Professional Documents
Culture Documents
K5 - Fisiologi Penginderaan 1
K5 - Fisiologi Penginderaan 1
Uploaded by
Bintang Fortuna0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views60 pagesOriginal Title
K5_Fisiologi Penginderaan 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views60 pagesK5 - Fisiologi Penginderaan 1
K5 - Fisiologi Penginderaan 1
Uploaded by
Bintang FortunaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 60
PHYSIOLOGY OF
THE SPECIAL
SENSES 1
dr. Sophie Yolanda, MBiomed
REVIEW
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
REFLEX ARC
SENSORY PATHWAY
STIMULUS: PROPERTIES
• Modality
• Location
• Intensity and Duration
MODALITY
• Each type of stimulus will be responded
by a specific receptor (except pain →
polymodal)
• The brain associates a signal coming from
a specific group of receptors with a
specific modality → labeled line coding
LOCATION
• The location of a stimulus is coded
by these mechanisms:
• Receptive field
• Lateral inhibition
• Somatotopy
→ Two point
discrimination/sensitivity/acuity
RECEPTIVE FIELD
LATERAL INHIBITION
SOMATOTOPY
TWO POINT DISCRIMINATION
INTENSITY AND DURATION
• Intensity and duration of a stimulus are
coded by these mechanisms:
• Frequency and duration of action potential
• Receptor adaptation
FREQUENCY AND DURATION
OF ACTION POTENTIAL
RECEPTOR ADAPTATION
SENSORY PATHWAY
The process of learning and
memory begin with sensation…
The beginning of sensation is
at the receptor!
Minarma Siagian
SENSORY RECEPTORS
SENSORY PATHWAY
TRANSDUCTION
• The process of converting stimulus
energy into information that can be
processed by the nervous system →
electrical energy (change in membrane
potential → receptor potential → action
potential)
TRANSDUCTION
SITE OF ACTION POTENTIAL
INITIATION
SENSORY PATHWAY
SENSORY PATHWAY
SENSORY CORTEX
PERCEPTION
SENSORY PATHWAY
PERCEPTION
“Beauty is in the eye of the beholder”
quoted from Plato
VISION
VISION
• Stimulus: Light
Refraction
• Receptor: Retina
Transduction
• Afferent Pathway: Optic Nerve
• Center: Visual Cortex
• Perception
LIGHT
Ultra- Short- AC
Gamma X rays violet Infrared Radar FM TV wave AM electricity
-12 -8 -4 4 8
10 10 10 1 10 10
Wavelength in meters (m)
Visible light
400 nm 500 nm 600 nm 700 nm
Wavelength in nanometers (nm)
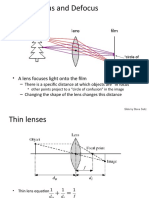
REFRACTION
REFRACTION MEDIA:
THE EYE
IRIS AND PUPIL
Pupillary constriction/miosis Pupillary dilation/midriasis
LENS: ACCOMODATION
FOCUSING THE LIGHT
REFRACTION
ABNORMALITIES
REFRACTION
ABNORMALITIES
RETINA
• 2 photoreceptors
• Rods
• Cones
• 4 neurons
• Horizontal cells
• Bipolar cells
• Amacrine cells
• Ganglion cells
PHOTORECEPTORS
PHOTORECEPTORS
RETINA
RETINA:
BLIND SPOT, MACULA
PHOTOTRANSDUCTION
FURTHER RETINAL
PROCESSING
• Bipolar cells respond differentially
to color, intensity, form, depth and
movement
• Ganglion cells respond to changes
in photoreceptor membrane
potentials by transmitting trains of
action potentials
FURTHER RETINAL
PROCESSING
RETINAL
PROCESSING
LINK TO VIDEOS
• http://www.interactive-
biology.com/category/ibtv/physiolo
gy/
• Senses: video 029
• Visual System: videos 030-035
VISUAL PATHWAY
“. . . And please let Mom, Dad, Rex,
Ginger, Tucker, me and all the rest of the
family see color.”
COLOR VISION
• L-cones, most sensitive to red light (610 nm)
• M-cones, most sensitive to green light (560 nm)
• S-cones, most sensitive to blue light (430 nm)
LIGHT DARK ADAPTATION
SUMMARY
REFERENCES
• Bear MF, Connors BW, Paradiso MA. Neuroscience
exploring the Brain, 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott
Williams and Wilkins. 2007.
• Sherwood L. Human Physiology from cells to
system, 7th ed. Australia. Brooks/Cole Cengange
Learning. 2011.
• Silverthorn DU. Human physiology: an integrated
approach. 5th ed. San Francisco. Pearson
Education, Inc. 2010.
• Biotech Review. Visual phototransduction. 2011.
Available from:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JIPE3in2EcQ
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Chapter 2a (Uv-Vis) .PPT Chm260Document67 pagesChapter 2a (Uv-Vis) .PPT Chm260Nurhayati HasanahNo ratings yet
- Non Destructive Testing: Subject Code: Kme 061Document24 pagesNon Destructive Testing: Subject Code: Kme 061Sapna Rai100% (1)
- SpectrosDocument37 pagesSpectrosKiruthick DonNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document38 pagesPresentation 1Kiruthick DonNo ratings yet
- Siskomoptik: Ref: Berbagai SumberDocument23 pagesSiskomoptik: Ref: Berbagai SumberFariNo ratings yet
- Performance Task 5 - SPECTROPHOTOMETRYDocument2 pagesPerformance Task 5 - SPECTROPHOTOMETRYKeith BagangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Part B) Instruments For Optical Absorption MeasurementsDocument38 pagesChapter 2 (Part B) Instruments For Optical Absorption MeasurementsaisyahNo ratings yet
- 1 - Basics of Molecular SpectrosDocument56 pages1 - Basics of Molecular SpectroscalfontibonNo ratings yet
- W1-6 Biochemistry of Vision and Hearing Lecture PDFDocument75 pagesW1-6 Biochemistry of Vision and Hearing Lecture PDFSAHIL AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation II (Elv)Document64 pagesInstrumentation II (Elv)kristina100% (1)
- Laser RetinaDocument70 pagesLaser RetinaSatya Hutama100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Analytical MethodsDocument104 pagesChapter 4 Analytical MethodsCL SanchezNo ratings yet
- On Laser TheoryDocument18 pagesOn Laser Theorynnarashi692No ratings yet
- A Lens Focuses Light Onto The FilmDocument57 pagesA Lens Focuses Light Onto The FilmYogesh KatreNo ratings yet
- Anachem Lecture (Spectro) - FinalsDocument35 pagesAnachem Lecture (Spectro) - FinalsAldrin Patrick Galvez EstocapioNo ratings yet
- FTIR (Things We Need To Know)Document3 pagesFTIR (Things We Need To Know)Keith Jaszer AgarradoNo ratings yet
- Microscopy: "Micro" (Small) "Scopeo" (To Watch)Document70 pagesMicroscopy: "Micro" (Small) "Scopeo" (To Watch)Originate RecordsNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Infra Red (FTIR) : Group 3 Dwi Yuliantiningsih Wifqul Laili Riski Ayu Candra Rina RukaenahDocument19 pagesFourier Transform Infra Red (FTIR) : Group 3 Dwi Yuliantiningsih Wifqul Laili Riski Ayu Candra Rina RukaenahWifqul LailyNo ratings yet
- Components of Optical InstrumentsDocument45 pagesComponents of Optical InstrumentsMasudRanaNo ratings yet
- L&P 15 ApplicationsDocument29 pagesL&P 15 ApplicationsWilda PrihastyNo ratings yet
- 105 ReceptorsDocument31 pages105 Receptorssanofazal786No ratings yet
- P1W4 - Application of SpectrophotometryDocument63 pagesP1W4 - Application of SpectrophotometryJoshua Richard Jr Tubiano PayopaninNo ratings yet
- IR SpectrosDocument24 pagesIR Spectroslalvenhimachhangte690No ratings yet
- Instrumental Analysis - UV - VS - AAS - CTLE - FINAL - ReyesDocument57 pagesInstrumental Analysis - UV - VS - AAS - CTLE - FINAL - ReyesMar MoncedaNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme SendoriDocument50 pagesMekanisme Sendorireni munazirNo ratings yet
- Unit V SpectrosDocument19 pagesUnit V SpectrossabiarshNo ratings yet
- Flow Cytometry: By: Dr. Megha Gupta & Dr. Tashi AgarwalDocument116 pagesFlow Cytometry: By: Dr. Megha Gupta & Dr. Tashi Agarwalanggaririn100% (1)
- Flowcytometry 150403122734 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocument116 pagesFlowcytometry 150403122734 Conversion Gate01 PDFsachindra kumar100% (1)
- Molecular Cell Biology: MicrosDocument26 pagesMolecular Cell Biology: Microsantonio latenNo ratings yet
- Analytic TechniquesDocument112 pagesAnalytic TechniquesolaytaaubreymaeNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Analytical Methods and InstrumentationDocument74 pagesWeek 4 Analytical Methods and Instrumentationpuno ric0% (1)
- UV Based Detection A Beginner S Guide 1698138618Document59 pagesUV Based Detection A Beginner S Guide 1698138618Andrés PacompíaNo ratings yet
- SPECTOPHOT corrected finalDocument68 pagesSPECTOPHOT corrected finalCyma PhoneNo ratings yet
- Gelombang Cahaya Tampak (Visible Light)Document12 pagesGelombang Cahaya Tampak (Visible Light)Dwipayana Sang PembunuhNo ratings yet
- 2 Micros PDFDocument59 pages2 Micros PDFcloudiest euniceNo ratings yet
- Spectro Photo Me TryDocument3 pagesSpectro Photo Me TryAshley Nicole DelizoNo ratings yet
- LaserDocument38 pagesLaserTamarai selviNo ratings yet
- 2 FT IrDocument25 pages2 FT Irsana siddiqueNo ratings yet
- 1.7. LaserDocument52 pages1.7. Laseraevadf760No ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy: Theory and PrinciplesDocument28 pagesFourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy: Theory and PrinciplesmaopacificNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MOLECULAR ABSORPTION SPECTROSDocument134 pagesChapter 2 MOLECULAR ABSORPTION SPECTROSaisyahNo ratings yet
- Analytical Method PDFDocument85 pagesAnalytical Method PDFiaderzNo ratings yet
- Phototransduction PuneetDocument60 pagesPhototransduction Puneetcoccoccoc232323No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MOLECULAR ABSORPTION SPECTROSDocument144 pagesChapter 2 MOLECULAR ABSORPTION SPECTROSSiti Zulaika Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Ftir (DR MRR Kooh) 2023Document80 pagesLec 2 Ftir (DR MRR Kooh) 2023Retro lashNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Applications of Infrared SpectrometryDocument20 pagesIntroduction & Applications of Infrared SpectrometryMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Optics Ebook FinalDocument38 pagesFundamentals of Optics Ebook FinalSuman RachaNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-Guided By:-: Ms. Anshu ToshniwalDocument30 pagesPresented By:-Guided By:-: Ms. Anshu ToshniwalaritrachatterjeebNo ratings yet
- Flow Cytometry: Priyanka, Roll No 25, Second Year B.Pharm.Document33 pagesFlow Cytometry: Priyanka, Roll No 25, Second Year B.Pharm.PriyankaKanjiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Part A) Components of Instrument For Optical SpectrosDocument28 pagesChapter 2 (Part A) Components of Instrument For Optical SpectrosaisyahNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument22 pagesFinalAreej ShabbirNo ratings yet
- EN ASFA AU Koplik - Infrared - Spectros PDFDocument25 pagesEN ASFA AU Koplik - Infrared - Spectros PDFalfitra mahendraNo ratings yet
- Fisika Dan Geometri Optik New EditDocument90 pagesFisika Dan Geometri Optik New EditBay BayuNo ratings yet
- Ftir PDFDocument40 pagesFtir PDFWahyuni EkaNo ratings yet
- Biophysics of Hearing SystemDocument17 pagesBiophysics of Hearing SystemMarius LețNo ratings yet
- Fluorescence MicrosDocument22 pagesFluorescence MicrosjohnpatrickhaleblueskyNo ratings yet
- CHE029 Spectroscopic-AnalysisDocument6 pagesCHE029 Spectroscopic-AnalysisCarla Mae OlvenarioNo ratings yet
- 5-High Resolution MicrosDocument23 pages5-High Resolution MicrosSneakyRiderNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2-MOLECULAR ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY - Part 4Document59 pagesCHAPTER 2-MOLECULAR ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY - Part 4fatin harrisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Instruments For Optical SpectrosDocument19 pagesLecture 2 - Instruments For Optical SpectrosBelay HaileNo ratings yet
- SP 23 Unit 2.4 PortfolioDocument13 pagesSP 23 Unit 2.4 PortfolioAnahi ByersNo ratings yet
- Họ, tên thí sinh:..................................................................... Mã số: ............................Document6 pagesHọ, tên thí sinh:..................................................................... Mã số: ............................Long BùiNo ratings yet
- Vision PhysiologyDocument37 pagesVision PhysiologyAnshu MishraNo ratings yet
- Color Universal Design HandbookDocument13 pagesColor Universal Design HandbookIndah DwiNo ratings yet
- MODULE 16 The Special SensesDocument60 pagesMODULE 16 The Special SensesMaxine Nicole WPNo ratings yet
- Osram-Os Led-Fundamentals Mesopic Vision v1 4-2-141Document16 pagesOsram-Os Led-Fundamentals Mesopic Vision v1 4-2-141Adolf ReyesNo ratings yet
- Digital Image FundamentalsDocument48 pagesDigital Image FundamentalsVishwanath Narayanan100% (1)
- Y10 Co Ordination and ResponseDocument88 pagesY10 Co Ordination and ResponseelizabethNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument21 pagesPhysicsEricka ArceNo ratings yet
- Class11 Biology Biology - 2019 Set - 1Document11 pagesClass11 Biology Biology - 2019 Set - 1priyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Eye Tracking and Tobii Eye TrackersDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Eye Tracking and Tobii Eye TrackersJon Ward100% (1)
- NSSBIO3E Chapter Test Ch15 eDocument17 pagesNSSBIO3E Chapter Test Ch15 e托普斯No ratings yet
- Sense Organs: Structure of Human EyeDocument8 pagesSense Organs: Structure of Human EyeRanveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Light Lesson 1 - MergedDocument94 pagesLight Lesson 1 - Mergedrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception: James A. Mccubbin, PHD Clemson University Worth PublishersDocument64 pagesSensation and Perception: James A. Mccubbin, PHD Clemson University Worth PublishersCristina RoubicekNo ratings yet
- Perception and Perceptual ProcessDocument17 pagesPerception and Perceptual ProcessDhrub Arka DekaNo ratings yet
- Input-Output ChannelsDocument4 pagesInput-Output ChannelsLona Jean AberillaNo ratings yet
- 3.8 Explanation Text Practice 2 (Clara Laura Lorenza)Document3 pages3.8 Explanation Text Practice 2 (Clara Laura Lorenza)Andre WahyuNo ratings yet
- What Makes Up An EyeDocument3 pagesWhat Makes Up An EyenandhantammisettyNo ratings yet
- 1718 - BInggris XI K13Document13 pages1718 - BInggris XI K13Cin Poenya Ta100% (1)
- Full Download Sensation and Perception 9th Edition Goldstein Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Sensation and Perception 9th Edition Goldstein Test Bankezrak2martin100% (39)
- Digital Image Fundamentals: Those Who Wish To Succeed Must Ask The Right Preliminary Questions. AristotleDocument37 pagesDigital Image Fundamentals: Those Who Wish To Succeed Must Ask The Right Preliminary Questions. AristotleAdiFest OrganizerNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument6 pagesSpecial Sensesvivian.obadeNo ratings yet
- Coordination & Response 3 QP - Marking SchemeDocument10 pagesCoordination & Response 3 QP - Marking SchemeSiti FairuzNo ratings yet
- Revision Slides Human Factors and Systems DesignDocument90 pagesRevision Slides Human Factors and Systems DesignLouis TeoNo ratings yet
- Color BlindnessDocument2 pagesColor BlindnessLJBernardoNo ratings yet
- Question Bank EBB 2023Document46 pagesQuestion Bank EBB 2023Muhammad SamyNo ratings yet
- Ia Biology IbDocument7 pagesIa Biology IbAlicia BNo ratings yet
- DIP Intro Class1Document88 pagesDIP Intro Class1Daniel FalcoffNo ratings yet