Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lu 5
Lu 5
Uploaded by
lydia seliCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Perfomance BudjectingDocument72 pagesPerfomance BudjectingAnithaNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Your MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Instructions To Pdri SpreadsheetDocument2 pagesInstructions To Pdri SpreadsheetsiklebNo ratings yet
- Basics of Structured Finance PDFDocument22 pagesBasics of Structured Finance PDFNaomi Alberg-BlijdNo ratings yet
- Explain in Details These Budgeting Approaches Used in The Preparation of BudgetsDocument3 pagesExplain in Details These Budgeting Approaches Used in The Preparation of BudgetsPule JackobNo ratings yet
- Budgetary Systems: Performance HierarchyDocument5 pagesBudgetary Systems: Performance HierarchyFaizan KhanNo ratings yet
- BUD 2242 Budgeting Small SchoolsDocument73 pagesBUD 2242 Budgeting Small SchoolsMaria Faye MarianoNo ratings yet
- 4 Behavioural Approaches BudgetingDocument16 pages4 Behavioural Approaches BudgetingSunny XuNo ratings yet
- ACCA Integrated Workbook F5 Chapter8Document20 pagesACCA Integrated Workbook F5 Chapter8Sunny Kumar10No ratings yet
- Presentation Bpme..Document13 pagesPresentation Bpme..wadhwacommunisation0001No ratings yet
- Budget ConrolDocument15 pagesBudget ConrolLokesh dNo ratings yet
- Budgetary Control: Dr.R.VasanthagopalDocument15 pagesBudgetary Control: Dr.R.VasanthagopalSameer GoyalNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Reliance MutuaDocument8 pagesProject Report On Reliance MutuaPRADYUMNA .SNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three - Budgetary ControlsDocument27 pagesChapter Three - Budgetary ControlsbavanthinilNo ratings yet
- Budgeting: By: M. Luqman RafiqDocument7 pagesBudgeting: By: M. Luqman RafiqsulukaNo ratings yet
- Zero Base Budgeting A and Performance BudgetingDocument9 pagesZero Base Budgeting A and Performance Budgetingankit_kataryaNo ratings yet
- Budgeting ConceptsDocument6 pagesBudgeting ConceptssoulniacsipamNo ratings yet
- Budgetary ControlDocument16 pagesBudgetary ControlKushal ParekhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - BudgetingDocument22 pagesLesson 2 - BudgetingRochelle UrbodaNo ratings yet
- Budgeting StrategiesDocument4 pagesBudgeting StrategiesJaya ShankarNo ratings yet
- 32 BudgetsDocument17 pages32 Budgetsayza.aftab24No ratings yet
- 3.performance Budgeting Refers To A Budget in Terms Of: BenchmarkDocument3 pages3.performance Budgeting Refers To A Budget in Terms Of: BenchmarkUsama TariqNo ratings yet
- ECONOMY HANDOUT-4 (CLASS-4) BATCH-2 Forms of BudgetingDocument18 pagesECONOMY HANDOUT-4 (CLASS-4) BATCH-2 Forms of Budgetingankitkumar7150singhNo ratings yet
- Budgetary Control and Standard CostingDocument15 pagesBudgetary Control and Standard CostingPratyay DasNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Budgetary Control SystemDocument17 pagesPresentation On: Budgetary Control SystemTechnical networkNo ratings yet
- Lazy Notes BudgetDocument2 pagesLazy Notes BudgetAngeline MiparanumNo ratings yet
- Energy Management Plan Guide: Energy Efficiency and Conservation Programme July 2017Document5 pagesEnergy Management Plan Guide: Energy Efficiency and Conservation Programme July 2017Justine Kei Lim-OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Definition of Budgetary ControlDocument10 pagesMeaning and Definition of Budgetary ControlHardeep KaurNo ratings yet
- ZBB Theory & Budgetary ControlDocument5 pagesZBB Theory & Budgetary Controlmanan chandakNo ratings yet
- Long Term PlanningDocument11 pagesLong Term PlanninghelperforeuNo ratings yet
- Budgeting and Budgetary ControlDocument31 pagesBudgeting and Budgetary ControlpulsaraminNo ratings yet
- Chap. III Budgeting-200422Document53 pagesChap. III Budgeting-200422Gedion EndalkachewNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Budgeting For Planning and ControlDocument1 page4.1 Budgeting For Planning and ControlLea GerodiazNo ratings yet
- Government BudgetingDocument23 pagesGovernment BudgetingChristopher John MwakipesileNo ratings yet
- Budgeting For Planning & ControlDocument30 pagesBudgeting For Planning & ControlrizkyameNo ratings yet
- BudgetingDocument5 pagesBudgetingSHIBANI MNo ratings yet
- Aeco2 MidtermDocument5 pagesAeco2 MidtermvsplanciaNo ratings yet
- Pact Project-3-Mark TorioDocument9 pagesPact Project-3-Mark Torioangelotorio27No ratings yet
- TheoryDocument3 pagesTheorykingaisyah01No ratings yet
- Zero Base BudgetingDocument15 pagesZero Base BudgetingSumitasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document3 pagesChapter 3Mixx MineNo ratings yet
- Performance Measurement and AssessmentDocument25 pagesPerformance Measurement and AssessmentVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Week Five: A Budget Is A ContractDocument25 pagesWeek Five: A Budget Is A ContractNizam JewelNo ratings yet
- SCMA Unit - IV Budgetary ControlDocument9 pagesSCMA Unit - IV Budgetary Control22wj1e0050No ratings yet
- MS 3406 Short-Term Budgeting Additional Financing Needed and ForecastingDocument7 pagesMS 3406 Short-Term Budgeting Additional Financing Needed and ForecastingMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Ma 13 TheoryDocument1 pageMa 13 TheorySai AmruthaNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting MasDocument6 pagesCapital Budgeting MasHainiel ReforzadoNo ratings yet
- Budget Mid FinalDocument9 pagesBudget Mid Final841388No ratings yet
- URP-4103 Public and Municipal FinanceDocument7 pagesURP-4103 Public and Municipal FinanceSabbir Rahman LeonNo ratings yet
- Pact Project-3-Vj Fransyne TagubaDocument9 pagesPact Project-3-Vj Fransyne Tagubaangelotorio27No ratings yet
- Budget As An Instrument of ControlDocument8 pagesBudget As An Instrument of Controlgoyalvikas86No ratings yet
- Chapter - Three Budgets and Budgetary ControlDocument83 pagesChapter - Three Budgets and Budgetary ControlHace AdisNo ratings yet
- Budgeting & Budgetary ControlDocument30 pagesBudgeting & Budgetary ControlStacy CopelandNo ratings yet
- PM - Budgeting and ControlDocument16 pagesPM - Budgeting and Controljohn markNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Compilation (b5 Notebook)Document3 pagesReviewer Compilation (b5 Notebook)Jessica AlbaracinNo ratings yet
- Q # 1. Explain How Budgetary Systems Fit Within The Performance Hierarchy?Document5 pagesQ # 1. Explain How Budgetary Systems Fit Within The Performance Hierarchy?Hammad AnwarNo ratings yet
- What Is A BUDGET ?Document7 pagesWhat Is A BUDGET ?arunishthNo ratings yet
- BCD Budgeting and Budgetary Control 2021Document55 pagesBCD Budgeting and Budgetary Control 2021Oreratile KeorapetseNo ratings yet
- Budget and BudgetingDocument2 pagesBudget and Budgetingnitika88No ratings yet
- Budget and Budgetary Control A Comprehensive AnalysisDocument2 pagesBudget and Budgetary Control A Comprehensive AnalysisSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- BUDGETINGDocument7 pagesBUDGETINGMarjorie ManuelNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Environment (Final)Document3 pagesManagement Accounting Environment (Final)Mica R.No ratings yet
- Master Budgeting and Forecasting for Hospitality Industry-Teaser: Financial Expertise series for hospitality, #1From EverandMaster Budgeting and Forecasting for Hospitality Industry-Teaser: Financial Expertise series for hospitality, #1No ratings yet
- Yankee Pressure Test TAPPIDocument4 pagesYankee Pressure Test TAPPImgmqroNo ratings yet
- 0LB - Unilever's Lifebuoy Assignment (A&b) - WrittenDocument3 pages0LB - Unilever's Lifebuoy Assignment (A&b) - WrittenMonil Chheda100% (1)
- AHR 2016previewDocument29 pagesAHR 2016previewAnonymous XhkjXCxxsTNo ratings yet
- Sankalp Research Paper 2023Document22 pagesSankalp Research Paper 2023Shivansh SinghNo ratings yet
- A1 - Tabangin - FINAL GREENTECH SUMMIT 2023 Disclaimer v2Document39 pagesA1 - Tabangin - FINAL GREENTECH SUMMIT 2023 Disclaimer v2garthraymundo123No ratings yet
- The Application of Fiber Optic Distributed Temperature Sensor To Fault Detection of XLPE Insulated Underground Cable - Google SearchDocument2 pagesThe Application of Fiber Optic Distributed Temperature Sensor To Fault Detection of XLPE Insulated Underground Cable - Google SearchUG CABLENo ratings yet
- BitumenDocument4 pagesBitumenBangeen JalalNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of MEMS and ASIC Monolithic Integration: Iain Rutherford - X-FAB MEMS FoundryDocument17 pagesMaking Sense of MEMS and ASIC Monolithic Integration: Iain Rutherford - X-FAB MEMS FoundryEduardo MarquesNo ratings yet
- Bussiness MathematicsDocument3 pagesBussiness MathematicsPatric CletusNo ratings yet
- Ansys ModelDocument11 pagesAnsys Modelsrini_meha100% (1)
- TB 152Document9 pagesTB 152emiliano ZappaterraNo ratings yet
- En 300 330 V2.1.0 PDFDocument74 pagesEn 300 330 V2.1.0 PDFSosialNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Airport - Intro 2180602Document52 pagesLecture 1 Airport - Intro 2180602Ujjval Solanki67% (3)
- Globaltouch West Africa Limited A Case For Reinvestment Toward ProfitabilityDocument7 pagesGlobaltouch West Africa Limited A Case For Reinvestment Toward ProfitabilityDyaji Charles BalaNo ratings yet
- Wind Rose Plot: DisplayDocument1 pageWind Rose Plot: Displaydhiecha309No ratings yet
- URS R404aDocument1 pageURS R404aironiteNo ratings yet
- Surface Defects in Steel ProductsDocument41 pagesSurface Defects in Steel ProductsShilaj PNo ratings yet
- MQREIT Circular 22 11 2016Document137 pagesMQREIT Circular 22 11 2016fefefNo ratings yet
- Tablet CoatingDocument7 pagesTablet CoatingLakmi Nurul UciiNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography On Land Research in Nepal (2011)Document50 pagesAnnotated Bibliography On Land Research in Nepal (2011)Kristoff Sven100% (1)
- COSHH Assessment FormDocument2 pagesCOSHH Assessment Formsupriyo sarkar100% (1)
- Performance-Based Seismic Engineering: The Need For A Reliable Conceptual Comprehensive ApproachDocument26 pagesPerformance-Based Seismic Engineering: The Need For A Reliable Conceptual Comprehensive ApproachEduardo Daniel Farfán DuránNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Perioperatif Operasi Arterial Switch PadaDocument12 pagesManajemen Perioperatif Operasi Arterial Switch Padacomiza92No ratings yet
- Cdi 3 Pre TestDocument4 pagesCdi 3 Pre TestKazuya KinoshitaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum VitaeDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitaech MuzammalNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Information Systems PDFDocument164 pagesFundamentals of Information Systems PDFharshithaNo ratings yet
Lu 5
Lu 5
Uploaded by
lydia seliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lu 5
Lu 5
Uploaded by
lydia seliCopyright:
Available Formats
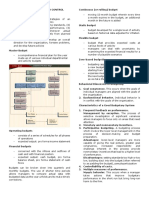
LU 5 TRADITIONAL BUDGETING SYSTEM
Definition The traditional budgeting system is a historical approach where
budgets are prepared based on the previous year's budget adjusted
for inflation, revenue forecasts, and changes in policy.
Characteristics Incremental: Budgets are typically adjusted incrementally from the
previous year's budget.
Annual: Budgets are prepared on an annual basis.
Line-item Detail: Focuses on line-item expenditures and revenues.
Advantages Simplicity: Easy to understand and implement.
Stability: Provides a stable financial plan.
Disadvantages Rigidity: Does not accommodate changes or shifting priorities
effectively.
Focus on Inputs: Emphasizes inputs rather than outcomes or
performance.
Assumptions 1. All activities making up last year's spending were essential to
achieve the ongoingobjectives
2. All activities must be continued during the coming years and
are more urgent than newly created programmes
3. All increases are because of the increase in costs of material
and labour due to inflation
PROGRAMME AND PERFORMANCE BUDGETING SYSTEM
Definition This system links budget allocations directly to the objectives and
outcomes of programs or activities
Characteristics Outcome-Oriented: Emphasizes achieving specific program
objectives.
Performance Measures: Uses performance indicators to assess
efficiency and effectiveness.
Budget by Objectives: Funds allocated based on desired outcomes
rather than historical expenditures.
Advantages Alignment: Aligns budget decisions with organizational goals.
Accountability: Enhances accountability through clear performance
metrics.
Complexity: Requires robust performance measurement and
Disadvantages reporting systems.
Subjectivity: Setting performance measures can be subjective and
challenging.
MODIFIED BUDGETING SYSTEM
Definition A hybrid approach that combines elements of traditional and
programme/performance budgeting systems
Characteristics Flexible: Allows for adjustments based on both historical data and
performance outcomes.
Incremental with Conditions: Adjusts previous budgets with
conditions tied to performance targets.
Focus on Efficiency: Seeks to improve efficiency while maintaining
some stability.
Advantages Adaptability: More adaptable than traditional budgeting but retains
some stability.
Performance Focus: Encourages performance improvements while
maintaining budget controls.
Disadvantages Complexity: Can be more complex to implement and manage than
traditional budgeting alone.
Resource Intensive: Requires resources for monitoring and evaluating
performance.
OUTCOME-BASED BUDGETING
Definition A budgeting approach that focuses on the outcomes and results achieved
from the use of resources, rather than inputs or outputs.
Characteristics Outcome Emphasis: Budget decisions are based on achieving specific
outcomes or results.
Long-term Perspective: Considers long-term impacts and benefits.
Performance Evaluation: Uses rigorous performance evaluation to
allocate resources.
Advantages Efficiency: Promotes efficient resource allocation based on outcomes.
Effectiveness: Enhances effectiveness by focusing on achieving desired
results.
Disadvantages Measurement Challenges: Difficulties in measuring and attributing
outcomes to budget allocations.
Complexity: Requires advanced performance measurement and
evaluation systems.
You might also like
- Perfomance BudjectingDocument72 pagesPerfomance BudjectingAnithaNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Your MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Instructions To Pdri SpreadsheetDocument2 pagesInstructions To Pdri SpreadsheetsiklebNo ratings yet
- Basics of Structured Finance PDFDocument22 pagesBasics of Structured Finance PDFNaomi Alberg-BlijdNo ratings yet
- Explain in Details These Budgeting Approaches Used in The Preparation of BudgetsDocument3 pagesExplain in Details These Budgeting Approaches Used in The Preparation of BudgetsPule JackobNo ratings yet
- Budgetary Systems: Performance HierarchyDocument5 pagesBudgetary Systems: Performance HierarchyFaizan KhanNo ratings yet
- BUD 2242 Budgeting Small SchoolsDocument73 pagesBUD 2242 Budgeting Small SchoolsMaria Faye MarianoNo ratings yet
- 4 Behavioural Approaches BudgetingDocument16 pages4 Behavioural Approaches BudgetingSunny XuNo ratings yet
- ACCA Integrated Workbook F5 Chapter8Document20 pagesACCA Integrated Workbook F5 Chapter8Sunny Kumar10No ratings yet
- Presentation Bpme..Document13 pagesPresentation Bpme..wadhwacommunisation0001No ratings yet
- Budget ConrolDocument15 pagesBudget ConrolLokesh dNo ratings yet
- Budgetary Control: Dr.R.VasanthagopalDocument15 pagesBudgetary Control: Dr.R.VasanthagopalSameer GoyalNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Reliance MutuaDocument8 pagesProject Report On Reliance MutuaPRADYUMNA .SNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three - Budgetary ControlsDocument27 pagesChapter Three - Budgetary ControlsbavanthinilNo ratings yet
- Budgeting: By: M. Luqman RafiqDocument7 pagesBudgeting: By: M. Luqman RafiqsulukaNo ratings yet
- Zero Base Budgeting A and Performance BudgetingDocument9 pagesZero Base Budgeting A and Performance Budgetingankit_kataryaNo ratings yet
- Budgeting ConceptsDocument6 pagesBudgeting ConceptssoulniacsipamNo ratings yet
- Budgetary ControlDocument16 pagesBudgetary ControlKushal ParekhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - BudgetingDocument22 pagesLesson 2 - BudgetingRochelle UrbodaNo ratings yet
- Budgeting StrategiesDocument4 pagesBudgeting StrategiesJaya ShankarNo ratings yet
- 32 BudgetsDocument17 pages32 Budgetsayza.aftab24No ratings yet
- 3.performance Budgeting Refers To A Budget in Terms Of: BenchmarkDocument3 pages3.performance Budgeting Refers To A Budget in Terms Of: BenchmarkUsama TariqNo ratings yet
- ECONOMY HANDOUT-4 (CLASS-4) BATCH-2 Forms of BudgetingDocument18 pagesECONOMY HANDOUT-4 (CLASS-4) BATCH-2 Forms of Budgetingankitkumar7150singhNo ratings yet
- Budgetary Control and Standard CostingDocument15 pagesBudgetary Control and Standard CostingPratyay DasNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Budgetary Control SystemDocument17 pagesPresentation On: Budgetary Control SystemTechnical networkNo ratings yet
- Lazy Notes BudgetDocument2 pagesLazy Notes BudgetAngeline MiparanumNo ratings yet
- Energy Management Plan Guide: Energy Efficiency and Conservation Programme July 2017Document5 pagesEnergy Management Plan Guide: Energy Efficiency and Conservation Programme July 2017Justine Kei Lim-OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Definition of Budgetary ControlDocument10 pagesMeaning and Definition of Budgetary ControlHardeep KaurNo ratings yet
- ZBB Theory & Budgetary ControlDocument5 pagesZBB Theory & Budgetary Controlmanan chandakNo ratings yet
- Long Term PlanningDocument11 pagesLong Term PlanninghelperforeuNo ratings yet
- Budgeting and Budgetary ControlDocument31 pagesBudgeting and Budgetary ControlpulsaraminNo ratings yet
- Chap. III Budgeting-200422Document53 pagesChap. III Budgeting-200422Gedion EndalkachewNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Budgeting For Planning and ControlDocument1 page4.1 Budgeting For Planning and ControlLea GerodiazNo ratings yet
- Government BudgetingDocument23 pagesGovernment BudgetingChristopher John MwakipesileNo ratings yet
- Budgeting For Planning & ControlDocument30 pagesBudgeting For Planning & ControlrizkyameNo ratings yet
- BudgetingDocument5 pagesBudgetingSHIBANI MNo ratings yet
- Aeco2 MidtermDocument5 pagesAeco2 MidtermvsplanciaNo ratings yet
- Pact Project-3-Mark TorioDocument9 pagesPact Project-3-Mark Torioangelotorio27No ratings yet
- TheoryDocument3 pagesTheorykingaisyah01No ratings yet
- Zero Base BudgetingDocument15 pagesZero Base BudgetingSumitasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document3 pagesChapter 3Mixx MineNo ratings yet
- Performance Measurement and AssessmentDocument25 pagesPerformance Measurement and AssessmentVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Week Five: A Budget Is A ContractDocument25 pagesWeek Five: A Budget Is A ContractNizam JewelNo ratings yet
- SCMA Unit - IV Budgetary ControlDocument9 pagesSCMA Unit - IV Budgetary Control22wj1e0050No ratings yet
- MS 3406 Short-Term Budgeting Additional Financing Needed and ForecastingDocument7 pagesMS 3406 Short-Term Budgeting Additional Financing Needed and ForecastingMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Ma 13 TheoryDocument1 pageMa 13 TheorySai AmruthaNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting MasDocument6 pagesCapital Budgeting MasHainiel ReforzadoNo ratings yet
- Budget Mid FinalDocument9 pagesBudget Mid Final841388No ratings yet
- URP-4103 Public and Municipal FinanceDocument7 pagesURP-4103 Public and Municipal FinanceSabbir Rahman LeonNo ratings yet
- Pact Project-3-Vj Fransyne TagubaDocument9 pagesPact Project-3-Vj Fransyne Tagubaangelotorio27No ratings yet
- Budget As An Instrument of ControlDocument8 pagesBudget As An Instrument of Controlgoyalvikas86No ratings yet
- Chapter - Three Budgets and Budgetary ControlDocument83 pagesChapter - Three Budgets and Budgetary ControlHace AdisNo ratings yet
- Budgeting & Budgetary ControlDocument30 pagesBudgeting & Budgetary ControlStacy CopelandNo ratings yet
- PM - Budgeting and ControlDocument16 pagesPM - Budgeting and Controljohn markNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Compilation (b5 Notebook)Document3 pagesReviewer Compilation (b5 Notebook)Jessica AlbaracinNo ratings yet
- Q # 1. Explain How Budgetary Systems Fit Within The Performance Hierarchy?Document5 pagesQ # 1. Explain How Budgetary Systems Fit Within The Performance Hierarchy?Hammad AnwarNo ratings yet
- What Is A BUDGET ?Document7 pagesWhat Is A BUDGET ?arunishthNo ratings yet
- BCD Budgeting and Budgetary Control 2021Document55 pagesBCD Budgeting and Budgetary Control 2021Oreratile KeorapetseNo ratings yet
- Budget and BudgetingDocument2 pagesBudget and Budgetingnitika88No ratings yet
- Budget and Budgetary Control A Comprehensive AnalysisDocument2 pagesBudget and Budgetary Control A Comprehensive AnalysisSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- BUDGETINGDocument7 pagesBUDGETINGMarjorie ManuelNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Environment (Final)Document3 pagesManagement Accounting Environment (Final)Mica R.No ratings yet
- Master Budgeting and Forecasting for Hospitality Industry-Teaser: Financial Expertise series for hospitality, #1From EverandMaster Budgeting and Forecasting for Hospitality Industry-Teaser: Financial Expertise series for hospitality, #1No ratings yet
- Yankee Pressure Test TAPPIDocument4 pagesYankee Pressure Test TAPPImgmqroNo ratings yet
- 0LB - Unilever's Lifebuoy Assignment (A&b) - WrittenDocument3 pages0LB - Unilever's Lifebuoy Assignment (A&b) - WrittenMonil Chheda100% (1)
- AHR 2016previewDocument29 pagesAHR 2016previewAnonymous XhkjXCxxsTNo ratings yet
- Sankalp Research Paper 2023Document22 pagesSankalp Research Paper 2023Shivansh SinghNo ratings yet
- A1 - Tabangin - FINAL GREENTECH SUMMIT 2023 Disclaimer v2Document39 pagesA1 - Tabangin - FINAL GREENTECH SUMMIT 2023 Disclaimer v2garthraymundo123No ratings yet
- The Application of Fiber Optic Distributed Temperature Sensor To Fault Detection of XLPE Insulated Underground Cable - Google SearchDocument2 pagesThe Application of Fiber Optic Distributed Temperature Sensor To Fault Detection of XLPE Insulated Underground Cable - Google SearchUG CABLENo ratings yet
- BitumenDocument4 pagesBitumenBangeen JalalNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of MEMS and ASIC Monolithic Integration: Iain Rutherford - X-FAB MEMS FoundryDocument17 pagesMaking Sense of MEMS and ASIC Monolithic Integration: Iain Rutherford - X-FAB MEMS FoundryEduardo MarquesNo ratings yet
- Bussiness MathematicsDocument3 pagesBussiness MathematicsPatric CletusNo ratings yet
- Ansys ModelDocument11 pagesAnsys Modelsrini_meha100% (1)
- TB 152Document9 pagesTB 152emiliano ZappaterraNo ratings yet
- En 300 330 V2.1.0 PDFDocument74 pagesEn 300 330 V2.1.0 PDFSosialNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Airport - Intro 2180602Document52 pagesLecture 1 Airport - Intro 2180602Ujjval Solanki67% (3)
- Globaltouch West Africa Limited A Case For Reinvestment Toward ProfitabilityDocument7 pagesGlobaltouch West Africa Limited A Case For Reinvestment Toward ProfitabilityDyaji Charles BalaNo ratings yet
- Wind Rose Plot: DisplayDocument1 pageWind Rose Plot: Displaydhiecha309No ratings yet
- URS R404aDocument1 pageURS R404aironiteNo ratings yet
- Surface Defects in Steel ProductsDocument41 pagesSurface Defects in Steel ProductsShilaj PNo ratings yet
- MQREIT Circular 22 11 2016Document137 pagesMQREIT Circular 22 11 2016fefefNo ratings yet
- Tablet CoatingDocument7 pagesTablet CoatingLakmi Nurul UciiNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography On Land Research in Nepal (2011)Document50 pagesAnnotated Bibliography On Land Research in Nepal (2011)Kristoff Sven100% (1)
- COSHH Assessment FormDocument2 pagesCOSHH Assessment Formsupriyo sarkar100% (1)
- Performance-Based Seismic Engineering: The Need For A Reliable Conceptual Comprehensive ApproachDocument26 pagesPerformance-Based Seismic Engineering: The Need For A Reliable Conceptual Comprehensive ApproachEduardo Daniel Farfán DuránNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Perioperatif Operasi Arterial Switch PadaDocument12 pagesManajemen Perioperatif Operasi Arterial Switch Padacomiza92No ratings yet
- Cdi 3 Pre TestDocument4 pagesCdi 3 Pre TestKazuya KinoshitaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum VitaeDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitaech MuzammalNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Information Systems PDFDocument164 pagesFundamentals of Information Systems PDFharshithaNo ratings yet