mg increments to max 10mg IV
Diltiazem IV (not available)
Cons: temporary; negative inotrope
Metoprolol 5-10mg IV over 2mins
Indication: >48hrs of AF
For 24hrs prior if: acute
no thrombus on TOE and no structural disease on echo
For 3/52 prior (and 1/12 after) if: chronic / thrombus on echo
Warfarin: if prev CVA/TIA
Anti- >75yrs + HTN / DM / vascular disease
valve disease / CCF
coagulation impaired LV function of echo
cardioversion with >48hrs duration
CHADS2 score 2 or more
Effect: 60% RRR for CVA; 2.5%/yr ARR for 1Y prevention, 8.5%/yr ARR for 2Y
prevention
End point: INR 2.5-3.5 if RHD / INR 2-3 if >75yrs / INR 2 if <75yrs
SE: 1%/yr haemorrhage risk; 2x risk of CVA if INR <1.7
Warfarin or aspirin: if >65yrs and low risk
<75yrs + HTN / DM / vascular disease
CHADS2 score 1
Anti-
Management Aspirin: if <65yrs and not on warfarin
coagulation
CHADS2 score 1 or lower
Effect: 1.5%/yr ARR for 1Y prevention, 2.5%/yr ARR for 2Y prevention; 20% decr
risk of CVA
Atrial Flutter
Aetiology: MI (in 2% MI’s), CCF, PE, myocarditis, chest trauma, digitoxicity
ECG: HR 250-300; 2:1 block usually; Flutter waves 2-3mm in amplitude (in II, III, aVF (inverted), V1);
QRS <0.1s (unless flutter waves buried in QRS)
Rate control: as per AF
Cardioversion: flecainide; cardioversion pharmacologically less likely than in AF (eg. 10% reversion with
verapamil, although 90% if assoc with MI)
50J if unstable; atrial overdrive pacing
Anticoagulation: as per AF
You might also like
- ACLS PharmacologyDocument6 pagesACLS PharmacologyEunice Angela Fulgueras86% (7)
- Queensland RMO Application GuideDocument18 pagesQueensland RMO Application GuideSOMANATHAN UMAHSUTHANNo ratings yet
- Stroke Topic DiscussionDocument19 pagesStroke Topic Discussionapi-648714317No ratings yet
- CVS MCQsDocument36 pagesCVS MCQssk100% (1)
- Antiarrhythmic Drug Classes MnemonicDocument6 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drug Classes MnemonicMcat NotensionNo ratings yet
- Q. Write Down The ECG Criteria of AF?: Atrial Fibrillation (D-470)Document5 pagesQ. Write Down The ECG Criteria of AF?: Atrial Fibrillation (D-470)DR.SANJOY GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation: Dr. Zirath + Dr. MehtaDocument29 pagesAtrial Fibrillation: Dr. Zirath + Dr. MehtaAjayNo ratings yet
- AF Update May2020 IVDocument71 pagesAF Update May2020 IVThanc FishNo ratings yet
- Atrial FibrillationDocument47 pagesAtrial Fibrillationvikrannth vNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To AFDocument32 pagesClinical Approach To AFEmdan SengadjiNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation Management: Mini-LectureDocument21 pagesAtrial Fibrillation Management: Mini-LectureFahmi RaziNo ratings yet
- Topic - ADocument4 pagesTopic - Aapi-549451092No ratings yet
- Anti Coagulation For Surgery GuidelineDocument3 pagesAnti Coagulation For Surgery GuidelineNur SusiawantyNo ratings yet
- ATrial FibrillationDocument21 pagesATrial FibrillationMohammad Farouq OmarNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation FinalDocument67 pagesAtrial Fibrillation FinalHafiz Wajid SadiqNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Flash CardsDocument5 pagesCardiology Flash CardsRodrigo FonsecaNo ratings yet
- 8.hypertension 2019Document92 pages8.hypertension 2019Taima FayezNo ratings yet
- TD Hypertensive Crises 1Document3 pagesTD Hypertensive Crises 1api-539267574No ratings yet
- Glomerular Diseases - Natural HistoryDocument14 pagesGlomerular Diseases - Natural HistoryAnand ChellappanNo ratings yet
- Betablockers FinallyDocument51 pagesBetablockers FinallyAlaa MahdiNo ratings yet
- Management of Stroke: in The Name of God The Most Gracious The Most MercifulDocument29 pagesManagement of Stroke: in The Name of God The Most Gracious The Most MercifulHaider Nadhem AL-rubaiNo ratings yet
- Atrial FibrillationDocument3 pagesAtrial FibrillationececasselNo ratings yet
- Afib For JCU 2Document33 pagesAfib For JCU 2Sofia KusumadewiNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation TDDocument6 pagesAtrial Fibrillation TDapi-594366475No ratings yet
- Af IndigoDocument60 pagesAf IndigoLalrin ChhanaNo ratings yet
- AntiarrhythmicsDocument2 pagesAntiarrhythmicsdacc1337No ratings yet
- City Hospitals Sunderland A&E Department: Information Card PackDocument47 pagesCity Hospitals Sunderland A&E Department: Information Card PackMulki HakamNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation 2021 - YCDocument24 pagesAtrial Fibrillation 2021 - YCHamza AldiriNo ratings yet
- Risk Stratification Flowchart - 1Document4 pagesRisk Stratification Flowchart - 1wuddafrenNo ratings yet
- HTN CDocument26 pagesHTN CharviliaNo ratings yet
- Arrythmia Management in Primary CareDocument51 pagesArrythmia Management in Primary CarecelinamannaNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Crises - Current ApproachDocument35 pagesHypertensive Crises - Current ApproachShre RanjithamNo ratings yet
- Recitation Final 2022Document11 pagesRecitation Final 2022api-662601291No ratings yet
- Acls-Bradycardia (Case Illustartion: Atrioventricular Block)Document40 pagesAcls-Bradycardia (Case Illustartion: Atrioventricular Block)Narisa Felinka KusumaNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation in Atrial FibrillationDocument22 pagesAnticoagulation in Atrial FibrillationprobowurNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier: Episode 6 - Transient Ischemic AttacksDocument5 pagesPrepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier: Episode 6 - Transient Ischemic AttacksJesily JoyNo ratings yet
- Empagliflozin The Foundation Therapy in Heart FailureDocument48 pagesEmpagliflozin The Foundation Therapy in Heart FailureAkhil SharmaNo ratings yet
- HPN in CKDDocument27 pagesHPN in CKDLeigh Picardal Caragos-MerinNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disease: DR - Ahsan AyubDocument52 pagesCardiovascular Disease: DR - Ahsan AyubarshmeentariqNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Withdrawal: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument30 pagesAlcohol Withdrawal: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and TreatmentNab ShaayaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Diseasea and The ElderlyDocument31 pagesCardiovascular Diseasea and The ElderlyArifin SiregarNo ratings yet
- Hipertensi - SMT 6 2017 - 1Document101 pagesHipertensi - SMT 6 2017 - 1yussikafernandaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Withdrawal Management: Recognition and Management of DTS, Seizures and Wernicke'S EncephalopathyDocument32 pagesAlcohol Withdrawal Management: Recognition and Management of DTS, Seizures and Wernicke'S EncephalopathySangkaran KumarNo ratings yet
- nsg-432 Careplan 2Document11 pagesnsg-432 Careplan 2api-521003884No ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyDocument1 pageCollege of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Shock and Inotropes With DR Sumesh AroraDocument54 pagesShock and Inotropes With DR Sumesh AroraAhmed AhmedNo ratings yet
- QR HypertensionDocument8 pagesQR Hypertensionwaniaqilah workNo ratings yet
- Final NWCN AF Guidelines (Issue 3 - Jun2011)Document2 pagesFinal NWCN AF Guidelines (Issue 3 - Jun2011)herlinNo ratings yet
- Blood Sample Normal Panic Values For Abgs: Clinical SignificanceDocument7 pagesBlood Sample Normal Panic Values For Abgs: Clinical SignificanceJennifer KanouffNo ratings yet
- PolycythemiaDocument26 pagesPolycythemiaFuad Aman AbjNo ratings yet
- Acute Heart Failure in Acute Coronary Syndrome: Buying Time To RevascularizationDocument43 pagesAcute Heart Failure in Acute Coronary Syndrome: Buying Time To RevascularizationMunasir BahriNo ratings yet
- Astra End HipDocument47 pagesAstra End HipIlze KonrādeNo ratings yet
- PHC 550 Case-Based Learning 1Document24 pagesPHC 550 Case-Based Learning 1Atiqah AzmiNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Salimbagat, Christine. P Section: 262Document2 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Salimbagat, Christine. P Section: 262Christine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- 09.5 Hard Cases of NSTEMI Achmad Lefi MD FIHADocument29 pages09.5 Hard Cases of NSTEMI Achmad Lefi MD FIHAEmdan SengadjiNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive EmergencyDocument51 pagesHypertensive EmergencyRaudzah RamliNo ratings yet
- Hypertension PPPT Kcotc Dec 2012Document32 pagesHypertension PPPT Kcotc Dec 2012simonchabili123No ratings yet
- Curs Urg HtaDocument45 pagesCurs Urg HtaMada DobosNo ratings yet
- Approach To ThrombophiliaDocument58 pagesApproach To ThrombophiliaVanessa EdizaNo ratings yet
- Infective eDocument29 pagesInfective eFuad Aman AbjNo ratings yet
- Blood Sample Normal Panic Values For Abgs: Clinical SignificanceDocument7 pagesBlood Sample Normal Panic Values For Abgs: Clinical SignificancegeonarcisoNo ratings yet
- Stroke Conference PDFDocument729 pagesStroke Conference PDFgelvin27No ratings yet
- "Pulmonary Hypertension": Jimmy Ford, MD Pulmonary and Critical CareDocument51 pages"Pulmonary Hypertension": Jimmy Ford, MD Pulmonary and Critical CareSohil ElfarNo ratings yet
- Cath PCI EdukasiDocument7 pagesCath PCI EdukasiAgnesthesiaNo ratings yet
- Basic Sciences QN PaperDocument29 pagesBasic Sciences QN PapermanorasmanthewNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Disease IM 8-12 NewDocument80 pagesValvular Heart Disease IM 8-12 NewRachilla Arandita SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Esc PPCMDocument17 pages2019 Esc PPCMJayden WaveNo ratings yet
- Chronic Stable Angina NEJM 2005Document10 pagesChronic Stable Angina NEJM 2005RebeccaNo ratings yet
- DeVega TV RepairDocument8 pagesDeVega TV Repairndang01No ratings yet
- DR Amao Core Principles of Interpreting Ecg TracingDocument39 pagesDR Amao Core Principles of Interpreting Ecg Tracingdan ekelemeNo ratings yet
- First Aid of Heart AttackDocument3 pagesFirst Aid of Heart Attackarram madhaviNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cath LabDocument2 pagesCardiac Cath Labapi-542649907No ratings yet
- Full Download Book Diagnosis and Treatment of Mitral Valve Disease A Multidisciplinary Approach PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Diagnosis and Treatment of Mitral Valve Disease A Multidisciplinary Approach PDFviolette.craig390100% (27)
- Post Transplant Proteinuria Clinical AuditDocument20 pagesPost Transplant Proteinuria Clinical AuditOmkar NilangiNo ratings yet
- Congenital Cardiac Defects PPT PDF 211Document47 pagesCongenital Cardiac Defects PPT PDF 211Ahmed YasserNo ratings yet
- 2nd Announcement PIT XXIIDocument12 pages2nd Announcement PIT XXIIdr sutjiNo ratings yet
- Report Gisenyi DHDocument17 pagesReport Gisenyi DHjean uwakijijweNo ratings yet
- Multivessel Pci Nejm - AppendixDocument47 pagesMultivessel Pci Nejm - Appendixmajeid saidNo ratings yet
- Research Essay 1Document12 pagesResearch Essay 1api-432883682No ratings yet
- Acute Heart FailureDocument24 pagesAcute Heart FailureTeddy MauriceNo ratings yet
- 2013 ESC Stabilna Koronarna BolestDocument66 pages2013 ESC Stabilna Koronarna BolestМилан ЛабудовићNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine - Nephrology: Topic: Cystic Kidney Diseases Lecturer: Dra. Myrna NgoDocument3 pagesInternal Medicine - Nephrology: Topic: Cystic Kidney Diseases Lecturer: Dra. Myrna NgoVon HippoNo ratings yet
- A Case of Myocardial Bridging: Marco Guglielmo, MD, Feacvi, FSCCTDocument23 pagesA Case of Myocardial Bridging: Marco Guglielmo, MD, Feacvi, FSCCTRaul CincaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Assessment Algorithm: Is Patient at Risk For CKD?Document1 pageChronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Assessment Algorithm: Is Patient at Risk For CKD?Sirsefti AnggiNo ratings yet
- Books For Cardiology FellowshipDocument4 pagesBooks For Cardiology FellowshipRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease Presentation and ManagementDocument4 pagesCongenital Heart Disease Presentation and ManagementCh RajeshNo ratings yet
- What Causes An Enlarged HeartDocument5 pagesWhat Causes An Enlarged HeartmosesNo ratings yet
- Definition and Criteria For Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pagesDefinition and Criteria For Chronic Kidney DiseaseImelda Nicolas GarciaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Review: Brash Syndrome: Bradycardia, Renal Failure, Av Blockade, Shock, and HyperkalemiaDocument8 pagesClinical Review: Brash Syndrome: Bradycardia, Renal Failure, Av Blockade, Shock, and HyperkalemiaSyed Shahrul Naz SyedNo ratings yet