Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views19EE307-Unit-5 - 2 Marks
19EE307-Unit-5 - 2 Marks
Uploaded by
Nanda KishoreCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chapter 3 - Transducer and Sensors Part 1Document46 pagesChapter 3 - Transducer and Sensors Part 1Zersh Ethio100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Transducer and Sensors Part 1Document46 pagesChapter 3 - Transducer and Sensors Part 1Zersh EthioNo ratings yet
- Bendix Ec-15 Antilock Controller Assembly: DescriptionDocument24 pagesBendix Ec-15 Antilock Controller Assembly: DescriptionrowanNo ratings yet
- Sensors and TransducersDocument15 pagesSensors and TransducersWaqas AhmadNo ratings yet
- Transducer Instrumentation & ControlDocument8 pagesTransducer Instrumentation & Control401-Arsh AlamNo ratings yet
- Resistive TransducerDocument75 pagesResistive TransducerDhineshSKNo ratings yet
- Subject: Electronics Semester: 5 Paper Title: Electronic Instrumentation Unit IV: Transducers Topic:Electrical Transducers and Their SelectionDocument2 pagesSubject: Electronics Semester: 5 Paper Title: Electronic Instrumentation Unit IV: Transducers Topic:Electrical Transducers and Their SelectionDespicari PiratesNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Measurements: Engr. Muhammad Usman Sardar Lecturer, EEDocument29 pagesInstrumentation and Measurements: Engr. Muhammad Usman Sardar Lecturer, EEMuhammad HarisNo ratings yet
- Emi Unit 5Document28 pagesEmi Unit 5neha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- Bee CHPT6Document5 pagesBee CHPT6khan adilNo ratings yet
- 4 - Sensors and TransducersDocument30 pages4 - Sensors and TransducersClarence TanNo ratings yet
- Sensors and TransducersDocument15 pagesSensors and TransducersNirjhar FilmsNo ratings yet
- Review of Sensor / Transducers Review of Sensor / TransducersDocument21 pagesReview of Sensor / Transducers Review of Sensor / TransducersdhineshpNo ratings yet
- IoT Unit-IDocument144 pagesIoT Unit-IADITYA SACHIN NEVENo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document46 pagesChapter 2kidanemariam tesera100% (1)
- Resistance TransducerDocument6 pagesResistance TransducerNurul Assikin Binti AriffinNo ratings yet
- Review of Transducer and SensorDocument113 pagesReview of Transducer and SensorSyedZameerNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Eng. Dept.: Sensors & Signal ConditioningDocument11 pagesMechanical Eng. Dept.: Sensors & Signal Conditioningعلي الساعديNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Eng. Dept.: Sensors & Signal ConditioningDocument11 pagesMechanical Eng. Dept.: Sensors & Signal Conditioninghaker linkisNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction: What Are Transducers?Document14 pagesModule 1: Introduction: What Are Transducers?SAKSHI CHIKSHENo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Sensors and TransducersDocument42 pagesUnit 2 Sensors and Transducersbhuyanuttam7No ratings yet
- BEEE-Unit VI TransducerDocument71 pagesBEEE-Unit VI TransducerAisha JainNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document15 pagesModule 6syamalaNo ratings yet
- Generalized Performance Characteristics of Instruments: Resistive TransducersDocument18 pagesGeneralized Performance Characteristics of Instruments: Resistive TransducersSaketh DahagamNo ratings yet
- EM & I Unit-5Document30 pagesEM & I Unit-5Sai Ravi TejaNo ratings yet
- Lesson #9 Sensors and Transducers-2Document70 pagesLesson #9 Sensors and Transducers-2Nyoka DunnNo ratings yet
- Unit Module1Document19 pagesUnit Module1veenadivyakishNo ratings yet
- Resistance TransducerDocument8 pagesResistance TransducerJuBi1461No ratings yet
- Oic751-Transducer Engineering 2 Marks, 13 Marks and Problem With AnswersDocument32 pagesOic751-Transducer Engineering 2 Marks, 13 Marks and Problem With AnswersPoovarasan S100% (1)
- TransducerDocument42 pagesTransducerShreyash SargarNo ratings yet
- EMDocument18 pagesEMSuprava GhoshPaulNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document42 pagesChap 2Azimah Zainal OfficiqlNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Sensors and Application: Dept. of Electrical and Computer Eng. Addis Ababa by Biruk TDocument40 pagesChapter Two Sensors and Application: Dept. of Electrical and Computer Eng. Addis Ababa by Biruk TabenuNo ratings yet
- Eee 308Document52 pagesEee 308Samuel SamsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Sensors and ApplicationsDocument58 pagesChapter Two: Sensors and ApplicationsDebebe YirgaNo ratings yet
- EMI BasicsDocument11 pagesEMI BasicsTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - Transducer and Sensors PDFDocument49 pagesCHAPTER 3 - Transducer and Sensors PDFROYALNEWSS100% (1)
- Dynamic CharacteristicsDocument51 pagesDynamic CharacteristicsShahadat HossainNo ratings yet
- Variable Resistor-ReviewDocument21 pagesVariable Resistor-ReviewHimanshu DiwakarNo ratings yet
- SensorsDocument21 pagesSensorsUsman AliNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics CHAPTER 4Document52 pagesMechatronics CHAPTER 4NahomNo ratings yet
- Transducer Basics ModifiedDocument78 pagesTransducer Basics ModifiedAmit RegeNo ratings yet
- TransducersDocument61 pagesTransducersAryan jay vermaNo ratings yet
- Unit V Transducers and Data Acquisition Systems TransducersDocument13 pagesUnit V Transducers and Data Acquisition Systems TransducersViswanathan ASNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document37 pagesModule 2october87No ratings yet
- MAIN TOPIC - Non-Electrical Quantities in InstrumentationDocument90 pagesMAIN TOPIC - Non-Electrical Quantities in InstrumentationArctic FoxNo ratings yet
- 66 - 15575 - EC 732 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 2 - Chapter 1Document11 pages66 - 15575 - EC 732 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 2 - Chapter 1ዘረአዳም ዘመንቆረርNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks EE 2201Document20 pages2 Marks EE 2201Karthik KolliparaNo ratings yet
- BSM 2Document26 pagesBSM 2Kripa NNo ratings yet
- Transducer Unit 1Document10 pagesTransducer Unit 1SARDAR PATELNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - ASVDocument24 pagesUnit 1 - ASVAnup S. Vibhute DITNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Slide NoteDocument35 pagesWeek 10 Slide NoteJunsyaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IV Part-3 Sensors and TransducersDocument26 pagesUNIT-IV Part-3 Sensors and TransducersmahiNo ratings yet
- Lecure-2 Sensors For Biomedical ApplicationsDocument98 pagesLecure-2 Sensors For Biomedical ApplicationsDivya Aseeja0% (1)
- Physics of Sensors 23-24 - StudentsDocument63 pagesPhysics of Sensors 23-24 - Studentsommayekar19No ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Sensors & TransducersDocument29 pagesUnit 5 - Sensors & TransducerssatyaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Sensors and Transducers Term PaperDocument14 pagesIndustrial Sensors and Transducers Term PaperKumater TerNo ratings yet
- Interview QaDocument86 pagesInterview QaNavin SabbanNo ratings yet
- TRANSDUCERDocument14 pagesTRANSDUCERmicah micahNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document9 pagesLab 5aliNo ratings yet
- Modulo Encoder ABB RTAC-03Document28 pagesModulo Encoder ABB RTAC-03Ruben RodaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Bachelor of EngineeringDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Bachelor of EngineeringMansi PatelNo ratings yet
- Training Contactor PDFDocument11 pagesTraining Contactor PDFAnonymous JBF08eAbtNo ratings yet
- Aim Infotech: Rpm-Ecu Coil Adapter - Arp03Document5 pagesAim Infotech: Rpm-Ecu Coil Adapter - Arp03Suhail AhamedNo ratings yet
- FACTs Devices in Smart GridDocument56 pagesFACTs Devices in Smart GridAnubhav PandeyNo ratings yet
- 8 Lesson-07 LOUDSPEAKERSDocument13 pages8 Lesson-07 LOUDSPEAKERSMr RadientNo ratings yet
- Esd - Exp 2 - Div A - Roll No. 62 - Sahil VavhalDocument5 pagesEsd - Exp 2 - Div A - Roll No. 62 - Sahil VavhalKalpit RautNo ratings yet
- Voltage Shunt Feedback AmplifierDocument18 pagesVoltage Shunt Feedback AmplifierHimanshu Singh100% (1)
- Non - Oriented - Bulletin AK Steel PDFDocument16 pagesNon - Oriented - Bulletin AK Steel PDFkoalaboiNo ratings yet
- Glossary 1Document19 pagesGlossary 1Sehasa PathiranaNo ratings yet
- Remote-Operated Source-Changeover Systems: 2 Compact NSX100/630 DevicesDocument15 pagesRemote-Operated Source-Changeover Systems: 2 Compact NSX100/630 DevicescyberindsurferNo ratings yet
- Am 5888Document10 pagesAm 5888Andres AlegriaNo ratings yet
- Nodal Analysis of Electric CircuitsDocument5 pagesNodal Analysis of Electric Circuitsapi-26587237100% (3)
- EMMI Lab PDFDocument31 pagesEMMI Lab PDFSarithareddy AvuluriNo ratings yet
- Sci9 LoresDocument16 pagesSci9 Loresra9800003No ratings yet
- Digital Battery ChargerDocument6 pagesDigital Battery ChargerarmadityaNo ratings yet
- Info Iec60947-3 (Ed4.0) BDocument23 pagesInfo Iec60947-3 (Ed4.0) Babouadnane imaneNo ratings yet
- Pa 110 BdaDocument8 pagesPa 110 BdaIvan Arturo Barrientos PreciadoNo ratings yet
- UTC324 Youwang PDFDocument6 pagesUTC324 Youwang PDFSD BappiNo ratings yet
- Max1987 1988Document45 pagesMax1987 1988s_vallespinNo ratings yet
- Gazette Notice - Shedule of Tarrifs For The Supply of Electrical Energy by KPLC PDFDocument7 pagesGazette Notice - Shedule of Tarrifs For The Supply of Electrical Energy by KPLC PDFgeraldmrkNo ratings yet
- Galaxy VL Gvl200k500dsDocument3 pagesGalaxy VL Gvl200k500dssonNo ratings yet
- Current Limiting ReactorsDocument3 pagesCurrent Limiting ReactorsLanstein Joe E PNo ratings yet
- Detection of Illegal Electricity Usage Via Powerline CommunicationsDocument26 pagesDetection of Illegal Electricity Usage Via Powerline CommunicationsNaveen Lingamkunta100% (1)
- Airtech 1710-02811 Dt. 14.10.2017 With ThyristorDocument3 pagesAirtech 1710-02811 Dt. 14.10.2017 With ThyristorMohsin ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Electric Clutch TestingDocument2 pagesElectric Clutch Testingkentpeg100% (1)
- Ferroresonance Suppression in Distribution Networks: Ryzhkova Y.N., Tsyruk S.ADocument4 pagesFerroresonance Suppression in Distribution Networks: Ryzhkova Y.N., Tsyruk S.Anam321985No ratings yet
- Curtis Mayberry Final Report ECE4415 LNA ProjectDocument28 pagesCurtis Mayberry Final Report ECE4415 LNA ProjectZarion JacobsNo ratings yet
- Mpac1000 SpecDocument6 pagesMpac1000 SpecalstomNo ratings yet
19EE307-Unit-5 - 2 Marks
19EE307-Unit-5 - 2 Marks
Uploaded by
Nanda Kishore0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pages19EE307-Unit-5 - 2 Marks
19EE307-Unit-5 - 2 Marks
Uploaded by
Nanda KishoreCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Unit - 5
2 Marks
1. What is a static error? Categorize the different forms of static error.
● A static error is defined as the difference between the measured value and the true value
of the quantity. The true value is the exact value of the measurement which is
impossible to obtain.Hence the approximate true value of the measurement should be
taken into consideration.
● Types: Human error, systematic error and random error.
2. Compare accuracy and precision.
3. Compare reproducibility and repeatability.
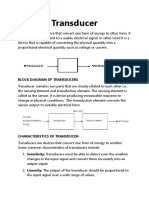
4. What is a transducer? Give examples.
A Transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form i.e,. the
given non-electrical energy is converted into an electrical energy.
Examples: Microphones, loudspeakers, thermometers, position and pressure sensors and
antenna. Although not generally thought of as transducers, photocells, LEDs
(light-emitting diodes), and even common light bulbs are transducers.
5. List any four applications of LVDT.
● Displacement
● Force
● Weight
● Pressure
● Position
6. What is the principle of working in RTD.
● Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTD) operates on the principle that the
electrical resistance of a metal changes predictably in an essentially linear and
repeatable manner with changes in temperature.
● RTD have a positive temperature coefficient.
7. List any four applications of thermistor.
● Measurement of temperature.
● Control of temperature.
● Temperature compensation.
● Measurement of power at high frequencies.
8. List any four applications of piezo electric transducers.
● Measurement of force.
● Measurement of pressure.
● They are mainly employed in high frequency accelerometers.
● They are used in seismographs to measure vibrations in rockets.
9. The true value of a voltage is 100 V. The values indicated by a measuring instrument are
104, 103, 105 and 105 volts. Find the accuracy and precision of the measurement.
Average reading = {Sum of all readings} / {total number of readings} = 104.25
Precision = max { (Average voltage - minimum voltage) , (maximum voltage -
average voltage) }
Average voltage - minimum voltage = 104.25 - 103 = 1.25 V
Maximum voltage - average voltage= 105 - 104.25 = 0.75 V
Precision = max {1.25, 0.75} = 1.25 V
Accuracy = max { (True voltage - minimum voltage) , (Maximum voltage - true
voltage) }
True voltage - minimum voltage = 100 - 103 = -3 V
Maximum voltage - true voltage = 105 - 100 = 5 V
Accuracy = max {-3 , 5} = 5 V
10.Compare Active and Passive transducers.
You might also like
- Chapter 3 - Transducer and Sensors Part 1Document46 pagesChapter 3 - Transducer and Sensors Part 1Zersh Ethio100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Transducer and Sensors Part 1Document46 pagesChapter 3 - Transducer and Sensors Part 1Zersh EthioNo ratings yet
- Bendix Ec-15 Antilock Controller Assembly: DescriptionDocument24 pagesBendix Ec-15 Antilock Controller Assembly: DescriptionrowanNo ratings yet
- Sensors and TransducersDocument15 pagesSensors and TransducersWaqas AhmadNo ratings yet
- Transducer Instrumentation & ControlDocument8 pagesTransducer Instrumentation & Control401-Arsh AlamNo ratings yet
- Resistive TransducerDocument75 pagesResistive TransducerDhineshSKNo ratings yet
- Subject: Electronics Semester: 5 Paper Title: Electronic Instrumentation Unit IV: Transducers Topic:Electrical Transducers and Their SelectionDocument2 pagesSubject: Electronics Semester: 5 Paper Title: Electronic Instrumentation Unit IV: Transducers Topic:Electrical Transducers and Their SelectionDespicari PiratesNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Measurements: Engr. Muhammad Usman Sardar Lecturer, EEDocument29 pagesInstrumentation and Measurements: Engr. Muhammad Usman Sardar Lecturer, EEMuhammad HarisNo ratings yet
- Emi Unit 5Document28 pagesEmi Unit 5neha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- Bee CHPT6Document5 pagesBee CHPT6khan adilNo ratings yet
- 4 - Sensors and TransducersDocument30 pages4 - Sensors and TransducersClarence TanNo ratings yet
- Sensors and TransducersDocument15 pagesSensors and TransducersNirjhar FilmsNo ratings yet
- Review of Sensor / Transducers Review of Sensor / TransducersDocument21 pagesReview of Sensor / Transducers Review of Sensor / TransducersdhineshpNo ratings yet
- IoT Unit-IDocument144 pagesIoT Unit-IADITYA SACHIN NEVENo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document46 pagesChapter 2kidanemariam tesera100% (1)
- Resistance TransducerDocument6 pagesResistance TransducerNurul Assikin Binti AriffinNo ratings yet
- Review of Transducer and SensorDocument113 pagesReview of Transducer and SensorSyedZameerNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Eng. Dept.: Sensors & Signal ConditioningDocument11 pagesMechanical Eng. Dept.: Sensors & Signal Conditioningعلي الساعديNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Eng. Dept.: Sensors & Signal ConditioningDocument11 pagesMechanical Eng. Dept.: Sensors & Signal Conditioninghaker linkisNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction: What Are Transducers?Document14 pagesModule 1: Introduction: What Are Transducers?SAKSHI CHIKSHENo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Sensors and TransducersDocument42 pagesUnit 2 Sensors and Transducersbhuyanuttam7No ratings yet
- BEEE-Unit VI TransducerDocument71 pagesBEEE-Unit VI TransducerAisha JainNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document15 pagesModule 6syamalaNo ratings yet
- Generalized Performance Characteristics of Instruments: Resistive TransducersDocument18 pagesGeneralized Performance Characteristics of Instruments: Resistive TransducersSaketh DahagamNo ratings yet
- EM & I Unit-5Document30 pagesEM & I Unit-5Sai Ravi TejaNo ratings yet
- Lesson #9 Sensors and Transducers-2Document70 pagesLesson #9 Sensors and Transducers-2Nyoka DunnNo ratings yet
- Unit Module1Document19 pagesUnit Module1veenadivyakishNo ratings yet
- Resistance TransducerDocument8 pagesResistance TransducerJuBi1461No ratings yet
- Oic751-Transducer Engineering 2 Marks, 13 Marks and Problem With AnswersDocument32 pagesOic751-Transducer Engineering 2 Marks, 13 Marks and Problem With AnswersPoovarasan S100% (1)
- TransducerDocument42 pagesTransducerShreyash SargarNo ratings yet
- EMDocument18 pagesEMSuprava GhoshPaulNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document42 pagesChap 2Azimah Zainal OfficiqlNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Sensors and Application: Dept. of Electrical and Computer Eng. Addis Ababa by Biruk TDocument40 pagesChapter Two Sensors and Application: Dept. of Electrical and Computer Eng. Addis Ababa by Biruk TabenuNo ratings yet
- Eee 308Document52 pagesEee 308Samuel SamsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Sensors and ApplicationsDocument58 pagesChapter Two: Sensors and ApplicationsDebebe YirgaNo ratings yet
- EMI BasicsDocument11 pagesEMI BasicsTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - Transducer and Sensors PDFDocument49 pagesCHAPTER 3 - Transducer and Sensors PDFROYALNEWSS100% (1)
- Dynamic CharacteristicsDocument51 pagesDynamic CharacteristicsShahadat HossainNo ratings yet
- Variable Resistor-ReviewDocument21 pagesVariable Resistor-ReviewHimanshu DiwakarNo ratings yet
- SensorsDocument21 pagesSensorsUsman AliNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics CHAPTER 4Document52 pagesMechatronics CHAPTER 4NahomNo ratings yet
- Transducer Basics ModifiedDocument78 pagesTransducer Basics ModifiedAmit RegeNo ratings yet
- TransducersDocument61 pagesTransducersAryan jay vermaNo ratings yet
- Unit V Transducers and Data Acquisition Systems TransducersDocument13 pagesUnit V Transducers and Data Acquisition Systems TransducersViswanathan ASNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document37 pagesModule 2october87No ratings yet
- MAIN TOPIC - Non-Electrical Quantities in InstrumentationDocument90 pagesMAIN TOPIC - Non-Electrical Quantities in InstrumentationArctic FoxNo ratings yet
- 66 - 15575 - EC 732 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 2 - Chapter 1Document11 pages66 - 15575 - EC 732 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 2 - Chapter 1ዘረአዳም ዘመንቆረርNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks EE 2201Document20 pages2 Marks EE 2201Karthik KolliparaNo ratings yet
- BSM 2Document26 pagesBSM 2Kripa NNo ratings yet
- Transducer Unit 1Document10 pagesTransducer Unit 1SARDAR PATELNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - ASVDocument24 pagesUnit 1 - ASVAnup S. Vibhute DITNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Slide NoteDocument35 pagesWeek 10 Slide NoteJunsyaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IV Part-3 Sensors and TransducersDocument26 pagesUNIT-IV Part-3 Sensors and TransducersmahiNo ratings yet
- Lecure-2 Sensors For Biomedical ApplicationsDocument98 pagesLecure-2 Sensors For Biomedical ApplicationsDivya Aseeja0% (1)
- Physics of Sensors 23-24 - StudentsDocument63 pagesPhysics of Sensors 23-24 - Studentsommayekar19No ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Sensors & TransducersDocument29 pagesUnit 5 - Sensors & TransducerssatyaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Sensors and Transducers Term PaperDocument14 pagesIndustrial Sensors and Transducers Term PaperKumater TerNo ratings yet
- Interview QaDocument86 pagesInterview QaNavin SabbanNo ratings yet
- TRANSDUCERDocument14 pagesTRANSDUCERmicah micahNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document9 pagesLab 5aliNo ratings yet
- Modulo Encoder ABB RTAC-03Document28 pagesModulo Encoder ABB RTAC-03Ruben RodaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Bachelor of EngineeringDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Bachelor of EngineeringMansi PatelNo ratings yet
- Training Contactor PDFDocument11 pagesTraining Contactor PDFAnonymous JBF08eAbtNo ratings yet
- Aim Infotech: Rpm-Ecu Coil Adapter - Arp03Document5 pagesAim Infotech: Rpm-Ecu Coil Adapter - Arp03Suhail AhamedNo ratings yet
- FACTs Devices in Smart GridDocument56 pagesFACTs Devices in Smart GridAnubhav PandeyNo ratings yet
- 8 Lesson-07 LOUDSPEAKERSDocument13 pages8 Lesson-07 LOUDSPEAKERSMr RadientNo ratings yet
- Esd - Exp 2 - Div A - Roll No. 62 - Sahil VavhalDocument5 pagesEsd - Exp 2 - Div A - Roll No. 62 - Sahil VavhalKalpit RautNo ratings yet
- Voltage Shunt Feedback AmplifierDocument18 pagesVoltage Shunt Feedback AmplifierHimanshu Singh100% (1)
- Non - Oriented - Bulletin AK Steel PDFDocument16 pagesNon - Oriented - Bulletin AK Steel PDFkoalaboiNo ratings yet
- Glossary 1Document19 pagesGlossary 1Sehasa PathiranaNo ratings yet
- Remote-Operated Source-Changeover Systems: 2 Compact NSX100/630 DevicesDocument15 pagesRemote-Operated Source-Changeover Systems: 2 Compact NSX100/630 DevicescyberindsurferNo ratings yet
- Am 5888Document10 pagesAm 5888Andres AlegriaNo ratings yet
- Nodal Analysis of Electric CircuitsDocument5 pagesNodal Analysis of Electric Circuitsapi-26587237100% (3)
- EMMI Lab PDFDocument31 pagesEMMI Lab PDFSarithareddy AvuluriNo ratings yet
- Sci9 LoresDocument16 pagesSci9 Loresra9800003No ratings yet
- Digital Battery ChargerDocument6 pagesDigital Battery ChargerarmadityaNo ratings yet
- Info Iec60947-3 (Ed4.0) BDocument23 pagesInfo Iec60947-3 (Ed4.0) Babouadnane imaneNo ratings yet
- Pa 110 BdaDocument8 pagesPa 110 BdaIvan Arturo Barrientos PreciadoNo ratings yet
- UTC324 Youwang PDFDocument6 pagesUTC324 Youwang PDFSD BappiNo ratings yet
- Max1987 1988Document45 pagesMax1987 1988s_vallespinNo ratings yet
- Gazette Notice - Shedule of Tarrifs For The Supply of Electrical Energy by KPLC PDFDocument7 pagesGazette Notice - Shedule of Tarrifs For The Supply of Electrical Energy by KPLC PDFgeraldmrkNo ratings yet
- Galaxy VL Gvl200k500dsDocument3 pagesGalaxy VL Gvl200k500dssonNo ratings yet
- Current Limiting ReactorsDocument3 pagesCurrent Limiting ReactorsLanstein Joe E PNo ratings yet
- Detection of Illegal Electricity Usage Via Powerline CommunicationsDocument26 pagesDetection of Illegal Electricity Usage Via Powerline CommunicationsNaveen Lingamkunta100% (1)
- Airtech 1710-02811 Dt. 14.10.2017 With ThyristorDocument3 pagesAirtech 1710-02811 Dt. 14.10.2017 With ThyristorMohsin ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Electric Clutch TestingDocument2 pagesElectric Clutch Testingkentpeg100% (1)
- Ferroresonance Suppression in Distribution Networks: Ryzhkova Y.N., Tsyruk S.ADocument4 pagesFerroresonance Suppression in Distribution Networks: Ryzhkova Y.N., Tsyruk S.Anam321985No ratings yet
- Curtis Mayberry Final Report ECE4415 LNA ProjectDocument28 pagesCurtis Mayberry Final Report ECE4415 LNA ProjectZarion JacobsNo ratings yet
- Mpac1000 SpecDocument6 pagesMpac1000 SpecalstomNo ratings yet