Professional Documents
Culture Documents
National Museum of Cambodia Board
National Museum of Cambodia Board
Uploaded by
loeundalin080402Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Collins - Mission Françias - Pupil Book 1Document146 pagesCollins - Mission Françias - Pupil Book 1get thosebooks0% (1)
- Architecture in Cambodia: GeologicalDocument8 pagesArchitecture in Cambodia: GeologicalJohnBenedictRazNo ratings yet
- AP Art Midterm Short AnswerDocument8 pagesAP Art Midterm Short AnswerhollqNo ratings yet
- Stone Sculpture: History, Types, Materials, TechniquesDocument6 pagesStone Sculpture: History, Types, Materials, TechniquesAlly DeanNo ratings yet
- Visual Art Ss 1 First TermDocument26 pagesVisual Art Ss 1 First Termpalmer okiemuteNo ratings yet
- LAS 3 History of ArtDocument21 pagesLAS 3 History of ArtREYNAN ZAMORANo ratings yet
- Pre Historic Times Stone Age To Bronze Age ArtDocument3 pagesPre Historic Times Stone Age To Bronze Age ArtUzziel Galinea TolosaNo ratings yet
- Art HistoryDocument3 pagesArt HistoryKyla AlegroNo ratings yet
- Group 2 ReportDocument27 pagesGroup 2 ReportYanyan TumaldingNo ratings yet
- Big AP ReviewDocument226 pagesBig AP ReviewLaura MesaNo ratings yet
- Douglas and Sorensen Mineralogical Characteristics of Khmer SculptureDocument10 pagesDouglas and Sorensen Mineralogical Characteristics of Khmer SculptureLynda AlbertsonNo ratings yet
- ARTA 211 Midterm Discussion GuideDocument5 pagesARTA 211 Midterm Discussion GuidexeanNo ratings yet
- Art and CultureDocument181 pagesArt and Culturepranshubaghel001No ratings yet
- HUM1Document9 pagesHUM1Edsh Rose Rosales100% (1)
- Asian ArtDocument23 pagesAsian ArtChosen Josiah HuertaNo ratings yet
- Ged3 Art AppreciationDocument17 pagesGed3 Art AppreciationVincentNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument11 pagesArt AppreciationMary Grace TolentinoNo ratings yet
- LAS 2 Art Chapter 2Document20 pagesLAS 2 Art Chapter 2Kyle LañaNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation 2pptDocument6 pagesArt Appreciation 2pptMax Moon PENo ratings yet
- LAS 2 Teaching ArtDocument21 pagesLAS 2 Teaching ArtApril Joy CalilanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Reviewer Art AppDocument3 pagesModule 3 Reviewer Art AppQueenemitchfe PulgadoNo ratings yet
- China, India, Japan, SE Asia.: Buquiron - Jazul - SerraDocument65 pagesChina, India, Japan, SE Asia.: Buquiron - Jazul - SerraHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Week7 HMN101 ART HISTORYDocument8 pagesWeek7 HMN101 ART HISTORYNovelyn Degones DuyoganNo ratings yet
- ART APPRECIATION With ASSESSMENTDocument28 pagesART APPRECIATION With ASSESSMENTremacor tagannaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 ArtsDocument16 pagesModule 5 ArtsRobbie YbanezNo ratings yet
- EMP PrayerDocument78 pagesEMP PrayerCHRISTIAN JAY CJ PRESIDENTENo ratings yet
- History of Construction Field Trips 50083Document73 pagesHistory of Construction Field Trips 50083Jiu ShitzukiNo ratings yet
- Arts 9 Unit 1 PDFDocument37 pagesArts 9 Unit 1 PDFLOLNo ratings yet
- Nok Culture - WikipediaDocument18 pagesNok Culture - WikipediaoffyNo ratings yet
- Prehistoric and Ancient Period Sculpture HandoutsDocument2 pagesPrehistoric and Ancient Period Sculpture HandoutsSittie Asraleah AgatonNo ratings yet
- Asian ArtDocument16 pagesAsian ArtAdrienne James SantillanNo ratings yet
- Art App g6Document53 pagesArt App g6lorrainefavoritoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To World Art and Culture 2Document56 pagesIntroduction To World Art and Culture 2lajbymehakguptaNo ratings yet
- Key Elements:: Art Pieces Stone AgeDocument9 pagesKey Elements:: Art Pieces Stone AgeHanie FordNo ratings yet
- Prehistoric Art - Origins, Types, Characteristics, ChronologyDocument15 pagesPrehistoric Art - Origins, Types, Characteristics, Chronologyarchitectfemil6663100% (1)
- 555555Document5 pages555555Lhea Dacillo San JoaquinNo ratings yet
- PART II Reliefs of AngkorDocument22 pagesPART II Reliefs of AngkorUday DokrasNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6.ArtsAppreciation 075455Document64 pagesCHAPTER 6.ArtsAppreciation 075455April Rose Pabadora RojasNo ratings yet
- Bas Reliefs at AngkorDocument43 pagesBas Reliefs at AngkorudayNo ratings yet
- GED3Document17 pagesGED3VincentNo ratings yet
- Arts-Quarter I: 7 Elements of ArtDocument5 pagesArts-Quarter I: 7 Elements of ArtLeuweyne SerranoNo ratings yet
- Prehistoric ArtDocument20 pagesPrehistoric Artespinarishel14No ratings yet
- Architecture of IndiaDocument60 pagesArchitecture of IndiaLaxmi MaradaNo ratings yet
- Journal Pone 0250230Document26 pagesJournal Pone 0250230James Ricardo Zorro MonrroyNo ratings yet
- Art App Midterms (Finale)Document4 pagesArt App Midterms (Finale)Shaira MirandaNo ratings yet
- Module 7.1: Art History: Reading The Image Prehistoric Cave PaintingsDocument70 pagesModule 7.1: Art History: Reading The Image Prehistoric Cave PaintingsAnony MousNo ratings yet
- Technology in Ancient India Michel DaninDocument98 pagesTechnology in Ancient India Michel DaninSarthak MeenaNo ratings yet
- Early Visual Works of Art in Other CountriesDocument10 pagesEarly Visual Works of Art in Other CountriesPIC LIBRARYNo ratings yet
- Activity For Art AppDocument8 pagesActivity For Art AppKath DayagNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation With AssessmentDocument39 pagesArt Appreciation With AssessmentJean VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- الماوى الصخري كوم بوجاي ص27Document15 pagesالماوى الصخري كوم بوجاي ص27atheerNo ratings yet
- Jomon Pottery Cord-Imitating Decoration: Irina ZhushchikhovskayaDocument9 pagesJomon Pottery Cord-Imitating Decoration: Irina ZhushchikhovskayaSidemen For LifeNo ratings yet
- Ancient Art9Document41 pagesAncient Art9xenaNo ratings yet
- Aurora Pioneers Memorial College: Ge Elec 111 - Arts and HumanitiesDocument4 pagesAurora Pioneers Memorial College: Ge Elec 111 - Arts and Humanitiescherry batalunaNo ratings yet
- B5 HUM 1 Finals ReviewerDocument27 pagesB5 HUM 1 Finals ReviewerVenous LakarNo ratings yet
- Ancient Pottery (From 18,000 BCE) : Evolution of ArtDocument13 pagesAncient Pottery (From 18,000 BCE) : Evolution of ArtyowNo ratings yet
- Art Sculptures 2Document22 pagesArt Sculptures 2Gulliver LabraNo ratings yet
- Midterm LessonDocument41 pagesMidterm LessonCriszel Mae DedaseNo ratings yet
- Roblo - BMC - Group 1 ProjectDocument21 pagesRoblo - BMC - Group 1 ProjectLesther RobloNo ratings yet
- Art App - MidtermDocument8 pagesArt App - MidtermMeriiiNo ratings yet
- Prehistoric Art - Cave Dwellers Edition - History for Kids | Asian, European, African, Americas & Oceanic Regions | 4th Grade Children's Prehistoric BooksFrom EverandPrehistoric Art - Cave Dwellers Edition - History for Kids | Asian, European, African, Americas & Oceanic Regions | 4th Grade Children's Prehistoric BooksNo ratings yet
- CV Camille HenrotDocument22 pagesCV Camille HenrotChloe VellaNo ratings yet
- Caitlin J. Keefe - CVDocument2 pagesCaitlin J. Keefe - CVckeef002No ratings yet
- 1.2 Present Tenses - Question FormsDocument1 page1.2 Present Tenses - Question Formsмария паловаNo ratings yet
- Visual Analysis of Joshua Johnson's Painting: Letita Grace McCurdyDocument8 pagesVisual Analysis of Joshua Johnson's Painting: Letita Grace McCurdysara kahnNo ratings yet
- Ottoman Istanbul WebsiteDocument54 pagesOttoman Istanbul WebsitebosLooKNo ratings yet
- 14 Case Study Shanghai World Financial Center PDFDocument6 pages14 Case Study Shanghai World Financial Center PDFyusriandiNo ratings yet
- Butuan SilverDocument9 pagesButuan SilverCasio Je-urNo ratings yet
- Innovation in The Public Sector - Linking Capacity and Leadership (Governance and Public Management)Document263 pagesInnovation in The Public Sector - Linking Capacity and Leadership (Governance and Public Management)ผศ.ดร.ทวิพันธ์ พัวสรรเสริญ100% (1)
- Rezolvare Variante Bac 2009 Problema 4Document8 pagesRezolvare Variante Bac 2009 Problema 4Serban OnofreiNo ratings yet
- U07754QOSM - Project O & M Manual Auditorium SeatingDocument13 pagesU07754QOSM - Project O & M Manual Auditorium SeatingRithesh Shetty100% (1)
- American PresidentsDocument209 pagesAmerican PresidentsDrAbdul-Settar Abdul-Latif MalallahNo ratings yet
- The Germ of An Idea Contagionism, Religion, and S Ociety in Britain, 1660-1730Document318 pagesThe Germ of An Idea Contagionism, Religion, and S Ociety in Britain, 1660-1730MarthaNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Tieng Anh 6 Bai 9Document25 pagesBai Tap Tieng Anh 6 Bai 9Quyen DangNo ratings yet
- Username: Password:: File Hosting Search Login RegisterDocument3 pagesUsername: Password:: File Hosting Search Login RegisterAditya JoshiNo ratings yet
- Porting C To RustDocument216 pagesPorting C To RustBartoszSowulNo ratings yet
- Opel GM Grandland X 2020 Wiring DiagramsDocument22 pagesOpel GM Grandland X 2020 Wiring Diagramsmissrebeccacolon240796mxe100% (117)
- David (Charles Wendell) - Narratio de Itinere Navali Peregrinorum Hierosolymam Tendentium Et Silviam Capientium, A. D. 1189Document90 pagesDavid (Charles Wendell) - Narratio de Itinere Navali Peregrinorum Hierosolymam Tendentium Et Silviam Capientium, A. D. 1189Jean-Pierre Molénat100% (1)
- Further Practice Unit 2-2023Document5 pagesFurther Practice Unit 2-2023Trần PhápNo ratings yet
- My Personal Guide: TripwolfDocument12 pagesMy Personal Guide: TripwolfEgle CerNo ratings yet
- Programming React NativeDocument172 pagesProgramming React NativeTomislav Knežević100% (3)
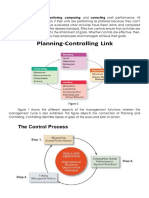
- Controlling HandoutDocument6 pagesControlling HandoutJeremy Paul Gecolea100% (1)
- CICTESTDocument9 pagesCICTESTratulray2006No ratings yet
- LabVIEW Basics I Course Manual 6 (1) .0Document388 pagesLabVIEW Basics I Course Manual 6 (1) .0Dinh Thang LeNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument10 pagesJavaNisha Mary GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Matisse PicassoDocument6 pagesMatisse PicassoGeorgi PagolaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Catholicismand Nineteenth-Centuryfiction: More InformationDocument8 pagesAnti-Catholicismand Nineteenth-Centuryfiction: More Informationbudinha007No ratings yet
- João Álvaro Carvalho - Information System - Which One Do You MeanDocument24 pagesJoão Álvaro Carvalho - Information System - Which One Do You MeanLuis FelipeNo ratings yet
- Lotus Domino Designer 8.5.1 Classic Notes Applications (DDCNA851)Document5 pagesLotus Domino Designer 8.5.1 Classic Notes Applications (DDCNA851)marializaestellaNo ratings yet
- Design May 2016Document5 pagesDesign May 2016ArtdataNo ratings yet
National Museum of Cambodia Board
National Museum of Cambodia Board
Uploaded by
loeundalin080402Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
National Museum of Cambodia Board
National Museum of Cambodia Board
Uploaded by
loeundalin080402Copyright:
Available Formats
NATIONAL MUSEUM OF CAMBODIA
National Polytechnic Institute Of Cambodia
Faculty Of Civil Engineering and Architecture
Teacher : San Phearom
Students : Loeun Dalin Pao SreyDuong Sorn ChhaySreng Kith Channa Doung Davey
Architecture Year 4 “B” Group 6 Email: (sphearom510@gmail.com)
Demystifying National Museum Objectives : The National Museum of Cambodia houses one of the world's
The museum is bordered by Streets 178 (to the north), Street 13 (to the east) greatest collections of Khmer cultural material including sculpture, ceramics
and Street 184 (to the south).The museum buildings were constructed and ethnographic objects from the prehistoric, pre-Angkorian, Angkorian and
between 1917 and 1924, with the inauguration of the museum in 1920. The post-Angkorian periods. The Museum promotes awareness, understanding
central section of the east facade was renovated in 1968 under the supervision and appreciation of Cambodia's heritage through the presentation,
of Cambodian architect, Vann Molyvann. conservation, safekeeping, interpretation and acquisition of Cambodian
cultural material. It aims to educate and inspire its visitors.
Concept : The Buildings of the museum
are inspired by Khmer temple architecture.
There are more than 14,0000 items
housed in the museum.
West Facade mostly exhibits the statues
v
and sculptures during the Angkor era(900-
1500AD), Which consists of Brahma Statues.
South Facade: is divided into two
galleries that exhibit the art objects
of two eras : the Pre-Angkor era
(600-800AD) and the Angkor era
(900AD-1500AD).
East Facade: Where is the main gate North Facade is the ethnic gallery that
of the museum, this facade consists of exhibits the statues and sculptures during the
a Pre-History booth, a Bronze booth, Post-Angkor era (1500-Mid-2000AD). The
Non- permanent exhibitions, a Stone eastern section of the gallery is the booth of
Conversation Workshop and a Mental ceramic and pottery sculptures and booth of
Conversation Workshop. Prehistory daily Buddha statues of the post-Angkor era and
living during the stone age, the bronze many art objects.
age and iron age.
Architecture Symbolism
Naga played the most important role in Jaffa rugs are part of the
Cambodian society in the terms of folk roof structure of Khmer
beliefs as well as in the field of art and architectura l buildin gs.
arch itectu re . Th e dragon s ym bolizes Generally, in the back cover of Red Painting
immortality and is made up of a the roof for Khmer traditional Symbolizes the
combination of water and earth. In Khmer construction, white mortar is
blood and bravery.
temple’s architecture, dragon has had added along the back of the
indispensable role since in pre-Angkorian roof to connect to the back of
and Angkorian times, as well as today. the Jaffa, which is why it is
called the Jaffa back carpet.
Artifacts Inside Museum
Ceramic Stone Wood
The ancient Khmers produced three Khmer sculpture is divided into freestanding,
Wo o d wa s a l s o
main categories of ceramics: for bas-relief, and high-relief categories. Two
c o m m on l y u se d
archite ctural de coration (roo f kinds of stone were used, schist and sandstone
du rin g th e pr e-
tiles, decorative finial motifs, and etc.) ( b l a c k , re d , g re y, a n d wh i te ) . Mos t o f
Angkorian period
the religious sculpture was carved in sandstone.
Legends Conclusion
Conclusion: A visit to the National Museum of Cambodia is an enriching
journey through the annals of the country's history and cultural heritage.
The museum's collection of artifacts and sculptures provides a glimpse
into the artistic achievements of the Khmer Empire and beyond.
Acknowledgement
Understand the classification of buildings according to the function and
architecture of Khmer temples, that. The National Museum of Cambodia
houses one of the world's greatest collections of Khmer cultural material
including sculpture, ceramics and ethnographic objects from the
prehistoric, pre-Angkorian, Angkorian and post-Angkorian periods.
Reference
https://www.cambodiamuseum.info/en_khmer_art_history.html
https://intocambodia.org/content/national-museum-cambodia
You might also like
- Collins - Mission Françias - Pupil Book 1Document146 pagesCollins - Mission Françias - Pupil Book 1get thosebooks0% (1)
- Architecture in Cambodia: GeologicalDocument8 pagesArchitecture in Cambodia: GeologicalJohnBenedictRazNo ratings yet
- AP Art Midterm Short AnswerDocument8 pagesAP Art Midterm Short AnswerhollqNo ratings yet
- Stone Sculpture: History, Types, Materials, TechniquesDocument6 pagesStone Sculpture: History, Types, Materials, TechniquesAlly DeanNo ratings yet
- Visual Art Ss 1 First TermDocument26 pagesVisual Art Ss 1 First Termpalmer okiemuteNo ratings yet
- LAS 3 History of ArtDocument21 pagesLAS 3 History of ArtREYNAN ZAMORANo ratings yet
- Pre Historic Times Stone Age To Bronze Age ArtDocument3 pagesPre Historic Times Stone Age To Bronze Age ArtUzziel Galinea TolosaNo ratings yet
- Art HistoryDocument3 pagesArt HistoryKyla AlegroNo ratings yet
- Group 2 ReportDocument27 pagesGroup 2 ReportYanyan TumaldingNo ratings yet
- Big AP ReviewDocument226 pagesBig AP ReviewLaura MesaNo ratings yet
- Douglas and Sorensen Mineralogical Characteristics of Khmer SculptureDocument10 pagesDouglas and Sorensen Mineralogical Characteristics of Khmer SculptureLynda AlbertsonNo ratings yet
- ARTA 211 Midterm Discussion GuideDocument5 pagesARTA 211 Midterm Discussion GuidexeanNo ratings yet
- Art and CultureDocument181 pagesArt and Culturepranshubaghel001No ratings yet
- HUM1Document9 pagesHUM1Edsh Rose Rosales100% (1)
- Asian ArtDocument23 pagesAsian ArtChosen Josiah HuertaNo ratings yet
- Ged3 Art AppreciationDocument17 pagesGed3 Art AppreciationVincentNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument11 pagesArt AppreciationMary Grace TolentinoNo ratings yet
- LAS 2 Art Chapter 2Document20 pagesLAS 2 Art Chapter 2Kyle LañaNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation 2pptDocument6 pagesArt Appreciation 2pptMax Moon PENo ratings yet
- LAS 2 Teaching ArtDocument21 pagesLAS 2 Teaching ArtApril Joy CalilanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Reviewer Art AppDocument3 pagesModule 3 Reviewer Art AppQueenemitchfe PulgadoNo ratings yet
- China, India, Japan, SE Asia.: Buquiron - Jazul - SerraDocument65 pagesChina, India, Japan, SE Asia.: Buquiron - Jazul - SerraHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Week7 HMN101 ART HISTORYDocument8 pagesWeek7 HMN101 ART HISTORYNovelyn Degones DuyoganNo ratings yet
- ART APPRECIATION With ASSESSMENTDocument28 pagesART APPRECIATION With ASSESSMENTremacor tagannaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 ArtsDocument16 pagesModule 5 ArtsRobbie YbanezNo ratings yet
- EMP PrayerDocument78 pagesEMP PrayerCHRISTIAN JAY CJ PRESIDENTENo ratings yet
- History of Construction Field Trips 50083Document73 pagesHistory of Construction Field Trips 50083Jiu ShitzukiNo ratings yet
- Arts 9 Unit 1 PDFDocument37 pagesArts 9 Unit 1 PDFLOLNo ratings yet
- Nok Culture - WikipediaDocument18 pagesNok Culture - WikipediaoffyNo ratings yet
- Prehistoric and Ancient Period Sculpture HandoutsDocument2 pagesPrehistoric and Ancient Period Sculpture HandoutsSittie Asraleah AgatonNo ratings yet
- Asian ArtDocument16 pagesAsian ArtAdrienne James SantillanNo ratings yet
- Art App g6Document53 pagesArt App g6lorrainefavoritoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To World Art and Culture 2Document56 pagesIntroduction To World Art and Culture 2lajbymehakguptaNo ratings yet
- Key Elements:: Art Pieces Stone AgeDocument9 pagesKey Elements:: Art Pieces Stone AgeHanie FordNo ratings yet
- Prehistoric Art - Origins, Types, Characteristics, ChronologyDocument15 pagesPrehistoric Art - Origins, Types, Characteristics, Chronologyarchitectfemil6663100% (1)
- 555555Document5 pages555555Lhea Dacillo San JoaquinNo ratings yet
- PART II Reliefs of AngkorDocument22 pagesPART II Reliefs of AngkorUday DokrasNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6.ArtsAppreciation 075455Document64 pagesCHAPTER 6.ArtsAppreciation 075455April Rose Pabadora RojasNo ratings yet
- Bas Reliefs at AngkorDocument43 pagesBas Reliefs at AngkorudayNo ratings yet
- GED3Document17 pagesGED3VincentNo ratings yet
- Arts-Quarter I: 7 Elements of ArtDocument5 pagesArts-Quarter I: 7 Elements of ArtLeuweyne SerranoNo ratings yet
- Prehistoric ArtDocument20 pagesPrehistoric Artespinarishel14No ratings yet
- Architecture of IndiaDocument60 pagesArchitecture of IndiaLaxmi MaradaNo ratings yet
- Journal Pone 0250230Document26 pagesJournal Pone 0250230James Ricardo Zorro MonrroyNo ratings yet
- Art App Midterms (Finale)Document4 pagesArt App Midterms (Finale)Shaira MirandaNo ratings yet
- Module 7.1: Art History: Reading The Image Prehistoric Cave PaintingsDocument70 pagesModule 7.1: Art History: Reading The Image Prehistoric Cave PaintingsAnony MousNo ratings yet
- Technology in Ancient India Michel DaninDocument98 pagesTechnology in Ancient India Michel DaninSarthak MeenaNo ratings yet
- Early Visual Works of Art in Other CountriesDocument10 pagesEarly Visual Works of Art in Other CountriesPIC LIBRARYNo ratings yet
- Activity For Art AppDocument8 pagesActivity For Art AppKath DayagNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation With AssessmentDocument39 pagesArt Appreciation With AssessmentJean VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- الماوى الصخري كوم بوجاي ص27Document15 pagesالماوى الصخري كوم بوجاي ص27atheerNo ratings yet
- Jomon Pottery Cord-Imitating Decoration: Irina ZhushchikhovskayaDocument9 pagesJomon Pottery Cord-Imitating Decoration: Irina ZhushchikhovskayaSidemen For LifeNo ratings yet
- Ancient Art9Document41 pagesAncient Art9xenaNo ratings yet
- Aurora Pioneers Memorial College: Ge Elec 111 - Arts and HumanitiesDocument4 pagesAurora Pioneers Memorial College: Ge Elec 111 - Arts and Humanitiescherry batalunaNo ratings yet
- B5 HUM 1 Finals ReviewerDocument27 pagesB5 HUM 1 Finals ReviewerVenous LakarNo ratings yet
- Ancient Pottery (From 18,000 BCE) : Evolution of ArtDocument13 pagesAncient Pottery (From 18,000 BCE) : Evolution of ArtyowNo ratings yet
- Art Sculptures 2Document22 pagesArt Sculptures 2Gulliver LabraNo ratings yet
- Midterm LessonDocument41 pagesMidterm LessonCriszel Mae DedaseNo ratings yet
- Roblo - BMC - Group 1 ProjectDocument21 pagesRoblo - BMC - Group 1 ProjectLesther RobloNo ratings yet
- Art App - MidtermDocument8 pagesArt App - MidtermMeriiiNo ratings yet
- Prehistoric Art - Cave Dwellers Edition - History for Kids | Asian, European, African, Americas & Oceanic Regions | 4th Grade Children's Prehistoric BooksFrom EverandPrehistoric Art - Cave Dwellers Edition - History for Kids | Asian, European, African, Americas & Oceanic Regions | 4th Grade Children's Prehistoric BooksNo ratings yet
- CV Camille HenrotDocument22 pagesCV Camille HenrotChloe VellaNo ratings yet
- Caitlin J. Keefe - CVDocument2 pagesCaitlin J. Keefe - CVckeef002No ratings yet
- 1.2 Present Tenses - Question FormsDocument1 page1.2 Present Tenses - Question Formsмария паловаNo ratings yet
- Visual Analysis of Joshua Johnson's Painting: Letita Grace McCurdyDocument8 pagesVisual Analysis of Joshua Johnson's Painting: Letita Grace McCurdysara kahnNo ratings yet
- Ottoman Istanbul WebsiteDocument54 pagesOttoman Istanbul WebsitebosLooKNo ratings yet
- 14 Case Study Shanghai World Financial Center PDFDocument6 pages14 Case Study Shanghai World Financial Center PDFyusriandiNo ratings yet
- Butuan SilverDocument9 pagesButuan SilverCasio Je-urNo ratings yet
- Innovation in The Public Sector - Linking Capacity and Leadership (Governance and Public Management)Document263 pagesInnovation in The Public Sector - Linking Capacity and Leadership (Governance and Public Management)ผศ.ดร.ทวิพันธ์ พัวสรรเสริญ100% (1)
- Rezolvare Variante Bac 2009 Problema 4Document8 pagesRezolvare Variante Bac 2009 Problema 4Serban OnofreiNo ratings yet
- U07754QOSM - Project O & M Manual Auditorium SeatingDocument13 pagesU07754QOSM - Project O & M Manual Auditorium SeatingRithesh Shetty100% (1)
- American PresidentsDocument209 pagesAmerican PresidentsDrAbdul-Settar Abdul-Latif MalallahNo ratings yet
- The Germ of An Idea Contagionism, Religion, and S Ociety in Britain, 1660-1730Document318 pagesThe Germ of An Idea Contagionism, Religion, and S Ociety in Britain, 1660-1730MarthaNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Tieng Anh 6 Bai 9Document25 pagesBai Tap Tieng Anh 6 Bai 9Quyen DangNo ratings yet
- Username: Password:: File Hosting Search Login RegisterDocument3 pagesUsername: Password:: File Hosting Search Login RegisterAditya JoshiNo ratings yet
- Porting C To RustDocument216 pagesPorting C To RustBartoszSowulNo ratings yet
- Opel GM Grandland X 2020 Wiring DiagramsDocument22 pagesOpel GM Grandland X 2020 Wiring Diagramsmissrebeccacolon240796mxe100% (117)
- David (Charles Wendell) - Narratio de Itinere Navali Peregrinorum Hierosolymam Tendentium Et Silviam Capientium, A. D. 1189Document90 pagesDavid (Charles Wendell) - Narratio de Itinere Navali Peregrinorum Hierosolymam Tendentium Et Silviam Capientium, A. D. 1189Jean-Pierre Molénat100% (1)
- Further Practice Unit 2-2023Document5 pagesFurther Practice Unit 2-2023Trần PhápNo ratings yet
- My Personal Guide: TripwolfDocument12 pagesMy Personal Guide: TripwolfEgle CerNo ratings yet
- Programming React NativeDocument172 pagesProgramming React NativeTomislav Knežević100% (3)
- Controlling HandoutDocument6 pagesControlling HandoutJeremy Paul Gecolea100% (1)
- CICTESTDocument9 pagesCICTESTratulray2006No ratings yet
- LabVIEW Basics I Course Manual 6 (1) .0Document388 pagesLabVIEW Basics I Course Manual 6 (1) .0Dinh Thang LeNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument10 pagesJavaNisha Mary GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Matisse PicassoDocument6 pagesMatisse PicassoGeorgi PagolaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Catholicismand Nineteenth-Centuryfiction: More InformationDocument8 pagesAnti-Catholicismand Nineteenth-Centuryfiction: More Informationbudinha007No ratings yet
- João Álvaro Carvalho - Information System - Which One Do You MeanDocument24 pagesJoão Álvaro Carvalho - Information System - Which One Do You MeanLuis FelipeNo ratings yet
- Lotus Domino Designer 8.5.1 Classic Notes Applications (DDCNA851)Document5 pagesLotus Domino Designer 8.5.1 Classic Notes Applications (DDCNA851)marializaestellaNo ratings yet
- Design May 2016Document5 pagesDesign May 2016ArtdataNo ratings yet