Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sample Paper 01 - Class 12th NEET 2024 - Chemistry - Vijay Gupta - Questions 2
Sample Paper 01 - Class 12th NEET 2024 - Chemistry - Vijay Gupta - Questions 2
Uploaded by
adityavd179Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sample Paper 01 - Class 12th NEET 2024 - Chemistry - Vijay Gupta - Questions 2
Sample Paper 01 - Class 12th NEET 2024 - Chemistry - Vijay Gupta - Questions 2
Uploaded by
adityavd179Copyright:
Available Formats
Sample Paper-01 Class 12th NEET (2024)
CHEMISTRY
SECTION-A 7. Consider a first order gas phase decomposition
1. If mercury is used as cathode in the electrolysis of reaction given below:
aqueous NaCl solution, the ions discharged at A(g) ⎯⎯ → B(g) + C(g)
cathode are; The initial pressure of the system before
(1) H+ (2) Na+ decomposition of A was Pi. After lapse of time ‘t’,
(3) OH– (4) Cl– total pressure of the system increased by x units
and became ‘Pt’.
The rate constant k for reaction is given as:
2. 1 mole of urea is dissolved in 9 moles of water.
2.303 Pi
If vapour pressure of pure water is 40 mmHg. (1) k = log
t Pi − Pt
The vapour pressure of solution is:
2.303 Pi
(1) 32.6 mmHg (2) 36 mmHg (2) k = log
(3) 42 mmHg (4) 34.8 mmHg t 2Pi − Pt
2.303 Pi
(3) k = log
3. Which of the following on addition in 1.0 molal KI t 2Pi + Pt
solution will give rise to increase a vapour 2.303 Pi
(4) k = log
pressure? t Pi + x
(1) addition of NaCl
(2) addition of Na2SO4 8. Which of the following statements is correct?
(3) addition of 1.00 molal KI (1) Ecell and G of cell reaction both are extensive
(4) addition of water properties.
(2) Ecell and G of cell reaction both are intensive
4. A solution containing 8.6 g urea in one litre was properties.
(3) Ecell is an intensive properties while G of cell
found to be isotonic with a 5% (mass/volume)
is an extensive property.
solution of an organic non-volatile solute.
(4) Ecell is an extensive properties while G of
The molar mass of solute is; cell is an intensive property.
(1) 348.83 (2) 34.89
(3) 3489 (4) 861.2 9. For the reaction A + B → C + D. The variation of
the concentration of the products is given by the
curve:
5. Van't Hoff factor is; Y
(1) more than one in case of association Z
(2) less than one in case of dissociation
Conc.
normal molecular mass
(3) W
observed molecular mass
observed molecular mass X
(4) Time
normal molecular mass (1) X (2) Y
(3) Z (4) W
6. A 5% solution (by mass) of cane sugar in water has
10. Which statement is true about a galvanic cell
freezing point of 271 K and freezing point of pure
employing Pb, Cu, Pb2+ and Cu2+?
water is 273.15 K. The freezing point of a 5%
E 0 2+ = − 0.127 V ; E 0 2+ = + 0.518 V
solution (by mass) of glucose in water is; Pb /Pb Cu /Cu
(1) 271K (1) Spontaneous cell-reaction will be in the cell
(2) 273.15K Pb |Pb2+ || Cu+ | Cu
(3) 269.07K (2) E0cell = 0.645 V
(4) 277.23K (3) Both (1) and (2) are correct
(4) None of the above
11. Assertion (A): In rate law, unlike in the expression 16. 0.1435 m solution of a non-volatile, non-electrolyte
for equilibrium constants, the exponents for solute has the freezing point 0.73 degrees lower
concentrations do not necessarily match the
than that of benzene. What is the value of molal
stoichiometric coefficients.
Reason (R): It is the mechanism and not the freezing point depression constant of benzene?
balanced chemical equation for the overall change (1) 5.087 Km–1 (2) 40.0 Km–1
that governs the reaction rate.
(3) 0.52 Km–1 (4) 1.86 Km–1
(1) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the
true, and Reason (R) is a correct explanation
of Assertion (A). 17. Which one of the following will most readily be
(2) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the
dehydrated in acidic conditions?
true, but Reason (R) is not a correct
explanation of Assertion (A). (1) (2)
(3) Assertion (A) is true, and Reason (R) is false.
(4) Assertion (A) is false, and Reason (R) is true.
12. 2-Phenylethanol may be prepared by the reaction (3) (4)
of phenyl magnesium bromide with:
(1) HCHO
(2) CH3CHO
(3) CH3COCH3 18. Statement I: On increasing dilution, the specific
conductance keep on increasing.
(4) Statement II: On increasing dilution, degree of
ionisation of weak electrolyte increases and
13. Assertion (A): If the activation energy of a mobility of ions also increases.
reaction is zero, temperature will have no effect on (1) Statement I and Statement II both are correct.
the rate constant. (2) Statement I is correct, but Statement II is
Reason (R): Lower the activation energy, faster is incorrect.
the reaction.
(3) Statement I is incorrect, but Statement II is
(1) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the
true, and Reason (R) is a correct explanation correct.
of Assertion (A). (4) Statement I and Statement II both are
(2) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the incorrect.
true, but Reason (R) is not a correct
explanation of Assertion (A). 19. Statement I: During electrolysis of CuSO4 (aq)
(3) Assertion (A) is true, and Reason (R) is false.
(4) Assertion (A) is false, and Reason (R) is true. using copper electrodes, copper is dissolved at
anode and deposited at cathode.
14. The diamagnetic species is;
Statement II: Oxidation takes place at anode and
(I) [Cu(CN)4]3– (II) [Co(NH3)6]3+
(III) [Ni(NH3)6] 2+
(IV) [Fe(CN)6]3– reduction at cathode.
(1) I, III (2) I, II (1) Statement I and Statement II both are correct.
(3) III, IV (4) only IV
(2) Statement I is correct, but Statement II is
15. What happens when 2,4,6-Trinitrochlorobenzene incorrect.
is just warmed with water? (3) Statement I is incorrect, but Statement II is
(1) No reaction takes place correct.
(2) A hydrate is formed
(3) 2,4-Dinitrophenol is formed (4) Statement I and Statement II both are
(4) Picric acid is formed incorrect.
20. Statement I: The order of a reaction can have 24. Nitrogen forms stable N2 molecule but phosphorus
fractional value. is converted P4 from P2. The reason for this is:
Statement II: The order of a reaction cannot be (1) triple bond is present between phosphorus
written from balanced equation of a reaction. atoms.
(1) Statement I and Statement II both are correct. (2) p − p bonding is weak.
(2) Statement I is correct, but Statement II is (3) p − p bonding is strong.
incorrect. (4) multiple bond is formed easily.
(3) Statement I is incorrect, but Statement II is
correct. 25. At low temperature, phenol reacts with Br2 in CS2 to
(4) Statement I and Statement II both are form _____.
incorrect. (1) m-bromophenol
(2) o and p-bromophenol
21. The standard reduction potentials, E0, for the half (3) p-bromophenol
reactions are (4) 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol
Zn2+ + 2e– → Zn ; E0 = – 0.76V
Fe2+ + 2e– → Fe ; E0 = – 0.41 V 26. A sample of CHCl3 before being used as an
The EMF for the cell reaction anaesthetic agent is tested by _____.
Fe2+ + Zn → Zn2+ + Fe is; (1) fehling’s solution.
(1) –0.35 V (2) +0.35 V (2) ammonical solution of cuprous chloride.
(3) + 1.17 V (4) –1.17 V (3) silver nitrate solution in cold.
(4) silver nitrate solution after boiling with
22. Match List-I with List-II to find out the correct alcoholic KOH.
option.
List-I List-II 27. Which of the following valence shell configuration
(A) XeF4 (I) Distorted belongs to transition elements?
octahedral
(1) 3s23p63d54s1
(B) XeF6 (II) Square planar
(2) 3s23p63d104s24p3
(C) XeO3 (III) Pyramidal (3) 3s23p63d104s24p1
(D) XeO4 (IV) Tetrahedral (4) 4s24p64d105s25p1
(1) A → II; B → I; C → IV; D → III
(2) A → III; B → II; C → I; D → IV 28. Match List-I with List-II to find out the correct
(3) A → II; B → I; C → III; D → IV option.
(4) A → IV; B → III; C → II; D → I List-I List-II
(A) Oleum (I) H2S2O8
23. The order of a reaction and rate constant for a (B) Caro’s acid (II) H2SO5
chemical change having log t50% νs log [A]0 curve (C) Marshall’s acid (III) H2S2O7
as (1) A → I; B → II; C → III
(2) A → III; B → II; C → I
(3) A → II; B → III; C → I
log t50% (4) A → III; B → I; C → II
29. The correct order of acidic strength of the following
45°
compounds is _____.
log [A] 0
(1) Cl2O7 > SO2 > P4O10
would be;
(2) K2O > CaO > MgO
1 (3) CO2 > N2O5 > SO3
(1) 0, (2) 1, 1
2 (4) Na2O > MgO > Al2O3
(3) 2, 2 (4) 0, 1
30. The product(s) obtained when KMnO4 and HCl SECTION-B
react together to form H2O and Cl2 along with: 36. For metal-carbon bond in the metal carbonyls
(1) KCl (2) MnCl2 which is/are correct?
(3) Both (1) & (2) (4) None of these (1) M-C σ bond is formed by the donation of lone
pair of electrons of the carbonyl carbon into a
31. Which statement is correct ? vacant orbital of metal.
(1) SO2 dissolve in water & forms sulphurous (2) The M–C π bond is formed by the donation of
acid. a pair of electrons from a filled orbital of metal
(2) SO2 act as a bleaching agent. into the vacant antibonding π* orbital of
(3) SO2 has pungent odour. carbon monoxide.
(4) All of these (3) M–C σ bond is formed by the donation of a
lone pair of electrons from a filled orbital of
32. Consider the following reaction metal into the vacant antibonding π* orbital of
carbon monoxide.
(4) Both (1) and (2)
37. The coordination compound that can be used for
Major product (P) is; the hydrogenation of alkene is;
CH3 (1) [Ag(S2O3)2]3– (2) [Rh(PPh3)3Cl]
(1) CH3 CH C (3) [PtC2H4Cl3]– (4) [Au(CN)2]–
CH3
CH3 38. IUPAC name of the linkage isomer of
(2) CH CH CH [Co(NH3)5(ONO)]Cl2 will be:
3
CH3 (1) pentaamminenitrito–O–cobalt (III) chloride
OMe (2) pentaamminenitrito–N–cobalt (III) chloride
CH3 (3) cobalt (III) pentaamminenitrito–O–chloride
(3) CH2 CH CH (4) pentaamminenitrito–N–cobalt (III) dichloride
CH3
(4) CH3 CH2 C CH2 39. Which of the following is not -acid ligand?
(1) CN– (2) SH–
CH3
(3) CO (4) NO+
33. Incorrect statement among the following is:
(1) Carbonium ion intermediate is formed in SN1 40. Which of the following is tetrahedral complex?
reaction. (1) [Ni(CO)4] (2) [Ni(CN)4]2–
(2) Five membered transition state is formed in (2) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]2+ (4) [Cu(NH3)4]2+
SN2 reaction.
(3) SN1 reaction is accelerated in polar protic 41. Which of the following is the correct
solvent. representation of spectrochemical series?
(4) DMSO is polar protic solvent.
(1) Cl– < NO2– < CN– < CO
34. When isopropyl bromide is reacted with AgCN (2) Cl– < Br– < O–2 < OH–
then the product formed is; (3) NO2– < CO < CN– < Cl–
(1) Isoproyl cyanide (2) Isopropyl isocyanide (4) SCN– < Cl– < OH– < S–2
(3) Pentanenitrile (4) Propane nitrile
42. Which is a diamagnetic complex?
35. IUPAC name of neopentyl bromide is; (1) [Fe(H2O)6]+3
(1) 1–ؘBromo–4,4–dimethylpentane
(2) [Fe(H2O)6]+2
(2) 1–Bromo–3–methylbutane
(3) 1–Bromo–2,2–dimethylpropane (3) [Fe(CN)6]3–
(4) 2–Bromo–2–methylbutane (4) [Fe(CN)6]4–
43. Select the ligand having highest trans–effect; 48. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center?
(1) H2O (2) CN– (1) Valine
(3) CH3− (4) OH– (2) Leucine
(3) Glycine
(4) Iso-leucine
44. ⎯⎯→
49. The disaccharide present in the milk is;
(1) maltose
(2) lactose
(3) sucrose
This reaction is called;
(4) cellulose
(1) Benzilic acid rearrangement.
(2) Claisen rearrangement.
50. Assertion (A):
(3) Fries rearrangement.
(4) Schottenbaumann reaction.
45. Which of the following reagent can be used to
oxidize 1° alcohol to aldehyde?
(1) KMnO4 (2) BCC .
(3) H2O2 (4) PCC
Reason (R): Delocalisation of lone pair of
electrons decreases the basic strength.
46. (1) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the
Major product formed in the above mentioned true, and Reason (R) is a correct explanation
reaction is:
of Assertion (A).
(1) (2)
(2) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the
(3) (4) true, but Reason (R) is not a correct
explanation of Assertion (A).
(3) Assertion (A) is true, and Reason (R) is false.
47. Which of the following is a basic amino acid?
(1) Glycine (2) Alanine (4) Assertion (A) is false, and Reason (R) is true.
(3) Leucine (4) Lysine
PW Web/App - https://smart.link/7wwosivoicgd4
Library- https://smart.link/sdfez8ejd80if
You might also like
- Sample Paper - Campus Recruitment Test-Chemistry Medical PDFDocument4 pagesSample Paper - Campus Recruitment Test-Chemistry Medical PDFAbhijeet Parkhi50% (2)
- Dye - Blue Dye - Folium (Chrozophora Tinctoria)Document9 pagesDye - Blue Dye - Folium (Chrozophora Tinctoria)RHNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper 1 1Document5 pagesPractice Paper 1 1DurgadeviNo ratings yet
- Aakash Chemistry CPP CH 2 SolutionDocument9 pagesAakash Chemistry CPP CH 2 Solutionthakartanishq07No ratings yet
- Assignment Unit IV-1Document32 pagesAssignment Unit IV-1najwaNo ratings yet
- BHU MSC EntranceDocument90 pagesBHU MSC EntranceAbhay VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- XI-Chemistry Chapter Test-7-EquilibriumDocument5 pagesXI-Chemistry Chapter Test-7-Equilibriumcakof67215No ratings yet
- Class 12th NEET Chemistry Sample Paper 4 Alka Meena Mem Vijay Kr. Kashyap Questions Final 1Document5 pagesClass 12th NEET Chemistry Sample Paper 4 Alka Meena Mem Vijay Kr. Kashyap Questions Final 1revathiprasady1987No ratings yet
- Equilibrium: K PK K PK K P KDocument11 pagesEquilibrium: K PK K PK K P KNafeesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2022Document11 pagesChemistry 2022Dibyajyoti ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - Campus Recruitment Test-Chemistry MedicalDocument4 pagesSample Paper - Campus Recruitment Test-Chemistry MedicalRani PandeyNo ratings yet
- Topic Test 2 RevisionDocument11 pagesTopic Test 2 RevisionHykal FaridNo ratings yet
- Xicbse Electrochemistry Ass 4 QPDocument2 pagesXicbse Electrochemistry Ass 4 QPkavidivikannan2005No ratings yet
- BHU ch2011Document15 pagesBHU ch2011LORD RAVANNo ratings yet
- Energy From Chemicals (5070) : Instagram@saadi - ShahidDocument1 pageEnergy From Chemicals (5070) : Instagram@saadi - ShahidIntelligence EmpireNo ratings yet
- NEETriumph PHYSICAL CHEMISTRYDocument133 pagesNEETriumph PHYSICAL CHEMISTRYHiral Mayank ShahNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument12 pagesChemical EquilibriumRaj RastogiNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument11 pagesElectrochemistrysaranya ganesanNo ratings yet
- 29-Poll - C-29 (Chemistry) SolutionsDocument4 pages29-Poll - C-29 (Chemistry) SolutionsNandish PatelNo ratings yet
- Board Pattern - 01 - Chemistry Test Paper - Lakshya NEET Fastrack 2024Document4 pagesBoard Pattern - 01 - Chemistry Test Paper - Lakshya NEET Fastrack 2024Janhavi kulkarniNo ratings yet
- CU-2021 B.Sc. (Honours) Biochemistry Part-I Paper-IA QPDocument3 pagesCU-2021 B.Sc. (Honours) Biochemistry Part-I Paper-IA QPsh50.257.22No ratings yet
- CT 1Document7 pagesCT 1anushreej078No ratings yet
- Chemistry Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesChemistry Review QuestionsEMİRCAN İPEKNo ratings yet
- NEET Full Length Mock Test QP - 08Document20 pagesNEET Full Length Mock Test QP - 08oraclepucollegecptNo ratings yet
- Full Syllabus Test Paper No-11 - Dr. Rishabh Sir - AnilDocument16 pagesFull Syllabus Test Paper No-11 - Dr. Rishabh Sir - Anilpadhi8480No ratings yet
- Monthly Test-2 MayDocument3 pagesMonthly Test-2 MayAnimesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- F6 Home Package Chemistry QuestionsDocument34 pagesF6 Home Package Chemistry QuestionsKelvin CharlesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sample Paper 2023-2024 XiDocument6 pagesChemistry Sample Paper 2023-2024 XiRandom UserNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - Assignment - Yakeen 3.0 2024Document13 pagesThermodynamics - Assignment - Yakeen 3.0 2024gssharmaa2017No ratings yet
- This Page Is Intentionally Left BlankDocument30 pagesThis Page Is Intentionally Left Blankdivakars100% (1)
- Chem 2014-2016 Mock Questions Ch5Document6 pagesChem 2014-2016 Mock Questions Ch5Sude KüçükNo ratings yet
- MCQs For Class XII ChemistryDocument29 pagesMCQs For Class XII Chemistryjkc collegeNo ratings yet
- XI Chemistry Pre-Annual 02.02.2022Document5 pagesXI Chemistry Pre-Annual 02.02.2022Ankit TanwarNo ratings yet
- Che - 12th Chem GUJCET-5Document5 pagesChe - 12th Chem GUJCET-5Mayursinh rathodNo ratings yet
- NEET Full Test - 4Document7 pagesNEET Full Test - 4Yash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Chem. Assig.Document8 pagesChem. Assig.aryan asliaNo ratings yet
- Chem - 24.03.2020 - Full Test - Naresh Sir: ChemistryDocument7 pagesChem - 24.03.2020 - Full Test - Naresh Sir: ChemistryDrNaresh SahuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Complete PaperDocument5 pagesChemistry Complete PaperNitin HansNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions & ElectrochemistyDocument24 pagesRedox Reactions & ElectrochemistyDeep Chavan100% (1)
- 3.2.1 Enthalpy Changes QP MultiDocument21 pages3.2.1 Enthalpy Changes QP MultiHadiyaNo ratings yet
- Sem 2 Uppp 1 2017Document7 pagesSem 2 Uppp 1 2017Wong Lee FongNo ratings yet
- HKALE Chemistry 2001 Marking SchemeDocument7 pagesHKALE Chemistry 2001 Marking SchemeHon KwanNo ratings yet
- BCHCT 133Document16 pagesBCHCT 133Md YusufNo ratings yet
- (Done Edu - Joshuatly.com) Kedah STPM Trial 2010 Chemistry (W Ans) (33E48B52)Document0 pages(Done Edu - Joshuatly.com) Kedah STPM Trial 2010 Chemistry (W Ans) (33E48B52)BlaireNo ratings yet
- +1 Chemistry Second Term Exam 2023 - Answer KeyDocument6 pages+1 Chemistry Second Term Exam 2023 - Answer KeymickeycaratNo ratings yet
- Chmical Thermodynamics PDFDocument8 pagesChmical Thermodynamics PDFFn BotNo ratings yet
- 2017 Y5 T4 Chem Focus - KineticsDocument4 pages2017 Y5 T4 Chem Focus - KineticsxmxmxmxmxmNo ratings yet
- 11-Chemistry-A1-Annual Exam 2023-24Document8 pages11-Chemistry-A1-Annual Exam 2023-24harshitsharmasportsNo ratings yet
- Cell R Cell R Cell R Cell RDocument2 pagesCell R Cell R Cell R Cell Rpalash guptaNo ratings yet
- 02-Neet-Pt02 C+P+B - 26-03-2024 - M2Document31 pages02-Neet-Pt02 C+P+B - 26-03-2024 - M2Deepa SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Chem Halfyrly 2020Document6 pagesChem Halfyrly 2020ShraddhaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium - DPP 02 (Of Lec 03) - Arjuna JEE 2024Document3 pagesChemical Equilibrium - DPP 02 (Of Lec 03) - Arjuna JEE 2024gamerfree980No ratings yet
- Class 11Document3 pagesClass 11bikasonoinam321No ratings yet
- JEE Main Full Mock Test 8Document10 pagesJEE Main Full Mock Test 8Aditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Aieee-2012 Chemistry SolutionsDocument3 pagesAieee-2012 Chemistry SolutionsAditya RamNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 16 17 XIII Che Study Package 3 SET 1 Chapter 11Document44 pagesCLS Aipmt 16 17 XIII Che Study Package 3 SET 1 Chapter 11Asma khanNo ratings yet
- 12TH Neet Ans - 25 - 02 - 2024Document6 pages12TH Neet Ans - 25 - 02 - 2024vbedre59No ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision Sheet (JEE MAINS PART-II) (Day by Day) (Without Ans) Tiwari Sir 20.02.2024Document16 pagesChemistry Revision Sheet (JEE MAINS PART-II) (Day by Day) (Without Ans) Tiwari Sir 20.02.2024Priyansh jasejaNo ratings yet
- PT 2 Class 11-CHEMISTRYDocument3 pagesPT 2 Class 11-CHEMISTRYkaisNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Mpemba Effect When Can Hot Water Freeze Faster Than ColdDocument10 pagesThe Mpemba Effect When Can Hot Water Freeze Faster Than Cold陳琮方No ratings yet
- Gravedad Especifico PDFDocument1 pageGravedad Especifico PDFCrisca FumeNo ratings yet
- Chem 3153 Exam 1 NewDocument7 pagesChem 3153 Exam 1 Newdewa pradiptaNo ratings yet
- Me Solar Energy First AssignmentDocument19 pagesMe Solar Energy First AssignmentAlgem Cris CrusisNo ratings yet
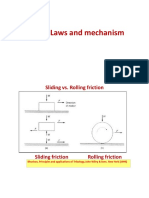
- FrictionDocument14 pagesFrictionManvendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment - 2Document6 pagesHome Assignment - 2Rounak MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Unsteady State Heat TransferDocument26 pagesExperiment 5 Unsteady State Heat TransferFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Dapus TerbaruDocument4 pagesDapus TerbaruElvina iskandarNo ratings yet
- 0620 w21 Ms 62 PDFDocument8 pages0620 w21 Ms 62 PDFEndeavor Med TutorsNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2: Quarter 4: Week 3 - Module 3 Total Internal ReflectionDocument16 pagesGeneral Physics 2: Quarter 4: Week 3 - Module 3 Total Internal ReflectionJELANY AQUINONo ratings yet
- Silicon Photonics: ApplicationsDocument7 pagesSilicon Photonics: ApplicationscadmoscelticNo ratings yet
- Methods of SeparationDocument2 pagesMethods of SeparationAjay LakshmananNo ratings yet
- Analysis - To - Determine - Optimum - Steam - Pressure - Before DeaeratorDocument9 pagesAnalysis - To - Determine - Optimum - Steam - Pressure - Before DeaeratorMas ZuhadNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 Theoretical Models of Chemical Processes PDFDocument18 pagesCh-2 Theoretical Models of Chemical Processes PDFSparsh NegiNo ratings yet
- Metal Powder Specific Surface Area by Physical Adsorption: Standard Test Method ForDocument4 pagesMetal Powder Specific Surface Area by Physical Adsorption: Standard Test Method Formohamed senoussiNo ratings yet
- MSM QPDocument1 pageMSM QPAnil ChauvanNo ratings yet
- Cblechpl 08Document8 pagesCblechpl 08BigsmokeNo ratings yet
- IC@N Research Projects - SPMS - May 2022Document13 pagesIC@N Research Projects - SPMS - May 2022keshavNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Brazing of Alumina To Titanium For Implantable Feedthroughs Using Pure Gold As The Braze MetalDocument7 pagesVacuum Brazing of Alumina To Titanium For Implantable Feedthroughs Using Pure Gold As The Braze MetalMohammad SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- 1999 Andreozzi - Advanced Oxidation Processes AOP For Water Purification and RecoveryDocument9 pages1999 Andreozzi - Advanced Oxidation Processes AOP For Water Purification and RecoveryHerick Bulhões100% (1)
- ISC Physics ProjectDocument9 pagesISC Physics ProjectDev PatelNo ratings yet
- Written Exam Supramolecular Chemistry Winter 2018 F. Diederich, Y. YamakoshiDocument5 pagesWritten Exam Supramolecular Chemistry Winter 2018 F. Diederich, Y. YamakoshiSelim RezaNo ratings yet
- MWF Training - Level 1 CourseDocument37 pagesMWF Training - Level 1 Coursevivek nuthiNo ratings yet
- Heat Integration: Pinch Method and Network DesignDocument38 pagesHeat Integration: Pinch Method and Network DesignTheepa SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- EVT 637 Paper ReportDocument5 pagesEVT 637 Paper ReportAdleen SyahieraaNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Three in One ADocument7 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Three in One ADanny DanNo ratings yet
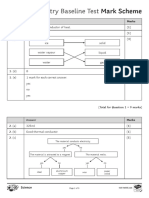
- KS3 Chemistry Baseline Test - Mark SchemeDocument5 pagesKS3 Chemistry Baseline Test - Mark Schemefadua barakatNo ratings yet
- WHB PERHITUNGAN Coba 1Document24 pagesWHB PERHITUNGAN Coba 1Ayu permata sariNo ratings yet
- Final Project Thesis-9.5Document50 pagesFinal Project Thesis-9.5leninbtechNo ratings yet