Professional Documents
Culture Documents
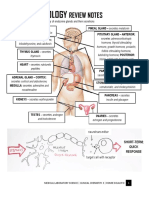
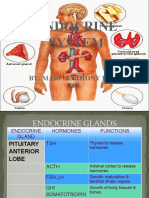
Endocrine Anatomy
Endocrine Anatomy
Uploaded by
PimpamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine Anatomy
Endocrine Anatomy
Uploaded by
PimpamCopyright:
Available Formats
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY THYROID HORMONES
Control cellular metabolic activity
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Accelerate metabolic process
Enhance cell replication for growth
DUCTLESS GLANDS ► THYROXINE (T4)
Growth and development - 4 iodine atoms in each molecule.
Metabolism of energy ► TRIIODOTHYRONINE (T3)
Muscle and adipose tissue - 3 iodine atoms IEM.
Distribution ► CALCITONIN/THYROCALCITONIN
Sexual development - Secreted in response to high plasma levels of CA+.
Fluid and electrolyte balance - Reduces plasma CA+ by increasing deposition in
Inflammation and immune responses bones.
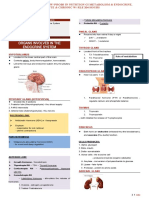
DUCTLESS GLANDS
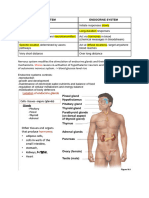
PARATHYROID GLAND
Cellular metabolism
Growth & development of the body 4 Structures
Reproduction function Situated in the neck
Blood sugar levels Embedded in the posterior aspect of the thyroid gland
► PARATHORMONE
STIMULUS OF HORMONE RELEASE - Regulates calcium & phosphorus metabolism.
HORMONES - Increases calcium absorption from the kidney,
Released into blood intestines & bones raising the blood calcium levels.
CONTROL OF HORMONE RELEASE - Reduces the reabsorption of phosphate from the
Hormonal stimulus proximal tubule of the kidney lowering blood phosphorus level
Humoral stimulus through the urine.
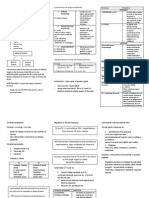
Neural stimulus ADRENAL GLAND
Pair of organ attached to the upper portion of each kidney.
HOMEOSTASIS Each gland is 2 glands w/ separate independent functions.
► NEGATIVE FEEDBACK ► ADRENAL MEDULLA
- Change in condition triggers action that reverses the - Inner portion
change. - SNS (Neural control)
Reduces change, Responsible for change, Maintains a stable - Catecholamines
state. ► ADRENAL CORTEX
EXAMPLE: Temperature, BP, Osmoregulation - Outer portion
► POSITIVE FEEDBACK - HPA Axis (Hormonal control)
- Amplifying change. - Glucocorticoids, Mineralocorticoids, androgens
Reaction increase, Move away from equilibrium
EXAMPLE: Fruit ripening, Child birth, Blood clot CATECHOLAMINES
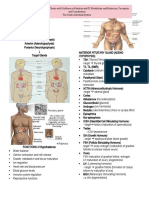
PITUITARY GLAND ► EPINEPHRINE & NOREPINEPHRINE
- Fight or flight
Anterior and Posterior lobe - Regulate metabolic pathways to promote catabolism
Hypophysis and stored fuels to meet caloric needs from endogenous source.
“Master Gland” - Decrease blood flow to tissues not needed in ES.
Controlled by Hypothalamic Hormones - Increase blood flow for effective FoF.
- Elevate the blood glucose levels & basal metabolic
ANTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND rate.
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS - glandular component GLUCOCORTICOIDS
HORMONES ► CORTISOL
SOMATOTROPIN / Growth hormone (GH) - Influence metabolism on all organs especially on
PROLACTIN (PRL) Glucose metabolism: increasing blood glucose levels.
THYROID STIMULATING HORMONE (TSH) - Inhibit the inflammatory response to tissue injury &
ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE (ACTH) to suppress allergic manifestations.
GONADOTROPIC HORMONES - LH & FSH - Indirectly constrict blood vessels slowing blood loss &
MELANOCYTE STIMULATING HORMONE prevents inflammation after an injury.
- Indirectly acts on bone by blocking calcium
POSTERIOR PUITARY GLAND absorption which decreases bone cell growth.
NEUROPHYPOPHYSIS- glandular component
HORMONES MINERALOCORTICOIDS
VASOPRESSIN/ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE (ADH) ► ALDOSTERONE
OXYTOCIN - Electrolyte metabolism (blood volume & salt)
- Increase sodium ions reabsorption at the renal
THYROID GLAND tubules & GI epithelium in exchange for potassium/hydrogen ions
Butterfly shaped organ excretions.
Lower neck, anterior of trachea - Conserves water and increases blood pressure
2 lateral lobes connected by an isthmus (important in compensating for fluid loss from severe bleeding)
MINERALOCORTICOIDS FATS AND PROTEINS
► ANDROGEN Gluconeogenesis
- Steroid hormones that exert effects similar to those generation of glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon
of the male sex hormones. substances such as fatty acids and amino acids in the liver
- Adrenal gland may also secrete small amounts of especially during hypoglycemia
some estrogens, or female sex hormones.
ENDOCRINE PANCREAS
Relies on humoral control.
Influence also by neural factors for enzymatic and hormonal
secretion.
EXOCRINE PANREAS
Secretion of pancreatic enzymes into the gastrointestinal (GI)
tract through the pancreatic duct.
ENDOCRINE PANREAS
Secretion of insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin directly into
the bloodstream.
► ISLETS OF LANGERHANS
- Collection of cells embedded in the pancreatic tissue.
- ALPHA CELLS: Glucagon
- BETA CELLS: Insulin
- DELTA CELLS: Somatostatin
► INSULIN
- lowers blood glucose levels
- stimulate glycogenesis
- transports & metabolizes glucose for energy
- inhibits glycogenolysis & gluconeogenesis
- enhances storage of dietary fat in adipose tissue
- accelerates transport of amino acids (from dietary
protein) into cells.
► GLUCAGON
- raises blood glucose levels
- stimulates glycogenolysis
► HYPOPITUITARISM
- growth hormone inhibiting hormone (GHIH)
- lower blood glucose levels by inhibiting GH and
glucagon release.
NUTRIENT METABOLISM AND STORAGE
CARBOHYDRATES
► GLUCOSE
- Quick source of energy and fuel needed for vital
functions.
► GLYCOGEN
- Stored form glucose in liver.
► GLYCOGENESIS
- Conversion of extra glucose into glycogen in liver.
► GLYCOGENOLYSIS
- Conversion of glycogen back to glucose in liver during
hypoglycemia.
FATS
Most efficient form of fuel storage.
when there is a high saturation of glycogen, excess glucose is
converted into fatty acids stored as triglycerides.
PROTEINS
Essential for formation of all body structure:
Genes Bone matrix
Enzymes Blood
Muscles
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.
You might also like
- FAA Newcomer's Packet Online VersionDocument48 pagesFAA Newcomer's Packet Online VersionPeyton Brooke100% (4)
- A GCE Biology 2804 01 January 2008 Question PaperDocument24 pagesA GCE Biology 2804 01 January 2008 Question PaperVeer Ramloghun0% (1)
- Clinical Chemistry 3: EndocrinologyDocument21 pagesClinical Chemistry 3: EndocrinologyRomie Solacito100% (3)
- Anti Diabetic DrugsDocument58 pagesAnti Diabetic DrugsDaniel Wang100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument21 pagesEndocrine SystemMark DimarucutNo ratings yet
- Adenohypophysis: HormonesDocument4 pagesAdenohypophysis: HormonesTomilynjan GarpaNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM and Disorders LectureDocument153 pagesENDOCRINE SYSTEM and Disorders LectureAnthony Riggs100% (1)
- Endocrine HormonesDocument2 pagesEndocrine HormonesJoe SanoneNo ratings yet
- Endocrine New EditionDocument150 pagesEndocrine New Editiondigracia manatigaNo ratings yet
- Review Endocrine Disorders FINALDocument166 pagesReview Endocrine Disorders FINALmeranith100% (10)
- Endocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyDocument28 pagesEndocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyHumaira BadatNo ratings yet
- Endo Reviewer 1Document8 pagesEndo Reviewer 1ANA DelafuenteNo ratings yet
- Endo ReviewerDocument5 pagesEndo ReviewerZIAN LABADIANo ratings yet
- Endorine SystemDocument27 pagesEndorine SystemBenjamin YickNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesThe Endocrine SystemtumisobeNo ratings yet
- General Biology Lesson 13Document13 pagesGeneral Biology Lesson 13GUCOR, LOVELY SHANE C.No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument106 pagesEndocrine Systemloveseeker06No ratings yet
- Effects Adrenal Hormones RegebDocument7 pagesEffects Adrenal Hormones RegebPraveena MoganNo ratings yet
- Week 16 Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesWeek 16 Endocrine Systemrichard respetoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 085347 PDFDocument30 pagesEndocrine System 085347 PDFClyde ReyesNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: Prof - DR. Didik Tamtomo, DR PAK, MM, MKK Pakar Anatomi KedokteranDocument78 pagesEndocrinology: Prof - DR. Didik Tamtomo, DR PAK, MM, MKK Pakar Anatomi KedokteranAnnisaInayati-msNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System-Ms3-Maam RioDocument5 pagesEndocrine System-Ms3-Maam RioLovely Hope LugatimanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document6 pagesChapter 5Shiny ChenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Endocrine GlandsDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Endocrine GlandsKatrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine SystemNovie Jane HontiverosNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine Systemden mNo ratings yet
- Cushing Syndrome Addisons 1Document6 pagesCushing Syndrome Addisons 1Czarena Ysabelle PayotNo ratings yet
- Regulasi Dan Mekanisme EndokrinDocument121 pagesRegulasi Dan Mekanisme Endokrinluthfiyya syafiqaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyIssaiah Nicolle CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Science: Endocrine & Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesScience: Endocrine & Nervous SystemLUISE DANIELLA DELOS REYES DOLOTALLASNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Mahayag Abuloc Labiste Sagayno VillaruelDocument32 pagesEndocrine System: Mahayag Abuloc Labiste Sagayno VillaruelJJ AlmagroNo ratings yet
- 2ND Gen Bio Prelim NotesDocument8 pages2ND Gen Bio Prelim NotesRalph RadazaNo ratings yet
- Med Surg Exam 3 Review UpdatedDocument9 pagesMed Surg Exam 3 Review UpdatedHana BenedictoNo ratings yet
- AdrenalDocument6 pagesAdrenalJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesWeek 5 Endocrine SystemJiro MarianoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Endocrine Physiology: DR EvaDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Endocrine Physiology: DR EvaEmmanuel Julius ChalighaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland: Dr. Fatimah Eliana, SPPD, KemdDocument46 pagesAdrenal Gland: Dr. Fatimah Eliana, SPPD, KemdZahra AstriantaniNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: FunctionDocument24 pagesEndocrine System: FunctionCzyvel KryzNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Endocrine SystemDocument24 pages2018 - Endocrine SystemCzyvel KryzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument4 pagesChapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationanuminiatureNo ratings yet
- Presented BY Prof. (Zoology) The Women University Multan: Dr. Nahid KaurarDocument34 pagesPresented BY Prof. (Zoology) The Women University Multan: Dr. Nahid KaurarSohaib NasirNo ratings yet
- CC2 SemifinalsDocument4 pagesCC2 SemifinalsAbc DefNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Part 3Document55 pagesEndocrine System Part 3Cristina RocheNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument3 pagesEndocrine DisordersIrish OrleansNo ratings yet
- ADRENALSDocument60 pagesADRENALSJyoti ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System SGDocument27 pagesEndocrine System SGmeaghan2215No ratings yet
- BIOS5130 Week 9 Slides W - o AnswersDocument47 pagesBIOS5130 Week 9 Slides W - o AnswersOkikiola JohnsonNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionaudreyNo ratings yet
- Sample TransDocument5 pagesSample TransNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland Physiology (DRDocument77 pagesAdrenal Gland Physiology (DRapi-3769252100% (4)
- Endosys ReviewerDocument9 pagesEndosys ReviewerJeminah Fae CalmaNo ratings yet
- Full Human Physiology Short NotesDocument11 pagesFull Human Physiology Short Notesseetharaman8341No ratings yet
- Biology Endocrine System Notes Compiled by Srikrshna p1 PDFDocument8 pagesBiology Endocrine System Notes Compiled by Srikrshna p1 PDFKazi AslamNo ratings yet
- PNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNDocument4 pagesPNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Summary 3 - Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesSummary 3 - Endocrine SystemAurélNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System DrugsDocument66 pagesEndocrine System DrugsRania HamamNo ratings yet
- Material 1 1700551347Document4 pagesMaterial 1 170055134717swabhiNo ratings yet
- Ana Upward Ballein ThrowDocument16 pagesAna Upward Ballein ThrowJohnny eawNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)Document3 pages11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)fariha khanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine NursingDocument5 pagesEndocrine NursingMiss GNo ratings yet
- Systemic Response To InjuryDocument56 pagesSystemic Response To InjuryFalling HateNo ratings yet
- DM PDFDocument27 pagesDM PDFMohab GarawanyNo ratings yet
- Hormones and Nutrient PartitioningDocument36 pagesHormones and Nutrient Partitioningbwade2_916499061No ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: A Comprehensive ReviewDocument10 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: A Comprehensive ReviewBidduth Kumar Sarkar0% (1)
- Biological Activities of Crude Extracts and Chemical Constituents of Aegle MarmelosDocument13 pagesBiological Activities of Crude Extracts and Chemical Constituents of Aegle MarmeloskavalapparaNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Module Study Guide 2023 FinalDocument24 pagesEndocrinology Module Study Guide 2023 Finaldomitam105No ratings yet
- PHARMACARDS GonzagaDocument38 pagesPHARMACARDS GonzagaJay Marie GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Krok1 EngDocument27 pagesKrok1 Engdeekshit dcNo ratings yet
- Jain Digestion To Be Discuused Kami Export - Human Nutrition 1 QPDocument11 pagesJain Digestion To Be Discuused Kami Export - Human Nutrition 1 QPHanaOmarNo ratings yet
- Reviws Antidiabetic Plants PDFDocument53 pagesReviws Antidiabetic Plants PDFعبير عبدالحفيظNo ratings yet
- Thesis - Diabetes Monitoring Support SystemDocument93 pagesThesis - Diabetes Monitoring Support SystemMitol Cepada100% (3)
- Forbes Teaching Project Outline (Final)Document5 pagesForbes Teaching Project Outline (Final)api-283946367No ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus GestationalDocument19 pagesDiabetes Mellitus GestationalYosefin RatnaningtyasNo ratings yet
- 2018 Question Paper Set C English CoreDocument12 pages2018 Question Paper Set C English CoreInder SinghNo ratings yet
- The Hospital Management of Hypoglycaemia in Adults With Diabetes Mellitus 3rd EditionDocument40 pagesThe Hospital Management of Hypoglycaemia in Adults With Diabetes Mellitus 3rd EditionRumahSehat N-CareNo ratings yet
- Cannula Calculation-Learning Syringe-Olsen - ch7 PDFDocument33 pagesCannula Calculation-Learning Syringe-Olsen - ch7 PDFzainikamal1975No ratings yet
- Lab Clin Test BankDocument87 pagesLab Clin Test Bankemms meNo ratings yet
- Biochem 1 NotesDocument141 pagesBiochem 1 NotesJyNadarilNo ratings yet
- Glucose MetabolismDocument48 pagesGlucose MetabolismJay R Plogio100% (1)
- F 2433 CMED Saxagliptin A Selective DPP 4 Inhibitor For The Treatment of Type 2 D.PDF 3311Document12 pagesF 2433 CMED Saxagliptin A Selective DPP 4 Inhibitor For The Treatment of Type 2 D.PDF 3311Ridha Surya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 The Endocrine System Chapter OutlineDocument23 pagesChapter 16 The Endocrine System Chapter OutlineMartina MicicNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Younes Ferwana Mohamed MehgizDocument43 pagesDiabetes Younes Ferwana Mohamed MehgizHakim oğluNo ratings yet
- A Review On Estimation of Metformin Hydrochloride and Vildagliptin in Pharmacutical Dosage FormDocument6 pagesA Review On Estimation of Metformin Hydrochloride and Vildagliptin in Pharmacutical Dosage FormEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Cure For Diabetes in SunnahDocument14 pagesCure For Diabetes in SunnahkoowaitkoowaitNo ratings yet
- Medical Complications of Type 2 DiabetesDocument422 pagesMedical Complications of Type 2 DiabetesMayracpp.16No ratings yet
- Final Pico Question InformaticsDocument5 pagesFinal Pico Question Informaticsapi-310396820No ratings yet
- Whats The Health - Any Way PDFDocument140 pagesWhats The Health - Any Way PDFparveshNo ratings yet
- J. Biol. Chem.-1941-Somogyi-219-27Document10 pagesJ. Biol. Chem.-1941-Somogyi-219-27gibrambo5770No ratings yet