Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MMW Finals Reviewer
MMW Finals Reviewer
Uploaded by
Janna MañozoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MMW Finals Reviewer
MMW Finals Reviewer
Uploaded by
Janna MañozoCopyright:
Available Formats
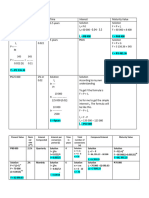
Linear Correlation Analysis Pearson’s Moment Correlation Coeffecient a=1.
001
Independent VS Dependent Variables N Σ xy −Σ x Σ y
1. An athletic trainer wants to be r=
√ ¿ ¿¿
able to predict the cardiac output
from his clients' level of exercise. Simple Linear Regression Analysis y = a + bx
Independent: level of exercise Coefficient of Determination y = 0.038 + 1.001x
2
Dependent: cardiac output •r
2. The more time spent studying, the • ranges from 0 to1 (always +) So if the lathe machine is used for
higher the GPA is • How much the independent 4.25 hours, the estimated income is:
Independent: Time spent studying variables affect the dependent
Dependent: GPA variables y = 0.038 + 1.001 x 4.25
3. A student is absent from class • measured in percentage (0% to y = 4.29225 x 100,000 Php
most of the time. Therefore, he got a 100%) y = 429,225 Php
low score on the long test given by From r = 0.61
the teacher r2 = 0.612
Independent: number of absences r2 = 0.37
Dependent: long test score Convert to percentage (x 100)
4. The smaller the ball, the faster it r2 = 0.37 x 100
drops to the ground r2 = 37%
37% of the income per month is explained by the
Independent: size of the ball
number of hours spent on the lathe machine.
Dependent: speed of falling Furthermore, there are other factors (63%) which
5. The length of time in a company are needed to explain the income per month of
the fabrication shop
guaranties high salary
Independent: length of time in a
company Simple Linear Regression Analysis
Dependent: salary • aims to develop an equation to
Correlation Analysis predict future values of dependent
• Study of relationship between variable (y) based on independent
independent (x) and dependent (y) variables (x)
variables Regression or Prediction Line
• Measures strength (perfect, y = a + bx
strong, no relationship) and y = predicted value of dependent
direction (+ or -) of continuous variable y
bivariate data (Examples: time and x = value of independent variable X
grades, mass and size) a = intercept
Correlation Coefficient b = slope
• r: determines if linear relationship
2
exists between variables ΣY Σ Χ −ΣΧ ΣΧY
• value = -1 to +1 a= 2
nΣ X −¿ ¿
• perfect negative linear
relationship: r = 1 62.8 x 329.3125−62.25 x 332.175
• perfect positive linear a= 2
relationship: r= +1 12 x 329.3125−62.2 5
• no linear relationship: r = 0 a=0.038
• strong negative linear relationship:
near -1
• strong positive linear relationship: nΣXY −ΣΧ ΣY
near +1 b¿ 2
Scatter Plot nΣ X −¿ ¿
12 x 332.175−62.25 x 62.8
a= 2
12 x 329.3125−62.2 5
You might also like
- Prob 3Document2 pagesProb 3shilpaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Homework - Fall 2021Document4 pagesWeek 3 Homework - Fall 2021zuhair khanNo ratings yet
- MMW Finals ReviewerDocument3 pagesMMW Finals ReviewerJanna MañozoNo ratings yet
- MMW Finals ReviewerDocument2 pagesMMW Finals ReviewerJanna MañozoNo ratings yet
- Lecture+8+ +Linear+RegressionDocument45 pagesLecture+8+ +Linear+RegressionSupaapt SrionNo ratings yet
- Week 9 ADocument26 pagesWeek 9 AKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document60 pagesLecture 4Amine HadjiNo ratings yet
- Topics: RegressionDocument26 pagesTopics: RegressionramNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression PDFDocument32 pagesLinear Regression PDFAravindNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document14 pagesChapter 9beshahashenafe20No ratings yet
- Why Do We Need Statistics? - P Values - T-Tests - Anova - Correlation33Document37 pagesWhy Do We Need Statistics? - P Values - T-Tests - Anova - Correlation33sikunaNo ratings yet
- Mhsagujar@neu Edu PHDocument44 pagesMhsagujar@neu Edu PHFia JungNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linear Regression and Correlation AnalysisDocument92 pagesIntroduction To Linear Regression and Correlation AnalysisKathiravan GopalanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 PDFDocument28 pagesLecture 15 PDFĐăng HảiNo ratings yet
- Corr Reg UpdatedDocument34 pagesCorr Reg UpdatedMugilan KumaresanNo ratings yet
- Stat Chapter 6Document23 pagesStat Chapter 6temesgenalemayehu488No ratings yet
- Unit 5Document104 pagesUnit 5downloadjain123No ratings yet
- Correlation & RegressionDocument30 pagesCorrelation & RegressionIshan kumar rathNo ratings yet
- 6.3 SSK5210 Parametric Statistical Testing - Analysis of Variance LR and Correlation - 2Document39 pages6.3 SSK5210 Parametric Statistical Testing - Analysis of Variance LR and Correlation - 2Sarveshwaran BalasundaramNo ratings yet
- Correlation and RegressionDocument54 pagesCorrelation and RegressionDiosdado II MarimonNo ratings yet
- Chap-11 Correlation and RegressionDocument42 pagesChap-11 Correlation and RegressionshubhNo ratings yet
- Corr RevisedDocument11 pagesCorr RevisedMarcy LumiwesNo ratings yet
- Stat (I) 4-6 MaterialDocument42 pagesStat (I) 4-6 Materialamareadios60No ratings yet
- Stastics ll:6Document22 pagesStastics ll:6muchedessieNo ratings yet
- Linear Discriminant Functions: Minimum Squared Error Procedures: Ho-Kashyap ProceduresDocument22 pagesLinear Discriminant Functions: Minimum Squared Error Procedures: Ho-Kashyap ProceduresRachnaNo ratings yet
- Correlation and RegressionDocument43 pagesCorrelation and RegressionShruti DasNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Regression.Document20 pagesLec 3 Regression.Katende ChrisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Measurements and Vector Analysis PDFDocument51 pagesChapter 1 - Measurements and Vector Analysis PDFJackkkkNo ratings yet
- Regression Analysis Estimation and Interpretation of Regression Equation Dummy Independent VariableDocument39 pagesRegression Analysis Estimation and Interpretation of Regression Equation Dummy Independent VariableTaimoor WaraichNo ratings yet
- Week 3 RegressionDocument21 pagesWeek 3 RegressionBENHARD TITA THIONONo ratings yet
- ReliabilityDocument25 pagesReliabilityshiranthaNo ratings yet
- L5 - Simple Linear Regression StudentsDocument33 pagesL5 - Simple Linear Regression StudentsKelyn KokNo ratings yet
- DPB 1013 - Statistic Correlation and Linear RegressionDocument23 pagesDPB 1013 - Statistic Correlation and Linear RegressionAdriana ZolkeplyNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Satistics and ProbabilityDocument17 pagesModule 4 Satistics and Probabilitydivinesapanta12345No ratings yet
- 8.regression AnalysisDocument5 pages8.regression AnalysisTasbir HasanNo ratings yet
- Pearson Correlation CoefficientDocument14 pagesPearson Correlation CoefficientGideon GallardoNo ratings yet
- Sonek Linear Regression NotesDocument11 pagesSonek Linear Regression NotesAlfredNo ratings yet
- Datamining Lecture6Document41 pagesDatamining Lecture6Vi LeNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument21 pagesChapter Fourbeshahashenafe20No ratings yet
- Sec D CH 12 Regression Part 2Document66 pagesSec D CH 12 Regression Part 2Ranga Sri100% (1)
- Simple Linear RegressionDocument50 pagesSimple Linear RegressionRangothri Sreenivasa Subramanyam100% (1)
- Regression and CorrelationDocument27 pagesRegression and CorrelationDinah Jane MartinezNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear Regression Part 1Document63 pagesSimple Linear Regression Part 1_vanitykNo ratings yet
- Regression: Regression. But Quite Often The Values of A Particular Phenomenon May Be Affected by Multiplicity ofDocument8 pagesRegression: Regression. But Quite Often The Values of A Particular Phenomenon May Be Affected by Multiplicity ofAnees Abdul LatheefNo ratings yet
- Pearson's Correlation CoefficientDocument7 pagesPearson's Correlation Coefficientyasas_bandaraNo ratings yet
- 5 - 7. MR - EstimationDocument12 pages5 - 7. MR - EstimationNikhilesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- LINEAR REGRESSION Feu DilimanDocument11 pagesLINEAR REGRESSION Feu DilimanlysaNo ratings yet
- T-Tests, Anova and Regression: Lorelei Howard and Nick Wright MFD 2008Document37 pagesT-Tests, Anova and Regression: Lorelei Howard and Nick Wright MFD 2008Mohammed BilalNo ratings yet
- Materi M13. Multiple CorelationDocument25 pagesMateri M13. Multiple CorelationRicky Syah putraNo ratings yet
- Engineering Apps: Session 4-Introduction To DADocument37 pagesEngineering Apps: Session 4-Introduction To DAMohamed Hesham GadallahNo ratings yet
- Reference Material - Linear - RegressionDocument12 pagesReference Material - Linear - Regressionsonal100% (1)
- BS Set 4 Linear RegressionDocument20 pagesBS Set 4 Linear RegressionAshley GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Multiple Linear RegressionDocument34 pagesMultiple Linear RegressionShameer P HamsaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document47 pagesLecture 12traceynguyen1205No ratings yet
- Statistics For Management Decisions MG913: Correlation and RegressionDocument25 pagesStatistics For Management Decisions MG913: Correlation and RegressionAshraf SeragNo ratings yet
- Regression AnalysisDocument43 pagesRegression AnalysisPRIYADARSHI GOURAV100% (1)
- Describing Bivariate Numerical Data - Honors 281Document34 pagesDescribing Bivariate Numerical Data - Honors 281Jennifer HaddonNo ratings yet
- 05 - Statind2 - Regresi Linier Sederhana Dan KorelasiDocument15 pages05 - Statind2 - Regresi Linier Sederhana Dan KorelasiM Luthfi El GhazruNo ratings yet
- T-Tests, Anova and Regression: Lorelei Howard and Nick Wright MFD 2008Document37 pagesT-Tests, Anova and Regression: Lorelei Howard and Nick Wright MFD 2008kapil1248No ratings yet
- Introduction To Correlation and Linear RegressionDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Correlation and Linear RegressionArun nathNo ratings yet
- Rank Correction-Spear, Kendal-Day and EveningDocument22 pagesRank Correction-Spear, Kendal-Day and Eveningjeth mctarvishNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- MMW Finals ReviewerDocument3 pagesMMW Finals ReviewerJanna MañozoNo ratings yet
- Las 4 - Normal DistributionDocument10 pagesLas 4 - Normal DistributionJanna MañozoNo ratings yet
- Gen Math 2nd Quarter Week 2Document2 pagesGen Math 2nd Quarter Week 2Janna MañozoNo ratings yet
- Gen Math 2nd Quarter Week 1Document5 pagesGen Math 2nd Quarter Week 1Janna MañozoNo ratings yet
- Gen Math 2nd Quarter Week 3-4Document5 pagesGen Math 2nd Quarter Week 3-4Janna MañozoNo ratings yet
- Las 1 - Random-VariablesDocument5 pagesLas 1 - Random-VariablesJanna MañozoNo ratings yet
- Buying and Selling 1Document3 pagesBuying and Selling 1Janna MañozoNo ratings yet
- Astm - G16Document14 pagesAstm - G16Norbey Arias100% (1)
- Lab 4 - Support Vector Machines: Part BDocument5 pagesLab 4 - Support Vector Machines: Part Bshahima khanNo ratings yet
- Calculating Factor ScoresDocument32 pagesCalculating Factor ScoresBorna sfmopNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Problem 1: My Dog Ate My CodebookDocument7 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology: Problem 1: My Dog Ate My CodebookkebarclaNo ratings yet
- STS 401 e (Ex. 8)Document2 pagesSTS 401 e (Ex. 8)MostafaMimoNo ratings yet
- Elementary Statistics A Step by Step Approach 7th Edition Bluman Test BankDocument14 pagesElementary Statistics A Step by Step Approach 7th Edition Bluman Test Bankfelicitycurtis9fhmt7100% (37)
- 9 - Independence of EventsDocument13 pages9 - Independence of Eventsjulianne sanchezNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines University of Northeastern Philippines Iriga City School of Graduate Studies and ResearchDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines University of Northeastern Philippines Iriga City School of Graduate Studies and ResearchDINA CANDELARIANo ratings yet
- Marketing Research Quiz 005: CheckDocument4 pagesMarketing Research Quiz 005: CheckFayesheli DelizoNo ratings yet
- Experimental ResearchDocument7 pagesExperimental ResearchPaulane NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Four Derivations of The Black-Scholes FormulaDocument19 pagesFour Derivations of The Black-Scholes FormulaShi LohNo ratings yet
- Inferential Statistic: 1 Estimation of A Population MeanDocument8 pagesInferential Statistic: 1 Estimation of A Population MeanshahzebNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Econometrics With R: Christoph Hanck, Martin Arnold, Alexander Gerber, and Martin SchmelzerDocument481 pagesIntroduction To Econometrics With R: Christoph Hanck, Martin Arnold, Alexander Gerber, and Martin SchmelzerFrancisco SilvaNo ratings yet
- Identification by Heteroskedasticity or Non-Gaussianity: 2016 Lutz Kilian and Helmut L UtkepohlDocument40 pagesIdentification by Heteroskedasticity or Non-Gaussianity: 2016 Lutz Kilian and Helmut L UtkepohlJoseph BabcockNo ratings yet
- Math 1280 - Learning Journal Unit 8Document2 pagesMath 1280 - Learning Journal Unit 8habib oyeroNo ratings yet
- Tabel Jumlah Peringkat WilcoxonDocument2 pagesTabel Jumlah Peringkat WilcoxonDimas ArrezaNo ratings yet
- R Intro 2011Document115 pagesR Intro 2011marijkepauwelsNo ratings yet
- Ec35a5 Simulation of Communication Systems Question PaperDocument2 pagesEc35a5 Simulation of Communication Systems Question Paperanilnv.itdNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Robustness and Robust StatiticsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Robustness and Robust StatiticsUmesh Sai GurramNo ratings yet
- Check One: STA303 - STA1002Document19 pagesCheck One: STA303 - STA1002Micheal HongNo ratings yet
- Chap, 9,8,7,6Document1 pageChap, 9,8,7,6Jaf ShahNo ratings yet
- ContinuousDocument1 pageContinuousReizelNo ratings yet
- Local Media6460876862289465897Document61 pagesLocal Media6460876862289465897Ian Angel Benaning OsnanNo ratings yet
- Time Series DecompositionDocument4 pagesTime Series DecompositionGagan Deep SinghNo ratings yet
- Class 3 Navie BayesDocument21 pagesClass 3 Navie Bayesshrey patelNo ratings yet
- Intrebari Grila Econometrie Exemple PT EXAMEN PusDocument7 pagesIntrebari Grila Econometrie Exemple PT EXAMEN PusLaura RacovitaNo ratings yet
- M2. Understanding A Data Set IIDocument33 pagesM2. Understanding A Data Set IIMYo OoNo ratings yet
- On The Computation of The RMSEA and CFI From The Mean-And-Variance Corrected Test Statistic With Nonnormal Data in SEMDocument12 pagesOn The Computation of The RMSEA and CFI From The Mean-And-Variance Corrected Test Statistic With Nonnormal Data in SEMNorberth Ioan OkrosNo ratings yet