Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Separate Inheritance-1
Biology Separate Inheritance-1
Uploaded by
aishwarayagreyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Separate Inheritance-1
Biology Separate Inheritance-1
Uploaded by
aishwarayagreyCopyright:
Available Formats
4-6 Inheritance – Biology
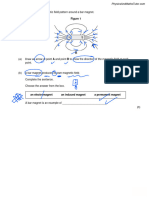
1.0 Figure 1 shows a cell from the small intestine.
Figure 1
1.1 Which part of the cell contains chromosomes?
[1 mark]
Circle one part from the list.
Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria
1.2 Chromosomes contain many genes. Genes have different forms.
What is the name given to different forms of a gene?
[1 mark]
_______________________________________________________________
1.3 Eye colour is controlled by genes.
In a genetic diagram:
• B = brown
• b = blue
The genotype of one individual is bb.
Which words can be used to describe the genotype of this person?
[2 marks]
Circle two words from the list.
Dominant Heterozygous Homozygous Recessive Phenotype
1.4 Tobacco plants have 48 chromosomes.
State how many chromosomes tobacco plant pollen cells have.
[1 mark]
_______________________________________________________________
2.0 Mitosis and meiosis are types of cell division.
© Exampro 2017 Page 1
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
2.1 For each feature in the table, tick one box to show if the feature occurs:
• only in mitosis
• only in meiosis.
[2 marks]
Only in Only in
Feature mitosis meiosis
( ) ( )
Produces new cells during growth and repair
Produces gametes (sex cells)
Produces genetically identical cells
2.2 Name the organ that produces gametes (sex cells) in:
[2 marks]
A man ____________________
A woman __________________
2.3 X and Y chromosomes are the sex chromosomes. They determine a person’s sex.
What sex chromosomes will be found in the body cells of a woman?
[1 mark]
_______________________________________________________________
2.4 A man and a woman decide to have a child.
What is the chance that the child will be a boy?
[1 mark]
_______________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 2
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
3.0 CRAM is an inherited condition which causes muscle breakdown.
The breakdown products enter the urine, making it dark-coloured.
Figure 2 shows the inheritance of CRAM in one family.
Figure 2
CRAM is caused by a recessive allele, n.
The allele for normal health is N.
3.1 Give evidence from the diagram that CRAM is caused by a recessive allele.
[1 mark]
_______________________________________________________________
3.2 None of person 2’s children have CRAM.
Explain why.
[1 mark]
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
3.3 Persons 7 and 8 want to have another child.
What is the probability that this child will have CRAM?
Complete the Punnett square diagram in Figure 3 to explain your answer.
[4 marks]
Figure 3
Person 7
Person 8
Probability = _______________
© Exampro 2017 Page 3
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
4.0 In recent years, more crops grown in the world are genetically modified (GM) crops
4.1 Give two reasons why some crops are genetically modified.
[2 marks]
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
4.2 Give one reason why some scientists are concerned about GM crops.
[1 mark]
_______________________________________________________________
5.0 Many strains of bacteria have developed resistance to antibiotics.
Table 1 shows the number of people infected with a resistant strain of one species of
bacterium in the UK.
Table 1
Year 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008
Number of people infected
3499 3553 3767 3809 4131
with the resistant strain
5.1 Calculate the percentage increase in the number of people infected with the resistant
strain between 2004 and 2008.
[2 marks]
Percentage increase = _____________ %
5.2 Explain, in terms of natural selection, why the number of people infected with the
resistant strain of the bacterium is increasing.
[3 marks]
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 4
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
6.1 Asexual and sexual reproduction are two different processes.
Figure 4 shows a komodo dragon, which can reproduce both sexually and asexually.
Figure 4
There are advantages of both asexual and sexual reproduction.
Compare the advantages of asexual reproduction with the advantages of sexual
reproduction in animals like komodo dragons.
[4 marks]
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 5
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
7.0 In 2012 scientists cloned a wild coyote using skin cells.
Figure 5 show the cloning process.
Figure 5
7.1 What type of cell is cell A?
[1 mark]
Choose one word from the list.
Egg cell Embryo cell Skin cell Sperm cell
7.2 Part B is removed from cell A.
What part of the cell is part B?
[1 mark]
Choose one word from the list.
Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Ribosomes
7.3 Explain why part B is removed from cell A.
[1 mark]
_______________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 6
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
7.4 After cell C is formed, it divides into embryo cells.
What is done to cell C to make it divide?
[1 mark]
Choose one phrase from the list.
Cell C is…
treated with added to other mixed with given an
enzymes egg cells sperm cells electric shock
Image acknowledgements
Komodo dragon
By Dezidor - Own work, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=2583986
Coyote
By Yathin S Krishnappa – Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=21284376
Dog
By derivative work: Djmirko (talk)YellowLabradorLooking.jpg: User:Habj – YellowLabradorLooking.jpg, CC BY-SA 3.0,
https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=4469919
© Exampro 2017 Page 7
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
MARK SCHEME
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
1.1 nucleus 1
1.2 alleles ignore ref to homozygous/heterozygous 1
1.3 homozygous 1
recessive 1
1.4 24 1
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
2.1 Feature Mitosis Meiosis all three correct = 2 marks 2
only only
Produces new 2 correct = 1 mark
cells during growth
and repair 0 or 1 correct = 0 marks
Produces gametes
(sex cells)
Produces
genetically
identical cells
2.2 (a man) testes/testis accept testicle 1
(a woman) ovary/ovaries do not accept ‘ova’/ovule 1
2.3 XX 1
2.4 ½ / 0.5 / 50% / 1:1 / 1 in 2 do not accept 1:2 / 50/50 1
allow 50:50
allow 2 in 4
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
3.1 unaffected parents have an allow 7 and 8 have 10 1
affected child allow skips a generation
3.2 (all) inherit N/normal/ ignore they are carriers 1
dominant allele from 1/from
father
3.3 gametes correct or parental 1
genotypes correct:
N and n + N and n or Nn + Nn accept alternative
symbols, if defined
derivation of offspring 1
genotypes:
NN + Nn + Nn + nn allow alternative if correct
nn identified as CRAM or parental gametes 1
correct probability: 0.25 accept ¼ / 25% / 1 in 4 /
1 out of 4 / 1:3 1
do not accept 3:1 / 1:4
© Exampro 2017 Page 8
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
4.1 (so plants are) resistant to attack or 1
resistant to herbicides
increase yield 1
allow frost resistance
4.2 any one from: 1
• possible effect on wild flowers
• possible effect on insects
• possible effect on human health
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
5.1 18.06 / 18 / 18.1 correct answer gains 2 marks 2
allow 1 mark for,
• (4131 – 3499) ÷ 3499 × 100
• 632 ÷ 3499 × 100
• ((4131 ÷ 3499) × 100 ) – 100
• 0.18
5.2 antibiotics kill non-resistant accept resistant strain is the successful 1
strain or resistant strain competitor
bacteria survive do not accept intentional adaptation
ignore strongest/fittest survive
ignore mutation
ignore people do not finish antibiotic
course
resistant strain bacteria
reproduce or resistant strain 1
bacteria pass on genes
population of resistant strain increases or allow high numbers of resistant bacteria 1
proportion of resistant bacteria increases
or
people more likely to be infected by
resistant strain (than non-resistant strain)
© Exampro 2017 Page 9
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
6.1
Clear and accurate account of the advantages of sexual and asexual reproduction for 3–4
Level 2:
the komodo dragon. The account is clear and logical.
Relevant statements are made about the advantages of sexual or asexual 1–2
Level 1: reproduction. The statements may not be related to the komodo dragon and the
account may not be logical.
No relevant content. 0
Indicative content
Advantages of asexual reproduction for the komodo dragon
• Komodo dragon can have offspring when no male dragon is available
• The komodo dragon does not need to expend energy searching for a mate
• Producing an offspring is quicker than waiting to reproduce sexually
Advantages of sexual reproduction for the komodo dragon
• The offspring of the komodo dragon will show variation
• (and therefore) not as susceptible to genetic disorders
• if the environment changes the komodo dragon will possibly be more able to adapt
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
7.1 egg cell 1
7.2 nucleus 1
7.3 because this contains the dog 1
genes/chromosomes
7.4 electric shock accept genetic information/DNA/alleles 1
© Exampro 2017 Page 10
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5824)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 8464 C 1H QP CombinedScienceTrilogy G 27may22 AMDocument28 pages8464 C 1H QP CombinedScienceTrilogy G 27may22 AMRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Electronics (F) QPDocument48 pagesElectronics (F) QPRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- AQA 8464 C 1H Final MS Jun22 v1.0Document22 pagesAQA 8464 C 1H Final MS Jun22 v1.0Ramy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Biology 2023 CRDocument1 pageBiology 2023 CRRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- AQA 8464 C 1F Final MS Jun22 v1.0Document22 pagesAQA 8464 C 1F Final MS Jun22 v1.0Ramy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism (F) QPDocument20 pagesMagnetism and Electromagnetism (F) QPRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Sum Myp2Document8 pagesSum Myp2Ramy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Energy ChangesDocument4 pagesEnergy ChangesRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- GCSE Combined Science Physics NOV 21 Higher Paper 1 QPDocument24 pagesGCSE Combined Science Physics NOV 21 Higher Paper 1 QPRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Au SC 1667462342 Parts of A Sound Wave Labelling Activity - Ver - 2Document2 pagesAu SC 1667462342 Parts of A Sound Wave Labelling Activity - Ver - 2Ramy MohamedNo ratings yet
- B6 Inheritance Triple 1Document1 pageB6 Inheritance Triple 1Ramy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure 1Document6 pagesAtomic Structure 1Ramy MohamedNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument9 pagesWavesRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- b6 Inheritance Notes Biology TripleDocument30 pagesb6 Inheritance Notes Biology TripleRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- KS4 Energy Stores Worksheet AnswersDocument1 pageKS4 Energy Stores Worksheet AnswersRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument8 pagesWavesRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Dp1 HL Paper1Document9 pagesDp1 HL Paper1Ramy MohamedNo ratings yet
- 4.6b Inheritance Variation and EvolutionDocument85 pages4.6b Inheritance Variation and EvolutionRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- ChecklistDocument1 pageChecklistRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document1 pageTask 1Ramy MohamedNo ratings yet
- 4.6c Inheritance Variation and EvolutionDocument102 pages4.6c Inheritance Variation and EvolutionRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Much and ManyDocument1 pageMuch and ManyRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Make Your Pizza Countable Uncountable Nouns Conversation Topics Dialogs - 117707Document1 pageMake Your Pizza Countable Uncountable Nouns Conversation Topics Dialogs - 117707Ramy MohamedNo ratings yet