Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Movement in and Out of The Cell - Biology
Movement in and Out of The Cell - Biology
Uploaded by
hola2468013579hOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Movement in and Out of The Cell - Biology
Movement in and Out of The Cell - Biology
Uploaded by
hola2468013579hCopyright:
Available Formats
Movement in and out of the cell
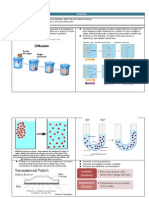
Diffusion: it's the net movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area
of lower concentration. Its a passive transport, which means the molecules don't need
energy to move, it's a natural process
Factors that affect the rate of diffusion.
Temperature, the higher the temperature, the more kinetic energy the particles will have, so
they will move faster, making diffusion happen a lot faster
Surface area, the greater the surface area of the membrane, the faster the diffusion, you can
think about it like there are more entry and exit areas for the molecules to move.
Concentration Gradient, the greater the difference between the concentration of a substance
in two different areas, the faster diffusion will be
Osmosis:it's the diffusion of water molecules from an area of higher water potential to an
area of lower water potential through a partially permeable membrane. It's a passive form of
transport.
Water goes where there is less water and more solute
If…..
More water outside an animal cell, water will continuously enter the cell, until it explodes
More water inside an animal cell, water will continuously leave the cell, until it shrinks
More water outside a plant cell, water will continuously enter the cell, but only the vacuole
and cytoplasm will swell because of the strong cell wall
More water inside a plant cell, water will continuously leave the cell, but the cell will remain
the same.
Active Transport: It's the movement of molecules and ions through a partially permeable
membrane against a concentration gradient, in other words, from an area of low
concentration to an area of high concentration.
Special transport proteins pick up the molecules from outside the cell and push them inside
the cell.
You might also like
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument4 pagesMovement in and Out of Cellshillskimberly24No ratings yet
- Personal NotesDocument7 pagesPersonal NoteslayshengNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Chapter 3: Movement in & Out of CellsDocument7 pagesIGCSE Biology Chapter 3: Movement in & Out of CellsNabil Ahmed100% (1)
- Movement Into and Out of Cells Objectives:3.1Document12 pagesMovement Into and Out of Cells Objectives:3.1Army ForeverNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells 1Document10 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells 1saadNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument34 pagesUnit 3 Movement Into and Out of Cellsgvm6wfg6sqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Movement Into and Out of The CellDocument17 pagesChapter 3 - Movement Into and Out of The CellshammmssNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of The CellDocument17 pagesMovement Into and Out of The CellsamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- 3 Diffusion & OsmosisDocument27 pages3 Diffusion & OsmosisnasserkhanNo ratings yet
- Active & Passive TransportDocument22 pagesActive & Passive TransportnobdyNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport and HomeostasisDocument2 pagesCell Transport and Homeostasishomamunfat100% (1)
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument6 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisCharlesNo ratings yet
- Diffusion, Osmosis AND Active TransportDocument18 pagesDiffusion, Osmosis AND Active TransportScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Gene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisDocument5 pagesGene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisbodurr571No ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellDocument6 pagesMovement in and Out of CellMahamudul HassanNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Diffusion: Diffusion in Living OrganismsDocument12 pages3.1 Diffusion: Diffusion in Living OrganismsX GamerNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Diffusion in Living Organisms: Diffusion Across The Cell MembraneDocument11 pagesDiffusion Diffusion in Living Organisms: Diffusion Across The Cell MembraneRahil BhavanNo ratings yet
- Membran: Kusumo Hariyadi Blok 3Document10 pagesMembran: Kusumo Hariyadi Blok 3YUFFANo ratings yet
- In and Out of CellsDocument3 pagesIn and Out of CellsA personNo ratings yet
- Movement in and OutDocument35 pagesMovement in and OutzefanyaNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells NotesDocument9 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells Notesmanarehab35No ratings yet
- Osmosis and DiffusionDocument1 pageOsmosis and DiffusionChristine Kylene AycardoNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument12 pagesCell TransportAirinne GuardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Doc 4Document4 pagesChapter 1 Doc 4Enju ChipepeNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Vs OsmosisDocument3 pagesDiffusion Vs OsmosisK TanNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument10 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsMoni VillalbaNo ratings yet
- BS 1Document12 pagesBS 1JAHANZEB NAZIRNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Osmosis and Active TransportDocument18 pagesDiffusion Osmosis and Active TransportThompson Ta Ta JevonNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument40 pagesMovement in and Out of CellslubaajamesNo ratings yet
- Bio Grade 11 U-4 Note-2Document15 pagesBio Grade 11 U-4 Note-2betelhemwondimu421No ratings yet
- Movement - S-Cool, The Revision WebsiteDocument8 pagesMovement - S-Cool, The Revision WebsiteThilini BadugeNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY SUMMARY TOPIC 3 IgcseDocument5 pagesBIOLOGY SUMMARY TOPIC 3 IgcsesameehaNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells - NOTESDocument5 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells - NOTESAnonymousNo ratings yet
- MF009 3A Transportation Across Cell Membrane James L2Document33 pagesMF009 3A Transportation Across Cell Membrane James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- Science 2.1 ReviewDocument6 pagesScience 2.1 ReviewInes GarciaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Movement of ParticlesDocument18 pagesIgcse Movement of ParticlesYusra Sultan AliNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 3 Movement in and Out of Cells - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument1 pageDefinitions - Topic 3 Movement in and Out of Cells - CAIE Biology IGCSEisraa jaaboNo ratings yet
- Movement Across The Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesMovement Across The Cell MembraneUmi Zaheera AzharNo ratings yet
- Las-Q3-Wk6.1 2Document12 pagesLas-Q3-Wk6.1 2Jhude JosephNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology: Membrane Transport: Prepared By: Mr. Charlie C. Falguera, RN, MANDocument15 pagesCell Physiology: Membrane Transport: Prepared By: Mr. Charlie C. Falguera, RN, MANchfalgueraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document11 pagesChapter 11Atharva SchoolsNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument23 pagesCell Transport7104No ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument16 pagesTransport Across The Cell MembraneJagruti MaratheNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Movement in and Out of CellsDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Movement in and Out of CellsWezu heavenNo ratings yet
- SiglerDocument2 pagesSigleri kmnwNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Cellular TransportDocument22 pagesLesson 3 Cellular Transportjansameh16No ratings yet
- Bio 100 - 2Document19 pagesBio 100 - 2Duain Areed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument17 pagesMovement Into and Out of CellsFaiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- BioCLab Mod3Document11 pagesBioCLab Mod3Samantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument2 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisMera FunportalNo ratings yet
- Section 2cDocument9 pagesSection 2cdrsohaireNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument9 pagesMovement Into and Out of CellsMuhammad Ahmad NoorNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport MechanismsDocument8 pagesCell Transport MechanismsNhorielyn Joy Disbaro BaltazarNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Movement in and Out of The CellDocument10 pagesCH 3 Movement in and Out of The CellAmal HassanNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants PDFDocument10 pagesTransport in Plants PDFAlhiza JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument30 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsEmy AnkrahNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport NotesDocument10 pagesCell Transport NotesReyad BarbarNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Cells in Its EnvironmentDocument14 pagesGrade 7 Science Cells in Its Environmentapi-235404570100% (1)
- Cell Transport ReviewerDocument9 pagesCell Transport ReviewerNa LuNo ratings yet