Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PED 103 Theories of Motor Control
PED 103 Theories of Motor Control
Uploaded by
ronelbatulatamamioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PED 103 Theories of Motor Control
PED 103 Theories of Motor Control
Uploaded by
ronelbatulatamamioCopyright:
Available Formats
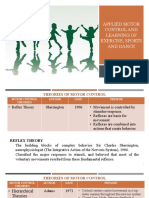
Theories of Motor Control
Assumptions Clinical Implications Limitations
Reflex Theory - Sherrington - Use sensory input to control motor output - Reflex can’t be basic unit of behavior
- “Peripheralist” - Stimulate good reflexes - Doesn’t explain fast mvmts
- Reflexes are basis for all mvmt - Inhibit undesirable (primitive) reflexes - Doesn’t explain how single stimulus results
- External stimulus leads to mvmt - Relies heavily on feedback in varying responses.
- Nervous System – triggers, coordinates, & - Doesn’t explain voluntary mvmts.
activates muscles
Hierarchical Theory - JH Jackson - Identify & prevent primitive reflexes - Doesn’t explain dominance of reflexive
- “Centralist” - Reduce hyperactive stretch behaviors in normal adults
- “Top-Down” unidirectional flow - Normalize tone - Everyone’s developmental pattern is diff.
- Voluntary mvmts initiated by “will” (higher - Facilitate “normal” mvmt patterns - Hands-on approach pt may become very
levels) - DEVELOPMENTAL SEQUENCE passive
- Reflexive mvmts dominate only after CNS - Recapitulation
damage.
Systems Theory - Bernstein - Identifiable, functional tasks - Very broad – many diff. systems
- Goal-directed behavior (Task Oriented) - Practice under a variety of conditions - Doesn’t focus as heavily on the interaction of
- Synergies to master redundant degrees of - Modify environmental contexts the organism w/ the environment.
freedom
- Feedback (closed loop)
Motor Programming - Central Motor Pattern – motor response w/o - Abnormal mvmt – not just reflexive, also - Not intended to replace importance of
Theory sensory stimulus/reflex including abnormalities in central pattern sensory input in controlling mvmt
- Central pattern generators (CPGs) – spinal motor generators or higher level motor programs. - Central motor program can’t be sole
programs that can produce mvmt w/o cortical or - Help pts relearn the correct rules for action determinant of action
sensory input - Retrain mvmts important to fxn’al task - Doesn’t explain nervous sys. dealing w/ both
- Higher-level motor programs – store rules for - Do not just reeducate muscles in isolation musculoskeletal & environment variables
generating mvmts.
Dynamical Action - New mvmt emerges 2o to change in control - Mvmt is an emergent property from the - Nervous sys. has unimportant role
Theory parameter. interaction of multiple elements. - Presumption that the relationship b/w the
- De-emphasize commands from CNS in - Understand the physical & dynamic properties physical sys. & environment determines
controlling mvmt and emphasize physical of the body behavior.
explanations for mvmt - i.e.) Velocity- important for dynamics of
- Attractor state – preferred pattern (vice-versa) mvmt. May be good to encourage faster mvmt
- Deeper attractor well more stable pattern in pts to produce momentum and therefore help
- Stable patterns become more variable prior to weak pts move w/ greater ease.
transition to new mvmt pattern.
Ecological Theory - James Gibson - Help pt explore multiple ways in achieving - Gives less emphasis on nervous sys.
- Perception-action system fInal task discovering best solution for pt,
- Perception focuses on detecting information in given the set of limitations.
the environment that will support the actions
necessary to achieve the goal.
You might also like
- RBT Study GuideDocument6 pagesRBT Study GuideDiana Andriescu100% (1)
- The Unconscious Patterning of Behavior in Society - SapirDocument9 pagesThe Unconscious Patterning of Behavior in Society - Sapirbullfrog3No ratings yet
- For Review Only: Assimilating and Differentiating: The Curvilinear Effect of Social Class On Green ConsumptionDocument71 pagesFor Review Only: Assimilating and Differentiating: The Curvilinear Effect of Social Class On Green ConsumptionRemaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Theories of Neurological RehabilitationDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Theories of Neurological RehabilitationHibaAli67% (3)
- NEW CREW Fast Start PlannerDocument9 pagesNEW CREW Fast Start PlannerAnonymous oTtlhP100% (3)
- Theories of Motor ControlDocument1 pageTheories of Motor ControlAqembunNo ratings yet
- Motor Control TheoriesDocument26 pagesMotor Control TheoriesSardarChangezKhanNo ratings yet
- Theories of Motor LearningDocument1 pageTheories of Motor LearningPrincess GarciaNo ratings yet
- Neuro Concept NotesDocument35 pagesNeuro Concept Noteshoney requermeNo ratings yet
- Applied Motor ControlDocument8 pagesApplied Motor Controljeanrose.maderazoNo ratings yet
- Motor Control Theories: What Is A Class On Motor Control About?Document7 pagesMotor Control Theories: What Is A Class On Motor Control About?Joaquin Napoleon QuejadaNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes For MovementDocument2 pagesSummary Notes For Movementbobadilla.sarah19No ratings yet
- Motor ControlDocument8 pagesMotor Controlarold bodoNo ratings yet
- 1-5 Motor Control TheoriesDocument51 pages1-5 Motor Control TheoriesNatrayanRamesh100% (1)
- Prepared By: Dr. Qindeel ShafaqDocument30 pagesPrepared By: Dr. Qindeel ShafaqHibaAliNo ratings yet
- Neurological Physical Therapy Course Code: Shs 422Document53 pagesNeurological Physical Therapy Course Code: Shs 422AbdullahNo ratings yet
- TriChapter57-09-Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesTriChapter57-09-Nervous Systembao.nguyenthienadamsNo ratings yet
- NDT Workshop Nanda SirDocument67 pagesNDT Workshop Nanda SirAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Motor System: Three Types of Movement Generated by Motor SystemDocument10 pagesMotor System: Three Types of Movement Generated by Motor SystemVon Hippo100% (1)
- Science 10 NotesDocument15 pagesScience 10 NotesJuan MiguelNo ratings yet
- Theories of Motor ControlDocument33 pagesTheories of Motor ControlArslan Aslam100% (3)
- Psych 3260 NotesDocument45 pagesPsych 3260 NotesKinzaIqbalNo ratings yet
- Cog PsychDocument3 pagesCog PsychCrazy CrazyNo ratings yet
- The Sensorimotor SystemDocument4 pagesThe Sensorimotor SystemEmilie LakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Bped 3Document11 pagesChapter 1 Bped 3Renzo JakeNo ratings yet
- THE Organization of Knowledge in The MindDocument29 pagesTHE Organization of Knowledge in The Mindmylene davidNo ratings yet
- Motor ControlDocument34 pagesMotor ControlShree PatelNo ratings yet
- Ludwig Von Bertalanfry Gargi MamDocument19 pagesLudwig Von Bertalanfry Gargi Mamnathsujitkr1980No ratings yet
- Psychology FinalDocument5 pagesPsychology FinalIvan AramayoNo ratings yet
- Physiological Psychology Chapter 8 NotesDocument9 pagesPhysiological Psychology Chapter 8 NotesEsra AkgulNo ratings yet
- Cognitivepsych-Ch 3Document31 pagesCognitivepsych-Ch 3mylene davidNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3rd Quarter For Grade 10 BiologyDocument20 pagesScience Reviewer 3rd Quarter For Grade 10 BiologyTirao, Lizette Luz O.No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesNervous SystemArianne Jen GenotivaNo ratings yet
- Neuronal Pathways of Communication: COMS 5483Document50 pagesNeuronal Pathways of Communication: COMS 5483Michael MerlinNo ratings yet
- Welcome Ebook ENG FEB.-17 2022Document20 pagesWelcome Ebook ENG FEB.-17 2022André AmorimNo ratings yet
- Psych ReviewerDocument20 pagesPsych ReviewerEllen Joyce P. CarnajeNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Midterms 1H Book and PPT 1Document35 pagesAnaphy Midterms 1H Book and PPT 1Elizabeth Louwel ConchaNo ratings yet
- Control Motor - V.B.Document16 pagesControl Motor - V.B.MarianoborrachiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cortico Basal Ganglia Networks and TH 2014 Neurobiology of AlcohDocument19 pagesChapter 2 Cortico Basal Ganglia Networks and TH 2014 Neurobiology of AlcohAle López CastroNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - NeuropsychologyDocument53 pagesTopic 2 - Neuropsychologykhangduong.emailvnNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesNervous SystemCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- BPE16 - (Chapter 4 - BPED 3)Document8 pagesBPE16 - (Chapter 4 - BPED 3)Terry Jane JavelinaNo ratings yet
- BHN Kuliah K22 Mekanisme Kontrol Motorik Somatik Dan RefleksDocument34 pagesBHN Kuliah K22 Mekanisme Kontrol Motorik Somatik Dan RefleksRhena Fitria KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Copia de 13.12Document9 pagesCopia de 13.12INÉS TORIBIO ARGÜELLESNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: Spinal CordDocument12 pagesCentral Nervous System: Spinal CordHarly E. DeniegaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Motor LearningDocument29 pagesTheories of Motor LearningpalNo ratings yet
- Bernstein Turvey Kelso & Tuller Thelen 1967 1977 1984 1987Document5 pagesBernstein Turvey Kelso & Tuller Thelen 1967 1977 1984 1987Jewel GuintoNo ratings yet
- AnaKines NotesDocument3 pagesAnaKines NotesLorenzSantosHernandezNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Basis of Treatment TheraExDocument8 pagesTheoretical Basis of Treatment TheraExLall JingerppangNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Ap Exam Review Part 1Document160 pagesUltimate Ap Exam Review Part 1api-287575009No ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document27 pagesPresentation 1Junaisah P. PangaponNo ratings yet
- Spinal Motor SystemDocument23 pagesSpinal Motor SystemBenaya PhNo ratings yet
- Neuron and Skeletal Muscle Fibers)Document1 pageNeuron and Skeletal Muscle Fibers)Victor PetcuNo ratings yet
- ROOD'S ApproachDocument14 pagesROOD'S ApproachNeuroAxisTherapyNo ratings yet
- 5 Psychology BiopsychologyDocument7 pages5 Psychology BiopsychologyKawthar MajedNo ratings yet
- 10 CS1AC16 Artificial Intelligence SummaryDocument3 pages10 CS1AC16 Artificial Intelligence SummaryAnna AbcxyzNo ratings yet
- Computational Models of NeuromodulationDocument35 pagesComputational Models of Neuromodulationabhijit89No ratings yet
- NDT Sun WordDocument22 pagesNDT Sun WordRathina Kumar (Rathu baai)No ratings yet
- Psychology and Sociology Terms For The MCATDocument53 pagesPsychology and Sociology Terms For The MCATlukehongNo ratings yet
- The Mind: It'S Works As It FunctionsDocument61 pagesThe Mind: It'S Works As It FunctionsJohnlyn FigaroaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 & 4 Psychology Checklist: 1. Cambridge 2019 Chapter 1 Questions Nervous System FunctioningDocument2 pagesUnit 3 & 4 Psychology Checklist: 1. Cambridge 2019 Chapter 1 Questions Nervous System FunctioningJason FourisNo ratings yet
- SCT Post MidsemDocument29 pagesSCT Post MidsemSaumya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- The Gamble of LifeDocument11 pagesThe Gamble of LifeRocklein ConuiNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Midterm Gender and Society 1Document3 pagesTopic 3 Midterm Gender and Society 1Frenzle Dane SantosNo ratings yet
- Konrad Lorenz. On AggressionDocument73 pagesKonrad Lorenz. On AggressionKate100% (1)
- Havening BookDocument124 pagesHavening BookSasa ZivkovicNo ratings yet
- Autonomy Midterm Test 2023 - HandoutDocument2 pagesAutonomy Midterm Test 2023 - Handoutlechaunhi3007No ratings yet
- Character Traits and Values of MyanmarDocument3 pagesCharacter Traits and Values of MyanmarkakayNo ratings yet
- Pygmalion Act 4Document2 pagesPygmalion Act 4Morning QueensNo ratings yet
- The Big Five Personality Test - Truity123Document8 pagesThe Big Five Personality Test - Truity123jabruNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 87 For Gifted Students Grade 9 2022Document4 pagesPractice Test 87 For Gifted Students Grade 9 2022Tâm HoàngNo ratings yet
- EDUC 107 The Strengths and The Weaknesses of The Filipino CharacterDocument2 pagesEDUC 107 The Strengths and The Weaknesses of The Filipino Charactermelissa embuidoNo ratings yet
- T5 - Aksi NyataDocument1 pageT5 - Aksi NyataDesi ErfianaNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1 Multiple GraphDocument6 pagesWriting Task 1 Multiple GraphTangkas PriambodoNo ratings yet
- Formulating Evaluative StatementDocument4 pagesFormulating Evaluative StatementSalve SerranoNo ratings yet
- APA Vs Harvard Referencing - PDFDocument4 pagesAPA Vs Harvard Referencing - PDFTalo Contajazz Chileshe50% (2)
- College and Career Counseling: A Basic Understanding of Counseling PsychologyDocument4 pagesCollege and Career Counseling: A Basic Understanding of Counseling PsychologyVidushi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Filipino 9 CMDocument28 pagesFilipino 9 CMCloue Faye I. BasalloNo ratings yet
- Bleeding EdgeDocument216 pagesBleeding EdgeJason100% (1)
- Evaluation BsessDocument7 pagesEvaluation Bsessprecilladelacruz20No ratings yet
- Fs2 Learning Episode 1 Ma. Kathleen Irish T. Gregorio Bsed Uniting-ADocument5 pagesFs2 Learning Episode 1 Ma. Kathleen Irish T. Gregorio Bsed Uniting-ALeovelyn GervacioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3176Document31 pagesChapter 3176Allan NacidaNo ratings yet
- Question Text: FeedbackDocument12 pagesQuestion Text: FeedbackANGELU RANE BAGARES INTOLNo ratings yet
- (g12) Cultural Identity - ReadingDocument6 pages(g12) Cultural Identity - ReadingBui My HangNo ratings yet
- Session 4 Integrating DI in Inclusive ClassroomsDocument60 pagesSession 4 Integrating DI in Inclusive ClassroomsMaryjane Bailo LamelaNo ratings yet
- Language of ResearchDocument7 pagesLanguage of ResearchSheryl April Herrera IglesiasNo ratings yet
- FrankensteinDocument3 pagesFrankensteinClaraNo ratings yet
- English 2 Week 1Document4 pagesEnglish 2 Week 1Cy DacerNo ratings yet
- Uga Admissions EssayDocument4 pagesUga Admissions Essaytxmvblaeg100% (2)