Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsFluid Volume Excess
Fluid Volume Excess
Uploaded by
demilyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- NCP 3rd YearDocument6 pagesNCP 3rd YearTotoro AblogNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume PotentialDocument4 pagesNCP Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume PotentialArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Introduction Bio121 (BIO122)Document55 pagesChapter 1-Introduction Bio121 (BIO122)Aisyah Zahra Zairul Adli100% (3)
- Endocrine System Coloring Activity - LDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Coloring Activity - LBriannaCarpenterNo ratings yet
- 6 Assessment of The Thorax and LungsDocument6 pages6 Assessment of The Thorax and LungsFreisanChenMandumotan100% (1)
- Blodd Cell Poster PDFDocument2 pagesBlodd Cell Poster PDFGustavo Adolfo Piñero BorgesNo ratings yet
- Case Study 5Document6 pagesCase Study 5Anthony jesusNo ratings yet
- Excess Fluid Volume Liver CirrhosisDocument3 pagesExcess Fluid Volume Liver CirrhosisSHANIA HASEENAH SALAZARNo ratings yet
- C. Case Study thesis-NCP (Revised)Document5 pagesC. Case Study thesis-NCP (Revised)Lopirts NiganiNo ratings yet
- Overview of The DiseaseDocument12 pagesOverview of The DiseasePresciousNo ratings yet
- Facto NCPDocument3 pagesFacto NCPkkd nyleNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPJet Ray-Ann GaringanNo ratings yet
- NCP TyphoidDocument2 pagesNCP TyphoidMae Arra Lecobu-anNo ratings yet
- NCP PediatricDocument5 pagesNCP PediatricSL Hanna NebridaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care PlanKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planmust dietNo ratings yet
- NCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsDocument9 pagesNCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsAngie Mandeoya100% (1)
- Prado, Catherine BSN IIB (Activity 1 Case Scenario)Document52 pagesPrado, Catherine BSN IIB (Activity 1 Case Scenario)Catherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPDocument5 pagesAcute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPMyrvic Ortiz La OrdenNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarielle Chua100% (1)
- Clinical Learning Log 3 Go Solo - Docx-1Document11 pagesClinical Learning Log 3 Go Solo - Docx-1JezraleFame AntoyNo ratings yet
- Excess Fluid IntakeDocument3 pagesExcess Fluid Intakejasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- NCP 3rd ROTATIONDocument17 pagesNCP 3rd ROTATIONMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- NCP GI EditedDocument4 pagesNCP GI EditednicoleNo ratings yet
- NCP Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Knowledge DeficitRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- MS Soapie #1Document2 pagesMS Soapie #1Fatima KateNo ratings yet
- NCP ProperDocument9 pagesNCP Properstephanie eduarteNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STO: Within 4 Hour of DX: DX: Sto: Goal MetDocument5 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STO: Within 4 Hour of DX: DX: Sto: Goal MetRussel SantosNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)Document7 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)jajalerNo ratings yet
- HydroceleDocument10 pagesHydroceleRyan ReNo ratings yet
- NCP - DM - FatigueDocument12 pagesNCP - DM - FatigueJisel-Apple BulanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationbambem aevanNo ratings yet
- NCP With DsDocument11 pagesNCP With DsMissDyYournurseNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Document2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Congestive Cardiac FailureDocument22 pagesCongestive Cardiac FailureSampada GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Pedia NCPDocument6 pagesPedia NCPZel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Ckd-Janry FinalDocument6 pagesNcp-Ckd-Janry Finalcjpalapuz07No ratings yet
- ROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPDocument6 pagesROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPkimberly quitonNo ratings yet
- Ricafort, Maxine S. GRP 2H Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesRicafort, Maxine S. GRP 2H Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMaxine RicafortNo ratings yet
- NCP AgnDocument2 pagesNCP Agnj3nann3No ratings yet
- Waiters PATIENT CARE PLAN 2020 For PPHDocument3 pagesWaiters PATIENT CARE PLAN 2020 For PPHmp1757No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Patient's Name: Age: Sex: Address:: Nursing-Notes/communicable - Diseases - Notes/amoebiasisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Patient's Name: Age: Sex: Address:: Nursing-Notes/communicable - Diseases - Notes/amoebiasisGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEANo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- NCP Discharge PlanningDocument7 pagesNCP Discharge PlanningMarcieNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study (Isph-Gs Nursery)Document4 pagesNCP and Drug Study (Isph-Gs Nursery)Cristyl Shine BariaoNo ratings yet
- "Nanghihina Ako Tsaka Wala Akong Ganang Kumain" As VerbalizedDocument3 pages"Nanghihina Ako Tsaka Wala Akong Ganang Kumain" As VerbalizedAnonymous JtOaXOE1No ratings yet
- Gonzaga Rlems - NCPDocument3 pagesGonzaga Rlems - NCPShaynne Wencille A. GONZAGANo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesNursing DiagnosisUriel CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMargareth DandanNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanSheenaGuinoCullaNo ratings yet
- BOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageDocument4 pagesBOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageJam AliNo ratings yet
- Gi Bleeding CaseDocument28 pagesGi Bleeding CaseP BNo ratings yet
- Final NCP For PostpartumDocument8 pagesFinal NCP For PostpartumJam Ali100% (1)
- Postpartal Discharge InstructionsDocument3 pagesPostpartal Discharge InstructionsDuchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan NCPDocument24 pagesNursing Care Plan NCPRosemarie R. Reyes100% (1)
- F. NCP ProperDocument4 pagesF. NCP ProperAle SandraNo ratings yet
- Global City Innovative CollegeDocument3 pagesGlobal City Innovative CollegemadypadNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument14 pagesDengueKarenn Joy Concepcion OctubreNo ratings yet
- Dengue NCPDocument3 pagesDengue NCPingridNo ratings yet
- Rules and Regulations For BPTDocument54 pagesRules and Regulations For BPTSherin KNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument36 pagesCase Presentationalmas khanNo ratings yet
- Physiological Influences On PsychologyDocument14 pagesPhysiological Influences On PsychologyUMAIR JAMEELNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Functions TableDocument3 pagesCell Parts and Functions TableJade Mark CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Dendritic Cells PDFDocument370 pagesDendritic Cells PDFAnonymous YQawhb100% (1)
- Case Study - Plasma MembraneDocument5 pagesCase Study - Plasma MembranejajajaredredNo ratings yet
- A Case Report On Thiazide Induced Hyponatremia Addressing An Underestimated ComplicationDocument4 pagesA Case Report On Thiazide Induced Hyponatremia Addressing An Underestimated ComplicationIJAR JOURNAL100% (1)
- Psihountas V Jewish Hospital Et Al Complete FileDocument102 pagesPsihountas V Jewish Hospital Et Al Complete FilePeter M. HeimlichNo ratings yet
- 2 Effect of Drugs On Isolated Frog HeartDocument10 pages2 Effect of Drugs On Isolated Frog HeartVidhiNo ratings yet
- The Quran and Semen ProductionDocument10 pagesThe Quran and Semen ProductionDoctor Jones100% (2)
- Lab 3 - Dissection Guide - EarthwormDocument15 pagesLab 3 - Dissection Guide - Earthwormbszool006No ratings yet
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDocument42 pagesCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaErlangga SantosaNo ratings yet
- Olmetec-Ci e PDFDocument3 pagesOlmetec-Ci e PDFAlyssa Dannah RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology - Dra. ValerioDocument16 pagesCardiovascular Physiology - Dra. ValerioAlexandra Duque-David100% (2)
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument10 pagesCardiopulmonary ResuscitationLilay MakulayNo ratings yet
- Biochem Check For UnderstandingDocument5 pagesBiochem Check For UnderstandingMaria Vannesa Anne SalvacionNo ratings yet
- MangasinoroDocument8 pagesMangasinoroEd MagtibayNo ratings yet
- The p75 Neurotrophin Receptor and Neuronal ApoptosisDocument25 pagesThe p75 Neurotrophin Receptor and Neuronal ApoptosisValeria PNo ratings yet
- Skeletal C Tas DDocument5 pagesSkeletal C Tas DCaviles, Jasmin S.No ratings yet
- NEURODocument4 pagesNEUROSabrina LarracasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PhysiologyDocument114 pagesRespiratory Physiologypolymeraseus100% (4)
- L3, 16-18 Gross Anatomy of Pelvis and PerineumDocument37 pagesL3, 16-18 Gross Anatomy of Pelvis and PerineumБеатриса ШипNo ratings yet
- Larsens Human Embryology 6Th Edition Schoenwolf Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pagesLarsens Human Embryology 6Th Edition Schoenwolf Full Chapter PDFmiomiovetm100% (3)
- FLE - Critical Thinking Questions - F & E AnswersDocument1 pageFLE - Critical Thinking Questions - F & E AnswersRich StrozewskiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Placement Exam 2 Practice With Answers at End!Document9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Placement Exam 2 Practice With Answers at End!Olalekan OyekunleNo ratings yet
- OPIANA CHRISTIAN JOSEPH - PulmonaryDisorderDocument9 pagesOPIANA CHRISTIAN JOSEPH - PulmonaryDisorderChristian Joseph OpianaNo ratings yet
Fluid Volume Excess
Fluid Volume Excess
Uploaded by
demily0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesOriginal Title
FLUID-VOLUME-EXCESS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesFluid Volume Excess
Fluid Volume Excess
Uploaded by
demilyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
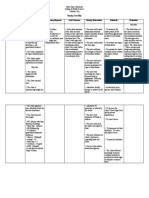
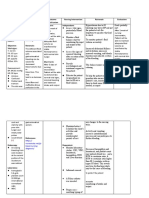
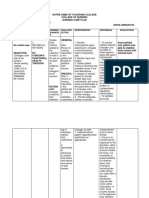
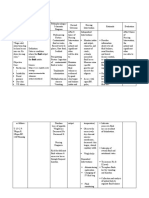
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING NURSING INTERVENTION EVALUATION
Subjective: “May Fluid volume Short term: INDEPENDENT After 1 hour of
mga manas ako sa excess related At the end of 2 >Explain the nursing intervention,
kamay at paa to fluid shift hours nursing importance of close the client verbalizes
mula nang mag from intervention, monitoring of weight, understanding of need
anim na buwan intracellular to the client will vital signs, I/O, for close monitoring
ang tiyan ko” as extracellular be able to urine protein and of weight, BP, urine
stated by the fluid as understand the edema. protein, and edema and
client. evidenced by need for close Rationale: So the engages in therapeutic
edema formation monitoring of client will become regimen and
weight, blood aware of her monitoring.
Objective: pressure, urine condition
Presence of protein and
edema in face edema and >Weigh patien.t After 3 days of
and upper and engages in regularly. Tell nursing intervention,
lower therapeutic client to record the client is free of
extremities regimen and weight at home in signs of generalized
monitoring as between visits. edema
Shiny, cold and indicated. Rationale: To
clammy skin identify if there is
Long term: an increase in fluid
Presence of After 3 days of retention
protein in the nursing
urine (2/20/19) intervention, >Monitor Vital signs
the client has Rationale: to
stabilized fluid determine the
BP: 200/140 volume as client’s
T: 37.0 °c evidenced by physiological state
PR: 85 bpm balanced I/O, DEPENDENT
RR: 20 cpm vital signs > Differentiate
within client’s physiological and
weight: 81kg normal limits, pathological edema of
Stable weight pregnancy. Locate and
and free of determine degree of
signs of edema. pitting.
Rationale: To define
characteristic of
excess fluid.
COLLABORATIVE
> Check on dietary
intake of proteins
and calories. Give
information as
needed.
Rationale: To
determine imbalances
in these areas that
are associated with
fluid imbalances
> Monitor intake and
output. Note urine
color, and measure
specific gravity as
indicated.
Rationale: To ensure
accurate picture of
fluid status
> Assess lung sounds
and respiratory
rate/effort.
Rationale: To assess
if there is a
pulmonary edema
>Administer
medications as
ordered
Rationale: To
identify medications
that can alter fluid
and electrolyte
balance.
You might also like
- NCP 3rd YearDocument6 pagesNCP 3rd YearTotoro AblogNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume PotentialDocument4 pagesNCP Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume PotentialArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Introduction Bio121 (BIO122)Document55 pagesChapter 1-Introduction Bio121 (BIO122)Aisyah Zahra Zairul Adli100% (3)
- Endocrine System Coloring Activity - LDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Coloring Activity - LBriannaCarpenterNo ratings yet
- 6 Assessment of The Thorax and LungsDocument6 pages6 Assessment of The Thorax and LungsFreisanChenMandumotan100% (1)
- Blodd Cell Poster PDFDocument2 pagesBlodd Cell Poster PDFGustavo Adolfo Piñero BorgesNo ratings yet
- Case Study 5Document6 pagesCase Study 5Anthony jesusNo ratings yet
- Excess Fluid Volume Liver CirrhosisDocument3 pagesExcess Fluid Volume Liver CirrhosisSHANIA HASEENAH SALAZARNo ratings yet
- C. Case Study thesis-NCP (Revised)Document5 pagesC. Case Study thesis-NCP (Revised)Lopirts NiganiNo ratings yet
- Overview of The DiseaseDocument12 pagesOverview of The DiseasePresciousNo ratings yet
- Facto NCPDocument3 pagesFacto NCPkkd nyleNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPJet Ray-Ann GaringanNo ratings yet
- NCP TyphoidDocument2 pagesNCP TyphoidMae Arra Lecobu-anNo ratings yet
- NCP PediatricDocument5 pagesNCP PediatricSL Hanna NebridaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care PlanKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planmust dietNo ratings yet
- NCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsDocument9 pagesNCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsAngie Mandeoya100% (1)
- Prado, Catherine BSN IIB (Activity 1 Case Scenario)Document52 pagesPrado, Catherine BSN IIB (Activity 1 Case Scenario)Catherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPDocument5 pagesAcute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPMyrvic Ortiz La OrdenNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarielle Chua100% (1)
- Clinical Learning Log 3 Go Solo - Docx-1Document11 pagesClinical Learning Log 3 Go Solo - Docx-1JezraleFame AntoyNo ratings yet
- Excess Fluid IntakeDocument3 pagesExcess Fluid Intakejasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- NCP 3rd ROTATIONDocument17 pagesNCP 3rd ROTATIONMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- NCP GI EditedDocument4 pagesNCP GI EditednicoleNo ratings yet
- NCP Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Knowledge DeficitRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- MS Soapie #1Document2 pagesMS Soapie #1Fatima KateNo ratings yet
- NCP ProperDocument9 pagesNCP Properstephanie eduarteNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STO: Within 4 Hour of DX: DX: Sto: Goal MetDocument5 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STO: Within 4 Hour of DX: DX: Sto: Goal MetRussel SantosNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)Document7 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)jajalerNo ratings yet
- HydroceleDocument10 pagesHydroceleRyan ReNo ratings yet
- NCP - DM - FatigueDocument12 pagesNCP - DM - FatigueJisel-Apple BulanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationbambem aevanNo ratings yet
- NCP With DsDocument11 pagesNCP With DsMissDyYournurseNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Document2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Congestive Cardiac FailureDocument22 pagesCongestive Cardiac FailureSampada GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Pedia NCPDocument6 pagesPedia NCPZel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Ckd-Janry FinalDocument6 pagesNcp-Ckd-Janry Finalcjpalapuz07No ratings yet
- ROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPDocument6 pagesROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPkimberly quitonNo ratings yet
- Ricafort, Maxine S. GRP 2H Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesRicafort, Maxine S. GRP 2H Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMaxine RicafortNo ratings yet
- NCP AgnDocument2 pagesNCP Agnj3nann3No ratings yet
- Waiters PATIENT CARE PLAN 2020 For PPHDocument3 pagesWaiters PATIENT CARE PLAN 2020 For PPHmp1757No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Patient's Name: Age: Sex: Address:: Nursing-Notes/communicable - Diseases - Notes/amoebiasisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Patient's Name: Age: Sex: Address:: Nursing-Notes/communicable - Diseases - Notes/amoebiasisGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEANo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- NCP Discharge PlanningDocument7 pagesNCP Discharge PlanningMarcieNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study (Isph-Gs Nursery)Document4 pagesNCP and Drug Study (Isph-Gs Nursery)Cristyl Shine BariaoNo ratings yet
- "Nanghihina Ako Tsaka Wala Akong Ganang Kumain" As VerbalizedDocument3 pages"Nanghihina Ako Tsaka Wala Akong Ganang Kumain" As VerbalizedAnonymous JtOaXOE1No ratings yet
- Gonzaga Rlems - NCPDocument3 pagesGonzaga Rlems - NCPShaynne Wencille A. GONZAGANo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesNursing DiagnosisUriel CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMargareth DandanNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanSheenaGuinoCullaNo ratings yet
- BOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageDocument4 pagesBOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageJam AliNo ratings yet
- Gi Bleeding CaseDocument28 pagesGi Bleeding CaseP BNo ratings yet
- Final NCP For PostpartumDocument8 pagesFinal NCP For PostpartumJam Ali100% (1)
- Postpartal Discharge InstructionsDocument3 pagesPostpartal Discharge InstructionsDuchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan NCPDocument24 pagesNursing Care Plan NCPRosemarie R. Reyes100% (1)
- F. NCP ProperDocument4 pagesF. NCP ProperAle SandraNo ratings yet
- Global City Innovative CollegeDocument3 pagesGlobal City Innovative CollegemadypadNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument14 pagesDengueKarenn Joy Concepcion OctubreNo ratings yet
- Dengue NCPDocument3 pagesDengue NCPingridNo ratings yet
- Rules and Regulations For BPTDocument54 pagesRules and Regulations For BPTSherin KNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument36 pagesCase Presentationalmas khanNo ratings yet
- Physiological Influences On PsychologyDocument14 pagesPhysiological Influences On PsychologyUMAIR JAMEELNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Functions TableDocument3 pagesCell Parts and Functions TableJade Mark CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Dendritic Cells PDFDocument370 pagesDendritic Cells PDFAnonymous YQawhb100% (1)
- Case Study - Plasma MembraneDocument5 pagesCase Study - Plasma MembranejajajaredredNo ratings yet
- A Case Report On Thiazide Induced Hyponatremia Addressing An Underestimated ComplicationDocument4 pagesA Case Report On Thiazide Induced Hyponatremia Addressing An Underestimated ComplicationIJAR JOURNAL100% (1)
- Psihountas V Jewish Hospital Et Al Complete FileDocument102 pagesPsihountas V Jewish Hospital Et Al Complete FilePeter M. HeimlichNo ratings yet
- 2 Effect of Drugs On Isolated Frog HeartDocument10 pages2 Effect of Drugs On Isolated Frog HeartVidhiNo ratings yet
- The Quran and Semen ProductionDocument10 pagesThe Quran and Semen ProductionDoctor Jones100% (2)
- Lab 3 - Dissection Guide - EarthwormDocument15 pagesLab 3 - Dissection Guide - Earthwormbszool006No ratings yet
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDocument42 pagesCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaErlangga SantosaNo ratings yet
- Olmetec-Ci e PDFDocument3 pagesOlmetec-Ci e PDFAlyssa Dannah RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology - Dra. ValerioDocument16 pagesCardiovascular Physiology - Dra. ValerioAlexandra Duque-David100% (2)
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument10 pagesCardiopulmonary ResuscitationLilay MakulayNo ratings yet
- Biochem Check For UnderstandingDocument5 pagesBiochem Check For UnderstandingMaria Vannesa Anne SalvacionNo ratings yet
- MangasinoroDocument8 pagesMangasinoroEd MagtibayNo ratings yet
- The p75 Neurotrophin Receptor and Neuronal ApoptosisDocument25 pagesThe p75 Neurotrophin Receptor and Neuronal ApoptosisValeria PNo ratings yet
- Skeletal C Tas DDocument5 pagesSkeletal C Tas DCaviles, Jasmin S.No ratings yet
- NEURODocument4 pagesNEUROSabrina LarracasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PhysiologyDocument114 pagesRespiratory Physiologypolymeraseus100% (4)
- L3, 16-18 Gross Anatomy of Pelvis and PerineumDocument37 pagesL3, 16-18 Gross Anatomy of Pelvis and PerineumБеатриса ШипNo ratings yet
- Larsens Human Embryology 6Th Edition Schoenwolf Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pagesLarsens Human Embryology 6Th Edition Schoenwolf Full Chapter PDFmiomiovetm100% (3)
- FLE - Critical Thinking Questions - F & E AnswersDocument1 pageFLE - Critical Thinking Questions - F & E AnswersRich StrozewskiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Placement Exam 2 Practice With Answers at End!Document9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Placement Exam 2 Practice With Answers at End!Olalekan OyekunleNo ratings yet
- OPIANA CHRISTIAN JOSEPH - PulmonaryDisorderDocument9 pagesOPIANA CHRISTIAN JOSEPH - PulmonaryDisorderChristian Joseph OpianaNo ratings yet