Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guide To Direct and Indirect Speech
Guide To Direct and Indirect Speech
Uploaded by
tonyfaerberboeck20 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Guide to Direct and Indirect Speech
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesGuide To Direct and Indirect Speech
Guide To Direct and Indirect Speech
Uploaded by
tonyfaerberboeck2Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Guide to Direct and Indirect Speech
1. Understanding Direct Speech:
a. Definition: Direct speech is the verbatim reporting of someone's words, enclosed in
quotation marks, without any changes to the original wording.
b. Example: "She said, 'I am going to the store.'"
2. Understanding Indirect Speech:
a. Definition: Indirect speech, also known as reported speech, involves paraphrasing
someone's words without using their exact words. It usually requires changes in
pronouns, tenses, and time expressions.
b. Example: "She said that she was going to the store."
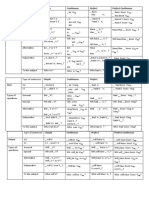
3. Changes in Tenses, Pronouns, and Time Expressions:
a. Tenses:
Direct Speech Indirect Speech
He said, "I like ice cream." He said that he liked ice cream.
She said, "I went to the park." She said that she had gone to the park.
They say, "We are studying." They say that they are studying.
He said, "I was reading a book." He said that he had been reading a book.
She says, "I will visit tomorrow." She says that she will visit the next day.
b. Pronouns:
• Pronouns in indirect speech may change based on the subject of the reporting
clause and the reported clause.
• First-person pronouns (I, we) usually change according to the subject of the
reporting clause.
• Second-person pronouns (you) may change based on the context and
relationship between the speaker and listener.
• Third-person pronouns (he, she, they) may change based on the gender and
number of the subject of the reporting clause.
c. Time Expressions:
• Time expressions often change in indirect speech to reflect the shift from the
time of speaking in the direct speech to the time of reporting in the indirect
speech.
• Words like "today" may change to "that day," "tomorrow" to "the next day,"
"yesterday" to "the previous day," etc.
4. Importance of Direct and Indirect Speech:
• Direct speech adds authenticity and immediacy to dialogues, allowing characters'
voices to be heard directly.
• Indirect speech is useful for summarizing or reporting conversations, thoughts, or
statements without using direct quotations.
5. Summary:
• Direct speech reproduces someone's words verbatim within quotation marks.
• Indirect speech paraphrases someone's words without using their exact words,
often requiring changes in tenses, pronouns, and time expressions.
• Understanding the rules for converting between direct and indirect speech is
essential for accurate reporting and effective communication.
You might also like
- Narration Notes (Class 11-12)Document12 pagesNarration Notes (Class 11-12)Anugrah Stanley80% (5)
- The Art of Subtitling: Before WatchingDocument1 pageThe Art of Subtitling: Before WatchingБибаNo ratings yet
- Centre of Excellence in Economics and Finance Language and Communication DepartmentDocument25 pagesCentre of Excellence in Economics and Finance Language and Communication DepartmentmariaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument1 pageReported SpeechDaniel Ovalle 10No ratings yet
- Communication SkillsDocument24 pagesCommunication SkillsHrithik SureshNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect Speechmanaalfasih123No ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document4 pagesLesson 5pablo.creeper.2.0.1No ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument18 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechSangay DemaNo ratings yet
- Repported Speech - Apuntes 2024Document2 pagesRepported Speech - Apuntes 2024Alba Rodriguez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Quoted and Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesQuoted and Reported SpeechPRECIOUS KAYE MARIE BANTIGUENo ratings yet
- Eng Class XiDocument65 pagesEng Class XiSaske OPNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech PresentationDocument30 pagesDirect Speech Presentationcyberexpert997No ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument15 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechDiosalette W. FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect Speech SDDocument24 pagesDirect Indirect Speech SDAqeelahNo ratings yet
- DirectindirectDocument1 pageDirectindirectWaleedNo ratings yet
- A Lesson Plan in English II Concept: Speech Is The Faculty or Act of Expressing or Describing Thoughts, Feelings, orDocument4 pagesA Lesson Plan in English II Concept: Speech Is The Faculty or Act of Expressing or Describing Thoughts, Feelings, orEdge CambaloNo ratings yet
- Direct and Reportd SpeechDocument16 pagesDirect and Reportd SpeechappawashNo ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect SpeechDocument7 pagesDirect & Indirect SpeechDebela AbidhuNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document2 pagesHW 1abdallh bakerNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument8 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeecharumimarcelNo ratings yet
- Direct SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect SpeechTria Farwani SinagaNo ratings yet
- 30 Reported SpeechDocument1 page30 Reported SpeechFrancisco S. ArjonaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech - Definitions, Examples, Exercise and RulesDocument7 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech - Definitions, Examples, Exercise and Rulesgoreshalan6No ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesReported SpeechOliver SKNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument7 pagesDirect and Indirect Speechhammyali4272No ratings yet
- Presentation - Reported SpeechDocument11 pagesPresentation - Reported SpeechValquiria SantosNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English 9 I. Objectives:: (The Teacher Lets The Students Write Their Sentence On The Board.)Document7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English 9 I. Objectives:: (The Teacher Lets The Students Write Their Sentence On The Board.)Billy Joe RavagoNo ratings yet
- Class 1.7 Warm Up (Activity in Class)Document2 pagesClass 1.7 Warm Up (Activity in Class)The black AreNo ratings yet
- Direct-Indirect Speech EnglishDocument82 pagesDirect-Indirect Speech EnglishYanuar NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument10 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechNur Asfiya KhustinaNo ratings yet
- Class X Lesson 6 Narrations or Direct and Indirect RulesDocument4 pagesClass X Lesson 6 Narrations or Direct and Indirect RulesMAREEZ E ISHQ MAREEZ E ISHQNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument10 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris Direct and Indirect SpeechJulia SharaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect NarrationDocument25 pagesDirect and Indirect NarrationKamran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pagesTugas Bahasa InggrisSyafira MpuhuNo ratings yet
- Tema 30iDocument5 pagesTema 30iKatarina DziegielewskaNo ratings yet
- Direct To Indirect SpeechDocument6 pagesDirect To Indirect Speechasimjalwana3836No ratings yet
- Direct Indirect Speech - HandoutDocument6 pagesDirect Indirect Speech - HandoutMantram JoshiNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect Speech Explanation Video What Is Direct and Indirect Speech Definition?Document21 pagesDirect Indirect Speech Explanation Video What Is Direct and Indirect Speech Definition?Estelle Nica Marie DunlaoNo ratings yet
- Class 10 English Grammar Ncert Solutions Direct Indirect SpeechDocument6 pagesClass 10 English Grammar Ncert Solutions Direct Indirect Speechishabalhara2004No ratings yet
- Lec File Narration PrintDocument9 pagesLec File Narration Printteshosta123No ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect SlidesDocument14 pagesDirect & Indirect Slidesshayanali1682003No ratings yet
- NarrationDocument30 pagesNarrationSteve MahashabdeNo ratings yet
- Direct - and - Indirect SpeechDocument11 pagesDirect - and - Indirect SpeechAbigail DizonNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument33 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechABChelleNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect Reported Speech U Mahasiswa - 2Document13 pagesDirect Indirect Reported Speech U Mahasiswa - 2เหยื่อผู้เคราะห์ร้ายที่บ้านหักNo ratings yet
- Thesis Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument7 pagesThesis Direct and Indirect SpeechJessica Henderson100% (2)
- Fundamental Rules For Indirect SpeechDocument1 pageFundamental Rules For Indirect SpeechWilma BundangNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 PEL135Document30 pagesUnit 3 PEL135JohnNo ratings yet
- 18-Reported Speech - Indirect SpeechDocument2 pages18-Reported Speech - Indirect SpeechtakinardiNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect Indirect SpeechstuartinsandeepNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Supplementary Notes About Reporting SpeechDocument4 pagesChapter Four: Supplementary Notes About Reporting SpeechBilisuma AmanteNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document13 pagesGroup 1Nur afni UlfianaNo ratings yet
- Studyandexam Com Direct Indirect Speech HTMLDocument3 pagesStudyandexam Com Direct Indirect Speech HTMLhamzaali227004No ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae Edir FerreiraDocument15 pagesCurriculum Vitae Edir FerreiraJorge JuniorNo ratings yet
- Eng 7 Quarter 4 W4Document4 pagesEng 7 Quarter 4 W4Jan Philip AbellonNo ratings yet
- NARRATIONS (Recovered)Document7 pagesNARRATIONS (Recovered)Debashish Paul100% (1)
- Direct and Indirect Speech RulesDocument4 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech RulesMayur MeenaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech Complete GuideDocument45 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech Complete GuideAmber FarhanNo ratings yet
- Background of The ProblemDocument12 pagesBackground of The ProblemKafiyah QisyaNo ratings yet
- Reported and Direct SpeechDocument19 pagesReported and Direct Speechshalopez166No ratings yet
- Compound Words Typographic Technical Series for Apprentices #36From EverandCompound Words Typographic Technical Series for Apprentices #36Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Tieng Anh 8 Sach Moi Giua Ky 1 Co Dap AnDocument3 pagesTieng Anh 8 Sach Moi Giua Ky 1 Co Dap AnĐào Nhật HiểnNo ratings yet
- Step 2: Answers - Base On The First Documents, Answer The Following QuestionsDocument4 pagesStep 2: Answers - Base On The First Documents, Answer The Following Questionsibeth urango moraNo ratings yet
- Linguistics - Module 1Document28 pagesLinguistics - Module 1Gerlyn Dangel100% (2)
- NAHW - +10-day+WB+FinalDocument53 pagesNAHW - +10-day+WB+FinalJiaul HudaNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous Tenseaffirmative Sentences With GR Grammar Guides - 13572Document2 pagesPast Continuous Tenseaffirmative Sentences With GR Grammar Guides - 13572Juan Esteban MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Simple Continuous Perfect Perfect-Continuous Present: Ing Ing Ing Ing IngDocument1 pageSimple Continuous Perfect Perfect-Continuous Present: Ing Ing Ing Ing IngОфеліяNo ratings yet
- Announcement TextDocument4 pagesAnnouncement TextMuhammad FaishalNo ratings yet
- Actividad Semana 4 Grado DecimoDocument4 pagesActividad Semana 4 Grado DecimoJuan David Casanova50% (2)
- All About Nouns: Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesAll About Nouns: Learning ObjectivesYanny OranteNo ratings yet
- Forsaken WifeDocument3 pagesForsaken WifeEnlai RooneyNo ratings yet
- Grammar File8 2Document1 pageGrammar File8 2Carlos SanchezNo ratings yet
- Philippine English - ReviewerDocument30 pagesPhilippine English - ReviewerRose Ann Montes AlogNo ratings yet
- JUNI-2193321059 LS EthnolinguisticsDocument3 pagesJUNI-2193321059 LS EthnolinguisticsNurhayati ManaluNo ratings yet
- Universidad Popular Del Cesar: UNIT 3: It Was Painted by Bansky! Group: Upc06Document2 pagesUniversidad Popular Del Cesar: UNIT 3: It Was Painted by Bansky! Group: Upc06Anha Noriega BarrazaNo ratings yet
- Phrasal Verb in Action From Phan QuynhDocument71 pagesPhrasal Verb in Action From Phan Quynhcandy_at90No ratings yet
- Mirror of Common ErrorsDocument145 pagesMirror of Common ErrorsMRUNAL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect Tense - ENGLISH PAGEDocument2 pagesPast Perfect Tense - ENGLISH PAGEpankaj kararNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Don Quixote Lesson 4Document28 pagesUnit 3 Don Quixote Lesson 4pyro samNo ratings yet
- 1st QTR ExamDocument4 pages1st QTR Examマグイ ジェシーNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect ObjectsDocument3 pagesDirect and Indirect ObjectsJOSUE DIAZ BOTELLONo ratings yet
- Mini - Lesson Plan 2Document4 pagesMini - Lesson Plan 2Sekeithia Merritt-LasterNo ratings yet
- Research Article On English Speeking ProDocument20 pagesResearch Article On English Speeking Promuhammad faheemNo ratings yet
- DISC - Ebook 1 CYCDocument15 pagesDISC - Ebook 1 CYCBhupendraNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Monolingual and Bilingual Dictionary On The Foreign Language Learners' AcquisitionDocument4 pagesThe Effect of Monolingual and Bilingual Dictionary On The Foreign Language Learners' AcquisitionLong NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Unit 35 Explanatory Texts. Structure and CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesUnit 35 Explanatory Texts. Structure and CharacteristicsMiriam Reinoso SánchezNo ratings yet
- AntecedentsDocument3 pagesAntecedentsMoNo ratings yet
- Pharr Answer KeyDocument58 pagesPharr Answer KeyGeorge RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Project English V - 3rd MidtermDocument4 pagesProject English V - 3rd MidtermKwon Min Wang LeeNo ratings yet
- Animals & Human LanguageDocument8 pagesAnimals & Human LanguageSara AHNo ratings yet