Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Network Models Part 1
Network Models Part 1
Uploaded by
pamela.luna0416050 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views8 pagesOriginal Title
NETWORK MODELS PART 1 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views8 pagesNetwork Models Part 1
Network Models Part 1
Uploaded by
pamela.luna041605Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
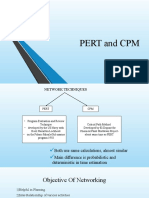
NETWORK MODELS PART 1 2.
The complexity of the nature of
the project involves many activities
Network management tools: or events.
Critical Path Method (CPM)
- 1957, Morgan R. Walker of 3. Delays in the project may
Du Pont and James E. require the payment of penalty
Kelly of Remington Rand. fees.
- Finding ways to reduce the
time required to perform 4. The sequential nature of
tasks, such as projects means that some activities
construction work and cannot begin until a certain
plant maintenance. condition or event had taken place.
- To determine the optimal
tradeoff of cost and time 5. Projects are carefully planned
was the goal of the activities that involve a unique
originators of CPM. undertaking.
Program Evaluation and Review Activity. Activity refers to an effort
Technique (PERT) that needs resources and time to
- Developed in 1958 by US accomplish a goal or a project.
Navy Special Projects
Office in conjunction with Event. A goal that has been
the consulting firm Booz, completed at a certain period is
Allen, and Hamilton. considered an event. An event can
- The US Navy, at that time, also be called as a milestone as it
was faced with the happens after all activities that
challenge of developing precede it must be accomplished.
Polaris submarine missile
project at the soonest Project. Series of events and
possible time. activities with a definable
- PERT was the tool used to beginning and a definable end,
plan and control the which is the goal.
duration of this project.
Network. Activities and events that
Characteristics of Project are arranged in a logical and
Management chronological order and presented
1. The time of completion of the graphically that demonstrate the
project can take weeks, months, or relationships among the different
even years.
activities and events that will lead CPM is a deterministic tool.
to the completion of a project. CPM needed only one estimate of
project duration.
Critical Activity. An activity that CPM includes an explicit estimate
has a strong impact on project of the cost
completion.
Minimum information that
Path. Represents a collection of PERT/CPM can provide:
activities that connects one event 1. Activities that are critical
to another 2. Activities that are noncritical
3. The slack time per noncritical
Critical Path. A path that is activity
comprised of a sequence of critical 4. Other information as needed by
activities that occur from the start management
of a project until full completion. It
is the longest path throughout the Solving CPM
project network.
"solution" is the second phase of
Immediate Predecessors. These PERT/CPM, which necessitates
are activities that must be the construction of a network.
accomplished before the start of
an activity in question. Forward pass aims to determine
the earliest start and earliest finish
Activity Slacks. Also termed as time of each activity by going
float activity, it is the length of time forward on the network.
that a task is allowed to be delayed
as it will not cause a delay for the Backward pass - identifies the
entire project. latest start and latest finish time of
each activity through the network.
PERT usually requires three
estimates to calculate the weighted
average of the expected
completion date of the project
based on the probability
distribution of time of completion.
PERT is a tool mainly focused on
planning and controlling time.
PERT is a probabilistic tool
NETWORK MODELS PART 2 PERT is more than a planning and
control tool as it can also be used
Program/Project Evaluation and to give management an indication
Review Technique (PERT) of possible delay in the completion
- is a network technique that of a project. With the use of PERT,
is used for project planning management can predict whether
and scheduling that the project will be completed on
applies probabilistic before, or after the scheduled
activity times. dates.
- used for dealing with
uncertain activity times. Cost-Time Relationships
Two PERT categories: "Crashing." - this can be done by
Stochastic PERT used for activity adding resources by a process
times that are of probabilistic
nature "Crashing the project." - this
process of expediting the
Deterministic PERT where the execution of a project to a time
activity time is assumed to be below the normal
known with certainty.
Crash duration - is the term for
Three Estimates of Activity Time the minimum possible duration for
an activity.
1. Optimistic estimate (to). An
estimate of the shortest possible These are the steps in the process
duration of an activity reaching its of crashing a project:
completion.
1. Determine the normal
2. Most likely estimate (t). The completion time and cost.
estimate of the duration would 2. Determine the crash schedule
occur most often if the activity is and the cost.
repeated under exactly the same 3. Compute the cost required to
conditions several times. expedite all activities from a
normal time and crash time.
3. Pessimistic estimate (t). The 4. Identify the least-cost plan for
longest time that an activity will be the crash time schedule.
completed "when everything went
wrong.”
MARKOV ANALYSIS 2. Retention Rate. The likelihood
of a company's present customers
Markov analysis to buy from the same company.
- is an analytical tool that uses the
current state and movement of a 3. Switching-out Rate. The
variable to predict future states likelihood of a company's present
and movement of said variable. customers to buy from another
- It was developed by Andrei A. company in the next period.
Markov, a Russian mathematician,
who was able to use this 4. Switching-in Rate. The
procedure to predict the behavior likelihood of a competitor's
of particles of gas in a closed customers to buy from the
container. company in the next period.
Markov Analysis Assumptions The matrix of transition
1. The process has a finite number probabilities provides more useful
of discrete states, meaning once a information.
state has been entered, it cannot
be removed. An equilibrium condition or
2. The process' condition or state steady state happens when in the
in any given period depends only long run, the process has
on its condition in the previous stabilized.
period and on the transition
probabilities. A stabilized system occurs when
3. The transition probabilities the shares do not change.
become constant over time.
4. Changes in the process happen
only once in every period.
5. All time duration is equal in
length.
6. The market size remains
constant in all periods.
1. Present Market Share. The
percentage of the market
accounted for by each of the
companies.
DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING Overlapping sub-problems -
manifest when a recursive
Dynamic programming algorithm visits the same sub-
- is a very powerful technique that problems repeatedly
is based on the "principle of
optimality." Solution by Dynamic Programming
- A principle that can be
summarized simply as "Every The dynamic programming method
optimal policy consists only of starts with the segmentation of the
optimal sub- policies." given problem into smaller
- It is a variant of the "divide and problems termed as stages.
conquer" method as the solution to
the problem is derived from State - is referred to as a condition
previous solutions of sub- in which a process or a problem is
problems. in a particular stage.
- is a problem-solving approach
that performs computations of Rollback analysis - means that
similar simpler sub- problems that the end of the problem is analyzed
would later build up the solution for ahead of the other problems.
a more complex problem.
- The method was invented by Six major terms
American mathematician Richard
Bellman in the 1950s to solve Stages. A stage is defined as a
optimization problems. particular decision point on the
course of the solution.
Philosophy of Dynamic
Programming States. In the example, the
traveler moved along bus stations
What distinguished dynamic from Manila to Ilocos Norte. Each
programming from the "divide and bus station is equivalent to a state.
conquer" method is that the
problem to be solved should have Decision Process. The decision
overlapping sub-problems. process in a dynamic programming
solution is done by moving from
Optimal substructure - optimal one stage to another. Directions
solution must contain an optimal can either go forward or backward.
sub-solutions.
Reward. The reward in the
example is the "hours of travel."
There are three types of reward:
1. Immediate Reward. The result
or payoff from moving between two
adjacent stages is referred to as
the immediate reward. It is shown
under the column "Distance to
Stage No._.”
2. Total Reward. The total reward
is equivalent to the sum of the
immediate reward and the optimal
reward obtained from the previous
stage.
3. Optimal Total Reward. The
optimal reward is the best of all
rewards in each state, for each
given stage. In the example, it is
the shortest route from one bus
station going to the destination.
Recursive Relation. Recursive
relation is the function that binds
the immediate reward, the total
reward, and the optimal total
reward. It is a relationship that is
based on the principle of
optimality.
Policy. In dynamic programming,
policy is about a predetermined
plan for making a decision.
1. The number of participants or
GAME THEORY "players" is an element. A game
can have a single player or a
Game theory group of individuals with one goal.
- is defined as a theory of In other cases, & game can have
independent and interdependent two, three, four, or more players.
decision-making.
- It involves strategies of two or 2. There should be conflicting
more autonomous players, in goals from each party.
which no single player has full
control of the outcome of the 3. A payoff or reward is the
game. consequence of the decisions
- Decision-makers with conflicting made by opposing parties. The
objectives make the decision average payoff per play is
complex for mathematical analysis. identified as the value of the game.
- has evolved as a mathematical A game with zero value is termed
process that results in optimal as a fair game.
solutions for problems under
competition or conflict. 4. Decisions of each party are
- John Von Neumann, a Hungarian made simultaneously. It means
mathematician, was the founding that one party cannot wait for the
father of game theory. decision of the other before
- In 1926, Neumann was able to making their own move.
develop the "minimax theory."
5. The availability of information to
Presentation of Game Theory both parties is important.
The normal form of presentation is Classification of Games
in a tabular format, and the entire
sequence of decisions for the Games of Skill - involves only one
game must be consolidated in a player who has the complete
single strategy. Such format is control of the game's outcome. An
limited to games with two players example of this is a person who is
only. taking an examination. The type of
game is not really classified as a
game at all because of the
Assumptions of Game Theory absence of interdependence.
Games of Chance - are also 3. The rewards or outcomes
single-player games against of all possible combination
nature. In this game, the player of strategies are known to
does not completely control the both decision-makers.
outcomes as the game also
depends on nature, which is 4. Both players are rational,
considered the "second player." which means that their
ultimate goal is to
Games of Strategy are games maximize their own
with two or more players, nature is payoffs.
not included, wherein each of the
players has partial control over the 5. There will be no
outcomes. bargaining among players.
The strategy selected by
A. Zero-sum Games. This is competing parties is
a strictly competitive game simultaneously chosen,
as the winner receives the without knowing the choice
entire amount of payoff or made by the other party.
reward as contributed by
the losing party. Zero-sum Nonzero-sum games. In nonzero-
games with two players sum games, the gains of one
are termed as "two- competitor are not equal to the
person, zero-sum games." losses of the other player. This
The requirements are as type of game sometimes involves
follows: cooperation and is not strictly
competitive.
1. Composed of two players
only. Each player can
choose one of the
definable sets of
strategies.
2. "Zero-sum," as the term
implies, states that any
gain by one player is
exactly equal to the loss of
the other player.
You might also like
- Earned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)From EverandEarned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- A Neo-Riemannian Approach To Jazz AnalysisDocument33 pagesA Neo-Riemannian Approach To Jazz AnalysisBrook Brooke100% (1)
- Network Models Part 1Document4 pagesNetwork Models Part 1pamela.luna041605No ratings yet
- Network Models Part 1Document9 pagesNetwork Models Part 1pamela.luna041605No ratings yet
- Operations Management Co2 MaterialDocument49 pagesOperations Management Co2 MaterialvamsibuNo ratings yet
- Co 2Document49 pagesCo 2vamsibuNo ratings yet
- Pert CPMDocument32 pagesPert CPMSamridhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Project Management: Network Analysis: It Is One of The Most Popular Techniques Used For PlanningDocument25 pagesProject Management: Network Analysis: It Is One of The Most Popular Techniques Used For PlanningPikki LovarajuNo ratings yet
- Quanti Slide 7 Pert CPMDocument49 pagesQuanti Slide 7 Pert CPMRheanneNo ratings yet
- 8567593Document27 pages8567593ArunNo ratings yet
- Pert nOTESDocument33 pagesPert nOTESNeerupa Rajiv SisodiaNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Critical Path Method (CPM) and Program Evaluation & Review Technique (Pert)Document6 pages5.3 Critical Path Method (CPM) and Program Evaluation & Review Technique (Pert)Charles VeranoNo ratings yet
- CPM PERT in Operations ManagementDocument16 pagesCPM PERT in Operations ManagementAnshul100% (1)
- 204 DS Notes Unit 4Document6 pages204 DS Notes Unit 4Jayasri MuraliNo ratings yet
- Assignment On CPM (Critical Path Method)Document12 pagesAssignment On CPM (Critical Path Method)unsaarshad100% (1)
- Notes CPM & PertDocument8 pagesNotes CPM & Pertvamsi krishna balaga50% (2)
- Ce 446Document28 pagesCe 446Jayson PagalNo ratings yet
- CPM Pert DocumentDocument14 pagesCPM Pert DocumentRahul Velamala100% (1)
- PP Lec 4 Project Management CPM - PERTDocument7 pagesPP Lec 4 Project Management CPM - PERTHitesh BalwaniNo ratings yet
- Crashing Pert Networks: A Simulation ApproachDocument15 pagesCrashing Pert Networks: A Simulation ApproachRavindra BharathiNo ratings yet
- PERT:-PERT Stands For "Programme Evaluation & Review Technique. PERT WasDocument4 pagesPERT:-PERT Stands For "Programme Evaluation & Review Technique. PERT WasTanvi AnandNo ratings yet
- NETWORK ANALYSIS NOTES CPMDocument32 pagesNETWORK ANALYSIS NOTES CPMshravani wodeyarNo ratings yet
- Critical Path MethodDocument54 pagesCritical Path MethodKenneth Bryan Copino100% (1)
- Project Management: Cpm/PertDocument24 pagesProject Management: Cpm/PertSachin BoradeNo ratings yet
- Pert CPMDocument10 pagesPert CPMJatinder ghumanNo ratings yet
- Network Technique-UpdatedDocument13 pagesNetwork Technique-UpdatedI MNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 11: Aim: To Study About Critical Path Method and Program Evaluation Review Technique Critical Path MethodDocument20 pagesExperiment No: 11: Aim: To Study About Critical Path Method and Program Evaluation Review Technique Critical Path Method90gaurangNo ratings yet
- Cps Unit 2 - NoRestrictionDocument47 pagesCps Unit 2 - NoRestrictionraaiNo ratings yet
- Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) : 1. Identify The Specific Activities and MilestonesDocument3 pagesProgram Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) : 1. Identify The Specific Activities and MilestonesAbuzar AliNo ratings yet
- Critical Path MethodDocument24 pagesCritical Path MethodRatnesh SinghNo ratings yet
- PMreviewerDocument5 pagesPMrevieweralysNo ratings yet
- Anugraha Vasan 1812560, 5bcomp ADocument2 pagesAnugraha Vasan 1812560, 5bcomp Aanugraha vasanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management: Cpm/PertDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Management: Cpm/PertPushpjit MalikNo ratings yet
- IMS-module 3Document7 pagesIMS-module 3Rithik Raj RanjuNo ratings yet
- Network ModelDocument69 pagesNetwork ModelAbdi NegassaNo ratings yet
- Project Management: Dr. S. Vijaya BhaskarDocument41 pagesProject Management: Dr. S. Vijaya BhaskarShreya DikshitNo ratings yet
- Pert and CPM NotesDocument32 pagesPert and CPM NotesSanjana DasNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument41 pagesProject ManagementNaganna ChettyNo ratings yet
- What Is Project ManagementDocument19 pagesWhat Is Project Managementgill27888No ratings yet
- CPM and PertDocument32 pagesCPM and PertJens GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Constrution ManagementDocument5 pagesConstrution ManagementCarl Andrew PimentelNo ratings yet
- Pert and CPMDocument5 pagesPert and CPMvaibhavkapse2010No ratings yet
- Application of PERT and CPM On Project Management and Network Scheduling - 16900119031Document6 pagesApplication of PERT and CPM On Project Management and Network Scheduling - 16900119031Shourja GangulyNo ratings yet
- Pert CPMDocument41 pagesPert CPMArchana PanwarNo ratings yet
- Optimizing The ProjectDocument10 pagesOptimizing The ProjectRiddhi PirogiwalNo ratings yet
- CH 6&5 ECO MicroDocument4 pagesCH 6&5 ECO MicroSayantan MajhiNo ratings yet
- Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)Document73 pagesProgram Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)Nagulan NagulNo ratings yet
- Project Management: Cpm/PertDocument24 pagesProject Management: Cpm/PertAceeNo ratings yet
- How To Manage Transport Documentation: Logistics and Supply ChainDocument9 pagesHow To Manage Transport Documentation: Logistics and Supply ChainalokNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis - CPM and PERTDocument3 pagesNetwork Analysis - CPM and PERTVishnu PrasadNo ratings yet
- PERTCPMDocument20 pagesPERTCPMbaby LhettyNo ratings yet
- CPM PertDocument24 pagesCPM PertMuhammad SaqlainNo ratings yet
- CPM and PERT Unit 2Document5 pagesCPM and PERT Unit 2SavantNo ratings yet
- Project Planning & Control Lec-7Document32 pagesProject Planning & Control Lec-7Add NoteNo ratings yet
- PERT and CPMDocument26 pagesPERT and CPMmathi sivaNo ratings yet
- POM - Project ManagementDocument8 pagesPOM - Project ManagementNur SagorNo ratings yet
- Paper Review of Software Cost EstimationDocument4 pagesPaper Review of Software Cost EstimationHayyu RageaNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis Development and Depiction: of ofDocument8 pagesNetwork Analysis Development and Depiction: of ofchanayireNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 (Project Network)Document21 pagesLecture 6 (Project Network)aron khanNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)From EverandCISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)Rating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (3)
- RIPH QuestionsDocument2 pagesRIPH Questionspamela.luna041605No ratings yet
- Marketing Plan TemplateDocument15 pagesMarketing Plan Templatepamela.luna041605No ratings yet
- GEC104 Lesson9-NEWDocument72 pagesGEC104 Lesson9-NEWpamela.luna041605No ratings yet
- Network Models Part 1Document9 pagesNetwork Models Part 1pamela.luna041605No ratings yet
- Network Models Part 1Document4 pagesNetwork Models Part 1pamela.luna041605No ratings yet
- Capitulo 9Document21 pagesCapitulo 9Diana Toro HernandezNo ratings yet
- 计算机控制系统手写重点Document10 pages计算机控制系统手写重点DF SDFNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Quadratic FunctionsDocument2 pagesChapter 2 Quadratic FunctionsWan HasliraNo ratings yet
- FVM Crash IntroDocument202 pagesFVM Crash IntroThierry Gnasiri Godwe HinsouNo ratings yet
- HiggsDocument36 pagesHiggsAchilleas Kapartzianis100% (1)
- Regression Analysis and Modeling-XiiDocument9 pagesRegression Analysis and Modeling-Xiidhakar_ravi1No ratings yet
- Chap 025Document75 pagesChap 025thinkstarzNo ratings yet
- EppDM5eMetric 10 04Document31 pagesEppDM5eMetric 10 04Hitesh NaikNo ratings yet
- Ch29 StudentDocument12 pagesCh29 StudentJA55EENo ratings yet
- Number Talks - Cycles 2 3 PresentationDocument26 pagesNumber Talks - Cycles 2 3 Presentationapi-508898016No ratings yet
- Lab Manual 02Document5 pagesLab Manual 02Muhammad AmirNo ratings yet
- Assignment SolutionDocument24 pagesAssignment SolutionOlumayegun OlumideNo ratings yet
- N-AM025 Topic 3 (APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION & INTEGRATION IN ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS)Document63 pagesN-AM025 Topic 3 (APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION & INTEGRATION IN ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS)nurauniatiqah49No ratings yet
- Ada Programming LanguageDocument32 pagesAda Programming LanguageRanny Codilla100% (1)
- Java Labratory ManualDocument135 pagesJava Labratory ManualZappyNet TutorialNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document3 pagesHomework 2Ishi TiwaNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument6 pages1 PDFMohamed MansourNo ratings yet
- 0580 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SeriesDocument4 pages0580 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 Series林欣颖WendyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Mathematics HOTs TrigonometryDocument17 pagesCBSE Class 10 Mathematics HOTs TrigonometryAbhayNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Inclined PlaneDocument67 pagesUnit Plan Inclined Planeapi-232523393No ratings yet
- Summary of TransformationsDocument1 pageSummary of TransformationsNgonidzashe ChirevaNo ratings yet
- Multiplying 2 Digit by 1 DigitDocument13 pagesMultiplying 2 Digit by 1 DigitRomnick Arenas100% (1)
- Electrical Engineering Fundamentals - V. Del ToroDocument62 pagesElectrical Engineering Fundamentals - V. Del ToroAVISH WAGDENo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of PhysicsDocument198 pagesFundamentals of PhysicsRichard シNo ratings yet
- Body Societyand SpaceDocument21 pagesBody Societyand Spacet HermNo ratings yet
- Tesfaye Kumsa Moroda ID. 2202954 Risk Individual AssignmentDocument9 pagesTesfaye Kumsa Moroda ID. 2202954 Risk Individual AssignmentTesfaye Kumsa MorodaNo ratings yet
- Zivot Eric - Financial Econometrics (Lectures)Document197 pagesZivot Eric - Financial Econometrics (Lectures)Ramli Abu ZidniNo ratings yet
- Univariate and Bivariate Statistical AnalysespdfDocument6 pagesUnivariate and Bivariate Statistical AnalysespdfBella100% (1)
- Agglomerative Hierarchical ClusteringDocument22 pagesAgglomerative Hierarchical ClusteringDaneil RadcliffeNo ratings yet