Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Characteristics of Living Things
The Characteristics of Living Things
Uploaded by
Arthanayaka NandikaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Cell Types SE GizmosDocument13 pagesCell Types SE Gizmosalex79% (14)
- Chapter 1 BC SC Probe 8Document36 pagesChapter 1 BC SC Probe 8api-265180883No ratings yet
- Oracle Utilities Meter Data Management Features and Functions Overview 388664Document39 pagesOracle Utilities Meter Data Management Features and Functions Overview 388664Mohammed Safwat100% (4)
- S.1 Bio Notes PDFDocument57 pagesS.1 Bio Notes PDFkitderoger_391648570100% (4)
- The Microscope and Its Use: Lab ReportDocument4 pagesThe Microscope and Its Use: Lab ReportArbab GillNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Cells Seen Under The MicroscopeDocument5 pagesLab Report Cells Seen Under The Microscopeorlandoe2560% (1)
- Biology Lab PracticalomgomgDocument215 pagesBiology Lab PracticalomgomgdNo ratings yet
- s.1 Biology Notes NewDocument52 pagess.1 Biology Notes NewTUMUSIIME INNOCENTNo ratings yet
- Biology BookDocument397 pagesBiology Bookmesh100% (1)
- General Biology Laboratory ModuleDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology Laboratory ModuleEunice Moureen MaravillaNo ratings yet
- MICROSDocument2 pagesMICROSharlyNo ratings yet
- sw8 chp04Document23 pagessw8 chp04api-115560904No ratings yet
- Medical Biology Lab Manual Lab - 1-Dr. Raz NawzadDocument15 pagesMedical Biology Lab Manual Lab - 1-Dr. Raz NawzadLa NiaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 MicrosDocument15 pagesLab 2 Microsjohn NisNo ratings yet
- Grade 8-CellTypesSE - Adam NasrDocument10 pagesGrade 8-CellTypesSE - Adam Nasradam.nasrNo ratings yet
- Cell Types Activity WordDocument3 pagesCell Types Activity WordHailey ParkerNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology NotesDocument547 pagesO Level Biology NotesSsonko Edrine100% (1)
- Unit C-Chapter 8 PowerpointDocument66 pagesUnit C-Chapter 8 Powerpointm_frajman100% (1)
- Science 7 - Q2 - Week 1 2Document68 pagesScience 7 - Q2 - Week 1 2• S h ı m m y •No ratings yet
- MiriaasdDocument52 pagesMiriaasdCreatia PertokiaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document6 pagesLab 1Momina SajidNo ratings yet
- 1.2. The World of Cells-2Document20 pages1.2. The World of Cells-2Sin RithyvannNo ratings yet
- Topic 1-1 Introduction To CellsDocument50 pagesTopic 1-1 Introduction To CellsjeffNo ratings yet
- Cell Types GizmoDocument7 pagesCell Types GizmoNithya Majeti50% (2)
- Bacte Lab - Laboratory Act 1Document4 pagesBacte Lab - Laboratory Act 1Eloisa LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Zool 11 MidtermDocument83 pagesZool 11 Midtermishigamisenku574No ratings yet
- (07Q2W1) MicroscopeDocument44 pages(07Q2W1) MicroscopeAldwinC EspirituNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument2 pagesMicrosAishahNo ratings yet
- Bio For Olevel PDFDocument422 pagesBio For Olevel PDFNalweyiso JoyceNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Introduction To MicroscopesDocument26 pagesLecture 2-Introduction To MicroscopesThuto SmithNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document28 pagesLab 1yousifshli0No ratings yet
- Lab 2 Microscopy and Biological MolecDocument18 pagesLab 2 Microscopy and Biological MolecAndrew MartiniNo ratings yet
- Station 1: Introduction To The Microscope: Care Parts FocusingDocument105 pagesStation 1: Introduction To The Microscope: Care Parts FocusingCatherine Yati OoNo ratings yet
- I Sem Non Chordata PracticalsDocument90 pagesI Sem Non Chordata Practicalsrafiyana begumNo ratings yet
- Lab NotebookDocument28 pagesLab NotebookpepeNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell TheoryDocument13 pagesCell and Cell TheoryAnaJeanJumawidMaranan100% (1)
- Cell Structure and Function NotesDocument8 pagesCell Structure and Function NotesShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- G7 2ND Module 2Document24 pagesG7 2ND Module 2Hibi FortolazoNo ratings yet
- Lab Worksheet - Exercise 2 PDFDocument5 pagesLab Worksheet - Exercise 2 PDFmariammanutdNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument7 pagesCellsJeremiah CromartieNo ratings yet
- Brightfield Microscope Definition: Microscope. It Is An Optical Microscope That Uses Light Rays To Produce ADocument5 pagesBrightfield Microscope Definition: Microscope. It Is An Optical Microscope That Uses Light Rays To Produce AShahriar ShamimNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function - Magnification CalculationDocument17 pagesCell Structure and Function - Magnification CalculationHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1 - Mic102Document10 pagesLab Report 1 - Mic102Suhada IdayuNo ratings yet
- Bio Module 12Document45 pagesBio Module 12afeefaNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument4 pagesMicrosEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Lap-Report-1 1 DDDDocument13 pagesLap-Report-1 1 DDDapi-340425129No ratings yet
- Microscopy WorkdoneDocument3 pagesMicroscopy WorkdoneCabaron, Khen P.No ratings yet
- Exp 1 Making An Invisible World VisibleDocument13 pagesExp 1 Making An Invisible World VisibleAina HaravataNo ratings yet
- Lecture MicroscopeDocument3 pagesLecture MicroscopeAlex LimcangcoNo ratings yet
- Bio LabDocument3 pagesBio LabAnonymous 5cO5bCdNo ratings yet
- MD 2Y2-1B Laboratory Group 1 Week 1 Laboratory ActivityDocument5 pagesMD 2Y2-1B Laboratory Group 1 Week 1 Laboratory ActivityAlea LinksNo ratings yet
- Genzoo Lab ReviewerDocument12 pagesGenzoo Lab ReviewerJohanna Daffny MadayagNo ratings yet
- Science 6Document10 pagesScience 6Mary Stephanie AlbarracinNo ratings yet
- Microscope UseDocument7 pagesMicroscope UsebegNo ratings yet
- Cell Types SeDocument16 pagesCell Types SeKendallNo ratings yet
- Microscope IdDocument17 pagesMicroscope Idapi-110789702100% (1)
- Microscope BasicsDocument15 pagesMicroscope Basicschadling.jim23No ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell Types: Vocabulary: ATP, Bacteria, Carbon Dioxide (CODocument11 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell Types: Vocabulary: ATP, Bacteria, Carbon Dioxide (CODhruti AsharNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument29 pagesMicrosJohn Gabriel AriasNo ratings yet
- Grade 06 Civic Education 1st Term Test Paper With Answers 2019 Sinhala Medium North Western ProvinceDocument7 pagesGrade 06 Civic Education 1st Term Test Paper With Answers 2019 Sinhala Medium North Western ProvinceArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- 2023 Grade 10 English Literature 1st Term Test PaperDocument6 pages2023 Grade 10 English Literature 1st Term Test PaperArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- Grade 06 Catholicism 1st Term Test Paper With Answers 2019 Sinhala Medium North Western ProvinceDocument5 pagesGrade 06 Catholicism 1st Term Test Paper With Answers 2019 Sinhala Medium North Western ProvinceArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- Movers Class 2Document19 pagesMovers Class 2Arthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- Science 1st Lesson Unit PaperDocument5 pagesScience 1st Lesson Unit PaperArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- 59098ece d0d9 4843 b42f 96854dd82e3b Writing Part 1email WritingDocument1 page59098ece d0d9 4843 b42f 96854dd82e3b Writing Part 1email WritingArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- 2022 02 17 Fast FashionDocument9 pages2022 02 17 Fast FashionArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- The Sky's The Limit January 14, 2022Document2 pagesThe Sky's The Limit January 14, 2022Arthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- Kids Care About Polar BearsDocument2 pagesKids Care About Polar BearsArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- 8 Questions For Autumn PeltierDocument2 pages8 Questions For Autumn PeltierArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- Mapping Coral ReefsDocument1 pageMapping Coral ReefsArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- Be-Pdp-Fr-07-E Papso Form Roanoke To Sa - j7Document2 pagesBe-Pdp-Fr-07-E Papso Form Roanoke To Sa - j7Ricardo Frank CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Role of Agriculture in Indian EconomyDocument21 pagesRole of Agriculture in Indian EconomyAseem1100% (3)
- Nombre de La Actividad: Actividad Integradora 3: Be My GuestDocument6 pagesNombre de La Actividad: Actividad Integradora 3: Be My GuestAngel Mazahua LeónNo ratings yet
- Paramahansa Yogananda - A TributeDocument7 pagesParamahansa Yogananda - A TributeDr Srinivasan Nenmeli -KNo ratings yet
- Excitation of Plasmons and Interband Transitions by Electrons PDFDocument2 pagesExcitation of Plasmons and Interband Transitions by Electrons PDFRobNo ratings yet
- Shock AmbossDocument40 pagesShock AmbossAshraf AlbhlaNo ratings yet
- I. Work/Practice Exercise: Hussin, Shadimeer Reyes Bs Biology 2-CDocument3 pagesI. Work/Practice Exercise: Hussin, Shadimeer Reyes Bs Biology 2-CScar ShadowNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Fits and Tolerances:: - by William B MoringDocument14 pagesInterpreting Fits and Tolerances:: - by William B Moringwillmors31No ratings yet
- Power System Lab QuizDocument2 pagesPower System Lab QuizVipin KumarNo ratings yet
- 2017Document12 pages2017ਸੁਖਬੀਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਮਾਂਗਟNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan ExampleDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Exampleapi-357485951No ratings yet
- Excel Master Data On Is 456-2000 & Is 3370-1965Document24 pagesExcel Master Data On Is 456-2000 & Is 3370-1965Thirumalaichettiar Rangarajan100% (1)
- Outdoor Commander Series Evacuation Signals WGEC24/ WGES24Document4 pagesOutdoor Commander Series Evacuation Signals WGEC24/ WGES24osamamaeNo ratings yet
- TechnicalProposal 20130710B Rev0Document3 pagesTechnicalProposal 20130710B Rev0JomaargNo ratings yet
- Honeywell DPR 2300 and 3000Document338 pagesHoneywell DPR 2300 and 3000kmpoulosNo ratings yet
- GSEB Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 IndiaDocument19 pagesGSEB Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 IndiaKriti ShahNo ratings yet
- Robin Sanders DissertationDocument18 pagesRobin Sanders DissertationlineajonNo ratings yet
- Healing Sound - Contemporary Methods For Tibetan Singing BowlsDocument18 pagesHealing Sound - Contemporary Methods For Tibetan Singing Bowlsjaufrerudel0% (1)
- The AlchemistDocument57 pagesThe Alchemistok100% (1)
- We Need Transformation, Not False Transcendence by RICHARD ROHR "TheDocument3 pagesWe Need Transformation, Not False Transcendence by RICHARD ROHR "Thefriarmike6027100% (1)
- The Earth As A PlanetDocument5 pagesThe Earth As A PlanetEgzon DalipiNo ratings yet
- Oh! To Be Like Thee: WORDS: Thomas O. Chisholm, Pub.1897. MUSIC: William J. Kirkpatrick, 1897. Public DomainDocument1 pageOh! To Be Like Thee: WORDS: Thomas O. Chisholm, Pub.1897. MUSIC: William J. Kirkpatrick, 1897. Public DomainAlonge EmmanuelNo ratings yet
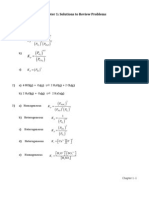
- Chapter 1 Solutions DetailedDocument30 pagesChapter 1 Solutions DetailedYeonjae JeongNo ratings yet
- Reliable and Cost-Effective Sump Pumping With Sulzer's EjectorDocument2 pagesReliable and Cost-Effective Sump Pumping With Sulzer's EjectorDavid Bottassi PariserNo ratings yet
- Pelatiham Pembuatan Minyak Kelapa Murni (Virgin Coconut Oil) Menggunakan Permentasi Ragi TempeDocument6 pagesPelatiham Pembuatan Minyak Kelapa Murni (Virgin Coconut Oil) Menggunakan Permentasi Ragi TempeProduksi Kelas ANo ratings yet
- Prinsipal Kode Produk Nama ProdukDocument40 pagesPrinsipal Kode Produk Nama ProdukjihanvrpNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Systems in Biology - Neville H. FletcherDocument348 pagesAcoustic Systems in Biology - Neville H. FletcherJosue PazNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument301 pagesPDFEddy TriyonoNo ratings yet
- The Power of A Praying Nation - Stormie Omartian (Naijasermons - Com.ng)Document126 pagesThe Power of A Praying Nation - Stormie Omartian (Naijasermons - Com.ng)joey1074No ratings yet
The Characteristics of Living Things
The Characteristics of Living Things
Uploaded by
Arthanayaka NandikaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Characteristics of Living Things
The Characteristics of Living Things
Uploaded by
Arthanayaka NandikaCopyright:
Available Formats
🌿
The Characteristics of Living
Things
What is called the characteristic of living things?
A feature that could be used to decide whether something was living or not is
called The Characteristic of Living Things
There are eight characteristics of living things. An object must possess all
eight
characteristics to be considered living. If an organism possesses seven out
of the eight characteristics, it is not a Living thing. What are those eight
features?
They
grow
move
reproduce
react to surroundings
excrete
obtain nutrition
respire
The Characteristics of Living Things 1
are cellular
All living organisms are composed of cells and the substances they
produce.
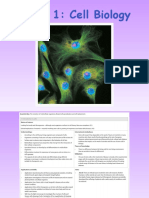
The following image contains cells from animals, plants, fungi, and bacteria:
Biologists study objects that vary enormously in size. It is partly because
of this that biologists use a number of different techniques and instruments
to examine organisms. What are the instruments that we can you to examine
organisms?
Naked Eye
Light Microscope
Electron Microscope
Magnifying Glass
How does a tree view the Naked eye and the other instruments?
📌Naked Eye - The whole organism
The Characteristics of Living Things 2
📌Magnifying Glass - A flower
📌Light Microscope - Cells inside the flower
📌Electron Microscope - Starch granules inside the plant’s cell
Hook’s Microscope
In 1665, Robert Hooke used a primitive light microscope to examine thin
slices of cork taken from the bark of an oak tree.
The cork (which was dead) was made up of small regions that he called
cells as they resembled the rooms, or cells, occupied by monks in
monasteries.
It has since been discovered that all living organisms are made up of
cells.
Cells vary in shape and size. The structure of a cell determines its function.
The sperm cell has a tail so that it can swim quickly through the water
The Characteristics of Living Things 3
The fat cell has a very large compartment that it uses to store fat.
The nerve cell is very long so it can carry signals over great distances.
The potato cell contains compartments for storing starch
The Characteristics of Living Things 4
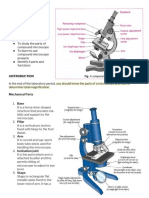
Parts of a Light Microscope
1. Eyepiece: The eyepiece magnifies the image. By using lenses in both the
eyepiece and the objective, the microscope magnifies images to over 100
times their normal size.
2. Coarse focus: The coarse focus moves the lenses to bring the object into
focus.
3. Fine focus: To get the perfect image, use the fine focus to make very small
adjustments to the focus of the microscope.
4. Arm: The arm is the best place to pick up the microscope if you need to lift
it.
5. Mirror: The mirror directs light from the light source onto the specimen.
6. Iris diaphragm: The iris diaphragm is used to control how much light goes
from the light source to the specimen.
7. Condenser: The condenser focuses the light from the light source onto the
specimen.
8. Stage: The specimen is placed on the stage so that it can be observed. With
this type of microscope, the specimen is always placed on a piece of glass
called a microscope slide.
9. Stage clip: The stage clip holds the specimen in position.
10. High power objective: Use a high power objective lens when you want to
magnify an object as much as possible.
11. Low power objective: Use a low power objective lens when searching for
your specimen or want to use less magnification than the high power
objective.
The Characteristics of Living Things 5
What is called Magnification?
Magnification is how much larger an object appears compared to its real
size.
If an object is magnified by a factor of five (x5), it will appear five times
as large as its real size.
How to calculate the magnification of a microscope?
The Characteristics of Living Things 6
Light from the specimen passes through two lenses before it reaches your
eye: the objective lens and the eyepiece.
Each lens has a magnification factor. For example, the eyepiece has a
magnification factor of x10 and the objective lens has a magnification
of x40.
If you used the eyepiece on its own, the specimen would appear ten
times as large as its real size.
If you used the objective lens on its own, the specimen would appear
forty times as large as its real size.
The total magnification of the microscope is equal to the magnification
of the eyepiece multiplied by the magnification of the objective. Total
magnification = 10 x 40.
Therefore, the total magnification of the microscope is 400 times. In
other words, a one-centimetre tall object would appear to be 4 metres
tall through this microscope (if the whole object could be viewed at once).
Field of view
If an image under a light microscope has a magnification of x 300 this
means the image viewed by the person is 300 times the object's
The Characteristics of Living Things 7
original size.
The area that you see when looking down a microscope is the field of
view.
The simplest way to determine the diameter of the field of view for a
particular magnification is by placing a ruler on the stage.
Magnifying your field of view
As magnification increases the diameter of the field of view decreases.
In the diagram below the field of view is 3.2 mm wide when the magnification is x
40. The field of view is only 1.3mm wide when the magnification is x 100.
What are the things you should know to calculate the diameter of the field
of view?
the magnification of the field of view that you are interested in -
magnification (new);
the size of the field of view at another magnification - field of view (old),
and;
the other magnification (magnification - old).
The formula for calculating the diameter of the field of view?
field of view (new) = field of view (old) x magnification (old) / magnification (new)
Determining the size of a magnified object: What is the actual size of an
object we are looking at in a picture taken using a microscope?
The size of an object in a magnified picture must be determined
mathematically.
To do this calculation you need to know:
the size of the object in the picture
the magnification of the picture
The formula for determining the size of a magnified object
The Characteristics of Living Things 8
size (actual) = size (image) / magnification
What is the quote we use to quote the size of a cell?
micrometre.
A micrometre (µm) is one-millionth of a meter.
The size of cells varies within the same organism and between organisms.
The human cheek cell and leaf cells have lengths of 56mm and 90mm
respectively. Plant cells tend to be larger than animal cells.
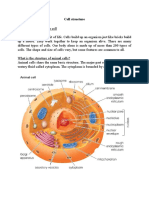
A typical animal cell
The diagram below shown a typical animal cell.
With a light microscope, you can see several structures inside the cell.
The Nucleus
Very few living cells do not possess a nucleus, although a nucleus has an
important role to play in the cell.
https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/secure.notion-static.com/13a8d43d
-f4da-4550-9904-f51d89053629/the_nucleus.mp4
The cell membrane
The cell membrane is very good at absorbing substances from outside
and retaining them in the cell. These useful substances are kept inside
The Characteristics of Living Things 9
the cell by the membrane. Some substances are able to pass freely
through the cell membrane such as water.
The membrane has special channels so that these substances can enter
the cell.
The cell membrane is very good at removing harmful substances or
blocking their entry into the cell.
The membrane has special channels so that these harmful substances
can leave the cell.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the name given to everything in the cell apart from the
nucleus and the cell membrane.
It is within the cytoplasm that most of the cell’s chemical reactions occur.
Most of the cytoplasm is a “jelly-like” substance.
Many important reactions take place in this “jelly-like” substance.
There are also numerous small structures called organelles that carry out
specific functions.
Mitochondria
Most organelles are too small to be seen with a light microscope but one
organelle called mitochondria can be seen with a very high-powered light
microscope.
Mitochondria are often referred to as the “powerhouse” of the cell as they
undergo a chemical process called aerobic respiration producing most of
a cell’s energy.
The Characteristics of Living Things 10
https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/secure.notion-static.com/b140d5d4
-ad05-491d-a882-f62ded300cef/the_mitochondrion.mp4
Structure and function of animal cells
Animal cells are very enormously in shape, size and function but they all
have the same basic components.
The Characteristics of Living Things 11
You might also like
- Cell Types SE GizmosDocument13 pagesCell Types SE Gizmosalex79% (14)
- Chapter 1 BC SC Probe 8Document36 pagesChapter 1 BC SC Probe 8api-265180883No ratings yet
- Oracle Utilities Meter Data Management Features and Functions Overview 388664Document39 pagesOracle Utilities Meter Data Management Features and Functions Overview 388664Mohammed Safwat100% (4)
- S.1 Bio Notes PDFDocument57 pagesS.1 Bio Notes PDFkitderoger_391648570100% (4)
- The Microscope and Its Use: Lab ReportDocument4 pagesThe Microscope and Its Use: Lab ReportArbab GillNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Cells Seen Under The MicroscopeDocument5 pagesLab Report Cells Seen Under The Microscopeorlandoe2560% (1)
- Biology Lab PracticalomgomgDocument215 pagesBiology Lab PracticalomgomgdNo ratings yet
- s.1 Biology Notes NewDocument52 pagess.1 Biology Notes NewTUMUSIIME INNOCENTNo ratings yet
- Biology BookDocument397 pagesBiology Bookmesh100% (1)
- General Biology Laboratory ModuleDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology Laboratory ModuleEunice Moureen MaravillaNo ratings yet
- MICROSDocument2 pagesMICROSharlyNo ratings yet
- sw8 chp04Document23 pagessw8 chp04api-115560904No ratings yet
- Medical Biology Lab Manual Lab - 1-Dr. Raz NawzadDocument15 pagesMedical Biology Lab Manual Lab - 1-Dr. Raz NawzadLa NiaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 MicrosDocument15 pagesLab 2 Microsjohn NisNo ratings yet
- Grade 8-CellTypesSE - Adam NasrDocument10 pagesGrade 8-CellTypesSE - Adam Nasradam.nasrNo ratings yet
- Cell Types Activity WordDocument3 pagesCell Types Activity WordHailey ParkerNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology NotesDocument547 pagesO Level Biology NotesSsonko Edrine100% (1)
- Unit C-Chapter 8 PowerpointDocument66 pagesUnit C-Chapter 8 Powerpointm_frajman100% (1)
- Science 7 - Q2 - Week 1 2Document68 pagesScience 7 - Q2 - Week 1 2• S h ı m m y •No ratings yet
- MiriaasdDocument52 pagesMiriaasdCreatia PertokiaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document6 pagesLab 1Momina SajidNo ratings yet
- 1.2. The World of Cells-2Document20 pages1.2. The World of Cells-2Sin RithyvannNo ratings yet
- Topic 1-1 Introduction To CellsDocument50 pagesTopic 1-1 Introduction To CellsjeffNo ratings yet
- Cell Types GizmoDocument7 pagesCell Types GizmoNithya Majeti50% (2)
- Bacte Lab - Laboratory Act 1Document4 pagesBacte Lab - Laboratory Act 1Eloisa LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Zool 11 MidtermDocument83 pagesZool 11 Midtermishigamisenku574No ratings yet
- (07Q2W1) MicroscopeDocument44 pages(07Q2W1) MicroscopeAldwinC EspirituNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument2 pagesMicrosAishahNo ratings yet
- Bio For Olevel PDFDocument422 pagesBio For Olevel PDFNalweyiso JoyceNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Introduction To MicroscopesDocument26 pagesLecture 2-Introduction To MicroscopesThuto SmithNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document28 pagesLab 1yousifshli0No ratings yet
- Lab 2 Microscopy and Biological MolecDocument18 pagesLab 2 Microscopy and Biological MolecAndrew MartiniNo ratings yet
- Station 1: Introduction To The Microscope: Care Parts FocusingDocument105 pagesStation 1: Introduction To The Microscope: Care Parts FocusingCatherine Yati OoNo ratings yet
- I Sem Non Chordata PracticalsDocument90 pagesI Sem Non Chordata Practicalsrafiyana begumNo ratings yet
- Lab NotebookDocument28 pagesLab NotebookpepeNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell TheoryDocument13 pagesCell and Cell TheoryAnaJeanJumawidMaranan100% (1)
- Cell Structure and Function NotesDocument8 pagesCell Structure and Function NotesShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- G7 2ND Module 2Document24 pagesG7 2ND Module 2Hibi FortolazoNo ratings yet
- Lab Worksheet - Exercise 2 PDFDocument5 pagesLab Worksheet - Exercise 2 PDFmariammanutdNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument7 pagesCellsJeremiah CromartieNo ratings yet
- Brightfield Microscope Definition: Microscope. It Is An Optical Microscope That Uses Light Rays To Produce ADocument5 pagesBrightfield Microscope Definition: Microscope. It Is An Optical Microscope That Uses Light Rays To Produce AShahriar ShamimNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function - Magnification CalculationDocument17 pagesCell Structure and Function - Magnification CalculationHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1 - Mic102Document10 pagesLab Report 1 - Mic102Suhada IdayuNo ratings yet
- Bio Module 12Document45 pagesBio Module 12afeefaNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument4 pagesMicrosEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Lap-Report-1 1 DDDDocument13 pagesLap-Report-1 1 DDDapi-340425129No ratings yet
- Microscopy WorkdoneDocument3 pagesMicroscopy WorkdoneCabaron, Khen P.No ratings yet
- Exp 1 Making An Invisible World VisibleDocument13 pagesExp 1 Making An Invisible World VisibleAina HaravataNo ratings yet
- Lecture MicroscopeDocument3 pagesLecture MicroscopeAlex LimcangcoNo ratings yet
- Bio LabDocument3 pagesBio LabAnonymous 5cO5bCdNo ratings yet
- MD 2Y2-1B Laboratory Group 1 Week 1 Laboratory ActivityDocument5 pagesMD 2Y2-1B Laboratory Group 1 Week 1 Laboratory ActivityAlea LinksNo ratings yet
- Genzoo Lab ReviewerDocument12 pagesGenzoo Lab ReviewerJohanna Daffny MadayagNo ratings yet
- Science 6Document10 pagesScience 6Mary Stephanie AlbarracinNo ratings yet
- Microscope UseDocument7 pagesMicroscope UsebegNo ratings yet
- Cell Types SeDocument16 pagesCell Types SeKendallNo ratings yet
- Microscope IdDocument17 pagesMicroscope Idapi-110789702100% (1)
- Microscope BasicsDocument15 pagesMicroscope Basicschadling.jim23No ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell Types: Vocabulary: ATP, Bacteria, Carbon Dioxide (CODocument11 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell Types: Vocabulary: ATP, Bacteria, Carbon Dioxide (CODhruti AsharNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument29 pagesMicrosJohn Gabriel AriasNo ratings yet
- Grade 06 Civic Education 1st Term Test Paper With Answers 2019 Sinhala Medium North Western ProvinceDocument7 pagesGrade 06 Civic Education 1st Term Test Paper With Answers 2019 Sinhala Medium North Western ProvinceArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- 2023 Grade 10 English Literature 1st Term Test PaperDocument6 pages2023 Grade 10 English Literature 1st Term Test PaperArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- Grade 06 Catholicism 1st Term Test Paper With Answers 2019 Sinhala Medium North Western ProvinceDocument5 pagesGrade 06 Catholicism 1st Term Test Paper With Answers 2019 Sinhala Medium North Western ProvinceArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- Movers Class 2Document19 pagesMovers Class 2Arthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- Science 1st Lesson Unit PaperDocument5 pagesScience 1st Lesson Unit PaperArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- 59098ece d0d9 4843 b42f 96854dd82e3b Writing Part 1email WritingDocument1 page59098ece d0d9 4843 b42f 96854dd82e3b Writing Part 1email WritingArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- 2022 02 17 Fast FashionDocument9 pages2022 02 17 Fast FashionArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- The Sky's The Limit January 14, 2022Document2 pagesThe Sky's The Limit January 14, 2022Arthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- Kids Care About Polar BearsDocument2 pagesKids Care About Polar BearsArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- 8 Questions For Autumn PeltierDocument2 pages8 Questions For Autumn PeltierArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- Mapping Coral ReefsDocument1 pageMapping Coral ReefsArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- Be-Pdp-Fr-07-E Papso Form Roanoke To Sa - j7Document2 pagesBe-Pdp-Fr-07-E Papso Form Roanoke To Sa - j7Ricardo Frank CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Role of Agriculture in Indian EconomyDocument21 pagesRole of Agriculture in Indian EconomyAseem1100% (3)
- Nombre de La Actividad: Actividad Integradora 3: Be My GuestDocument6 pagesNombre de La Actividad: Actividad Integradora 3: Be My GuestAngel Mazahua LeónNo ratings yet
- Paramahansa Yogananda - A TributeDocument7 pagesParamahansa Yogananda - A TributeDr Srinivasan Nenmeli -KNo ratings yet
- Excitation of Plasmons and Interband Transitions by Electrons PDFDocument2 pagesExcitation of Plasmons and Interband Transitions by Electrons PDFRobNo ratings yet
- Shock AmbossDocument40 pagesShock AmbossAshraf AlbhlaNo ratings yet
- I. Work/Practice Exercise: Hussin, Shadimeer Reyes Bs Biology 2-CDocument3 pagesI. Work/Practice Exercise: Hussin, Shadimeer Reyes Bs Biology 2-CScar ShadowNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Fits and Tolerances:: - by William B MoringDocument14 pagesInterpreting Fits and Tolerances:: - by William B Moringwillmors31No ratings yet
- Power System Lab QuizDocument2 pagesPower System Lab QuizVipin KumarNo ratings yet
- 2017Document12 pages2017ਸੁਖਬੀਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਮਾਂਗਟNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan ExampleDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Exampleapi-357485951No ratings yet
- Excel Master Data On Is 456-2000 & Is 3370-1965Document24 pagesExcel Master Data On Is 456-2000 & Is 3370-1965Thirumalaichettiar Rangarajan100% (1)
- Outdoor Commander Series Evacuation Signals WGEC24/ WGES24Document4 pagesOutdoor Commander Series Evacuation Signals WGEC24/ WGES24osamamaeNo ratings yet
- TechnicalProposal 20130710B Rev0Document3 pagesTechnicalProposal 20130710B Rev0JomaargNo ratings yet
- Honeywell DPR 2300 and 3000Document338 pagesHoneywell DPR 2300 and 3000kmpoulosNo ratings yet
- GSEB Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 IndiaDocument19 pagesGSEB Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 IndiaKriti ShahNo ratings yet
- Robin Sanders DissertationDocument18 pagesRobin Sanders DissertationlineajonNo ratings yet
- Healing Sound - Contemporary Methods For Tibetan Singing BowlsDocument18 pagesHealing Sound - Contemporary Methods For Tibetan Singing Bowlsjaufrerudel0% (1)
- The AlchemistDocument57 pagesThe Alchemistok100% (1)
- We Need Transformation, Not False Transcendence by RICHARD ROHR "TheDocument3 pagesWe Need Transformation, Not False Transcendence by RICHARD ROHR "Thefriarmike6027100% (1)
- The Earth As A PlanetDocument5 pagesThe Earth As A PlanetEgzon DalipiNo ratings yet
- Oh! To Be Like Thee: WORDS: Thomas O. Chisholm, Pub.1897. MUSIC: William J. Kirkpatrick, 1897. Public DomainDocument1 pageOh! To Be Like Thee: WORDS: Thomas O. Chisholm, Pub.1897. MUSIC: William J. Kirkpatrick, 1897. Public DomainAlonge EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Solutions DetailedDocument30 pagesChapter 1 Solutions DetailedYeonjae JeongNo ratings yet
- Reliable and Cost-Effective Sump Pumping With Sulzer's EjectorDocument2 pagesReliable and Cost-Effective Sump Pumping With Sulzer's EjectorDavid Bottassi PariserNo ratings yet
- Pelatiham Pembuatan Minyak Kelapa Murni (Virgin Coconut Oil) Menggunakan Permentasi Ragi TempeDocument6 pagesPelatiham Pembuatan Minyak Kelapa Murni (Virgin Coconut Oil) Menggunakan Permentasi Ragi TempeProduksi Kelas ANo ratings yet
- Prinsipal Kode Produk Nama ProdukDocument40 pagesPrinsipal Kode Produk Nama ProdukjihanvrpNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Systems in Biology - Neville H. FletcherDocument348 pagesAcoustic Systems in Biology - Neville H. FletcherJosue PazNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument301 pagesPDFEddy TriyonoNo ratings yet
- The Power of A Praying Nation - Stormie Omartian (Naijasermons - Com.ng)Document126 pagesThe Power of A Praying Nation - Stormie Omartian (Naijasermons - Com.ng)joey1074No ratings yet