Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Na Lab Manual
Na Lab Manual
Uploaded by
SravaniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Na Lab Manual
Na Lab Manual
Uploaded by
SravaniCopyright:
Available Formats
Series Resonance
Aim - Verify the Series Resonance
Apparatus required:
1. Voltmeters
2. Watt meter
3. Rheostat
4. Inductor
5. Capacitor
6. 1 KVA, autotransformer
Theory:
The resonance of a series RLC circuit occurs when the inductive and capacitive reactances are
equal in magnitude but cancel each other because they are 180 degrees apart in phase. The sharp
minimum in impedance which occurs is useful in tuning applications. The sharpness of the minimum
depends on the value of R and is characterized by the "Q" of the circuit. RLC series circuit V - the voltage
of the power source I - the current in the circuit R - the resistance of the resistor L - the inductance of
the inductor C - the capacitance of the capacitor
Processor: RLC series circuit
V - The voltage of the power source
I - the current in the circuit
R - The resistance of the resistor
L - The inductance of the inductor
C - The capacitance of the capacitor
1. The electrical connections are made as shown in circuit diagram.
2. The frequency multiplier is set to 1K and the amplitude knob is set to maximum.
Select sine function & select the voltage at 20V.
3. The frequency is increased in steps of 200 Hz up to 4200 Hz starting from 1000 Hz
and each time the corresponding mille-ammeter readings are noted down.
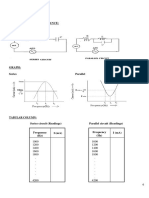
4. Graph of current versus frequency is plotted. The value of resonant frequency
corresponding to the peak value of the curve is noted. Then Inductance, Bandwidth and the
Quality factor are calculated by using the given formulae.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
TABULAR COLUMN:
Series circuit (Readings)
Frequency I (mA) Frequency I (mA)
(Hz) (Hz)
1000 1000
1200 1200
1400 1400
1600 1600
1800 1800
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
.
4200 4200
You might also like
- Fall 2019 PEE I LAB 5Document25 pagesFall 2019 PEE I LAB 5Andrew Park0% (1)
- Lab Manual For Series Parallel Rasonant CircuitDocument3 pagesLab Manual For Series Parallel Rasonant CircuitManoj PardhanNo ratings yet
- EEE222 - Electrical Circuit Analysis II: Lab AssessmentDocument8 pagesEEE222 - Electrical Circuit Analysis II: Lab Assessmenthassan shahidNo ratings yet
- Chapters RewDocument31 pagesChapters RewThirumurugan ThiruNo ratings yet
- Wa0015.Document10 pagesWa0015.SANJAY NILAVAN .S.76No ratings yet
- Lecture 08 Electronics Fall 2019Document61 pagesLecture 08 Electronics Fall 2019john kevinNo ratings yet
- Ee 210L Lab Manual - Activity 4Document3 pagesEe 210L Lab Manual - Activity 4Riah Ann CayananNo ratings yet
- Practical-Electronics-1967-12 Spring Line ReverbDocument7 pagesPractical-Electronics-1967-12 Spring Line ReverbJohan TaalanderwijsNo ratings yet
- Ac Circuits: Robertson A. LabanDocument42 pagesAc Circuits: Robertson A. LabanBenedict TumlosNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument181 pagesIlovepdf MergedZabeehullahmiakhailNo ratings yet
- Преобразователь Lumel P11ZDocument12 pagesПреобразователь Lumel P11ZАнтон ХмараNo ratings yet
- Rectifier Meters: Binoy B NairDocument20 pagesRectifier Meters: Binoy B NairSailes SenthilNo ratings yet
- Disjuntor Aberto Chint - NA1Document11 pagesDisjuntor Aberto Chint - NA1Tho LopesNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3:-: Measurement of Average and Rms Value of Different Signal WaveformsDocument6 pagesExperiment 3:-: Measurement of Average and Rms Value of Different Signal WaveformsWA Q ASNo ratings yet
- EE3115 DiscProb11 Sol Sp06 PDFDocument6 pagesEE3115 DiscProb11 Sol Sp06 PDFNajmoAdenNo ratings yet
- Ac MetersDocument35 pagesAc MetersJhoe TangoNo ratings yet
- Ec3462 Lic Lab ManualDocument62 pagesEc3462 Lic Lab ManualDivya PriyaNo ratings yet
- Series Resonance Using OrCAD PDFDocument33 pagesSeries Resonance Using OrCAD PDFbkmmizanNo ratings yet
- SGM6Document12 pagesSGM6Pamela Ellis DuqueNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document9 pagesExperiment 3SANJAY NILAVAN .S.76No ratings yet
- WEEK-11-MEASUREMENT OF CURRENT,VOLTAGE;RECTIFIERSDocument43 pagesWEEK-11-MEASUREMENT OF CURRENT,VOLTAGE;RECTIFIERSAyberk SungurtasNo ratings yet
- IEEE STD 946-2020 DC Short Circuit CalculationDocument3 pagesIEEE STD 946-2020 DC Short Circuit CalculationukritNo ratings yet
- AC Cur R Ent T Ransmitters Solid Cor E, High Cur R EntDocument2 pagesAC Cur R Ent T Ransmitters Solid Cor E, High Cur R Entluat1983No ratings yet
- Lab Report Operation of A RF Class-A Tuned AmplifierDocument7 pagesLab Report Operation of A RF Class-A Tuned AmplifierKugaa NesvaranNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4-Parallel RC and RL CircuitsDocument9 pagesExperiment No. 4-Parallel RC and RL CircuitsArct John Alfante Zamora100% (1)
- Et - FinalDocument59 pagesEt - FinalpragatinareshNo ratings yet
- RC Phase Shift OscillatorDocument4 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillatormanojkumar9No ratings yet
- EASA Electrical Fundamentals 4Document46 pagesEASA Electrical Fundamentals 4Marty008100% (1)
- Power Electronics Lab MannualDocument12 pagesPower Electronics Lab MannualAnupam Adarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- ElectronicDocument5 pagesElectronicVIMALARANI GNo ratings yet
- PIE - Assignment 2Document1 pagePIE - Assignment 2chetanNo ratings yet
- PoEC 16 RC CircuitsDocument64 pagesPoEC 16 RC Circuitssatti849100% (1)
- Institute of Physics, Academy of Sciences of The Czech Republic, V.V.I. Na Slovance 2, 182 21 Praha 8, Czech RepublicDocument33 pagesInstitute of Physics, Academy of Sciences of The Czech Republic, V.V.I. Na Slovance 2, 182 21 Praha 8, Czech RepublicCarolina CastelaNo ratings yet
- Experiment B6 Aim: Apparatus:: Characteristics of DiodeDocument9 pagesExperiment B6 Aim: Apparatus:: Characteristics of DiodeAnurag BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Class22 and 23 Op Amp-May9-AnnotatedDocument47 pagesClass22 and 23 Op Amp-May9-AnnotatedJagveer MeenaNo ratings yet
- Lic May-June 2017Document15 pagesLic May-June 2017santhosh sekarNo ratings yet
- Eee 224 Circuit Theory Ii Experiment 4: Wien-Bridge Oscillator Using OPAMP Instructor: Dr. Hüseyin BilgekulDocument3 pagesEee 224 Circuit Theory Ii Experiment 4: Wien-Bridge Oscillator Using OPAMP Instructor: Dr. Hüseyin BilgekulJames Adrian Abalde SaboNo ratings yet
- Ec8261 Lab ManualDocument94 pagesEc8261 Lab ManualJayamani Krishnan0% (1)
- Resonance in RLC Series and Parallel Circuit: ObjectivesDocument10 pagesResonance in RLC Series and Parallel Circuit: Objectivesayesha amjadNo ratings yet
- Mit Aec Labmanula 10esl37Document45 pagesMit Aec Labmanula 10esl37anon_70724250No ratings yet
- Ica and HDL LabDocument94 pagesIca and HDL LabBhagya SriNo ratings yet
- Lic Question Bank Test1Document2 pagesLic Question Bank Test1PrashanthNo ratings yet
- Study MaterialDocument37 pagesStudy MaterialAbhinay YadavNo ratings yet
- Half DeflectionDocument4 pagesHalf DeflectionUdit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 13: Objective: To Investigate The Use of JFET As A Constant Current Source & As Chopper ApparatusDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 13: Objective: To Investigate The Use of JFET As A Constant Current Source & As Chopper ApparatusUsama SagharNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab ReportDocument13 pagesPhysics Lab ReportitxgametimesNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Induction MachinesDocument46 pagesThree-Phase Induction MachinesWakgari TadesaNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 7 (Intro To AC)Document4 pagesTUTORIAL 7 (Intro To AC)zahirah najihahNo ratings yet
- EC6361 Lab ManualDocument214 pagesEC6361 Lab ManualPackirisamy NavaneethakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Ac Circuit Experiment: EquipmentDocument4 pagesAc Circuit Experiment: EquipmentBien BasbasNo ratings yet
- Exp 7 Exp 11 - Series and Parallel ResonanceDocument10 pagesExp 7 Exp 11 - Series and Parallel ResonanceakshithadharmasothNo ratings yet
- Islamic University of Technology (Iut)Document2 pagesIslamic University of Technology (Iut)shiamNo ratings yet
- MM LP200Document10 pagesMM LP200ivan.alb.vazzNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 9Document6 pagesLab Report 9esmekegemenNo ratings yet
- Leos 2003 1251748Document2 pagesLeos 2003 1251748sumanta.kundu318020No ratings yet
- AC Circuits LAB 1Document4 pagesAC Circuits LAB 1sarsm56No ratings yet
- Variable DC Power Using Full Bridge ConverterDocument6 pagesVariable DC Power Using Full Bridge Convertergoten10daNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Aim of The ExperimentDocument58 pagesExperiment 1: Aim of The ExperimentAryan KumarNo ratings yet
- Voltage Sensors Curr Ent Sensors: Technical CatalogueDocument53 pagesVoltage Sensors Curr Ent Sensors: Technical CatalogueALLA JITHENDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Figure 7. Impedance vs. Frequency Response of Electrolytic CapacitorDocument1 pageFigure 7. Impedance vs. Frequency Response of Electrolytic CapacitorJianghong ShenNo ratings yet
- Na Lesson Plan Ii-Ece-ADocument6 pagesNa Lesson Plan Ii-Ece-ASravaniNo ratings yet
- Em-Ii LPDocument6 pagesEm-Ii LPSravaniNo ratings yet
- Em 2 PP 3Document3 pagesEm 2 PP 3SravaniNo ratings yet
- EM2 MID1 QPDocument1 pageEM2 MID1 QPSravaniNo ratings yet
- Input Output Ports of 8051Document5 pagesInput Output Ports of 8051mukeshmbNo ratings yet
- A 40-nm Cryo-CMOS Quantum Controller IC For Superconducting QubitDocument14 pagesA 40-nm Cryo-CMOS Quantum Controller IC For Superconducting Qubitrakshit yaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits Chapter 2: BJT: Dr. Dung TrinhDocument69 pagesElectronic Circuits Chapter 2: BJT: Dr. Dung TrinhNGUYÊN NGUYỄN TRUNGNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Answer All QuestionsDocument1 pageInstructions: Answer All QuestionsnkaNo ratings yet
- CMOS Ternary Logic CircuitsDocument7 pagesCMOS Ternary Logic CircuitsSubhasis BiswasNo ratings yet
- Compensators - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument10 pagesCompensators - GATE Study Material in PDFnidhi tripathiNo ratings yet
- DAC0800/DAC0802 8-Bit Digital-to-Analog Converters: General DescriptionDocument0 pagesDAC0800/DAC0802 8-Bit Digital-to-Analog Converters: General DescriptionMiguel Angel García ValerioNo ratings yet
- 19ELE35 QUIZ 3C Quiz 2Document1 page19ELE35 QUIZ 3C Quiz 2avinash_yuvarajNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Robotics Reviewer Quarter 2 PDFDocument11 pagesGrade 9 Robotics Reviewer Quarter 2 PDFDane Gian Angelo TanNo ratings yet
- C62 - Fujitsu 100Gbps Coherent DemonstratorDocument2 pagesC62 - Fujitsu 100Gbps Coherent DemonstratorFujitsu Semiconductor EuropeNo ratings yet
- DT25 Power Amp ParametersDocument2 pagesDT25 Power Amp ParametersSergio VelosoNo ratings yet
- Tek Tr502 - SM Tracking GenDocument69 pagesTek Tr502 - SM Tracking GenayohaiNo ratings yet
- Voltage Peak Limiter Load Vs Power Tables FP+ Series: Dedicated Touring AmplifiersDocument2 pagesVoltage Peak Limiter Load Vs Power Tables FP+ Series: Dedicated Touring AmplifiersDimosthenis MarinidisNo ratings yet
- Engineering Circuit Analysis Sixth EditiDocument6 pagesEngineering Circuit Analysis Sixth EditiArnab ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Mic & RF SyllabusDocument1 pageMic & RF SyllabusSurya Kumar MaranNo ratings yet
- Multiplexer, andDocument43 pagesMultiplexer, andSovon BasuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6.6 Drain Induced Barrier LoweringDocument8 pagesLecture 6.6 Drain Induced Barrier LoweringDebdatta PraharajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document17 pagesChapter 8Yanendra SahNo ratings yet
- 4017 & 4026Document3 pages4017 & 4026Ronny SinagaNo ratings yet
- LicDocument26 pagesLicGopalakrishnan RenganathanNo ratings yet
- LMC 662Document26 pagesLMC 662gabriel taberneroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document25 pagesChapter 10Deivasigamani Subramaniyan0% (1)
- Compuerta 74 LS132Document3 pagesCompuerta 74 LS132richarbmwNo ratings yet
- Two Port NetworkDocument7 pagesTwo Port NetworkAzim KhanNo ratings yet
- Latch-Up Protection For MOSFET Drivers: Author: Cliff Ellison Microchip Technology IncDocument6 pagesLatch-Up Protection For MOSFET Drivers: Author: Cliff Ellison Microchip Technology Incrajat nimjeNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics LabDocument58 pagesDigital Electronics LabpatilrajucNo ratings yet
- Ic FabricationDocument27 pagesIc FabricationLuqman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Combinational CircuitsDocument128 pagesCombinational CircuitsmacharlasatyachaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Voice Otp Ic: Integrated Circuits IncDocument18 pagesVoice Otp Ic: Integrated Circuits IncpbhootNo ratings yet