Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IT Security and Risk Management
IT Security and Risk Management
Uploaded by
nevarevaibhav5Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CNS MCQ Question Bank AllDocument64 pagesCNS MCQ Question Bank AllMAK TV83% (6)
- Introduction To Ethical HackingDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Ethical HackingSanjeev S ChaodhariNo ratings yet
- Generic Privacy Policy TemplateDocument2 pagesGeneric Privacy Policy TemplateBagas PersonNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security BasicsDocument36 pagesCyber Security BasicsTausif RazaNo ratings yet
- Ias101 Sbit3l W8sum Vida, John Paul S.Document3 pagesIas101 Sbit3l W8sum Vida, John Paul S.Vida, John PaulNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Information Systems SecurityDocument34 pagesFundamentals of Information Systems SecurityTrialNo ratings yet
- Information Security in GeneralDocument12 pagesInformation Security in GeneralAliNo ratings yet
- Cy CR in deDocument32 pagesCy CR in deVishant IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Information Assurance Risk Management: Group 6Document11 pagesInformation Assurance Risk Management: Group 6Brent Christian ReplanNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENTDocument1 pageASSIGNMENTAbdiaziiz MuhumedNo ratings yet
- Security Concepts and Relationships 4Document11 pagesSecurity Concepts and Relationships 4Ifra IqbalNo ratings yet
- What Is The Types of Network Security Types There Are Two Types of Network Security. 1-Physical Security 2 - Logical SecurityDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Types of Network Security Types There Are Two Types of Network Security. 1-Physical Security 2 - Logical SecurityBillal HossainNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Cyber Security-2023-24Document54 pagesModule 1 Cyber Security-2023-24omwaje2023No ratings yet
- Computer Security Module@2022 - 23Document51 pagesComputer Security Module@2022 - 23senawagari07fNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cybersecurity Risk Assessment?Document3 pagesWhat Is A Cybersecurity Risk Assessment?Alan SebastianNo ratings yet
- Cyber SecurityDocument12 pagesCyber Securityyongki arviusNo ratings yet
- NIS Unit-1Document21 pagesNIS Unit-139-Ayush SolankeNo ratings yet
- Renewable2 0Document8 pagesRenewable2 073035537rishubrother95827594No ratings yet
- ISEC-210 UNIT 02 - Information Security Threats and AttacksDocument23 pagesISEC-210 UNIT 02 - Information Security Threats and AttacksKutemwa MithiNo ratings yet
- Monitor Threats To The NetworkDocument12 pagesMonitor Threats To The NetworkAlage TekaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Alison NotesDocument70 pagesCyber Security Alison Notessphaart12No ratings yet
- Cyber-Security Ses1Document6 pagesCyber-Security Ses1MOHIT ELECTROVISION FBDNo ratings yet
- Information Security Material For Exit Exam (IT)Document35 pagesInformation Security Material For Exit Exam (IT)alemuNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity 2024Document13 pagesCybersecurity 2024vijay52254No ratings yet
- Unit 5Document7 pagesUnit 5k.mustaq9999No ratings yet
- Advanced Audititing and AssuarenceDocument3 pagesAdvanced Audititing and AssuarenceromansegesaNo ratings yet
- Infosec RisksDocument15 pagesInfosec RisksJOENo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Need For SecurityDocument17 pagesChapter 2 - The Need For SecurityAshura OsipNo ratings yet
- Information Security and Ethics - Tutorial 3Document3 pagesInformation Security and Ethics - Tutorial 3Lai Chen ShengNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Ingles CibersegurityDocument14 pages3.1 Ingles CibersegurityFranco AngelNo ratings yet
- Threats and AttackDocument9 pagesThreats and Attackabusamansevt1925No ratings yet
- Need For Network SecurityDocument8 pagesNeed For Network SecurityRyan CooperNo ratings yet
- Network Security Is A Broad Term That Covers A Multitude of TechnologiesDocument3 pagesNetwork Security Is A Broad Term That Covers A Multitude of TechnologiesAnonymous zXwP003No ratings yet
- BTICS501 Network Security & Cryptography (Unit-1 To 5)Document90 pagesBTICS501 Network Security & Cryptography (Unit-1 To 5)svvv ganduNo ratings yet
- Final Week4 (IAS101)Document12 pagesFinal Week4 (IAS101)Detective RomejaneNo ratings yet
- Network Security Exam Short QuestionsDocument6 pagesNetwork Security Exam Short QuestionsDiom ShresthaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentBlack Heart100% (1)
- Information Security All ChapterDocument73 pagesInformation Security All ChapterbilisummaaNo ratings yet
- M8 Info SecurityDocument7 pagesM8 Info SecurityAnimesh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Ias - ReportDocument32 pagesGroup 4 Ias - ReportRegie GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document6 pagesTutorial 1Heng PhinNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Notes Unit 1Document9 pagesCyber Security Notes Unit 1Reshma BasuNo ratings yet
- Debremarkos University School of Computing Information Security (Chapter One)Document20 pagesDebremarkos University School of Computing Information Security (Chapter One)tadesse yizengawNo ratings yet
- NIS Project Final PMV 23Document3 pagesNIS Project Final PMV 23Pooja AbhangNo ratings yet
- Security Concepts: Unit - I Security Concepts: Introduction, The Need For Security, Security Approaches, Principles ofDocument47 pagesSecurity Concepts: Unit - I Security Concepts: Introduction, The Need For Security, Security Approaches, Principles ofSAI CHAND 18-522No ratings yet
- IT NS 1 - Chapter 1b Types of Attacks and DetectionDocument6 pagesIT NS 1 - Chapter 1b Types of Attacks and DetectionGALAPON FRANCISNo ratings yet
- Module 5 INFORMATION SECURITY OVERVIEWDocument15 pagesModule 5 INFORMATION SECURITY OVERVIEWlemonademagnumNo ratings yet
- 'FFFFDocument3 pages'FFFFajay pawaraNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Interview Questions For Freshers: 1. What Is The Main Objective of Cyber Security?Document24 pagesCyber Security Interview Questions For Freshers: 1. What Is The Main Objective of Cyber Security?Gilgamesh berserkerNo ratings yet
- UNIT 10 - SecurityDocument15 pagesUNIT 10 - Securitychilekwamichael26No ratings yet
- Cyber Security-NotesDocument49 pagesCyber Security-NotesReshma BasuNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document49 pagesSession 2Zhafran HanifNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering and Technology School of Computing and Informatics Department of Information TechnologyDocument16 pagesCollege of Engineering and Technology School of Computing and Informatics Department of Information TechnologyAbdataa waaqaaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Proposal - Protecting User Resources and Privacy Using Software Security-2Document41 pagesGroup 3 Proposal - Protecting User Resources and Privacy Using Software Security-2AdoreNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security IntroductionDocument10 pagesCyber Security IntroductionRitesh KelkarNo ratings yet
- Ifs Chap 1Document22 pagesIfs Chap 1moviesera851No ratings yet
- Implications of Misuse and CybersecurityDocument5 pagesImplications of Misuse and Cybersecuritykurdeisha.cupidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Cybersecurity and Risk Management TechnologyDocument30 pagesChapter 5. Cybersecurity and Risk Management Technologyarmando.lykajovel.dllNo ratings yet
- Managing Security of InformationDocument4 pagesManaging Security of InformationredNo ratings yet
- CYBER SECURITY HANDBOOK Part-1: Hacking the Hackers: Unraveling the World of CybersecurityFrom EverandCYBER SECURITY HANDBOOK Part-1: Hacking the Hackers: Unraveling the World of CybersecurityNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking: Exploring the Dark Art of Ethical Hacking and Penetration TestingFrom EverandCybersecurity and Ethical Hacking: Exploring the Dark Art of Ethical Hacking and Penetration TestingNo ratings yet
- Summary Report: Bandwidth and ApplicationsDocument6 pagesSummary Report: Bandwidth and ApplicationsDukeNo ratings yet
- مصطلحات امن المعلوماتDocument21 pagesمصطلحات امن المعلوماتmohammedNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument1 pageGujarat Technological Universityyicef37689No ratings yet
- Digital Signatures: Homework 6Document10 pagesDigital Signatures: Homework 6leishNo ratings yet
- Database Security: CSIT115 Data Management and SecurityDocument19 pagesDatabase Security: CSIT115 Data Management and SecurityЛюбовь ТарановаNo ratings yet
- AmanBalhara CNS 01014803118Document26 pagesAmanBalhara CNS 01014803118heysiri0804No ratings yet
- Technote ISAKMP 00Document26 pagesTechnote ISAKMP 00Saptarshi BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Cryptography Basics, Methods and Standards: ICT640 - Advanced Information SecurityDocument28 pagesCryptography Basics, Methods and Standards: ICT640 - Advanced Information SecurityDr Patrick CernaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security: By: Kshirod Kumar Dehury Registration No: 1821108022Document15 pagesCyber Security: By: Kshirod Kumar Dehury Registration No: 1821108022Shibajyoti PattanaikNo ratings yet
- Cryptographic Hash FunctionsDocument16 pagesCryptographic Hash FunctionsUrvil SitapareNo ratings yet
- Blok PornoDocument27 pagesBlok Pornodavid coronaNo ratings yet
- Network Security EssentialsDocument460 pagesNetwork Security Essentialsshahab zirakiNo ratings yet
- Zamba LesDocument25 pagesZamba LesAG R OhcnaNo ratings yet
- Ciber CrimeDocument12 pagesCiber CrimeAshutosh Shukla100% (1)
- CNS Previous Questions Paper-2023Document2 pagesCNS Previous Questions Paper-2023rajsing00004444No ratings yet
- Dark WebDocument12 pagesDark WebHARDIK SANGAL 211160No ratings yet
- Lectures 1 MergedDocument154 pagesLectures 1 MergedDiana IsmailNo ratings yet
- X.509 Authentication ServiceDocument34 pagesX.509 Authentication ServiceMuhammad Junaid Anjum75% (4)
- 11.4 Pubkey TrapdoorDocument11 pages11.4 Pubkey TrapdoorSiddharth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Certified Ethical Hacker Course ContentDocument36 pagesCertified Ethical Hacker Course ContentTamer DobalNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER Digital SignatureDocument16 pagesCHAPTER Digital SignatureTanvir HassanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Post Test ICTDocument1 pageLesson 2 - Post Test ICTImie Omamalin100% (2)
- Artigo 2 - The Evolution of CybercrimeDocument3 pagesArtigo 2 - The Evolution of CybercrimeZulu RasNo ratings yet
- Midterm ITERADocument8 pagesMidterm ITERAismael delosreyesNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument25 pagesSeminar ReportAbhishek SolankiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledBhumika MhatreNo ratings yet
- Obtain A Digital Certificate To Create A Digital SignatureDocument3 pagesObtain A Digital Certificate To Create A Digital SignaturePiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Cyber ch.4/1/2Document5 pagesCyber ch.4/1/2Suvarna LondheNo ratings yet
IT Security and Risk Management
IT Security and Risk Management
Uploaded by
nevarevaibhav5Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IT Security and Risk Management
IT Security and Risk Management
Uploaded by
nevarevaibhav5Copyright:
Available Formats
Q. 1 Differentiate between vulnerabilities, threats, and countermeasures in information security.
How do organizations identify and address vulnerabilities? Illustrate how a firewall plays an
important role in protecting networks from unauthorized access.
Ans.
Vulnerabilities –
Vulnerabilities are most often referred to weaknesses or flaws in a particular system or
application that can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access, steal data, or disrupt
business operations.
Vulnerabilities can be found in hardware, software, firmware or even physical security controls.
Few examples of vulnerabilities can be a software bug, security misconfigurations, injection,
broken access control or a missing security patch, etc.
Threats –
In information security, a threat refers to any potential danger or harmful event that can exploit a
vulnerability and cause harm to a system, organization, or individual.
These threats can be malicious actors (hackers), malware (viruses, worms), natural disasters
(floods, fires), or even human error.
Threats can be intentional or unintentional in nature.
o Intentional Threats - Intentional threats are deliberate actions or attacks carried out by
threat actors with malicious intent. These can include cyberattacks, such as malware
infections, malicious code or SQL injection attacks, ransomware, phishing attempts, and
distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
o Unintentional threats - Unintentional threats originate from human error or accidental
actions that can lead to security breaches. These threats include accidental disclosure of
sensitive information or falling victim to social engineering tactics.
o Natural and Physical Threats – In information security, natural and physical threats are
dangers that can harm your computer systems and the data they store. For example,
fires, floods, power failures, and other disastrous situations
Countermeasures in information security –
Countermeasures in information security are actions taken to reduce the risk associated with
vulnerabilities and threats.
These actions aim to mitigate or eliminate the potential for threats to exploit vulnerabilities
Identification and addressing vulnerabilities –
Role of firewall –
A firewall is a network security device that monitors and filters network traffic based on an
organization's security policies.
As firewall is one of the most critical and important part of the network, it plays a vital role in
securing the network perimeters of an organization. Firewall is usually placed at the boundary of the
internal network of an organization in order to protect the network traffic and information flow.
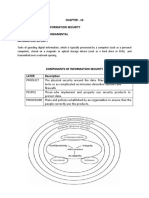
Fig. 1 shows the basic working of a firewall within the organization.
Fig. 1
Suppose there are three floors in an organization where in the users are seated and working. There is
a common router within the network to provide internet access to all the users. Now the firewall is
placed or installed right in between the router and the internet or we can say WAN. Here, firewall
plays an important role in regards to network security. Firewall placed between the internet and
router will be primary gateway for the data to flow in and out of the organization.
You might also like
- CNS MCQ Question Bank AllDocument64 pagesCNS MCQ Question Bank AllMAK TV83% (6)
- Introduction To Ethical HackingDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Ethical HackingSanjeev S ChaodhariNo ratings yet
- Generic Privacy Policy TemplateDocument2 pagesGeneric Privacy Policy TemplateBagas PersonNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security BasicsDocument36 pagesCyber Security BasicsTausif RazaNo ratings yet
- Ias101 Sbit3l W8sum Vida, John Paul S.Document3 pagesIas101 Sbit3l W8sum Vida, John Paul S.Vida, John PaulNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Information Systems SecurityDocument34 pagesFundamentals of Information Systems SecurityTrialNo ratings yet
- Information Security in GeneralDocument12 pagesInformation Security in GeneralAliNo ratings yet
- Cy CR in deDocument32 pagesCy CR in deVishant IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Information Assurance Risk Management: Group 6Document11 pagesInformation Assurance Risk Management: Group 6Brent Christian ReplanNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENTDocument1 pageASSIGNMENTAbdiaziiz MuhumedNo ratings yet
- Security Concepts and Relationships 4Document11 pagesSecurity Concepts and Relationships 4Ifra IqbalNo ratings yet
- What Is The Types of Network Security Types There Are Two Types of Network Security. 1-Physical Security 2 - Logical SecurityDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Types of Network Security Types There Are Two Types of Network Security. 1-Physical Security 2 - Logical SecurityBillal HossainNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Cyber Security-2023-24Document54 pagesModule 1 Cyber Security-2023-24omwaje2023No ratings yet
- Computer Security Module@2022 - 23Document51 pagesComputer Security Module@2022 - 23senawagari07fNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cybersecurity Risk Assessment?Document3 pagesWhat Is A Cybersecurity Risk Assessment?Alan SebastianNo ratings yet
- Cyber SecurityDocument12 pagesCyber Securityyongki arviusNo ratings yet
- NIS Unit-1Document21 pagesNIS Unit-139-Ayush SolankeNo ratings yet
- Renewable2 0Document8 pagesRenewable2 073035537rishubrother95827594No ratings yet
- ISEC-210 UNIT 02 - Information Security Threats and AttacksDocument23 pagesISEC-210 UNIT 02 - Information Security Threats and AttacksKutemwa MithiNo ratings yet
- Monitor Threats To The NetworkDocument12 pagesMonitor Threats To The NetworkAlage TekaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Alison NotesDocument70 pagesCyber Security Alison Notessphaart12No ratings yet
- Cyber-Security Ses1Document6 pagesCyber-Security Ses1MOHIT ELECTROVISION FBDNo ratings yet
- Information Security Material For Exit Exam (IT)Document35 pagesInformation Security Material For Exit Exam (IT)alemuNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity 2024Document13 pagesCybersecurity 2024vijay52254No ratings yet
- Unit 5Document7 pagesUnit 5k.mustaq9999No ratings yet
- Advanced Audititing and AssuarenceDocument3 pagesAdvanced Audititing and AssuarenceromansegesaNo ratings yet
- Infosec RisksDocument15 pagesInfosec RisksJOENo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Need For SecurityDocument17 pagesChapter 2 - The Need For SecurityAshura OsipNo ratings yet
- Information Security and Ethics - Tutorial 3Document3 pagesInformation Security and Ethics - Tutorial 3Lai Chen ShengNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Ingles CibersegurityDocument14 pages3.1 Ingles CibersegurityFranco AngelNo ratings yet
- Threats and AttackDocument9 pagesThreats and Attackabusamansevt1925No ratings yet
- Need For Network SecurityDocument8 pagesNeed For Network SecurityRyan CooperNo ratings yet
- Network Security Is A Broad Term That Covers A Multitude of TechnologiesDocument3 pagesNetwork Security Is A Broad Term That Covers A Multitude of TechnologiesAnonymous zXwP003No ratings yet
- BTICS501 Network Security & Cryptography (Unit-1 To 5)Document90 pagesBTICS501 Network Security & Cryptography (Unit-1 To 5)svvv ganduNo ratings yet
- Final Week4 (IAS101)Document12 pagesFinal Week4 (IAS101)Detective RomejaneNo ratings yet
- Network Security Exam Short QuestionsDocument6 pagesNetwork Security Exam Short QuestionsDiom ShresthaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentBlack Heart100% (1)
- Information Security All ChapterDocument73 pagesInformation Security All ChapterbilisummaaNo ratings yet
- M8 Info SecurityDocument7 pagesM8 Info SecurityAnimesh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Ias - ReportDocument32 pagesGroup 4 Ias - ReportRegie GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document6 pagesTutorial 1Heng PhinNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Notes Unit 1Document9 pagesCyber Security Notes Unit 1Reshma BasuNo ratings yet
- Debremarkos University School of Computing Information Security (Chapter One)Document20 pagesDebremarkos University School of Computing Information Security (Chapter One)tadesse yizengawNo ratings yet
- NIS Project Final PMV 23Document3 pagesNIS Project Final PMV 23Pooja AbhangNo ratings yet
- Security Concepts: Unit - I Security Concepts: Introduction, The Need For Security, Security Approaches, Principles ofDocument47 pagesSecurity Concepts: Unit - I Security Concepts: Introduction, The Need For Security, Security Approaches, Principles ofSAI CHAND 18-522No ratings yet
- IT NS 1 - Chapter 1b Types of Attacks and DetectionDocument6 pagesIT NS 1 - Chapter 1b Types of Attacks and DetectionGALAPON FRANCISNo ratings yet
- Module 5 INFORMATION SECURITY OVERVIEWDocument15 pagesModule 5 INFORMATION SECURITY OVERVIEWlemonademagnumNo ratings yet
- 'FFFFDocument3 pages'FFFFajay pawaraNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Interview Questions For Freshers: 1. What Is The Main Objective of Cyber Security?Document24 pagesCyber Security Interview Questions For Freshers: 1. What Is The Main Objective of Cyber Security?Gilgamesh berserkerNo ratings yet
- UNIT 10 - SecurityDocument15 pagesUNIT 10 - Securitychilekwamichael26No ratings yet
- Cyber Security-NotesDocument49 pagesCyber Security-NotesReshma BasuNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document49 pagesSession 2Zhafran HanifNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering and Technology School of Computing and Informatics Department of Information TechnologyDocument16 pagesCollege of Engineering and Technology School of Computing and Informatics Department of Information TechnologyAbdataa waaqaaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Proposal - Protecting User Resources and Privacy Using Software Security-2Document41 pagesGroup 3 Proposal - Protecting User Resources and Privacy Using Software Security-2AdoreNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security IntroductionDocument10 pagesCyber Security IntroductionRitesh KelkarNo ratings yet
- Ifs Chap 1Document22 pagesIfs Chap 1moviesera851No ratings yet
- Implications of Misuse and CybersecurityDocument5 pagesImplications of Misuse and Cybersecuritykurdeisha.cupidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Cybersecurity and Risk Management TechnologyDocument30 pagesChapter 5. Cybersecurity and Risk Management Technologyarmando.lykajovel.dllNo ratings yet
- Managing Security of InformationDocument4 pagesManaging Security of InformationredNo ratings yet
- CYBER SECURITY HANDBOOK Part-1: Hacking the Hackers: Unraveling the World of CybersecurityFrom EverandCYBER SECURITY HANDBOOK Part-1: Hacking the Hackers: Unraveling the World of CybersecurityNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking: Exploring the Dark Art of Ethical Hacking and Penetration TestingFrom EverandCybersecurity and Ethical Hacking: Exploring the Dark Art of Ethical Hacking and Penetration TestingNo ratings yet
- Summary Report: Bandwidth and ApplicationsDocument6 pagesSummary Report: Bandwidth and ApplicationsDukeNo ratings yet
- مصطلحات امن المعلوماتDocument21 pagesمصطلحات امن المعلوماتmohammedNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument1 pageGujarat Technological Universityyicef37689No ratings yet
- Digital Signatures: Homework 6Document10 pagesDigital Signatures: Homework 6leishNo ratings yet
- Database Security: CSIT115 Data Management and SecurityDocument19 pagesDatabase Security: CSIT115 Data Management and SecurityЛюбовь ТарановаNo ratings yet
- AmanBalhara CNS 01014803118Document26 pagesAmanBalhara CNS 01014803118heysiri0804No ratings yet
- Technote ISAKMP 00Document26 pagesTechnote ISAKMP 00Saptarshi BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Cryptography Basics, Methods and Standards: ICT640 - Advanced Information SecurityDocument28 pagesCryptography Basics, Methods and Standards: ICT640 - Advanced Information SecurityDr Patrick CernaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security: By: Kshirod Kumar Dehury Registration No: 1821108022Document15 pagesCyber Security: By: Kshirod Kumar Dehury Registration No: 1821108022Shibajyoti PattanaikNo ratings yet
- Cryptographic Hash FunctionsDocument16 pagesCryptographic Hash FunctionsUrvil SitapareNo ratings yet
- Blok PornoDocument27 pagesBlok Pornodavid coronaNo ratings yet
- Network Security EssentialsDocument460 pagesNetwork Security Essentialsshahab zirakiNo ratings yet
- Zamba LesDocument25 pagesZamba LesAG R OhcnaNo ratings yet
- Ciber CrimeDocument12 pagesCiber CrimeAshutosh Shukla100% (1)
- CNS Previous Questions Paper-2023Document2 pagesCNS Previous Questions Paper-2023rajsing00004444No ratings yet
- Dark WebDocument12 pagesDark WebHARDIK SANGAL 211160No ratings yet
- Lectures 1 MergedDocument154 pagesLectures 1 MergedDiana IsmailNo ratings yet
- X.509 Authentication ServiceDocument34 pagesX.509 Authentication ServiceMuhammad Junaid Anjum75% (4)
- 11.4 Pubkey TrapdoorDocument11 pages11.4 Pubkey TrapdoorSiddharth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Certified Ethical Hacker Course ContentDocument36 pagesCertified Ethical Hacker Course ContentTamer DobalNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER Digital SignatureDocument16 pagesCHAPTER Digital SignatureTanvir HassanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Post Test ICTDocument1 pageLesson 2 - Post Test ICTImie Omamalin100% (2)
- Artigo 2 - The Evolution of CybercrimeDocument3 pagesArtigo 2 - The Evolution of CybercrimeZulu RasNo ratings yet
- Midterm ITERADocument8 pagesMidterm ITERAismael delosreyesNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument25 pagesSeminar ReportAbhishek SolankiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledBhumika MhatreNo ratings yet
- Obtain A Digital Certificate To Create A Digital SignatureDocument3 pagesObtain A Digital Certificate To Create A Digital SignaturePiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Cyber ch.4/1/2Document5 pagesCyber ch.4/1/2Suvarna LondheNo ratings yet