Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class V Science Chapter 1 Long Answer Question Solution
Class V Science Chapter 1 Long Answer Question Solution
Uploaded by
Ananya ChakrabortyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class V Science Chapter 1 Long Answer Question Solution
Class V Science Chapter 1 Long Answer Question Solution
Uploaded by
Ananya ChakrabortyCopyright:
Available Formats
BHOLANANDA NATIONAL ACADEMY
Class – V
Chapter 1- More About Plants
Exercise:
Long Answer Questions.
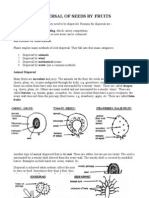
1. Define Seed Dispersal. Describe the different ways of seed dispersal.
Ans: - seed dispersal is carrying away of fruits and seeds to distant places form the parent plant
ensuring that new plants can grow in adult plants.
The different ways of seed dispersal are as follows:
1. Wind Dispersal: Some seeds have wings or hairs. When the wind blows, these seeds fly away from
the parent plant and land in new places. For example: Cotton and Dandelion.
2. Animal Dispersal: Animals like birds and mammals eat fruits containing seeds. Later, they poop out
the seeds in different locations, helping them grow in new places. For examples seeds of apple,
Jamun and many more are dispersed in this way.
3. Water Dispersal: Seeds can also travel in water. They float downstream in rivers or get carried by
ocean currents to new areas where they can grow. Seeds of Coconut and Lotus are dispersed in this
way.
4. Explosive Dispersal: Certain plants have seed pods that burst open when they are ripe, flinging the
seeds away from the parent plant. Poppy seeds and pea pods are examples of this.
2. What is agriculture? Explain its different stages.
Ans: - The practice of growing plants on a large scale for food or other purposes is called agriculture.
1. Ploughing: Ploughing is preparing the soil for planting. Farmers use a plough to turn over the
soil. This helps loosen the soil and remove any weeds or old crop remains.
2. Enrichment of Soil: After ploughing, farmers add things like super phosphate, ammonium sulphate
to the soil to make it better for plants to grow.
3. Sowing: Sowing is planting seeds in the soil. Farmers carefully place seeds or seedlings into the
ground, making sure they are spaced out evenly.
4. Irrigation: In agriculture, farmers use methods like watering cans, hoses, or even big sprinkler
systems to give the plants the water they need. This process is called irrigation.
5. Use of Chemicals: Sometimes, farmers need to use chemicals to protect their crops from pests,
diseases, or weeds that could harm them. These chemicals are called pesticides or fungicides.
6. Harvesting: When the crops are fully grown, it's time to harvest them. This means picking fruits,
vegetables, or grains from the plants.
3. Give reasons:
a. Tea cannot be planted in plains.
b. Soil is ploughed before sowing seeds.
Ans: - a. Plains often have the problem of waterlogging, where water gets stuck on the
surface because the land is flat. Tea plants can tolerate high humidity but need soil that
drains well. Thus, plains with waterlogging problem leads to low yield.
b. Ploughing helps to loosen the soil. By ploughing, farmers break up the soil, making it
softer and easier for seeds to grow roots and for young plants to push through the soil.
Ploughing allows farmers to mix in organic matter like compost or manure into the soil
making it more fertile. Ploughing can also help to improve drainage in the soil.
4. Explain the process of germination in detail.
Ans: - The different stage of germination are as follows:
1. Planting the Seed: The process of germination starts when a seed is planted in soil. The
seed contains everything the plant needs to start growing, including a tiny baby plant called
an embryo, stored food, and a protective seed coat.
2. Absorption of Water: When the seed is planted in the soil, it absorbs water through tiny
openings in its seed coat.
3. Root Growth: The first part to emerge from the seed is usually the root. The root grows
downward into the soil, anchoring the plant and absorbing water and nutrients from the soil.
4. Shoot Growth: As the root grows downward, a tiny stem, or shoot, begins to grow upward
towards the surface of the soil.
5. Emergence of Seedling: Finally, the shoot breaks through the soil surface and the seed
have successfully germinated.
5. Explain how plants grow from parts other than the seeds. Give examples.
Ans: -
1. Stems: Some plants can grow new plants from their stems. For example, plants like mint
and strawberry have stems called runners. These runners spread out along the ground and
can produce new roots and shoots, which grow into new plants.
2. Leaves: Certain plants, like Begonia and Bryophyllum grow buds along their edges. These
buds grow into new plants when they fall on the ground and get sufficient sunlight, air and
water.
3. Roots: Plants like sweet potato, carrot and the dahlia, can grow new plants from their
roots.
4. Spores: Some plants like mushrooms and ferns grow from spores which are located on
their leaves.
You might also like
- Tensor Rings The Ancient Technology That Was Lost Forgotten v2Document45 pagesTensor Rings The Ancient Technology That Was Lost Forgotten v2Kurnianto Legacy86% (14)
- Project Proposal FOR: Mineral Water Bottling PlantDocument39 pagesProject Proposal FOR: Mineral Water Bottling PlantTesfaye Degefa100% (3)
- CRPT 2 - 3Document5 pagesCRPT 2 - 3Gil Bustilla100% (2)
- Internship at Harrison Malayalam Ltd.Document49 pagesInternship at Harrison Malayalam Ltd.Soumya Nayak100% (2)
- OWING PLANTS - Learning MaterialDocument5 pagesOWING PLANTS - Learning MaterialpraviseNo ratings yet
- Class-5 Science Plant ReproductionDocument4 pagesClass-5 Science Plant ReproductionSandeep Shaw100% (1)
- Lesson 2Document11 pagesLesson 2christopher palacioNo ratings yet
- STD - Iii Sub - Science CH - Plants in Our SurroundingsDocument3 pagesSTD - Iii Sub - Science CH - Plants in Our SurroundingsSudip GhoshNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Reproduction in Plants: Class-5Document12 pagesChapter-2 Reproduction in Plants: Class-5Sejal NamdeoNo ratings yet
- Seed GerminationDocument7 pagesSeed Germinationganeshbalak2000No ratings yet
- Worksheet in Tle 6 (Agriculture Week 2) : I. What I Need To KnowDocument18 pagesWorksheet in Tle 6 (Agriculture Week 2) : I. What I Need To Knowjaypee vargasNo ratings yet
- 6 ThscicenceDocument4 pages6 Thscicencelearn4chatgptNo ratings yet
- Agri Lesson 2 Elements To Be Observed in Planting Trees and Fruit Bearing TreesDocument21 pagesAgri Lesson 2 Elements To Be Observed in Planting Trees and Fruit Bearing TreesLady RuedaNo ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument2 pagesAgriculturevim09480No ratings yet
- Home GardeningDocument6 pagesHome GardeningMuhammad Tayyab AhmadNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction Grade - 5Document3 pagesPlant Reproduction Grade - 5Sunil Nagar100% (1)
- Onahon (TLE - 2k Report)Document5 pagesOnahon (TLE - 2k Report)Sharmaine FabriaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HorticultureDocument26 pagesIntroduction To HorticultureGino R. MonteloyolaNo ratings yet
- Agriculture HandoutsDocument3 pagesAgriculture HandoutsShella Mae AmperNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument7 pagesReproduction in PlantsrupeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Review Science1Document9 pagesChapter 3 Review Science1api-263324472No ratings yet
- References: TECHNOLOGY and LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION 8 K-12 Edition Fe S.J. Mangalindan, Et Al. Page 179-186Document2 pagesReferences: TECHNOLOGY and LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION 8 K-12 Edition Fe S.J. Mangalindan, Et Al. Page 179-186eldrich balinbinNo ratings yet
- Sci7 Unit B Unit ReviewDocument16 pagesSci7 Unit B Unit Reviewapi-242221534No ratings yet
- EstherDocument17 pagesEsthersharonkathleen28No ratings yet
- TLE-Agriculture 9 Reviewer Q2Document4 pagesTLE-Agriculture 9 Reviewer Q2garciathomas0210No ratings yet
- Dispersal of Seeds by FruitsDocument6 pagesDispersal of Seeds by FruitsAnil PantNo ratings yet
- Elements To Be Observed in Planting TreesDocument18 pagesElements To Be Observed in Planting TreesDolores Dellosa Noga85% (13)
- 2ND Term S1 Agricultral ScienceDocument22 pages2ND Term S1 Agricultral ScienceDavidNo ratings yet
- Basics of Indoor GardeningDocument9 pagesBasics of Indoor Gardeningمصطفى جاسمNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Biology 6th ClassDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Biology 6th ClassManju kotturNo ratings yet
- Week 3-4 Methods and WAYS of PlantingDocument21 pagesWeek 3-4 Methods and WAYS of PlantingPen Molina de VeraNo ratings yet
- Establishing Horticultural ProjectDocument8 pagesEstablishing Horticultural ProjectWILMOR A. DIONESNo ratings yet
- Tropical Landscape ManagementDocument6 pagesTropical Landscape ManagementRafael LlabanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Elements To Be Observed in Planting Trees and FruitDocument4 pagesLesson 2 Elements To Be Observed in Planting Trees and FruitBimbo CuyangoanNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity: The Evolution and Classification of PlantsDocument23 pagesPlant Diversity: The Evolution and Classification of PlantsJose CariasNo ratings yet
- d6668f1f 68de 4182 bd3c Fd0df6031deDocument5 pagesd6668f1f 68de 4182 bd3c Fd0df6031deFatoom KazemiNo ratings yet
- Sexual Propagation in PlantsDocument8 pagesSexual Propagation in PlantsSreeja RajNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Agriculture Science Week 2 Lesson 1Document5 pagesGrade 8 Agriculture Science Week 2 Lesson 1Balram HaroldNo ratings yet
- Plant PropagationDocument4 pagesPlant PropagationChryselleNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument8 pagesReproduction in PlantsRenuNo ratings yet
- Stages of Germination in A Seed.: Seed Coat Breaks and The Baby Plant GrowsDocument3 pagesStages of Germination in A Seed.: Seed Coat Breaks and The Baby Plant GrowsSri sai DuttNo ratings yet
- Commmunitiy Nursery PracticesDocument44 pagesCommmunitiy Nursery PracticesKonrad Neil III100% (1)
- How Do Plants Grow? Botany Book for Kids | Children's Botany BooksFrom EverandHow Do Plants Grow? Botany Book for Kids | Children's Botany BooksNo ratings yet
- LESSON 40 WPS OfficeDocument13 pagesLESSON 40 WPS OfficeEbrada Nea GuintoNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument14 pagesBio Projectathish athishNo ratings yet
- TLE-Fruit Bearing Trees-Week 2Document6 pagesTLE-Fruit Bearing Trees-Week 2Michelle AcostaNo ratings yet
- Dispersal of Seeds-1Document10 pagesDispersal of Seeds-1samuelsimte024No ratings yet
- The Life Cycle of A Bean Plant: Seed Germination SeedlingDocument4 pagesThe Life Cycle of A Bean Plant: Seed Germination SeedlingMaira ibadullaNo ratings yet
- Agri MS 2012Document19 pagesAgri MS 2012Andrew ArahaNo ratings yet
- Elements To Be Observed in Planting TreesDocument18 pagesElements To Be Observed in Planting TreesDolores Dellosa Noga0% (1)
- RootsDocument8 pagesRootsLenovoNo ratings yet
- Growing Tomato ExperimentDocument6 pagesGrowing Tomato ExperimentPatrick Regidor83% (6)
- Daryl GuinayenDocument9 pagesDaryl GuinayenEmmanuel GallidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Growing Plants Question Bank With Answer KeyDocument21 pagesChapter-4 Growing Plants Question Bank With Answer KeySUHANEERIYA100% (1)
- Gr12 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument14 pagesGr12 - Reproduction in PlantsZelNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity and Evolution of Plant KingdomDocument12 pagesPlant Diversity and Evolution of Plant KingdomWardah BaigNo ratings yet
- Two Methods of Planting Gr.5Document2 pagesTwo Methods of Planting Gr.5abelNo ratings yet
- Aaua SIWES Report Compiled by OLATUNJI ODocument51 pagesAaua SIWES Report Compiled by OLATUNJI OAyodeleNo ratings yet
- Science - 111120 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument6 pagesScience - 111120 - Reproduction in PlantsDeepak Kansal100% (1)
- Grade 5 Science (CHPT 1)Document3 pagesGrade 5 Science (CHPT 1)Pankaj RajoriaNo ratings yet
- Fruits and SeedsDocument4 pagesFruits and Seedscornaga WirayudhaNo ratings yet
- Agriculture (Week1 Week4) Grade6Document91 pagesAgriculture (Week1 Week4) Grade6PIOLO LANCE SAGUNNo ratings yet
- The First Plants Grow on Land: The Golden Serie of History: From the First Life Forms to the Latest Humanoid Robot, #3From EverandThe First Plants Grow on Land: The Golden Serie of History: From the First Life Forms to the Latest Humanoid Robot, #3No ratings yet
- MicrobiologieDocument4 pagesMicrobiologieNonea GabrielNo ratings yet
- Heavy Metals in Soils From The Horticultural Areas of Sârca and Huşi (Romania)Document6 pagesHeavy Metals in Soils From The Horticultural Areas of Sârca and Huşi (Romania)Eugen TătaruNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For The Flushing of Chilled Water Pipes: Document Number: REE-MS-MOQH-HVAC-014 REV 00Document33 pagesMethod Statement For The Flushing of Chilled Water Pipes: Document Number: REE-MS-MOQH-HVAC-014 REV 00Boj Mingi0% (1)
- Rail Rehabilitation ReportDocument80 pagesRail Rehabilitation ReportOm SinghNo ratings yet
- 2014 Kayabali Yaldiz ENG PDFDocument14 pages2014 Kayabali Yaldiz ENG PDFStephanie SinghNo ratings yet
- Design of A Pile GroupBy UsingSoil PropertiesDocument12 pagesDesign of A Pile GroupBy UsingSoil PropertiesYogie Fian ZahriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Rev Sha 812013Document36 pagesChapter 2 Rev Sha 812013Azimah HamidonNo ratings yet
- Sample Ge QuestionsDocument8 pagesSample Ge QuestionsAditya SutarNo ratings yet
- Hydroponics Final Report PDFDocument137 pagesHydroponics Final Report PDFRobert Castro100% (1)
- Riparian ZonesDocument24 pagesRiparian ZonesJuan Villicaña Dapénzxu100% (1)
- No. 64 Management of Zinc-Deficient SoilsDocument20 pagesNo. 64 Management of Zinc-Deficient SoilsmtmustapaNo ratings yet
- Unified Soil Classification System: Symbol ChartDocument2 pagesUnified Soil Classification System: Symbol Chartdiscocyclina100% (1)
- Class 8 Ncert Geography: Chapter-1 ResourcesDocument51 pagesClass 8 Ncert Geography: Chapter-1 ResourcessatyamksspNo ratings yet
- Advancements in Ground Improvement Technique: Prepared ByDocument17 pagesAdvancements in Ground Improvement Technique: Prepared Byrudra katarmalNo ratings yet
- Vol IE Tender DrawingsDocument53 pagesVol IE Tender DrawingsAnnisa Nabilah Mohd HashimNo ratings yet
- CH 4 InfiltrationDocument31 pagesCH 4 Infiltrationmengistuberhanu2015No ratings yet
- Water Requirements For Crops: Chapter No 02 by Santosh Kumar GargDocument32 pagesWater Requirements For Crops: Chapter No 02 by Santosh Kumar GargUmer WaheedNo ratings yet
- Construction Equipments - Rollers: Presented byDocument16 pagesConstruction Equipments - Rollers: Presented byAditi BazajNo ratings yet
- The Design of Vibro Replacement (Priebe Teory)Document17 pagesThe Design of Vibro Replacement (Priebe Teory)paduco100% (3)
- Petrofisika TM2209 W10Document25 pagesPetrofisika TM2209 W10Hafiizhoh HanafiaNo ratings yet
- Credit Seminar Final 08-05-2020-1Document38 pagesCredit Seminar Final 08-05-2020-1Manoj Kumar LodhiNo ratings yet
- Case Studies UNDP: BAMBOO VILLAGE OF PHU AN, VietnamDocument13 pagesCase Studies UNDP: BAMBOO VILLAGE OF PHU AN, VietnamUNDP_EnvironmentNo ratings yet
- Agriculture - Mineral Nutrition - IntroductionDocument2 pagesAgriculture - Mineral Nutrition - IntroductionGunasridharan LakshmananNo ratings yet
- Seed PrimingDocument4 pagesSeed PrimingbigbangNo ratings yet
- Sts Module 3 Lesson 4 5 Edited For CBLDocument18 pagesSts Module 3 Lesson 4 5 Edited For CBLHanabi PandonganNo ratings yet
- Geosciences 10 00241Document18 pagesGeosciences 10 00241Karely González GálvezNo ratings yet
- Libro de ResumenDocument280 pagesLibro de ResumenGary Andree Perez ZevallosNo ratings yet