Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Test Study
Biology Test Study
Uploaded by
adamek.essidOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Test Study
Biology Test Study
Uploaded by
adamek.essidCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Respiratory system structure: (doc fixed by yours truly)
2. Difference between breathing, gas exchange, and respiration:
Breathing - Breathing are the body movements which permit air to get in and out of
your lungs.
Gas exchange - The movement of gasses across a respiratory surface. Simply, this is
the exchange of gas in the alveoli (respiratory surface, in this case) where the
oxygen goes into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide goes into the alveoli so that
it can be expelled from the body.
Respiration - Respiration is the release of energy from food.
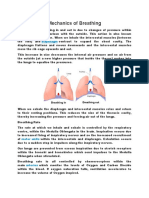
3. Mechanism of breathing:
When you breathe in:
* External intercostal muscles contract and push rib cage outwards and upwards.
* Diaphragm contracts and moves down.
* The lungs increase their volume, so pressure decreases.
* Air rushes in the lungs to equalize the pressure.
When you breathe out:
* Internal intercostal muscles relax and push rib cage inwards and downwards.
* Diaphragm returns to its original shape.
* The lungs, decrease their volume, which increases the pressure.
* Air is forced out of the lungs.
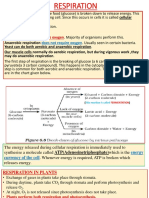
4. Aerobic and anaerobic respiration:
Aerobic respiration uses oxygen. It is much more efficient than anaerobic
respiration since it produces more energy. Most organisms use aerobic respiration.
The reaction for aerobic respiration is:
Glucose + Oxygen => Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP
C6H12O6 + 602 => 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Anaerobic respiration takes place in some organisms like bacteria and fungi.
(where oxygen is scarce).
There are 2 formulas for it:
1. In yeasts and some plants:
Glucose => Carbon dioxide + Ethanol + ATP
C6H1206 =>6C02 + C2H50H + ATP
2. In bacteria and muscle cells
Glucose => Lactic Acid + ATP
5. Excretion and waste products:
Excretion is the removal of waste products of metabolism.
Metabolism are all the chemical reactions in an organism.
Waste products of the human body:
* CO2, product of respiration which is removed from lungs.
* Urea, product of deamination of animo acids. Removed from kidneys.
* Excess water and minerals, removed through kidneys.
6. Kidney and urinary system structure and role of kidneys :
The role of kidneys are:
* Osmoregulation
* Filteration of blood
7. Control of blood glucose level:
When Blood glucose level is too high:
* Pancreas produce insulin
* Insulin converts glucose into glycogen
* Blood glucose level is decreased.
When Blood glucose level is too low:
* Pancreas produce glucagon
* Glucagon converts glycogen into glucose
* Blood glucose level rises.
8. What is vasoconstriction?
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of blood vessles. It is used to decrease body
temperature.
What is vasodilation?
Vasodialation is the opposite of vasalconstriction it is the widening of blood
vessels allowing more blood to flow through them and reduce blood pressure. It is
used to increase body temperature.
Thermoregulation
Thermoregulation is the homeostaic process that maintains a steady body temperature
even with changes external conditions.
You might also like
- Safety Devices in Air Compressors On ShipsDocument30 pagesSafety Devices in Air Compressors On ShipsSwarg Vibha100% (1)
- Velopi PMP Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pageVelopi PMP Cheat Sheet PDFAbhijith VJNo ratings yet
- Theme Meal ReportDocument10 pagesTheme Meal Reportapi-434982019No ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument24 pagesRespiration and Gas ExchangeEizelle100% (2)
- Human and Social Biology The Respiratory System 10 1 and 2Document35 pagesHuman and Social Biology The Respiratory System 10 1 and 2Science,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Notes RespirationDocument6 pagesNotes Respirationakheel7353No ratings yet
- Lec 17 Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesLec 17 Circulatory SystemEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument25 pagesRespiratory SystemAnonymous 5hYhEkINo ratings yet
- Respiration and BreathingDocument57 pagesRespiration and BreathingHarvagale BlakeNo ratings yet
- 4 A - RespirationDocument15 pages4 A - Respirationsalishfan1289No ratings yet
- Mechanics of BreathingDocument5 pagesMechanics of BreathingMark Lyndon M OrogoNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument6 pagesBiology NotesAmira FarahinNo ratings yet
- Respiration Science AssessmentDocument19 pagesRespiration Science Assessmentmarta.amsNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument3 pagesRespiration in Organismschrisbronzel56No ratings yet
- Biological SystemsDocument17 pagesBiological SystemspremilasathiyanandanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ScienceDocument12 pagesReviewer Scienceethansuico13No ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument7 pagesRespiration NotesTamisha JacobsNo ratings yet
- Notes Life Processes (Repiration)Document2 pagesNotes Life Processes (Repiration)07.joycharlieNo ratings yet
- Circulatory + Respiratory SystemDocument47 pagesCirculatory + Respiratory Systemguptamridul2009No ratings yet
- Respiration 2Document23 pagesRespiration 2api-233649346No ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument11 pagesRESPIRATIONCREATIVING TAMILANNo ratings yet
- G Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3Document14 pagesG Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3jhaorpratyushNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Human Respiratory SystemWei Ling KuahNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10 Respiration, Class-7Document11 pagesChapter-10 Respiration, Class-7Rajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- 9 RespirationDocument3 pages9 RespirationKavin ManimaranNo ratings yet
- Apuntes Science Tema 1Document6 pagesApuntes Science Tema 1larafernandezveloso10No ratings yet
- Respiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyDocument5 pagesRespiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyTechnical AyushNo ratings yet
- Biology U2Document10 pagesBiology U2Alima IqbalNo ratings yet
- Adm Modules Science 9 2021 Week 1 4 ValidatedDocument30 pagesAdm Modules Science 9 2021 Week 1 4 ValidatedAshley Nicole VallespinNo ratings yet
- Respiration BIOLOGY Year 9 PosterDocument7 pagesRespiration BIOLOGY Year 9 PostererinaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismDocument12 pagesRespiration in OrganismopsharpedgeNo ratings yet
- HOMEOSTASISDocument21 pagesHOMEOSTASISririrachma fitriahNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - 2Document9 pagesLife Processes - 2kishanth9410No ratings yet
- Respiration 10Document5 pagesRespiration 10Aditya DhawanNo ratings yet
- Sheniblog-Class 9 Biology Chapter 4 (Eng Med) NotesDocument3 pagesSheniblog-Class 9 Biology Chapter 4 (Eng Med) Notesdevu fav MohanNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument5 pagesRespirationDivyansh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Physiology PDFDocument121 pagesRespiratory System Physiology PDFVizhiNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms Class 7 NotesDocument37 pagesRespiration in Organisms Class 7 Notestrisha.sharma2347No ratings yet
- Lec-18 - Respiratory & Excretory SystemDocument23 pagesLec-18 - Respiratory & Excretory Systemfahadkhanbd911No ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument17 pagesRespiration in OrganismsSaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument30 pagesBiologyVictor OkosunNo ratings yet
- Midterm Activity - Fluids & ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesMidterm Activity - Fluids & Electrolytesnaranjah ongNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Respiratory SubstrateDocument8 pagesRespiration: Respiratory SubstrateEdwins MaranduNo ratings yet
- G7 ScienceDocument27 pagesG7 Scienceranjan.kvisNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument27 pagesChapter Iapi-290338101100% (1)
- Biology ScienceDocument9 pagesBiology SciencetalaNo ratings yet
- Science Notes WITH CHEMDocument11 pagesScience Notes WITH CHEMAlfredNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Power PointDocument24 pagesRespiratory System Power PointammarNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument29 pagesRespiration and Gas Exchangemiriam odonkorNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document138 pagesChapter 7Bëar MëNo ratings yet
- The Human Breathing SystemDocument23 pagesThe Human Breathing Systemailyn costalesNo ratings yet
- Pastel Illustration Computer UI English Class Education PresentationDocument30 pagesPastel Illustration Computer UI English Class Education PresentationElaiza marie VenusNo ratings yet
- CH 6 E - Notes RespirationDocument5 pagesCH 6 E - Notes RespirationRajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Bio NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 11 Bio NotesArabella ShepherdNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Lesson 1 FinalDocument11 pagesRespiratory System Lesson 1 FinaltayNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Ppt.Document21 pagesRespiratory System Ppt.Tino MabhizaNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Biology GCE Study BuddyDocument45 pagesRespiration: Biology GCE Study BuddyMaleeha HumayunNo ratings yet
- Gr. 9 Science LM (AG)Document33 pagesGr. 9 Science LM (AG)Aizalonica GalangNo ratings yet
- Respiration+and+PollutionDocument45 pagesRespiration+and+Pollutioncaceresrihany1206No ratings yet
- Respiration: - Respiration Is The Release of Energy From Food Substances in All Living CellsDocument8 pagesRespiration: - Respiration Is The Release of Energy From Food Substances in All Living CellsMandla RebirthNo ratings yet
- A Glimpse To A Human Person: Who Am I?: Front PageDocument17 pagesA Glimpse To A Human Person: Who Am I?: Front PageGabrielle May LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- Management of HyperlipidemiaDocument39 pagesManagement of HyperlipidemiaRajgopal100% (2)
- Fil. Oil Refinery Vs Fil Oil SupervisoryDocument1 pageFil. Oil Refinery Vs Fil Oil SupervisoryMekiNo ratings yet
- Lifting Operations Onboard ShipDocument3 pagesLifting Operations Onboard ShipGiorgi KandelakiNo ratings yet
- Picot Et Al 2023 Development and Validation of The Ankle Go Score For Discriminating and Predicting Return To SportDocument11 pagesPicot Et Al 2023 Development and Validation of The Ankle Go Score For Discriminating and Predicting Return To Sportpdelcampo1991No ratings yet
- Comparaison Internationale Atmofrance enDocument50 pagesComparaison Internationale Atmofrance enpeguy diffoNo ratings yet
- Carbo LoadingDocument8 pagesCarbo Loadinggolevila100% (1)
- Chapter 12Document16 pagesChapter 12서승찬100% (6)
- Revised Cambridge Reference SequenceDocument6 pagesRevised Cambridge Reference SequenceRiemha Tiquie PurpleNo ratings yet
- Final Paper 1Document27 pagesFinal Paper 1api-315734227No ratings yet
- Supply Chain Resilience and Healthcare Delivery in Disasters: A Structured ReviewDocument13 pagesSupply Chain Resilience and Healthcare Delivery in Disasters: A Structured ReviewShahnewaj SharanNo ratings yet
- Hisense E20 HLTE103E: User GuideDocument40 pagesHisense E20 HLTE103E: User GuideMiguel.ANo ratings yet
- Field Study 1 Episode 5Document8 pagesField Study 1 Episode 5Fredie RamosNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 1N914Document4 pagesDatasheet 1N914LucianoAlcatelmoNo ratings yet
- Hearing ImpairementDocument8 pagesHearing ImpairementMARY KENNETH SILVOSANo ratings yet
- Purchase Order: Barato Supply CompanyDocument4 pagesPurchase Order: Barato Supply CompanyFilna QuiñoNo ratings yet
- Medication Card HeparinDocument2 pagesMedication Card HeparinEllieNo ratings yet
- District Judge Barry Bloss' Criminal DispositionsDocument3 pagesDistrict Judge Barry Bloss' Criminal DispositionsYork Daily Record/Sunday NewsNo ratings yet
- Intro PaperDocument6 pagesIntro PaperbonnmengulloNo ratings yet
- Notes Muscle Relaxants Part 3Document62 pagesNotes Muscle Relaxants Part 3Charlotte FabrosNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lec 4 Anisakis KatDocument6 pagesParasitology Lec 4 Anisakis KatRachel Marie M. GaniaNo ratings yet
- Literary Criticsm The Greatest ShowmanDocument10 pagesLiterary Criticsm The Greatest ShowmanZafira MalikNo ratings yet
- Anaclitic (Dependent) DepressionDocument3 pagesAnaclitic (Dependent) DepressionMihaela IosubNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Medicare Insurance PlanDocument7 pagesDifferent Types of Medicare Insurance PlanGetmy PolicyNo ratings yet
- Friedreich AtaxiaDocument18 pagesFriedreich AtaxiaGamer MadaNo ratings yet
- Pec Self-Rating Questionnaire Scoring SheetDocument3 pagesPec Self-Rating Questionnaire Scoring SheetDanicaNo ratings yet
- Protective Device Coordination in An Industrial Power System With Multiple SourcesDocument10 pagesProtective Device Coordination in An Industrial Power System With Multiple SourcestechtricNo ratings yet