Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How To Calculate Bundle Diameter
How To Calculate Bundle Diameter
Uploaded by
YADEENDHIRAN SOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How To Calculate Bundle Diameter
How To Calculate Bundle Diameter
Uploaded by
YADEENDHIRAN SCopyright:
Available Formats
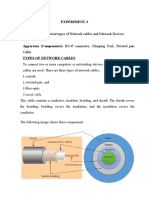
1.
How to calculate bundle diameter
-Calculate the total cross-sectional area including wire diameter, sleeves, spacing between cables
-Divide the total cross-sectional area by π (pi) (3.141)
2. What type of support you use to route harness
Tapes, cable tie, customized brackets, snaps, coming to cad we use dummy supports or points for routing.
3. Difference between electrical schematics and synoptic
Schematic contains complete electrical wire diagram
A synoptic diagram is typically used to provide a high-level view of a system, highlighting key components and
their connections, and allowing engineers and technicians to quickly understand the overall structure and
operation of the system.
4. What are situations of EMF, EMI, EMC & its remedies?
Electromagnetic field, electromagnetic interference, electromagnetic compatibility, to avoid such errors we
maintain segregation distance, we use sleeves and separates in ducts.
5. What are general requirement of harness.
Load, purpose, area,
6. Drip Loop
In external environment electrical component where exposed to moisture, to avoid well be using U bend, that u
bend is called Drip Loop
7. Difference between Earthing, Bonding and Grounding
Earthing – component external surface to ground surface
Bounding- components to body frame
Ground – natural wire to ground
8. What is slack
Slack is the extra length for the wire been installed, this slack helps for free movement of the component without
putting stress on the wire.
9. What is the difference between Global Slack and Local Slack
A. Global slack will be applicable for entire harness,
B. Local slack is applicable for one fixation to another where ever we need extra length we can use it.
10. Bend Radius Ratio.
A. We have to maintain 4 times of the dia of the cable for power cables
And 10 times of the dia of the fiber cables.
11. Types of sleeves
Heat shrink sleeves:
Expandable braided sleeves:
Non-split braided sleeves:
PVC Sleeves
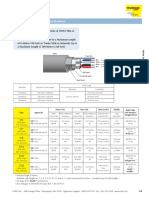
12. What are the class of cables
Class 1: This class of cables are intended for use in low voltage electrical systems, typically rated for less than 50
volts. They are used for lighting, control, and power circuits.
Class 2: This class of cables are also intended for use in low voltage electrical systems, typically rated for less than
50 volts, but are designed to meet more stringent safety requirements than Class 1 cables. They are used in
electronic equipment and communication systems.
Class 3: This class of cables are designed for use in high voltage electrical systems, typically rated for more than
50 volts. They are used in power generation, transmission, and distribution systems.
13. How can you arrest the harness
Cable trays, harness clamps, cable ties, Taping or wrapping, Clamping, Housings or enclosures.
14. How to start Routing Parameters and considerations during Routing the harness
Path planning,
Length of the harness with slack,
Bend radius,
Environmental condition, temperature, humidity, vibration,
Termination points:
15. What are the parameters you need to consider while selecting the connectors and types of connectors?
Consider the voltage and current ratings, resistance,
Environmental condition, temperature, humidity, vibration,(IP value)
Mounting method, the size and shape, and the required strength,
Consider the cost of the connector
Ease of installation & Ease of maintenance
Types of connector:
Circular, rectangular, modular connectors
16. How do you classify the size of cables?
American Wire Gauge (AWG): The American Wire Gauge is a standardized system that is commonly used in the
United States and other countries. It uses a numbering system to indicate the size of a cable, with lower numbers
indicating smaller cables and higher numbers indicating larger cables.
17. How do you select the conduit process?
High levels of moisture, heat, or vibration,
It will not be damaged during installation or operation.
Cost of materials, installation, and maintenance.
You might also like
- Wiring Harness QuestionsDocument3 pagesWiring Harness QuestionsSAN ENGINEERING100% (2)
- Installation and Estimation of Electrical LoadDocument59 pagesInstallation and Estimation of Electrical LoadShanmuka Sreenivas88% (8)
- Electronic System Design - ESD SyllabusDocument3 pagesElectronic System Design - ESD SyllabusAnoop MathewNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Eim 10Document17 pagesLesson 1 Eim 10stfup zeliaNo ratings yet
- Finals Module 1 2 Avt 4232Document54 pagesFinals Module 1 2 Avt 4232angeloNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Cables Questions & AnswersDocument7 pagesInstrumentation Cables Questions & AnswersJêmš NavikNo ratings yet
- Plate 7.1 WIRING METHOD PRACTICE ANGADocument13 pagesPlate 7.1 WIRING METHOD PRACTICE ANGAjason.angaNo ratings yet
- TLE 10 EPAS Week3Document6 pagesTLE 10 EPAS Week3Sittie Fahieda Aloyodan100% (2)
- Design of Wiring Lay-Out For A Residence and Estimate The Quantity of Materials Post - Lab QuestionsDocument3 pagesDesign of Wiring Lay-Out For A Residence and Estimate The Quantity of Materials Post - Lab QuestionsAswathy remeshNo ratings yet
- Power Cable SystemsDocument35 pagesPower Cable SystemsMohd Muzani100% (1)
- Fiber Optic Cable and Connector Selection: 1. Define Environmental RequirementsDocument5 pagesFiber Optic Cable and Connector Selection: 1. Define Environmental RequirementsRyan ZamoraNo ratings yet
- IPD and Illumination - 9 1Document14 pagesIPD and Illumination - 9 1Milan AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Cable and Connector Selection: 1. Define Environmental RequirementsDocument5 pagesFiber Optic Cable and Connector Selection: 1. Define Environmental RequirementshugoflgNo ratings yet
- Activity Performance Worksheet: Computer TechnologyDocument13 pagesActivity Performance Worksheet: Computer TechnologyJefferson CanalejaNo ratings yet
- 5 Key Factors To The Correct Cable Selection and ApplicationDocument7 pages5 Key Factors To The Correct Cable Selection and ApplicationSugeng SumarnoNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument4 pagesScriptj4240300No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document39 pagesChapter 3broNo ratings yet
- T & D Unit 3 & Unit 4 Question BankDocument3 pagesT & D Unit 3 & Unit 4 Question BankJungkookNo ratings yet
- Emi AND EmcDocument7 pagesEmi AND Emcmanojkumar9No ratings yet
- 220kV-400Kv-345KV Details of CableDocument26 pages220kV-400Kv-345KV Details of CableDhanaji Wakade100% (1)
- IS CableDocument4 pagesIS Cablewipi12No ratings yet
- Ug Fault PaperDocument13 pagesUg Fault PaperHarikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ex. No.3Document11 pagesEx. No.3MAYANKNo ratings yet
- Unwadike Emmanuel Project 333Document56 pagesUnwadike Emmanuel Project 333NjitnumNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument48 pagesBasic Electrical Engineeringjai prakashNo ratings yet
- Power CableDocument4 pagesPower CableHandNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document13 pagesLab 3nomanmasud94No ratings yet
- Introduction of CablesDocument14 pagesIntroduction of CablesRanganath SriNo ratings yet
- Electrical Cable Size Chart Amps UkDocument3 pagesElectrical Cable Size Chart Amps UknyroochillersNo ratings yet
- Design Report XXXDocument41 pagesDesign Report XXXashikin100% (1)
- Environmental Noise DisturbersDocument6 pagesEnvironmental Noise DisturbersjeswinchNo ratings yet
- Fiber Kinks and Breaks: Fiber Optic Testing - OTDRDocument5 pagesFiber Kinks and Breaks: Fiber Optic Testing - OTDRPedroNo ratings yet
- Aerial Fiber Optic Cable OverviewDocument7 pagesAerial Fiber Optic Cable OverviewSted KingNo ratings yet
- For Single Phase: Arr Marn Electric Engineering Group Co-Founder - Wai.N.Htun)Document55 pagesFor Single Phase: Arr Marn Electric Engineering Group Co-Founder - Wai.N.Htun)Aung Thein OoNo ratings yet
- Necesidades Par Colocar Varios DS18B20 Sensores Sobre Un Mismo CableDocument18 pagesNecesidades Par Colocar Varios DS18B20 Sensores Sobre Un Mismo CableRo VictorNo ratings yet
- Bee Unit 5Document50 pagesBee Unit 5DOMAKONDA NEHA SE(H)2019No ratings yet
- Module 6 TelecomDocument29 pagesModule 6 TelecomMADRIAGA, CYRILLE MAE RUMANo ratings yet
- Installation and Estimation of Electrical Load PDFDocument59 pagesInstallation and Estimation of Electrical Load PDFMohd AliNo ratings yet
- Electric LoadDocument58 pagesElectric LoadShanmuka SreenivasNo ratings yet
- Bus Bar Sizing Calculation For SubstatioDocument11 pagesBus Bar Sizing Calculation For SubstatioMuhammad AdeelNo ratings yet
- Cable SelectionDocument8 pagesCable SelectionaramirezbenitesNo ratings yet
- WWW Telebyteusa Com Primer Ch3Document8 pagesWWW Telebyteusa Com Primer Ch3159753ADANANo ratings yet
- Cable Fault DETECTORDocument5 pagesCable Fault DETECTORunluckyguyNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Domesting Wiring: Commencement of Supply or Consumer Terminals. From The Consumer Terminal Onwards, TheDocument39 pagesUnit-5 Domesting Wiring: Commencement of Supply or Consumer Terminals. From The Consumer Terminal Onwards, TheADITYA GEHLAWATNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering: Riphah International University, Islamabad, PakistanDocument6 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering: Riphah International University, Islamabad, PakistanBaqir HussainNo ratings yet
- Electrical InstallationDocument27 pagesElectrical Installationjodge18No ratings yet
- Cable CrimpingDocument12 pagesCable CrimpingSuresh RamNo ratings yet
- Wire Crimping PreperationDocument17 pagesWire Crimping PreperationJuanPabloJimenez100% (1)
- Ravi UltracabDocument7 pagesRavi UltracabRavi PatelNo ratings yet
- Boat ElectricsDocument34 pagesBoat ElectricsSquinkle100% (1)
- Electrical SafetyDocument26 pagesElectrical SafetyBolo TransportNo ratings yet
- Alumimium Bus Bar Calculation 4000ADocument11 pagesAlumimium Bus Bar Calculation 4000Aivan(D3)No ratings yet
- Lecture 34 Installations Tu 1440Document37 pagesLecture 34 Installations Tu 1440Andy LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Underground CablesDocument185 pagesUnderground Cablesmkpq100% (1)
- Cables SelectionDocument17 pagesCables SelectionKhaldoon Alnashi100% (1)
- 1 Wire App-NoteDocument36 pages1 Wire App-NotehuynhkhoaNo ratings yet
- Sem 6 Uni Slution EITDocument8 pagesSem 6 Uni Slution EITshahbaz khanNo ratings yet
- Bus Duct PPT - 27.07.20Document36 pagesBus Duct PPT - 27.07.20aslam shaikh100% (1)
- Lab 1 CCNDocument4 pagesLab 1 CCNAbdul AhadNo ratings yet
- BS en ISO 14344-2005 Welding and Allied Processes. Flux and Gas Shielded Electrical Welding ProcesseDocument18 pagesBS en ISO 14344-2005 Welding and Allied Processes. Flux and Gas Shielded Electrical Welding Processecirieh100% (3)
- Earth Wire Tension AssemblyDocument12 pagesEarth Wire Tension AssemblyaselabollegalaNo ratings yet
- Manuli Hose Catalog PDFDocument86 pagesManuli Hose Catalog PDFaldino020203100% (1)
- Phoenix Z10167Document2 pagesPhoenix Z10167Mohamed Sherif S MNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Sections of ASME B30.9 Standard: Alloy Steel Chain SlingsDocument2 pagesInterpretation of Sections of ASME B30.9 Standard: Alloy Steel Chain Slingsscofiel1No ratings yet
- DeviceNet™, Thin Cable SpecificationsDocument3 pagesDeviceNet™, Thin Cable SpecificationsIsraelNo ratings yet
- Macrame Bangle BraceletDocument6 pagesMacrame Bangle Braceletmahira_tippu100% (1)
- Dam Gate Maintenance BookDocument99 pagesDam Gate Maintenance BookDnyanesh Bodre100% (3)
- Borates in Wire Drawing: Technical BulletinDocument4 pagesBorates in Wire Drawing: Technical BulletinNguyen Thanh TrungNo ratings yet
- PWHT ProcedureDocument9 pagesPWHT ProcedureM. R. Shahnawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- AP 08 Ps em 04 Q A Metals and Non MetalsDocument3 pagesAP 08 Ps em 04 Q A Metals and Non Metalslakkysep16No ratings yet
- BSR Electrical 2017Document37 pagesBSR Electrical 2017sunmayu100% (2)
- DVB-S, S2 HD, SD Decoder User Manual PDFDocument44 pagesDVB-S, S2 HD, SD Decoder User Manual PDFJarvin AcendraNo ratings yet
- Project Based Multimedia BTLED IA 3ADocument22 pagesProject Based Multimedia BTLED IA 3AJoevan VillaflorNo ratings yet
- 4.3.10 - Astm F366-10 2011Document4 pages4.3.10 - Astm F366-10 2011Emílio DechenNo ratings yet
- ISP M2000 Head ManualDocument27 pagesISP M2000 Head ManualArezkiNo ratings yet
- CCableDocument13 pagesCCablevimal alaberahNo ratings yet
- 42,0410,2115Document52 pages42,0410,2115David Aguirre BurneoNo ratings yet
- Excel Control Systems C-2, Site-1, Panki Industrial Area, Kanpur - 208022 (U.P.)Document2,290 pagesExcel Control Systems C-2, Site-1, Panki Industrial Area, Kanpur - 208022 (U.P.)Amit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ashoka Enterprises (India) : POLYCAB WIRES PVT. LTD. - LIST PRICE NO-05/2020-21 Effective 15TH DEC-2020Document1 pageAshoka Enterprises (India) : POLYCAB WIRES PVT. LTD. - LIST PRICE NO-05/2020-21 Effective 15TH DEC-2020Shakthi RamNo ratings yet
- 2019 AWRF WRSLGDocument24 pages2019 AWRF WRSLGElias JarjouraNo ratings yet
- Steel Wire Patenting ProcessDocument3 pagesSteel Wire Patenting Processsmallik3No ratings yet
- Anillos Triples DutchesofwireAdjustableBeadRingDocument5 pagesAnillos Triples DutchesofwireAdjustableBeadRingJesus Antonio Ortega Peña100% (2)
- Prysmian BS5467HDocument9 pagesPrysmian BS5467HBen CheungNo ratings yet
- Liste de Normes Site WebDocument11 pagesListe de Normes Site WebKaother GhilenNo ratings yet
- Cee Section PropertiesDocument7 pagesCee Section PropertiessteelfaceNo ratings yet
- Ewp I PracticalDocument2 pagesEwp I Practicalkumar.suren84No ratings yet
- RE 2Y (ST) HDocument24 pagesRE 2Y (ST) HmritsoudisNo ratings yet
- Alicates LunoDocument7 pagesAlicates LunoJulio PaniuraNo ratings yet