Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transistor 11
Transistor 11
Uploaded by
idanzbhOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transistor 11
Transistor 11
Uploaded by
idanzbhCopyright:
Available Formats
Transistor
What is a transistor? A transistor is a type of semiconductor device that can be used to conduct
and insulate electric current or voltage. A transistor basically acts as a switch and an amplifier. In
simple words, we can say that a transistor is a miniature device that is used to control or regulate
the flow of electronic signals.
Transistors are one of the key components in most of the electronic devices that are present
today. Developed in the year 1947 by three American physicists, John Bardeen, Walter Brattain
and William Shockley, the transistor is considered one of the most important inventions in the
history of science.
Table of Contents
Parts of a Transistor
Types of Transistors
How Do Transistors Work?
Characteristics of Transistor
Advantages of Transistor
Parts of a Transistor
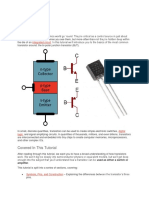
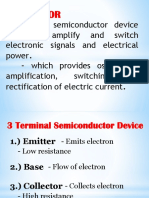
A typical transistor is composed of three layers of semiconductor materials or, more specifically,
terminals which help to make a connection to an external circuit and carry the current. A voltage
or current that is applied to any one pair of the terminals of a transistor controls the current
through the other pair of terminals. There are three terminals for a transistor. They are listed
below:
Base: This is used to activate the transistor.
Collector: It is the positive lead of the transistor.
Emitter: It is the negative lead of the transistor.
Well, the very basic working principle of a transistor is based on controlling the flow of current through
one channel by varying the intensity of a smaller current that is flowing through a second channel.
You might also like
- Transistor As Led Flasher: What Is A Transistor?Document7 pagesTransistor As Led Flasher: What Is A Transistor?study buddyNo ratings yet
- Example of TransistorsDocument12 pagesExample of TransistorslathageethaNo ratings yet
- AC Transistor - Muhammad Hanif Hidayat - LT3A - 33120016Document3 pagesAC Transistor - Muhammad Hanif Hidayat - LT3A - 33120016HandNo ratings yet
- LT3A - 06 - Ayu Novita Anggraeni - English Script Topic 4 (AC Transistor)Document5 pagesLT3A - 06 - Ayu Novita Anggraeni - English Script Topic 4 (AC Transistor)Ayu Novita AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument25 pagesTransistorAdnan Hyder SoomroNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Transistors: DiscussionDocument9 pagesTopic 3 Transistors: DiscussionEnitsuj Eam EugarbalNo ratings yet
- Transistor Basics: Semiconductor DeviceDocument2 pagesTransistor Basics: Semiconductor DeviceManmohan BishtNo ratings yet
- Transistor Unit 2Document5 pagesTransistor Unit 2DINESH SINGH100% (1)
- TransistorsDocument1 pageTransistorsAkshay DhandaNo ratings yet
- Task 7Document3 pagesTask 7Nesrine TitiNo ratings yet
- What Is A TransistorDocument5 pagesWhat Is A TransistorSOMOSCONo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument1 pageTransistorSummer WangNo ratings yet
- NextechDocument15 pagesNextechNEXTECH ElectroicsNo ratings yet
- Transistor: by P.Sai SrivathsaDocument15 pagesTransistor: by P.Sai Srivathsak.saikumarNo ratings yet
- Transistores (Ingles)Document4 pagesTransistores (Ingles)Santiago UlloaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TransistorsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Transistorsdivya jessiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Assignment Final 2.2Document16 pagesElectronic Assignment Final 2.2leon saifullahNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Modul 3Document10 pagesJurnal Modul 3Dasiah RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- TRANSISTOR PowerpointDocument5 pagesTRANSISTOR PowerpointAngel Rey LaysonNo ratings yet
- Asked By: Tony Whelan: Who Invented The Transistor? How Do Transistors Work?Document3 pagesAsked By: Tony Whelan: Who Invented The Transistor? How Do Transistors Work?samuelNo ratings yet
- AbebeDocument25 pagesAbebeAnteneh AbebeNo ratings yet
- Barcenas Electro Midterm Assignment#2Document1 pageBarcenas Electro Midterm Assignment#2Barcenas Roger Jr.No ratings yet
- Transistors Project For IscDocument37 pagesTransistors Project For Iscsandip biswas100% (1)
- EEE 202 Lecture Note On TransistorDocument7 pagesEEE 202 Lecture Note On Transistoralexapierre08No ratings yet
- Explain The Working of Fet With Neat Diagram and Relevant Characteristics. Indicate Each Region of The CharacteristicsDocument19 pagesExplain The Working of Fet With Neat Diagram and Relevant Characteristics. Indicate Each Region of The CharacteristicsS Dispiser100% (1)
- Introduction To TransistorsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To TransistorsKenzuToastNo ratings yet
- Ewp 5Document12 pagesEwp 5Aakansha PaunikarNo ratings yet
- L4 Basic-ElectronicsDocument16 pagesL4 Basic-Electronicstheo dominic silvosaNo ratings yet
- Transistor As A SwitchDocument5 pagesTransistor As A SwitchGeorge NGNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transistors: Administrator 2 CommentsDocument103 pagesIntroduction To Transistors: Administrator 2 CommentsArinaitwe IvanNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument2 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorAravind VinasNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Introduction BJTDocument3 pages2.1 Introduction BJTlizhi0007No ratings yet
- Transistor - WikipediaDocument18 pagesTransistor - WikipediaJayeshNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument3 pagesTransistorsSohaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument15 pagesTransistorAshvini SugaNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument26 pagesTransistorsSojida AbdurazakovaNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument41 pagesTransistorsJacobNo ratings yet
- Adisa MujakDocument19 pagesAdisa MujakAmraSmajlovicNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Final Project: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsDocument4 pagesBasic Electronics Final Project: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsMahnam Nasir Nasir NaeemNo ratings yet
- Transistors: Transistor DefinitionDocument30 pagesTransistors: Transistor DefinitionLaxman BabuNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument1 pageTransistorsJoão CorreiaNo ratings yet
- Practical 6Document11 pagesPractical 6Purva PatelNo ratings yet
- Electronic Assignment Final 2.2 LNXDocument17 pagesElectronic Assignment Final 2.2 LNXleon saifullahNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument10 pagesTransistorLeunam SalpadNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument3 pagesPhysics NotesashwinimodaleNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument1 pageTransistorsnaidooriNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - TransistorDocument41 pagesUnit 4 - TransistorRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Transistors Diodes Led & ETCDocument98 pagesTransistors Diodes Led & ETCSelvanNo ratings yet
- Introduction TransistorsDocument20 pagesIntroduction Transistorsshahzaib.hasnainNo ratings yet
- Task 08Document2 pagesTask 08Nesrine TitiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - TransistorDocument142 pagesUnit 4 - TransistorRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- PDF File Lesson ThreeDocument12 pagesPDF File Lesson ThreequelleNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument4 pagesTransistorshubhamNo ratings yet
- The TransistorDocument10 pagesThe Transistorapi-381737459No ratings yet
- Nurul FitriyaniDocument6 pagesNurul FitriyaniNurul FitriyaniNo ratings yet
- TRANSISTORDocument60 pagesTRANSISTORNaty SeyoumNo ratings yet
- BJT PresentationDocument24 pagesBJT PresentationzakireceNo ratings yet
- Resistors: Active Components Include Amplifying Components Such As Transistors, Triode Vacuum TubesDocument5 pagesResistors: Active Components Include Amplifying Components Such As Transistors, Triode Vacuum TubesifyNo ratings yet