Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Report
Report
Uploaded by
Harsh KumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Report
Report
Uploaded by
Harsh KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
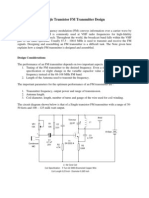
Low-Power FM Transmitter
Harsh Kumar,Harish Suyal,Ujjwal Gupta, Jaypee University Of Engineering & Technology,India 2 Department of Electronics & Communication,Guna, India
email2: harsh0914@gmail.com
Abstract: This report proposes a low power fm transmitter construction. The transmitter consists of a low noise biopotential amplifier and a voltage controlled oscillator used to transmit the amplifid signals at a frequency range of 88-108 MHz. It is designed to use an input from another sound source (such as a guitar or microphone), and transmits on the commercial FM band
the coil, weld the thread piece used as antenna second it turn of the coil L1.
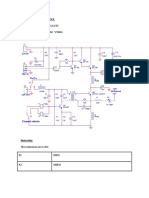
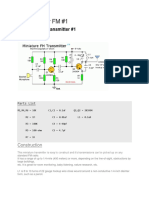
2. Circuit Diagram:
1. Introduction
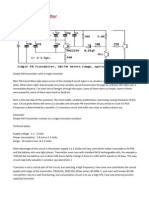
This small power FM transmitter can transmit more than 1 km in good conditions. The modulation can be made so much with a microphone or audio source. Circuit of power fm transmitter is built around 2n2218 transistor. Transmitter coil is 5 turns of enameled 22 AWG wire, with diameter of 1 cm without nucleus. Look at the capacitors that it should be ceramic. The antenna should possess from 15 to 40 cm. For transmission it ties a receiver of FM (radio) in the proximity to half volume in a free frequency (that there is not any radio operating), with a wood or plastic key, rotate the screw of CV to capture the frequency of the transmitter. If it has difficulties of fittings, remove the coil and wind her again with more or less it turns. Look at pinage of the transistor 2n2218. Mic1 is a microphone of electrets of two terminals, THE resistor R1 makes the polarization of the microphone, perhaps it is necessary to alter the value of R1 to adapt to your microphone, values of 1k up to 10k can be tested. Preferably use plate of glass fiber, that is the appropriate for high frequency. Perhaps for better frequency stability to be necessary to place the antenna on second turn of
3. Component Specification:
R1 = 3 a 10k (black, black, orange, gold) R2 = 6,8k (Blue, Gray, red, gold). R3=4,7k (yellow, violet, red, gold. ) R4 = 39 (Orange, White, black, gold. C1=4,7 nF (472 or 4n7 or 4700) C2=2,2 nF (2200 or 2n2 or 222) C3 = 4.7pF (4p7 or 4.7) C4 = 100 nF (100n, or 0.1 or 104) C5 = TRIMMER CV 3-30 PF. T1 = 2n2218
4. Circuit Layout:
coefficient, 750 parts per million per degree Celsius). The others should be NPO types, since temperature correction is not needed (nor is it desirable). If you cannot get N750 caps, don't worry too much, the frequency stability of the circuit is not that good anyway (as with all simple transmitters).
Inductors :
The inductors are nominally 5 turns (actually of 1cm diameter enamelled copper wire. Carefully scrape away the enamel where the coil ends will go through the board - all the enamel must be removed to ensure good contact.The nominal (and very approximate) inductance is calculated according to the formula ... L = N * r / (228r + 254l)... where L = inductance in microhenries (uH), N = number of turns, r = average coil radius, and l = coil length. All dimensions are in millimetres.
6. References: 5.Description
Capacitors: All capacitors must be ceramic (with the exception of C1, see below), with C2 and C6 preferably being N750 (Negative temperature 1.http://sound.westhost.com/project54.htm 2.http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FM_transmitter_( personal_device)
You might also like
- 2 KM FM TransmitterDocument1 page2 KM FM TransmitterradianfmNo ratings yet
- Intercom Using Lm386Document2 pagesIntercom Using Lm386triloksawantNo ratings yet
- CST Antenna Array WorkflowDocument39 pagesCST Antenna Array WorkflowNgô Văn Đức100% (1)
- 1KM Power FM TransmitterDocument4 pages1KM Power FM Transmitterekjon10% (1)
- AM Transmitter'n'receiver CircuitDocument9 pagesAM Transmitter'n'receiver Circuitkapil singh100% (1)
- FM Transmitter DesignDocument5 pagesFM Transmitter DesignLaty Bayb100% (2)
- Long Range FM Transmitter With 2 Watt Power and 1Document4 pagesLong Range FM Transmitter With 2 Watt Power and 1ashar565No ratings yet
- FM Receivers With PLLDocument6 pagesFM Receivers With PLLOndrej LomjanskiNo ratings yet
- 3V FM TransmitterDocument9 pages3V FM TransmitterHabib RkNo ratings yet
- FM TransmitterDocument9 pagesFM TransmitterMuhammad MujtabaNo ratings yet
- 3 Stage FM Transmitter (KI0232) : Assembly InstructionsDocument15 pages3 Stage FM Transmitter (KI0232) : Assembly Instructionsaka_1010No ratings yet
- Transistor Circuits Manual No4-1972Document34 pagesTransistor Circuits Manual No4-1972GuialtsenNo ratings yet
- Long-Range FM TransmitterDocument1 pageLong-Range FM TransmitterMallieswaran SubbaiyanNo ratings yet
- Long Range TransreceiverDocument7 pagesLong Range Transreceiverselva.natarajNo ratings yet
- 3V FM Transmitter 3V FM Transmitter CircuitDocument4 pages3V FM Transmitter 3V FM Transmitter Circuitpeter.gomes20087216No ratings yet
- Radio Frog QRP 7 MHZDocument6 pagesRadio Frog QRP 7 MHZCharles de Magalhães100% (1)
- Simple FM TransmitterDocument6 pagesSimple FM Transmitterxtra4web100% (1)
- Low Cost Transistorised IntercomDocument13 pagesLow Cost Transistorised IntercomaymangafferNo ratings yet
- Presentation On FM Transmitter ProjectDocument22 pagesPresentation On FM Transmitter Projectpandey9985% (20)
- Amplificador de Bulbos de Bajo CostoDocument6 pagesAmplificador de Bulbos de Bajo CostoNaelectronic UONo ratings yet
- Technical Characteristics BoosterDocument4 pagesTechnical Characteristics BoosterVany BraunNo ratings yet
- 300w tp9383 PDFDocument3 pages300w tp9383 PDFlu1agp100% (1)
- FM TransmitterDocument24 pagesFM Transmitterrethunkb5548100% (2)
- Amplificatore Audio AMDocument5 pagesAmplificatore Audio AMEchizen KinichiNo ratings yet
- 3V FM Transmitter CircuitDocument6 pages3V FM Transmitter CircuitMahmood AhmedNo ratings yet
- Long Range AM TransmitterDocument1 pageLong Range AM TransmitterAkshay KarveNo ratings yet
- Magneticremote ControlDocument3 pagesMagneticremote ControlBóza GyörgyNo ratings yet
- Interfon LM 386 InternetDocument3 pagesInterfon LM 386 InternetMihai TămagăNo ratings yet
- ck207 FMDocument3 pagesck207 FMMalay PatraNo ratings yet
- Simple AM Receiver&TransmitterDocument4 pagesSimple AM Receiver&TransmitterGokulk2011100% (2)
- AC Current Monitor by LM358Document14 pagesAC Current Monitor by LM358wlen2012No ratings yet
- t2fd 2Document9 pagest2fd 2Daniel Morales Poblete100% (1)
- Intercom Using LM386Document2 pagesIntercom Using LM386v1009980No ratings yet
- Analogue Electronics: 14. Transistor Circuits For The ConstructorDocument27 pagesAnalogue Electronics: 14. Transistor Circuits For The ConstructorNuraddeen MagajiNo ratings yet
- How To Make A Long Range FM Transmitter at Low CostDocument24 pagesHow To Make A Long Range FM Transmitter at Low CostRajesh VenkatramanNo ratings yet
- ECD Lab - CEA - Report..Document12 pagesECD Lab - CEA - Report..Muhammad kamran AmjadNo ratings yet
- Proiect PAMEDocument2 pagesProiect PAMEElaNo ratings yet
- Long Range FM TransmitterDocument2 pagesLong Range FM TransmittersathiyarasuNo ratings yet
- A Balanced Input For Microphones Can Solve Hum and Noise Pickup ProblemsDocument16 pagesA Balanced Input For Microphones Can Solve Hum and Noise Pickup ProblemsTitán SotoNo ratings yet
- An HF 50-W Linear AmplifierDocument8 pagesAn HF 50-W Linear AmplifierEdward Yanez100% (1)
- Magic Tee: StructureDocument5 pagesMagic Tee: Structurejhon deenNo ratings yet
- Line Follower RobotDocument14 pagesLine Follower RobotAmarjith ValancheryNo ratings yet
- Elf Circuit DesignDocument5 pagesElf Circuit DesignKatja GoiteNo ratings yet
- Rangkaian RangkaianDocument30 pagesRangkaian RangkaianAhmad JuheriNo ratings yet
- 5 KM Long Range FM TransmitterDocument6 pages5 KM Long Range FM Transmitterzafindravato bezalahyNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Radio Communications ReceiverDocument2 pagesAircraft Radio Communications Receiverdreyes3773No ratings yet
- Indoor 80 M TX LoopDocument6 pagesIndoor 80 M TX Loopbearbullride10No ratings yet
- FM Radio Jammer: DescriptionDocument4 pagesFM Radio Jammer: DescriptionnickususNo ratings yet
- CK 200Document3 pagesCK 200Shrikanth SundarNo ratings yet
- Electronics-Illustrated-1964-07 ExportDocument6 pagesElectronics-Illustrated-1964-07 ExportGaryNo ratings yet
- Analog Lab - CEA - RepoortDocument12 pagesAnalog Lab - CEA - RepoortMuhammad kamran AmjadNo ratings yet
- Analog Project ReportDocument3 pagesAnalog Project Reportfahadsaeed93No ratings yet
- Video AmplifierDocument13 pagesVideo AmplifierPradyumna Yambar100% (1)
- FM DhezDocument17 pagesFM DhezDesiree GarciaNo ratings yet
- Ak-270 Hex3653 FM Receiver Diy KitDocument13 pagesAk-270 Hex3653 FM Receiver Diy KitOséias Lima VieiraNo ratings yet
- Short Wave AM TransmitterDocument1 pageShort Wave AM Transmitter2711323No ratings yet
- WWW - Stanford.edu Jbarral Downloads JoelleBarral CoilDesignDocument9 pagesWWW - Stanford.edu Jbarral Downloads JoelleBarral CoilDesignSachin_AnchanNo ratings yet
- Analog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13From EverandAnalog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Lecture 13a: EE 344 Wave Propagation and AntennasDocument10 pagesLecture 13a: EE 344 Wave Propagation and AntennasOsama IkramNo ratings yet
- Antenna SpecificationsDocument3 pagesAntenna SpecificationsRobertNo ratings yet
- Computer Sciences Ekt Preparation Compressed PDFDocument31 pagesComputer Sciences Ekt Preparation Compressed PDFPrashika NikoseNo ratings yet
- Coaching Materials in Transmission Lines and Antennas Part 4 For ECE Board Exam PDFDocument6 pagesCoaching Materials in Transmission Lines and Antennas Part 4 For ECE Board Exam PDFchristineNo ratings yet
- Ds Opa65rbu4b v1 - 0 170803Document14 pagesDs Opa65rbu4b v1 - 0 170803JEGPTHGNo ratings yet
- ANT-ASI4518R10v18-1966-008 DatasheetDocument2 pagesANT-ASI4518R10v18-1966-008 DatasheetMauricioNo ratings yet
- Hrocat 5Document13 pagesHrocat 5Sparky73100% (1)
- (1 - Status of Military Satellite Communications - (Johnston - 1965)Document9 pages(1 - Status of Military Satellite Communications - (Johnston - 1965)LurzizareNo ratings yet
- Design of UHF RFID Reader and The Solution of Crosstalk ProblemsDocument6 pagesDesign of UHF RFID Reader and The Solution of Crosstalk Problemsmano012No ratings yet
- Soil Scout Brochure 2023Document12 pagesSoil Scout Brochure 2023Jason VanBuskirkNo ratings yet
- 006-Rev-00-IPTV System-11-03-17Document206 pages006-Rev-00-IPTV System-11-03-17samir rabiaNo ratings yet
- Technical Site Survey Report (TSSR)Document7 pagesTechnical Site Survey Report (TSSR)Stephen Amachi ChisatiNo ratings yet
- Model Radar Implementation Using Ultrasonic SensorDocument7 pagesModel Radar Implementation Using Ultrasonic SensorInternational Journal of Research in Science & TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Ace Technology Catalogue 2017Document209 pagesAce Technology Catalogue 2017Alex BowmanNo ratings yet
- RFS 1.8mDocument13 pagesRFS 1.8mMarius Tresor EdiboussieNo ratings yet
- Distributed Antenna SystemDocument5 pagesDistributed Antenna SystemAqeel HasanNo ratings yet
- CelTools TrainingDocument37 pagesCelTools TrainingBless MkhizeNo ratings yet
- NTC SyllabusDocument5 pagesNTC SyllabusRoshan Ghimire0% (1)
- 1987 Ku Band Distribution of Television Programming For The Cable IndustryDocument12 pages1987 Ku Band Distribution of Television Programming For The Cable Industrydaniel GimenezNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation From Telecommunication Networks PDFDocument21 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation From Telecommunication Networks PDFMonaElabbassiNo ratings yet
- EC 308 AWP Ch-10 Lens AntennaDocument11 pagesEC 308 AWP Ch-10 Lens Antennarrajmohan28No ratings yet
- H10010 FAA-450 EU1KY Antenna Analyzer Kit Operation Guide Rev1.0Document24 pagesH10010 FAA-450 EU1KY Antenna Analyzer Kit Operation Guide Rev1.0DanMocanuNo ratings yet
- 1982, Integral Equation Formulation of Microstrip AntennasDocument6 pages1982, Integral Equation Formulation of Microstrip AntennasRicha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Link BudgetDocument9 pagesLink BudgetSrinath SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Harper's Wireless BookDocument224 pagesHarper's Wireless Bookhds0405No ratings yet
- Yagi Antenna Design - NBSDocument30 pagesYagi Antenna Design - NBSmuni1100% (1)
- Actix CellrefsDocument24 pagesActix CellrefsPhong TaNo ratings yet
- Cma Ubdhh 6521 E1-10 H2Document1 pageCma Ubdhh 6521 E1-10 H2yevobimNo ratings yet
- Informe 02 AntenasDocument8 pagesInforme 02 Antenasismael duchiNo ratings yet