Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Industrial Electronics N3 QP Nov 2018
Industrial Electronics N3 QP Nov 2018
Uploaded by
neomogori9Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Industrial Electronics N3 QP Nov 2018
Industrial Electronics N3 QP Nov 2018
Uploaded by
neomogori9Copyright:
Available Formats
T770(E)(N30)T
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE
INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS N3
(8080613)
30 November 2018 (X-Paper)
09:00–12:00
Calculators may be used.
This question paper consists of 7 pages and 1 formula sheet.
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(8080613) -2- T770(E)(N30)T
DEPARTMENT OF HIGHER EDUCATION AND TRAINING
REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE
INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS N3
TIME: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Read ALL the questions carefully.
3. Number the answers according to the numbering system used in this question
paper.
4. ALL calculations must be shown.
5. ALL the final answers must be approximated accurately to THREE decimal
places.
6. Subsections of questions must be kept together.
7. Use π = 3,142.
8. Write neatly and legibly.
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(8080613) -3- T770(E)(N30)T
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Choose the
answer and write only 'true' or 'false' next to the question number
(1.1.1–1.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.1.1 Resonance can be produced in an R–C circuit.
1.1.2 The nucleus of an atom consists of neutrons and electrons.
1.1.3 A strain gauge transducer can be divided into PTC and NTC
materials.
1.1.4 Piezo-electric transducer can be used inside a microphone.
1.1.5 A measuring instrument is a device used to convert non electrical
signals into electrical signals.
(5 × 1) (5)
1.2 Choose the correct word(s) from those given in brackets. Write only the
word(s) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 es e se e e
1.2.2 The (voltage/current) will lead in a capacitive circuit.
1.2.3 A common emitter amplifier has got a (high/low) voltage gain.
1.2.4 In a (positive/negative) feedback the signal is fedback in antiphase
with the input signal.
1.2.5 A Dual (beam/trace) oscilloscope consists of two separate electron
guns.
(5 × 1) (5)
[10]
TOTAL SECTION A: 10
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(8080613) -4- T770(E)(N30)T
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
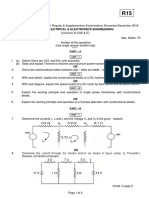
Study FIGURE 1 below and answer the following questions about the circuit:
I1 5Ω
A B
10 V I2
6Ω IX
9Ω 4Ω
D C
FIGURE 1
2.1 Express the current Ix using other variables. (1)
2.2 Formulate an equation for Loop ABDA and name it equation 1. (1)
2.3 Formulate an equation for Loop DCBD and name it equation 2. (1)
2.4 Calculate the value of the current I1. (3)
2.5 Calculate the value of the current I2. (2)
2.6 Calculate the value of the current Ix. (2)
[10]
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(8080613) -5- T770(E)(N30)T
QUESTION 3
3.1 Refer to FIGURE 2 below and calculate the following from the circuit.
5Ω 80 Ω 20 Ω
R L C
IT
120 V/60 Hz
FIGURE 2
3.1.1 The total impedance of the circuit. (3)
3.1.2 T e se eθ (2)
3.1.3 The capacitance of the capacitor in µF. (2)
3.1.4 The inductance of the inductor in mH. (2)
3.2 Draw the impedance phasor diagram of the circuit. (4)
3.3 Study FIGURE 3 below and briefly describe the graph in terms of the
impedance as well as the resonant frequency. Also state whether the graph
reflects a series or parallel resonant circuit.
f
fr
FIGURE 3 (2)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(8080613) -6- T770(E)(N30)T
3.4 Study FIGURE 4 below and briefly describe the graph in terms of the current
and the resonant frequency. Also state whether the graph reflects a series or
parallel resonant circuit.
f
fr
FIGURE 4 (2)
[17]
QUESTION 4
4.1 Briefly describe the term force of attraction on an orbiting electron. (2)
4.2 Briefly describe the term centrifugal force on an orbiting electron. (2)
4.3 Draw a neat labelled characteristic curve of a silicon diode and clearly
indicate the PIV point as well as the forward voltage drop point on the graph. (4)
4.4 Briefly describe the process of doping as applied to semiconductors. (3)
4.5 Describe the term reverse recovery time as applied to semiconductors. (2)
[13]
QUESTION 5
5.1 Draw a neat circuit of a half wave voltage doubler. (5)
5.2 Draw a neat circuit of an optocoupler configuration which uses a photo diode. (3)
[8]
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(8080613) -7- T770(E)(N30)T
QUESTION 6
6.1 Briefly describe the positioning of the Q-point for the following classes of
amplification as well as the flow of the output current in each case.
6.1.1 Class A
6.1.2 Class B
6.1.3 Class C
6.1.4 Class AB
(4 × 3) (12)
6.2 Briefly describe why coupling methods of transistors are necessary instead of
using a single transistor. (2)
6.3 Describe how those coupling methods in QUESTION 6.2 above are achieved. (2)
[16]
QUESTION 7
7.1 Draw a neat circuit symbol of a P-channel MOSFET and clearly label the
terminals. (2)
7.2 Name TWO advantages of field effect transistors. (2)
7.3 Draw a neat Op-Amp circuit which has a gain of unity and clearly indicate its
terminals. (3)
7.4 State the use of this circuit in QUESTION 7.3 above. (1)
[8]
QUESTION 8
8.1 Briefly describe the operating principle of the Wheatstone bridge. (4)
8.2 Describe the operating principle of a potentiometer transducer. (2)
[6]
QUESTION 9
9.1 Draw a neat labelled block diagram of a continuous balance DVM. (5)
9.2 Briefly explain the operating principle of this circuit in QUESTION 9.1 above. (7)
[12]
TOTAL SECTION B: 90
GRAND TOTAL: 100
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(8080613) -8- T770(E)(N30)T
INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS N3
FORMULA SHEET
Direct-current theory
V2
V IR P V I P
R
P I2 R
Alternating current theory:
1
X L 2fL XC Z R 2 (X L ~ X C )2
2fC
VT R
VT VR2 (VL ~ VC )2 I cos 1
Z Z
V IR V I XL V I XC
1 VT VT
fr IR IL
2 LC R XL
VT
IC IT I R2 I X2 I X I L ~ IC
XC
IX IR V
tan 1 cos 1 Z
IR IT IT
L V 1 1 R2
ZD IT fr 2
RC ZD 2 LC L
IC I RL Sin L IT I RL Cos L IT ITH 2 ITV 2
Transistors:
VCC
IC
RL
Transducers:
l k A Eo
R C
a d
Copyright reserved Please turn over
You might also like
- Industrial Electronics Question Memo N3 DownloadDocument21 pagesIndustrial Electronics Question Memo N3 DownloadNkanyiso ZondiNo ratings yet
- Expt 5.2Document6 pagesExpt 5.2Joel CatapangNo ratings yet
- 80k+ Priv8 IPTV (Userpass) CombolistDocument1,472 pages80k+ Priv8 IPTV (Userpass) CombolistJohn AndresNo ratings yet
- N4 Industrial Electronics April 2016Document9 pagesN4 Industrial Electronics April 2016advice nethengweNo ratings yet
- 2015 n3 August Industrial Electronics Question Paper PDFDocument9 pages2015 n3 August Industrial Electronics Question Paper PDFNkanyiso ZondiNo ratings yet
- T790 - Industrial Electronics N5 QP Apr 2019Document11 pagesT790 - Industrial Electronics N5 QP Apr 2019Kelsey BothaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics n4 2018 CombinedDocument247 pagesIndustrial Electronics n4 2018 Combinedmandisamsimango85No ratings yet
- T760 - INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS N2 QP AUG 2020 Sign OffDocument9 pagesT760 - INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS N2 QP AUG 2020 Sign Off2pietersmit1997No ratings yet
- N3 Industrial Electronics August 2021 PDFDocument10 pagesN3 Industrial Electronics August 2021 PDFKatlego MofommeNo ratings yet
- 15A02301 Electrical Circuits - IIDocument2 pages15A02301 Electrical Circuits - IIvenkat saiNo ratings yet
- Electrotechnics N5 April 2016Document7 pagesElectrotechnics N5 April 2016matetebanker27No ratings yet
- 15A02301 Electrical Circuits - IIDocument2 pages15A02301 Electrical Circuits - IIsuresh270No ratings yet
- 05 - T1650 - Strength of Materials and Structures N5 QP Nov 2018Document9 pages05 - T1650 - Strength of Materials and Structures N5 QP Nov 2018Dumi JacobNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Analysis II: Center For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electronics LabDocument8 pagesElectric Circuit Analysis II: Center For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electronics LabIrfan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Electrical Principles (Elp) Time Allowed: 1 Hours: Cems CodeDocument7 pagesElectrical Principles (Elp) Time Allowed: 1 Hours: Cems CodeLimNo ratings yet
- NET201 Network Theory Set-A AS2018Document6 pagesNET201 Network Theory Set-A AS2018SofelNo ratings yet
- Electrical Principles (Elp) Time Allowed: 1 Hours: Cems CodeDocument8 pagesElectrical Principles (Elp) Time Allowed: 1 Hours: Cems CodeLimNo ratings yet
- ET1006 1718S2 MST AnsDocument8 pagesET1006 1718S2 MST AnsfastNo ratings yet
- METV202 Test 3 (SICK) 2021 R3Document5 pagesMETV202 Test 3 (SICK) 2021 R3fipab44505No ratings yet
- 15A99301 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering - 3 PDFDocument2 pages15A99301 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering - 3 PDFMadhuSudanNo ratings yet
- MELZG632 Analog IC Design MidSem Make-Up 1573297948961Document3 pagesMELZG632 Analog IC Design MidSem Make-Up 1573297948961VEMURI RAVI TEJANo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document8 pagesLab 2Richard MillerNo ratings yet
- N4 Electrotechnics November 2016Document8 pagesN4 Electrotechnics November 2016Petro Susan BarnardNo ratings yet
- Electronics TEDocument9 pagesElectronics TEVipin JainNo ratings yet
- @NEETpassionate AIATS 3 (2021)Document41 pages@NEETpassionate AIATS 3 (2021)duraibiotechNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology Nov 2018 (Electronics) EngDocument33 pagesElectrical Technology Nov 2018 (Electronics) EngAuston LeshokaNo ratings yet
- MET22A - ETG125C-Unit1 - 2-MT - Qeustion-File C MemoDocument10 pagesMET22A - ETG125C-Unit1 - 2-MT - Qeustion-File C MemoTinyiko ChaukeNo ratings yet
- Set - A Beee QPDocument2 pagesSet - A Beee QPThiaga RajanNo ratings yet
- NET201 Network Theory Set-B AS2018Document7 pagesNET201 Network Theory Set-B AS2018SofelNo ratings yet
- N4 Electrotechnics April 2019Document8 pagesN4 Electrotechnics April 2019Petro Susan BarnardNo ratings yet
- Activity3 Group1Document16 pagesActivity3 Group1NicoNo ratings yet
- ADE Papaer IDocument3 pagesADE Papaer IPrabhat MishraNo ratings yet
- N4 Electrotechnics April 2016Document8 pagesN4 Electrotechnics April 2016Petro Susan BarnardNo ratings yet
- Spectral Analysis of Buck and Sepic ConvertersDocument7 pagesSpectral Analysis of Buck and Sepic ConvertersMuhammad Kamran MustafaNo ratings yet
- t530 - Electrotechnics n4 QP Nov 2018Document8 pagest530 - Electrotechnics n4 QP Nov 2018Petro Susan BarnardNo ratings yet
- Date: Time: 1hr 30 Min Sub: Edc-I (Iv Sem) Max. Marks: 40Document1 pageDate: Time: 1hr 30 Min Sub: Edc-I (Iv Sem) Max. Marks: 40Rupesh SushirNo ratings yet
- University of ZimbabweDocument6 pagesUniversity of ZimbabweTatenda BizureNo ratings yet
- ELA1501-2023-S1-Major Test 2Document4 pagesELA1501-2023-S1-Major Test 2Ayanda AyoNo ratings yet
- 2012 Mid Autumn EC21103 PDFDocument3 pages2012 Mid Autumn EC21103 PDFIndranilNo ratings yet
- 15A99301 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering - 1 PDFDocument2 pages15A99301 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering - 1 PDFMadhuSudanNo ratings yet
- EGH448 2022 Quiz 1Document4 pagesEGH448 2022 Quiz 1trung LeNo ratings yet
- Matlab Differential Protection ModelDocument9 pagesMatlab Differential Protection ModelEntertainment MediaNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: I B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, April/May - 2017 Electrical Circuit Analysis - IDocument8 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: I B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, April/May - 2017 Electrical Circuit Analysis - INVS TejaswiNo ratings yet
- ECX3230 - Electronics Assignment No. 02 (Due Date: See The Activity Diary)Document3 pagesECX3230 - Electronics Assignment No. 02 (Due Date: See The Activity Diary)Lalantha Munasinghe ArachchiNo ratings yet
- Dkk1352 Electrical Technology s1 0218Document5 pagesDkk1352 Electrical Technology s1 0218Kalterz UnionNo ratings yet
- NET201 Network Theory Set-A AS2019Document7 pagesNET201 Network Theory Set-A AS2019SofelNo ratings yet
- Advanced Proficiency Examination: Caribbean Examinations CouncilDocument15 pagesAdvanced Proficiency Examination: Caribbean Examinations Councilpetey78No ratings yet
- 2016 Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument4 pages2016 Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringRitik Chaturvedi RCNo ratings yet
- r05320403 Microwave EngineeringDocument8 pagesr05320403 Microwave EngineeringSRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- NET201 Network Theory Set-B AS2019Document6 pagesNET201 Network Theory Set-B AS2019SofelNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology Nov 2019 (Electronics) EngDocument23 pagesElectrical Technology Nov 2019 (Electronics) EngKhathutshelo KharivheNo ratings yet
- EEE 51 Assignment 4Document3 pagesEEE 51 Assignment 4Anton GarciaNo ratings yet
- 15A99301 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering1Document2 pages15A99301 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering1jagadeeshNo ratings yet
- Activity 3B Impedance of RC Circuits: Parallel RC Circuits 3B.1 Program Outcomes (Pos) Addressed by The ActivityDocument8 pagesActivity 3B Impedance of RC Circuits: Parallel RC Circuits 3B.1 Program Outcomes (Pos) Addressed by The ActivityNicoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Systems EC1021Document5 pagesElectrical Systems EC1021Sulaksha WimalasenaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit END Sem) Analysis 2022Document3 pagesElectrical Circuit END Sem) Analysis 2022Udit RanaNo ratings yet
- Analog Devices & Circuits: Inst Ruct Ions T O Candidat EsDocument2 pagesAnalog Devices & Circuits: Inst Ruct Ions T O Candidat EsAnmolNo ratings yet
- Physics CapacitanceDocument14 pagesPhysics CapacitanceHarshad SSNo ratings yet
- End Semester ExaminationDocument4 pagesEnd Semester ExaminationBitata Sarkar ee21s059No ratings yet
- r05010204 Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument11 pagesr05010204 Electronic Devices and CircuitsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Hilti HIT-V and HAS Threaded Rod and Hilti HIT-Z Anchor Rod: Specifications and Technical DataDocument8 pagesHilti HIT-V and HAS Threaded Rod and Hilti HIT-Z Anchor Rod: Specifications and Technical DataEdwin Ramos PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestDocument8 pagesHardness TestlvasuthavanNo ratings yet
- Randomized Controlled Trial On The Performance of Direct and in - 2021 - DentalDocument10 pagesRandomized Controlled Trial On The Performance of Direct and in - 2021 - Dentalnintendo anjayNo ratings yet
- DCC RiskAssessmentDocument74 pagesDCC RiskAssessmentgustavo caicedoNo ratings yet
- Toad For OracleDocument1,157 pagesToad For OraclesatsriniNo ratings yet
- A Bluetooth ModulesDocument19 pagesA Bluetooth ModulesBruno PalašekNo ratings yet
- Fundamntos Del Violonchelo-21-40Document20 pagesFundamntos Del Violonchelo-21-40Alejandro MoraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Econometrics Ii (Econ-3062) : Mohammed Adem (PHD)Document83 pagesIntroduction To Econometrics Ii (Econ-3062) : Mohammed Adem (PHD)ፍቅር እስከ መቃብር100% (2)
- Tassilipdf PDFDocument33 pagesTassilipdf PDFJustin LoucksNo ratings yet
- Coconut: Donesian Export Pro IleDocument39 pagesCoconut: Donesian Export Pro Ile764fqbbnf2No ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction Motor - Squirrel Cage: Data SheetDocument6 pagesThree Phase Induction Motor - Squirrel Cage: Data Sheetjulio100% (1)
- Assignment2 Santos CarlosJoaquin MECp1Document8 pagesAssignment2 Santos CarlosJoaquin MECp1Jake SantosNo ratings yet
- Promotion Safe Med ChildrensDocument64 pagesPromotion Safe Med ChildrensAbdul khodir jaelani100% (1)
- My Ideal Job BankerDocument4 pagesMy Ideal Job BankerAnne MaryNo ratings yet
- Christopher MontoyaDocument1 pageChristopher MontoyaUF Student GovernmentNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesLesson PlanVîrforeanu Nicolae AlinNo ratings yet
- Hotels in MandalayDocument149 pagesHotels in Mandalayzaw khaingNo ratings yet
- 6º Ano Ingles Unit4 Test3Document3 pages6º Ano Ingles Unit4 Test3Paula Lopes100% (1)
- On Advertising A Marxist CritiqueDocument13 pagesOn Advertising A Marxist CritiqueKisholoy AntiBrahminNo ratings yet
- Part-4-General English Set 3Document17 pagesPart-4-General English Set 3Yashwant SinghNo ratings yet
- The Brain and Nervous System (Psychology) Unit 14: An Academic ReportDocument7 pagesThe Brain and Nervous System (Psychology) Unit 14: An Academic ReportOlatokunbo SinaayomiNo ratings yet
- GMP Checklist Sanitary Facilities and ControlsDocument1 pageGMP Checklist Sanitary Facilities and ControlsATSEDENo ratings yet
- Circular Motion: American Journal of Physics July 2000Document8 pagesCircular Motion: American Journal of Physics July 2000GurjotNo ratings yet
- Gerund NounDocument15 pagesGerund NounNanda PutriNo ratings yet
- Wifi LBS - CiscoDocument206 pagesWifi LBS - Cisconassr_ismailNo ratings yet
- FS2 Ep 1Document9 pagesFS2 Ep 1Jovinson LozanoNo ratings yet
- PS2 VGA Diagram Rev by GillBert - Rev2 PDFDocument6 pagesPS2 VGA Diagram Rev by GillBert - Rev2 PDFwuemuraNo ratings yet
- Arduino UNO Rev3e SCH PDFDocument1 pageArduino UNO Rev3e SCH PDFHery Febrian DinogrohoNo ratings yet
- Cyctocyle - Care PlanDocument22 pagesCyctocyle - Care Planarchana vermaNo ratings yet