Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsQB Final Combine 1
QB Final Combine 1
Uploaded by
Rajvardhan JadhavCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Elements of Radio Servicing-William MarcusDocument368 pagesElements of Radio Servicing-William MarcusJShearerNo ratings yet
- A Review of Power Electronics Based Microgrids: Josep M. Guerrero, Xiongfei Wang, Zhe Chen, and Frede BlaabjergDocument5 pagesA Review of Power Electronics Based Microgrids: Josep M. Guerrero, Xiongfei Wang, Zhe Chen, and Frede BlaabjergSaksham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Applied EnerDocument12 pagesApplied Enersoumiya mekraziNo ratings yet
- Integration of Distributed ResourcesDocument235 pagesIntegration of Distributed Resourcesashikhmd4467No ratings yet
- Modelling and Design of PID Controller For Voltage Control of AC Hybrid Micro-GridDocument9 pagesModelling and Design of PID Controller For Voltage Control of AC Hybrid Micro-GridRevit Mep Khoa Đ-đtspktNo ratings yet
- Control of Microgrid For Different Modes of Operation IJERTV5IS051001Document6 pagesControl of Microgrid For Different Modes of Operation IJERTV5IS051001Seerat Aaftaab BarkatNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Control Strategies and Communications For Utility Integration of Photovoltaic Solar SitesDocument9 pagesAdaptive Control Strategies and Communications For Utility Integration of Photovoltaic Solar SitesYahya ZabenNo ratings yet
- TSG 2018 2843527Document9 pagesTSG 2018 2843527Aqeel AnwarNo ratings yet
- Guerrero 2013Document18 pagesGuerrero 2013Prisila DinantiNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review On Issues, Investigations, Control and Protection Trends, Technical Challenges and Future Directions For Microgrid TechnologyDocument16 pagesA Comprehensive Review On Issues, Investigations, Control and Protection Trends, Technical Challenges and Future Directions For Microgrid Technologyabel alejandro gonzález rodríguezNo ratings yet
- 2018-Optimal Control of Power of Two Interconnected MicrogridsDocument13 pages2018-Optimal Control of Power of Two Interconnected Microgridssupriyapallabi06No ratings yet
- A Literature Survey On Control Strategies in A MicrogridDocument8 pagesA Literature Survey On Control Strategies in A MicrogridricardoszfNo ratings yet
- Control Buck Boost Converters ForStand-Alone DC Microgrids ConferenceDocument9 pagesControl Buck Boost Converters ForStand-Alone DC Microgrids Conferenceaiam gorengNo ratings yet
- Distributed Generation in Power Systems: An Overview and Key IssuesDocument9 pagesDistributed Generation in Power Systems: An Overview and Key IssuesXahid YousafNo ratings yet
- 24IEC PaperDocument9 pages24IEC PaperJennifer LopezNo ratings yet
- Distributed Generation in Power Systems: An Overview and Key IssuesDocument9 pagesDistributed Generation in Power Systems: An Overview and Key Issuesأيمن الكزةNo ratings yet
- Integrating Photovoltaic Inverter Reliability Into Energy Yield Estimation With Markov Models 2010Document5 pagesIntegrating Photovoltaic Inverter Reliability Into Energy Yield Estimation With Markov Models 2010ali_alfaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Control Architectures For Intelligent Microgrids - Part Ii: Power Quality, Energy Storage, and Ac/Dc MicrogridsDocument1 pageAdvanced Control Architectures For Intelligent Microgrids - Part Ii: Power Quality, Energy Storage, and Ac/Dc MicrogridsvainateyagoldarNo ratings yet
- Distributed Generation in Power Systems: An Overview and Key IssuesDocument9 pagesDistributed Generation in Power Systems: An Overview and Key IssuesMohammed MateenNo ratings yet
- New-Age Condition Monitoring of On-Load Tap Changing TransformersDocument21 pagesNew-Age Condition Monitoring of On-Load Tap Changing TransformersnewrajasinghNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Techniques For Enhancing The Performance of Controllers in Power Converter-Based SystemsAn OverviewDocument10 pagesArtificial Intelligence Techniques For Enhancing The Performance of Controllers in Power Converter-Based SystemsAn Overviewindra setyawanNo ratings yet
- Generacion Distribuida PDFDocument17 pagesGeneracion Distribuida PDFFERNANDO BARROSNo ratings yet
- Publication 3Document15 pagesPublication 3aditya.gautamNo ratings yet
- ANN Based ApaperDocument8 pagesANN Based ApaperMr.T.Amar Kiran ASPEEENo ratings yet
- 10 1002@er 6064Document25 pages10 1002@er 6064sarray rawdhaNo ratings yet
- Stability Analysis and Controller Design of DC Microgrids With Constant Power LoadDocument8 pagesStability Analysis and Controller Design of DC Microgrids With Constant Power Loadpavan gangwarNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Review and Comparison of Single-Phase Grid-Tied Photovoltaic MicroinvertersDocument19 pagesComprehensive Review and Comparison of Single-Phase Grid-Tied Photovoltaic MicroinvertersJesus Alonso DiazNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Question Paper and Solved AnswerDocument11 pagesPrevious Year Question Paper and Solved AnswerShravan SajNo ratings yet
- Energy 07 06 9012Document24 pagesEnergy 07 06 9012JGT TNo ratings yet
- Related To Linear Current Control TechDocument11 pagesRelated To Linear Current Control TechPrasann KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Development of A MATLAB & Simulink Model of A Single-Phase Grid-Connected Photovoltaic System PDFDocument8 pagesDevelopment of A MATLAB & Simulink Model of A Single-Phase Grid-Connected Photovoltaic System PDFAshwani GargNo ratings yet
- Development of A MATLAB/Simulink Model of A Single-Phase Grid-Connected Photovoltaic SystemDocument8 pagesDevelopment of A MATLAB/Simulink Model of A Single-Phase Grid-Connected Photovoltaic SystemhmitlarNo ratings yet
- A Review of Optimal Power Ow Studies Applied To Smart Grids and MicrogridsDocument3 pagesA Review of Optimal Power Ow Studies Applied To Smart Grids and MicrogridsJohn Duran Prevención Daño MecánicoNo ratings yet
- 32-An Overview of Real Time Hardware-In-The-loop Capabilities in Digital Simulation For Electric MicrogridsDocument6 pages32-An Overview of Real Time Hardware-In-The-loop Capabilities in Digital Simulation For Electric MicrogridsZyad GhaziNo ratings yet
- Microgird'S Strategic Planning in KepcoDocument5 pagesMicrogird'S Strategic Planning in Kepcohanaa KarawiaNo ratings yet
- Fenrg 10 1101342Document2 pagesFenrg 10 1101342Dr. Jagabar Sathik Mohammed AliNo ratings yet
- Microgrid Communications - Protocols and Standards: July 2019Document37 pagesMicrogrid Communications - Protocols and Standards: July 2019Daniel Felipe Losada RamosNo ratings yet
- Strategy of Research and Application For The Microgrid Coordinated ControlDocument6 pagesStrategy of Research and Application For The Microgrid Coordinated Controlasdfvbnmghjk22No ratings yet
- ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZDocument19 pagesZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ4014 SharanNo ratings yet
- E3sconf Iaqvec2023 04018Document8 pagesE3sconf Iaqvec2023 04018Muzz HarryNo ratings yet
- Ijisa PaperDocument11 pagesIjisa PaperraghavNo ratings yet
- Optimal Design of Microgrids in Autonomous and Grid-Connected Modes Using Particle Swarm OptimizationDocument15 pagesOptimal Design of Microgrids in Autonomous and Grid-Connected Modes Using Particle Swarm OptimizationAhmed WestministerNo ratings yet
- Survey On Microgrid Control Strategies: Energy ProcediaDocument7 pagesSurvey On Microgrid Control Strategies: Energy Procediasureh32No ratings yet
- Power Swing in Systems With Inverter-Based ResourcesPart II Impact On Protection SystemsDocument15 pagesPower Swing in Systems With Inverter-Based ResourcesPart II Impact On Protection Systemspouyan HosseiniNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Hamdi Abdi, Soheil Derafshi Beigvand, Massimo La ScalaDocument25 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Hamdi Abdi, Soheil Derafshi Beigvand, Massimo La Scalafateh oualiNo ratings yet
- (R) - 2Document10 pages(R) - 2Nguyen Van QuyenNo ratings yet
- 11 Economic Dispatch of Micro-Grid Based On IPSODocument6 pages11 Economic Dispatch of Micro-Grid Based On IPSOMuhammad RidhwanNo ratings yet
- 2627 6534 1 PBDocument12 pages2627 6534 1 PB0overpower0No ratings yet
- Control of DC MicrogridDocument21 pagesControl of DC MicrogridsureshNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Opportunities For Inverters inDocument6 pagesChallenges and Opportunities For Inverters inSanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- 2.ISCA RJEngS 2017 059Document5 pages2.ISCA RJEngS 2017 059रवि धाकड़No ratings yet
- Microgrids Architectures Controls Protection and DemonstrationDocument14 pagesMicrogrids Architectures Controls Protection and DemonstrationNAAC sstcNo ratings yet
- Article Chahmi - BiraneDocument9 pagesArticle Chahmi - BiraneSaid MaatiNo ratings yet
- Micro-Grid Modeling and ControlDocument24 pagesMicro-Grid Modeling and Controldebjyoti chatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Plug Play DCmicrogridDocument11 pagesPlug Play DCmicrogridmaynaraNo ratings yet
- Microgrid Technologies Sharmeela Full ChapterDocument67 pagesMicrogrid Technologies Sharmeela Full Chapterbrian.collier318100% (22)
- 1 s2.0 S2405844022027049 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S2405844022027049 MainSiva NarayananNo ratings yet
- Power System RequirementsDocument37 pagesPower System RequirementsMahmood AlmoradyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Microgrids and Their Future Trends: Ritu Raj Shrivastwa, Ahmad Hably, Kaouthar Melizi, Seddik BachaDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Microgrids and Their Future Trends: Ritu Raj Shrivastwa, Ahmad Hably, Kaouthar Melizi, Seddik BachatripaNo ratings yet
- ANN Based Solar Power Forecasting in A Smart Microgrid System For Power Flow ManagementDocument6 pagesANN Based Solar Power Forecasting in A Smart Microgrid System For Power Flow ManagementKumar ChaturvedulaNo ratings yet
- Electrician 156165842Document31 pagesElectrician 156165842swami061009No ratings yet
- Konica Minolta Magicolor 4695MF Field Service ManualDocument501 pagesKonica Minolta Magicolor 4695MF Field Service ManualMarco DelsaltoNo ratings yet
- All Bu03A9SS Pricing Guide (02E-1114), NEW CompressDocument44 pagesAll Bu03A9SS Pricing Guide (02E-1114), NEW CompressMario0% (1)
- Mindanao State UniversityDocument3 pagesMindanao State UniversityRey Solis GenosaNo ratings yet
- Creative Inspire Speaker System T6100Document1 pageCreative Inspire Speaker System T6100Makss MNo ratings yet
- 2av56 SensorDocument1 page2av56 SensorbacktroNo ratings yet
- Discontinuous PWM Techniques For Open-End Winding Induction Motor Drive For Zero Sequence Voltage EliminationDocument13 pagesDiscontinuous PWM Techniques For Open-End Winding Induction Motor Drive For Zero Sequence Voltage EliminationarunkmepesNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase - Single Phase Motors & CktsDocument63 pages3 Phase - Single Phase Motors & CktsAriel DimacaliNo ratings yet
- BolometersDocument3 pagesBolometersRachit Jain100% (1)
- Sylvania Fluorescent Reflector Lamps Brochure 1957Document4 pagesSylvania Fluorescent Reflector Lamps Brochure 1957Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- ESC Manual Setting Options (Including Power Straight Version) 50A/60A/70A/80A/100A/125A/200ADocument4 pagesESC Manual Setting Options (Including Power Straight Version) 50A/60A/70A/80A/100A/125A/200APizda MaterinaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering 1st-year-LMDocument76 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering 1st-year-LMkunal beheraNo ratings yet
- Question 812038Document9 pagesQuestion 812038Rudrapalash ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Contact Less Tachometer Using Hall Effect SensorDocument4 pagesContact Less Tachometer Using Hall Effect SensorPragati SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Standard Electrical SpecificationDocument9 pagesStandard Electrical SpecificationmatshonaNo ratings yet
- FFT Hanning Window No DCDocument26 pagesFFT Hanning Window No DCjulio213180No ratings yet
- Hyster P2.0SEDocument451 pagesHyster P2.0SEAnthony TaitNo ratings yet
- Line Current Differential ProtectionDocument28 pagesLine Current Differential Protectionbvkaushik21100% (1)
- Philips Fluorescent LampDocument45 pagesPhilips Fluorescent LampMeilani Anugrah GustiNo ratings yet
- Lighting and Power LayoutDocument72 pagesLighting and Power LayoutErwin Jed RachoNo ratings yet
- Klee Analog BOMDocument2 pagesKlee Analog BOMsmm999999999No ratings yet
- New Sensor LessDocument10 pagesNew Sensor LessAbhishek AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Street: High Efficiency Led Street Luminaires Made in The EuDocument8 pagesStreet: High Efficiency Led Street Luminaires Made in The EumadhivananspNo ratings yet
- 02 Circuit Diagrams General PartDocument3 pages02 Circuit Diagrams General PartFirman SyahNo ratings yet
- Attachment B - HAZID WorksheetDocument9 pagesAttachment B - HAZID Worksheetwibowo wibowo100% (1)
- Soln 03Document12 pagesSoln 03awaisNo ratings yet
- GaN US20080296618A1 PDFDocument27 pagesGaN US20080296618A1 PDF張哲嘉No ratings yet
- EIC E 1001 0 DSG 01 Series Direction Control Valve PDFDocument12 pagesEIC E 1001 0 DSG 01 Series Direction Control Valve PDFmaherNo ratings yet
- Transformer-Based Uneven Doherty Power Amplifier in 90 NM CMOS For WLAN ApplicationsDocument13 pagesTransformer-Based Uneven Doherty Power Amplifier in 90 NM CMOS For WLAN Applicationsreddy balajiNo ratings yet
QB Final Combine 1
QB Final Combine 1
Uploaded by
Rajvardhan Jadhav0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOriginal Title
QB Final Combine 1-Copy b0c636fe3f45ebb712844a39bde34280
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesQB Final Combine 1
QB Final Combine 1
Uploaded by
Rajvardhan JadhavCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
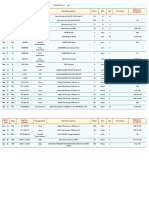
DC Microgrid and Control System
Question Bank for Unit- 1- 8 Hrs
Que Blooms
Questions (Statement) Questions CO PI
No. Level
Define the concept of a microgrid and explain how it differs
1 from conventional centralized power systems. Provide examples 5 L2 1.4.1
to illustrate your answer.
Discuss the role of distributed generation in the context of
2 microgrids. How does distributed generation contribute to the 5 L4 1.2.1
resilience and reliability of microgrid systems?
Compare and contrast AC and DC microgrids with respect to
3 their advantages and applications. Give examples of scenarios 5 L5 1.4.1
where each type of microgrid would be preferable.
Explain the significance of integrating renewable energy sources
4 into microgrid systems. How does this integration impact the 5 L5 1.4.1
overall efficiency and sustainability of the microgrid?
Compare and contrast AC and DC microgrids in terms of their CO1-To
architecture, components, and operational characteristics. understand the
5 10 concepts of L5 1.4.1
Analyze the advantages and disadvantages of each type of
microgrid. microgrids.
Analyze the challenges associated with the integration of
distributed energy resources (DERs) into microgrid systems.
6 10 L4 1.4.1
How can these challenges be addressed to ensure optimal
performance and reliability?
Discuss the control strategies employed in microgrids to ensure
stability and balance between energy supply and demand. How
7 10 L4 1.3.1
do these strategies differ from those used in conventional power
systems?
Evaluate the economic feasibility of implementing microgrid
systems compared to conventional centralized power systems in
8 10 L5 1.4.1, 6.2.1
rural electrification projects. Consider factors such as initial
investment, operational costs, and long-term benefits.
DC Microgrid and Control System
Question Bank for Unit- 2- 8 Hrs
Que Blooms
Questions (Statement) Questions CO PI
No. Level
Discuss the significance of power electronic converters in
1 microgrid applications. Explain how these converters contribute 5 L4 1.4.1
to the stability and efficiency of microgrids.
Compare and contrast the modulation techniques used in power
2 electronic converters for microgrid interfacing. Highlight the 5 L5 5.2.1
advantages and limitations of each technique.
Describe the modelling approach for AC/DC and DC/AC
3 converters in microgrid power systems. Explain the key 5 L3 5.2.2
parameters and considerations involved in the modelling process.
Explain the role of DC/DC converters in microgrid systems.
4 Discuss their importance in integrating renewable energy 5 L4 1.4.1
resources and managing energy storage within the microgrid.
Discuss the challenges and solutions associated with the CO2-To model
modelling of renewable energy resources in microgrid systems. PV power
5 Take examples of wind energy and photovoltaic systems, and 10 systems and L4 5.3.1
elaborate on the modelling methodologies used for accurate standard grid-
integration into microgrid simulations. tied inverter.
Analyze the control strategies employed for DC/DC converters
in microgrid applications. Discuss the significance of control in
6 10 L4 3.4.1
achieving optimal power flow and voltage regulation within the
microgrid system. Provide examples to support your explanation.
Evaluate the impact of energy storage systems on microgrid
stability and reliability. Discuss the modelling techniques used
7 10 L5 5.3.2
for energy storage systems and how their integration enhances
the overall performance of microgrids.
Explore the advancements in power electronic converters for
microgrid applications, focusing on recent research and
8 10 L4 5.1.1
innovations. Highlight any emerging trends or technologies that
are shaping the future of microgrid power electronics.
You might also like
- Elements of Radio Servicing-William MarcusDocument368 pagesElements of Radio Servicing-William MarcusJShearerNo ratings yet
- A Review of Power Electronics Based Microgrids: Josep M. Guerrero, Xiongfei Wang, Zhe Chen, and Frede BlaabjergDocument5 pagesA Review of Power Electronics Based Microgrids: Josep M. Guerrero, Xiongfei Wang, Zhe Chen, and Frede BlaabjergSaksham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Applied EnerDocument12 pagesApplied Enersoumiya mekraziNo ratings yet
- Integration of Distributed ResourcesDocument235 pagesIntegration of Distributed Resourcesashikhmd4467No ratings yet
- Modelling and Design of PID Controller For Voltage Control of AC Hybrid Micro-GridDocument9 pagesModelling and Design of PID Controller For Voltage Control of AC Hybrid Micro-GridRevit Mep Khoa Đ-đtspktNo ratings yet
- Control of Microgrid For Different Modes of Operation IJERTV5IS051001Document6 pagesControl of Microgrid For Different Modes of Operation IJERTV5IS051001Seerat Aaftaab BarkatNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Control Strategies and Communications For Utility Integration of Photovoltaic Solar SitesDocument9 pagesAdaptive Control Strategies and Communications For Utility Integration of Photovoltaic Solar SitesYahya ZabenNo ratings yet
- TSG 2018 2843527Document9 pagesTSG 2018 2843527Aqeel AnwarNo ratings yet
- Guerrero 2013Document18 pagesGuerrero 2013Prisila DinantiNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review On Issues, Investigations, Control and Protection Trends, Technical Challenges and Future Directions For Microgrid TechnologyDocument16 pagesA Comprehensive Review On Issues, Investigations, Control and Protection Trends, Technical Challenges and Future Directions For Microgrid Technologyabel alejandro gonzález rodríguezNo ratings yet
- 2018-Optimal Control of Power of Two Interconnected MicrogridsDocument13 pages2018-Optimal Control of Power of Two Interconnected Microgridssupriyapallabi06No ratings yet
- A Literature Survey On Control Strategies in A MicrogridDocument8 pagesA Literature Survey On Control Strategies in A MicrogridricardoszfNo ratings yet
- Control Buck Boost Converters ForStand-Alone DC Microgrids ConferenceDocument9 pagesControl Buck Boost Converters ForStand-Alone DC Microgrids Conferenceaiam gorengNo ratings yet
- Distributed Generation in Power Systems: An Overview and Key IssuesDocument9 pagesDistributed Generation in Power Systems: An Overview and Key IssuesXahid YousafNo ratings yet
- 24IEC PaperDocument9 pages24IEC PaperJennifer LopezNo ratings yet
- Distributed Generation in Power Systems: An Overview and Key IssuesDocument9 pagesDistributed Generation in Power Systems: An Overview and Key Issuesأيمن الكزةNo ratings yet
- Integrating Photovoltaic Inverter Reliability Into Energy Yield Estimation With Markov Models 2010Document5 pagesIntegrating Photovoltaic Inverter Reliability Into Energy Yield Estimation With Markov Models 2010ali_alfaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Control Architectures For Intelligent Microgrids - Part Ii: Power Quality, Energy Storage, and Ac/Dc MicrogridsDocument1 pageAdvanced Control Architectures For Intelligent Microgrids - Part Ii: Power Quality, Energy Storage, and Ac/Dc MicrogridsvainateyagoldarNo ratings yet
- Distributed Generation in Power Systems: An Overview and Key IssuesDocument9 pagesDistributed Generation in Power Systems: An Overview and Key IssuesMohammed MateenNo ratings yet
- New-Age Condition Monitoring of On-Load Tap Changing TransformersDocument21 pagesNew-Age Condition Monitoring of On-Load Tap Changing TransformersnewrajasinghNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Techniques For Enhancing The Performance of Controllers in Power Converter-Based SystemsAn OverviewDocument10 pagesArtificial Intelligence Techniques For Enhancing The Performance of Controllers in Power Converter-Based SystemsAn Overviewindra setyawanNo ratings yet
- Generacion Distribuida PDFDocument17 pagesGeneracion Distribuida PDFFERNANDO BARROSNo ratings yet
- Publication 3Document15 pagesPublication 3aditya.gautamNo ratings yet
- ANN Based ApaperDocument8 pagesANN Based ApaperMr.T.Amar Kiran ASPEEENo ratings yet
- 10 1002@er 6064Document25 pages10 1002@er 6064sarray rawdhaNo ratings yet
- Stability Analysis and Controller Design of DC Microgrids With Constant Power LoadDocument8 pagesStability Analysis and Controller Design of DC Microgrids With Constant Power Loadpavan gangwarNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Review and Comparison of Single-Phase Grid-Tied Photovoltaic MicroinvertersDocument19 pagesComprehensive Review and Comparison of Single-Phase Grid-Tied Photovoltaic MicroinvertersJesus Alonso DiazNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Question Paper and Solved AnswerDocument11 pagesPrevious Year Question Paper and Solved AnswerShravan SajNo ratings yet
- Energy 07 06 9012Document24 pagesEnergy 07 06 9012JGT TNo ratings yet
- Related To Linear Current Control TechDocument11 pagesRelated To Linear Current Control TechPrasann KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Development of A MATLAB & Simulink Model of A Single-Phase Grid-Connected Photovoltaic System PDFDocument8 pagesDevelopment of A MATLAB & Simulink Model of A Single-Phase Grid-Connected Photovoltaic System PDFAshwani GargNo ratings yet
- Development of A MATLAB/Simulink Model of A Single-Phase Grid-Connected Photovoltaic SystemDocument8 pagesDevelopment of A MATLAB/Simulink Model of A Single-Phase Grid-Connected Photovoltaic SystemhmitlarNo ratings yet
- A Review of Optimal Power Ow Studies Applied To Smart Grids and MicrogridsDocument3 pagesA Review of Optimal Power Ow Studies Applied To Smart Grids and MicrogridsJohn Duran Prevención Daño MecánicoNo ratings yet
- 32-An Overview of Real Time Hardware-In-The-loop Capabilities in Digital Simulation For Electric MicrogridsDocument6 pages32-An Overview of Real Time Hardware-In-The-loop Capabilities in Digital Simulation For Electric MicrogridsZyad GhaziNo ratings yet
- Microgird'S Strategic Planning in KepcoDocument5 pagesMicrogird'S Strategic Planning in Kepcohanaa KarawiaNo ratings yet
- Fenrg 10 1101342Document2 pagesFenrg 10 1101342Dr. Jagabar Sathik Mohammed AliNo ratings yet
- Microgrid Communications - Protocols and Standards: July 2019Document37 pagesMicrogrid Communications - Protocols and Standards: July 2019Daniel Felipe Losada RamosNo ratings yet
- Strategy of Research and Application For The Microgrid Coordinated ControlDocument6 pagesStrategy of Research and Application For The Microgrid Coordinated Controlasdfvbnmghjk22No ratings yet
- ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZDocument19 pagesZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ4014 SharanNo ratings yet
- E3sconf Iaqvec2023 04018Document8 pagesE3sconf Iaqvec2023 04018Muzz HarryNo ratings yet
- Ijisa PaperDocument11 pagesIjisa PaperraghavNo ratings yet
- Optimal Design of Microgrids in Autonomous and Grid-Connected Modes Using Particle Swarm OptimizationDocument15 pagesOptimal Design of Microgrids in Autonomous and Grid-Connected Modes Using Particle Swarm OptimizationAhmed WestministerNo ratings yet
- Survey On Microgrid Control Strategies: Energy ProcediaDocument7 pagesSurvey On Microgrid Control Strategies: Energy Procediasureh32No ratings yet
- Power Swing in Systems With Inverter-Based ResourcesPart II Impact On Protection SystemsDocument15 pagesPower Swing in Systems With Inverter-Based ResourcesPart II Impact On Protection Systemspouyan HosseiniNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Hamdi Abdi, Soheil Derafshi Beigvand, Massimo La ScalaDocument25 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Hamdi Abdi, Soheil Derafshi Beigvand, Massimo La Scalafateh oualiNo ratings yet
- (R) - 2Document10 pages(R) - 2Nguyen Van QuyenNo ratings yet
- 11 Economic Dispatch of Micro-Grid Based On IPSODocument6 pages11 Economic Dispatch of Micro-Grid Based On IPSOMuhammad RidhwanNo ratings yet
- 2627 6534 1 PBDocument12 pages2627 6534 1 PB0overpower0No ratings yet
- Control of DC MicrogridDocument21 pagesControl of DC MicrogridsureshNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Opportunities For Inverters inDocument6 pagesChallenges and Opportunities For Inverters inSanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- 2.ISCA RJEngS 2017 059Document5 pages2.ISCA RJEngS 2017 059रवि धाकड़No ratings yet
- Microgrids Architectures Controls Protection and DemonstrationDocument14 pagesMicrogrids Architectures Controls Protection and DemonstrationNAAC sstcNo ratings yet
- Article Chahmi - BiraneDocument9 pagesArticle Chahmi - BiraneSaid MaatiNo ratings yet
- Micro-Grid Modeling and ControlDocument24 pagesMicro-Grid Modeling and Controldebjyoti chatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Plug Play DCmicrogridDocument11 pagesPlug Play DCmicrogridmaynaraNo ratings yet
- Microgrid Technologies Sharmeela Full ChapterDocument67 pagesMicrogrid Technologies Sharmeela Full Chapterbrian.collier318100% (22)
- 1 s2.0 S2405844022027049 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S2405844022027049 MainSiva NarayananNo ratings yet
- Power System RequirementsDocument37 pagesPower System RequirementsMahmood AlmoradyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Microgrids and Their Future Trends: Ritu Raj Shrivastwa, Ahmad Hably, Kaouthar Melizi, Seddik BachaDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Microgrids and Their Future Trends: Ritu Raj Shrivastwa, Ahmad Hably, Kaouthar Melizi, Seddik BachatripaNo ratings yet
- ANN Based Solar Power Forecasting in A Smart Microgrid System For Power Flow ManagementDocument6 pagesANN Based Solar Power Forecasting in A Smart Microgrid System For Power Flow ManagementKumar ChaturvedulaNo ratings yet
- Electrician 156165842Document31 pagesElectrician 156165842swami061009No ratings yet
- Konica Minolta Magicolor 4695MF Field Service ManualDocument501 pagesKonica Minolta Magicolor 4695MF Field Service ManualMarco DelsaltoNo ratings yet
- All Bu03A9SS Pricing Guide (02E-1114), NEW CompressDocument44 pagesAll Bu03A9SS Pricing Guide (02E-1114), NEW CompressMario0% (1)
- Mindanao State UniversityDocument3 pagesMindanao State UniversityRey Solis GenosaNo ratings yet
- Creative Inspire Speaker System T6100Document1 pageCreative Inspire Speaker System T6100Makss MNo ratings yet
- 2av56 SensorDocument1 page2av56 SensorbacktroNo ratings yet
- Discontinuous PWM Techniques For Open-End Winding Induction Motor Drive For Zero Sequence Voltage EliminationDocument13 pagesDiscontinuous PWM Techniques For Open-End Winding Induction Motor Drive For Zero Sequence Voltage EliminationarunkmepesNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase - Single Phase Motors & CktsDocument63 pages3 Phase - Single Phase Motors & CktsAriel DimacaliNo ratings yet
- BolometersDocument3 pagesBolometersRachit Jain100% (1)
- Sylvania Fluorescent Reflector Lamps Brochure 1957Document4 pagesSylvania Fluorescent Reflector Lamps Brochure 1957Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- ESC Manual Setting Options (Including Power Straight Version) 50A/60A/70A/80A/100A/125A/200ADocument4 pagesESC Manual Setting Options (Including Power Straight Version) 50A/60A/70A/80A/100A/125A/200APizda MaterinaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering 1st-year-LMDocument76 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering 1st-year-LMkunal beheraNo ratings yet
- Question 812038Document9 pagesQuestion 812038Rudrapalash ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Contact Less Tachometer Using Hall Effect SensorDocument4 pagesContact Less Tachometer Using Hall Effect SensorPragati SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Standard Electrical SpecificationDocument9 pagesStandard Electrical SpecificationmatshonaNo ratings yet
- FFT Hanning Window No DCDocument26 pagesFFT Hanning Window No DCjulio213180No ratings yet
- Hyster P2.0SEDocument451 pagesHyster P2.0SEAnthony TaitNo ratings yet
- Line Current Differential ProtectionDocument28 pagesLine Current Differential Protectionbvkaushik21100% (1)
- Philips Fluorescent LampDocument45 pagesPhilips Fluorescent LampMeilani Anugrah GustiNo ratings yet
- Lighting and Power LayoutDocument72 pagesLighting and Power LayoutErwin Jed RachoNo ratings yet
- Klee Analog BOMDocument2 pagesKlee Analog BOMsmm999999999No ratings yet
- New Sensor LessDocument10 pagesNew Sensor LessAbhishek AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Street: High Efficiency Led Street Luminaires Made in The EuDocument8 pagesStreet: High Efficiency Led Street Luminaires Made in The EumadhivananspNo ratings yet
- 02 Circuit Diagrams General PartDocument3 pages02 Circuit Diagrams General PartFirman SyahNo ratings yet
- Attachment B - HAZID WorksheetDocument9 pagesAttachment B - HAZID Worksheetwibowo wibowo100% (1)
- Soln 03Document12 pagesSoln 03awaisNo ratings yet
- GaN US20080296618A1 PDFDocument27 pagesGaN US20080296618A1 PDF張哲嘉No ratings yet
- EIC E 1001 0 DSG 01 Series Direction Control Valve PDFDocument12 pagesEIC E 1001 0 DSG 01 Series Direction Control Valve PDFmaherNo ratings yet
- Transformer-Based Uneven Doherty Power Amplifier in 90 NM CMOS For WLAN ApplicationsDocument13 pagesTransformer-Based Uneven Doherty Power Amplifier in 90 NM CMOS For WLAN Applicationsreddy balajiNo ratings yet