Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2) Introduction
2) Introduction
Uploaded by
mzohair733Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2) Introduction
2) Introduction
Uploaded by
mzohair733Copyright:
Available Formats
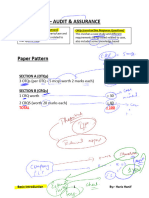
Paper AA (F8) – AUDIT & ASSURANCE
OTQs (Objective Test Questions) CRQs (constructive Response Questions)
This involves having a scenario/case and This involves a case study and different
MCQS are asked which are related to requirements being tested related to case,
that specific case. also includes some knowledge based
questions
Paper Pattern
SECTION A (OTQs)
3 OTQs (per OTQ = 5 mcqs worth 2 marks each) = 30
SECTION B (CRQs)
1 CRQ worth = 30
2 CRQS (worth 20 marks each) = 40
TOTAL = 100
Basic Introduction 1 By:- Haris Hanif
Some Basic overview
Auditor is external to the company (external firm)
Audit is of Financial statements
There may be misstatements in the financial statements, which is prepared by the
company.
o Misstatements:- Difference between Accounting standard and Accounting adopted by the
company.
Over state or under state
External audit is for the satisfaction of shareholders
It is the legal requirement for PLC to conduct external audit
Auditor is appointed by shareholders in the AGM
Auditor test/check the Financial statements and then thereafter express the OPINION
(no Guarantee)
Auditor tests the F.S. on sample basis
Auditor tests the material items
The auditor is NOT responsible to detect the fraud, he is there to check the application
of accounting standards
Auditor should think that there may be:-
- Errors
- Fraud
- Everything is genuine
Auditor prepare the audit report and express the opinion whether the FS is true and fair
or not
Basic Introduction 2 By:- Haris Hanif
Auditor has to perform the audit based on the systematic approach
The auditor has to do some work (actions) known as
AUDIT PROCEDURES
Basic Introduction 3 By:- Haris Hanif
Note: - Controls have impact on the Financial Statements
Basic Introduction 4 By:- Haris Hanif
Expectation Gap:-
It is the gap of the PUBLIC opinion about audit and what AUDIT actually is.
Some people may think that auditor tests 100%, but in the real, auditor works on
sample basis
People may think that auditor verifies all the items in the F.S. but in real, auditor tests
the material item
People usually think that auditor is giving the guarantee after the audit, but it instead
auditor gives the Opinion.
People may think that auditor is responsible for the detection of fraud, but in real, he is
not responsible to detect the fraud, he should ensure financial statements are free from
material misstatements whether due to error or fraud.
AGENCY
Principal appoint agent means
Shareholders appoint B.O.D or Auditor
STEWARDSHIP Stewards means caretaker
B.O.D have to pay Fiduciary duty to shareholders.
Fiduciary means duty to maintain trust.
ACCOUNTABILITY
Auditor and BOD are accountable to the shareholders.
Basic Introduction 5 By:- Haris Hanif
Audit Cycle (systematic approach)
Auditor’s Audit Engagement
Appointment/Reappointment Letter (A.E.L.)
Planning stage of
the Audit
Performing the
Audit
Review Stage
Opinion on F.S.
Basic Introduction 6 By:- Haris Hanif
Opinion of the AUDITOR
Basic Introduction 7 By:- Haris Hanif
You might also like
- Oss Bss PDFDocument27 pagesOss Bss PDFLaluMohan KcNo ratings yet
- F8 Notes Ahmed ShafiDocument69 pagesF8 Notes Ahmed ShafiMubashirNo ratings yet
- Auditing Exam Revision Notes PDFDocument3 pagesAuditing Exam Revision Notes PDFJonalyn GabrilloNo ratings yet
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - Audit (AUD)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - Audit (AUD)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Agile Executive Summary PDFDocument2 pagesAgile Executive Summary PDFimran24100% (1)
- 2) IntroductionDocument7 pages2) IntroductionkasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter I - CisDocument16 pagesChapter I - CisArielle CabritoNo ratings yet
- 3) AssuranceDocument7 pages3) Assurancemzohair733No ratings yet
- Audit Interview Answers CompilationDocument23 pagesAudit Interview Answers CompilationVeneela ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Nature of AuditingDocument32 pagesChap 1 Nature of AuditingAkash Gupta100% (1)
- Audit Framework and RegulationDocument16 pagesAudit Framework and RegulationTousif Galib100% (2)
- 1.introduction To Audit and AssuranceDocument23 pages1.introduction To Audit and AssuranceJaskaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Auditor's Opinion and Report, Materiality, Missatement & FraudDocument6 pagesAuditor's Opinion and Report, Materiality, Missatement & Fraudgimata kochomataNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory ReviewerDocument9 pagesAuditing Theory ReviewerChristian MaritoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Types of EngagementsDocument5 pagesLESSON 3 Types of EngagementsMcdonald MutsvangaNo ratings yet
- Nature of AuditingDocument37 pagesNature of Auditinganon_672065362No ratings yet
- Accounting 1Document44 pagesAccounting 1Kristan John ZernaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Lesson Outline - StudentDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - Lesson Outline - StudentKim Heok ChuaNo ratings yet
- 1 Basics of AuditingDocument4 pages1 Basics of AuditingFlying fishNo ratings yet
- Definition of AuditingDocument7 pagesDefinition of AuditingChristen HerceNo ratings yet
- Auditing 2Document4 pagesAuditing 2tooru oikawaNo ratings yet
- F8 ACCA Summary + Revision Notes 2017Document148 pagesF8 ACCA Summary + Revision Notes 2017Arbab JhangirNo ratings yet
- 10 General Accepted Auditing StandardsDocument7 pages10 General Accepted Auditing StandardsAureen TabamoNo ratings yet
- BA4 - CONTROLS - LMS - BOOK - 03 External Audit - Part 01Document11 pagesBA4 - CONTROLS - LMS - BOOK - 03 External Audit - Part 01Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document15 pagesCH 1Harsh DaneNo ratings yet
- Group 2 HandoutsDocument6 pagesGroup 2 Handoutshamidacali1212No ratings yet
- Auditing NotesDocument142 pagesAuditing NotesmohedNo ratings yet
- Comprehensively_Prepared_Document_of_the_Questions_and_Answers_for_the_Interview_of_Senior_Auditor.docx_filename_= UTF-8''Comprehensively Prepared Document of the Questions and Answers for the Interview of Senior AuDocument42 pagesComprehensively_Prepared_Document_of_the_Questions_and_Answers_for_the_Interview_of_Senior_Auditor.docx_filename_= UTF-8''Comprehensively Prepared Document of the Questions and Answers for the Interview of Senior AumalaknisarkakarNo ratings yet
- Review of Audit Process5Document17 pagesReview of Audit Process5Charmaine RosalesNo ratings yet
- AuditDocument1 pageAuditshivangiNo ratings yet
- Class Activity Problem Q Chap 2 and 3 Suggested SolutionsDocument6 pagesClass Activity Problem Q Chap 2 and 3 Suggested SolutionsHoney ShahNo ratings yet
- PrE 311 - Chapter 1Document6 pagesPrE 311 - Chapter 1John Paul MancillaNo ratings yet
- Audit and Assurance in Brief Summary of Main PointsDocument4 pagesAudit and Assurance in Brief Summary of Main PointsAssen HalatchevNo ratings yet
- Audit Notes - CompressedDocument214 pagesAudit Notes - CompressedAlexis ParrisNo ratings yet
- 1 Understanding BasicsDocument2 pages1 Understanding BasicsAtifa TanvirNo ratings yet
- C9ay1 HsijbDocument15 pagesC9ay1 HsijbEyob FirstNo ratings yet
- Auditing Auditing Report Cabral and de JesusDocument43 pagesAuditing Auditing Report Cabral and de JesusLalaine De JesusNo ratings yet
- Isa 200Document17 pagesIsa 200Mirza Ehsan Ullah MughalNo ratings yet
- Audit and Assurance (AA)Document30 pagesAudit and Assurance (AA)YousafNo ratings yet
- 3) AssuranceDocument7 pages3) AssurancekasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope of AuditingDocument23 pagesNature and Scope of AuditingPrachi GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Audit ProcessDocument20 pagesThe Audit ProcessChumani GqadaNo ratings yet
- ISA 705 - Modifications To The Opinion in The Independent Auditor's ReportDocument4 pagesISA 705 - Modifications To The Opinion in The Independent Auditor's Reportirmasuryaf100% (1)
- Audit-I - CH-2Document61 pagesAudit-I - CH-2tibebu5420No ratings yet
- Origin of Term "Audit": AUDIT Latin Word "Audire"Document17 pagesOrigin of Term "Audit": AUDIT Latin Word "Audire"ranjana7123No ratings yet
- ACCA F8 Audit Summary+ Revision Notes (1)Document148 pagesACCA F8 Audit Summary+ Revision Notes (1)Như Quỳnh Dương ThịNo ratings yet
- 1 - Overview of AuditingDocument13 pages1 - Overview of AuditingZooeyNo ratings yet
- AuditDocument90 pagesAuditSailesh GoenkkaNo ratings yet
- Audit and AssuranceDocument53 pagesAudit and Assuranceattaullah_niazi93No ratings yet
- Auditing Theory Salosagcol SummaryDocument32 pagesAuditing Theory Salosagcol Summarylily andrew0% (1)
- Module #04 - Financial Statement Audit ProcessDocument9 pagesModule #04 - Financial Statement Audit ProcessRhesus UrbanoNo ratings yet
- I. Definitions, Standards and PlanningDocument4 pagesI. Definitions, Standards and PlanninglauraoldkwNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Auditing (Autosaved) 4Document30 pagesIntroduction To Auditing (Autosaved) 4THATONo ratings yet
- AUDITING one 2015 √√√√√√√√√√√√πππππDocument41 pagesAUDITING one 2015 √√√√√√√√√√√√πππππoliifan HundeNo ratings yet
- CPA Exam - Aud Flashcards - QuizletDocument16 pagesCPA Exam - Aud Flashcards - QuizletWilliam SusetyoNo ratings yet
- WK 2 Audit Responsibilities and ObjectivesDocument96 pagesWK 2 Audit Responsibilities and ObjectivesKEITH WONG KANE YOUNGNo ratings yet
- Notes and ReviewerDocument1,116 pagesNotes and ReviewerJeric Ramos De LeonNo ratings yet
- Lecture Audit Theory CHAPTER 1Document2 pagesLecture Audit Theory CHAPTER 1MichelleNo ratings yet
- Non Audit Engagements0Document23 pagesNon Audit Engagements0Aaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Audit of Overview: Auditing IsDocument26 pagesAudit of Overview: Auditing IsMaria BeatriceNo ratings yet
- Internal Control of Fixed Assets: A Controller and Auditor's GuideFrom EverandInternal Control of Fixed Assets: A Controller and Auditor's GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Software Development Life Cycle Asm1Document17 pagesSoftware Development Life Cycle Asm1tuan anhNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 Cost System and Cost AccumulationDocument6 pagesBab 4 Cost System and Cost AccumulationAndi SupenoNo ratings yet
- Sharing - IHCC 30 Jun - Agile HC - MateriDocument32 pagesSharing - IHCC 30 Jun - Agile HC - MateriAndry YadisaputraNo ratings yet
- Performance Management and Reward Systems1Document449 pagesPerformance Management and Reward Systems1Shikhar MehtaNo ratings yet
- Handbook On General MGTDocument106 pagesHandbook On General MGTrupmukadam100% (3)
- TOS IA SchemeDocument4 pagesTOS IA SchemePradeep BiradarNo ratings yet
- Municipality of Siniloan: Republic of The Philippines Province of LagunaDocument8 pagesMunicipality of Siniloan: Republic of The Philippines Province of LagunaAj GemperoNo ratings yet
- Chief Operations OfficerDocument2 pagesChief Operations OfficerMalavika KvNo ratings yet
- SIM CEE 108 Week 1-3 PDFDocument28 pagesSIM CEE 108 Week 1-3 PDFIah Belleza MedelNo ratings yet
- Southwest Airlines Case StudyDocument1 pageSouthwest Airlines Case StudySaw Kyaw Kyaw NgweNo ratings yet
- 10 - Chapter 2 PDFDocument25 pages10 - Chapter 2 PDFJaydev JoshiNo ratings yet
- Vimala S Dasari: at A GlanceDocument3 pagesVimala S Dasari: at A GlanceSrichoudary DasariNo ratings yet
- Oracle EPM OverviewDocument39 pagesOracle EPM OverviewWishtree TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper - KPIs of Self ServiceDocument4 pagesWhitepaper - KPIs of Self ServiceAllan RoosmaaNo ratings yet
- Job Design & Its Impact On Organizational StructureDocument44 pagesJob Design & Its Impact On Organizational StructureGhaith Jouhari60% (5)
- Business Mission and StratergyDocument33 pagesBusiness Mission and StratergyShiela AdnanNo ratings yet
- Role of Information System in Tourism PDFDocument18 pagesRole of Information System in Tourism PDFMir AqibNo ratings yet
- DhidDocument9 pagesDhidTio LuNo ratings yet
- Marina Bay Sands Pratik Bisht: Electives 1Document3 pagesMarina Bay Sands Pratik Bisht: Electives 1Pratik BishtNo ratings yet
- Lean Six SigmaDocument14 pagesLean Six Sigmababudukku100% (10)
- Brain Dump For PMP PreparationDocument52 pagesBrain Dump For PMP Preparationtarik_choqwdhuy100% (4)
- Name: Yasmine Safsouf ID: 201702232 Instructor: Dr. Abdul Rahman Baydoun Subject: SM AssignmentDocument3 pagesName: Yasmine Safsouf ID: 201702232 Instructor: Dr. Abdul Rahman Baydoun Subject: SM AssignmentYasmine Kamal SafsoufNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-MISDocument17 pagesChapter 5-MISJob Dave ToledoNo ratings yet
- HRM NotesDocument225 pagesHRM NotesbuvanNo ratings yet
- PRODUCTION Budget: Prepared By:-Ankit Pandey & Yaman TiwariDocument16 pagesPRODUCTION Budget: Prepared By:-Ankit Pandey & Yaman Tiwariankitapr1988100% (1)
- Assignment of Strategic Management Topic: Mckinsey's 7-S Framework of NestleDocument6 pagesAssignment of Strategic Management Topic: Mckinsey's 7-S Framework of NestleNhư ÝNo ratings yet
- No Broad Level Report Tcode in SAP Options Available For Report ExecutionDocument16 pagesNo Broad Level Report Tcode in SAP Options Available For Report ExecutionAbhinavNo ratings yet
- MNM3711 International MarketingDocument70 pagesMNM3711 International MarketingKefiloe MoatsheNo ratings yet