Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Definition of Terms
Definition of Terms
Uploaded by
bpcadayong30Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition of Terms
Definition of Terms
Uploaded by
bpcadayong30Copyright:
Available Formats
Definition of Terms
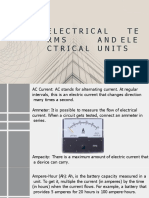
Module 1: Electric Charges, Induction, Conduction and Coulomb’s Law
Charging by Conduction- occurs when a charged object comes into contact
with a neutral object.
Charging by Induction- method of charging an object without physically
touching it to another charged object.
Coulomb’s Law- a law stating that opposing charges repel and similar charges
attract, with a force proportional to the product of the charges and inversely
proportional to the square of the distance between them
Conductors- materials the allow electrons to flow freely from particle to particle
Electrically charge- objects that have imbalance number of protons and
electrons
Electrons- negatively charged subatomic particles
Electrostatic Force- an example of non-contact forces or those that pull or push
on objects without actually contacting them.
Insulators- materials that block the flow of electron from particle to particle
Negative Charge- a charge that an object carries when it contains more
electrons
Neutral- objects that typically have equal number of protons and electrons
Neutrons- neutrally charged subatomic particles
Positive Charge- a charge that an object carries when it contains more protons
Protons- positively charged subatomic particles
Static Electricity - a fixed electric charge caused by friction that creates sparks
or crackling or attracts dust or hair
Van de Graaff generator- an electrostatic-accelerator used in science
investigations to achieve high voltages in a short period of time while maintaining
a high safety factor
Module 2: Electric Force, Electric Field, Electric Flux, Gauss Law
Electric field- a physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles and
exerts force on all other charged particles in the field, either attracting or repelling
them
Electric Flux- property of an electric field that may be thought of as the number
of electric lines of force (or electric field lines) that intersects a given area
Field Line- A graphical technique for viewing vector fields. It is made up of a
directed line that is perpendicular to the field vector at each point along its length.
Gauss’s Law- a law stating that the electric flux across any closed surface is
proportional to the net electric charge encompassed by the surface
Gaussian Surface- a three-dimensional closed surface through which the flux of
a vector field is computed; typically, electric field, magnetic field, the gravitational
field
Module 3: Electric Force, Electric Field, Electric Flux, Gauss Law
Electric Potential- the amount of work energy required to transport a unit of
electric charge in an electric field from a reference point to a particular point
Electric Potential Difference- also known as voltage, it is the external work
required to move a charge from one spot to another in an electric field.
Additionally, it is the change in potential energy experienced by a test charge
with a value of +1
Electric Potential Energy- the amount of energy required to move a charge
against an electric field
Equipotential- refers to an area of space in which every point has the same
electric potential.
Equipotential Lines- the places where electric potential is constant in two
dimensions
Equipotential Surfaces- the places where the electric potential is constant in
three dimensions
Reference Point- a location or object used for comparison to establish whether
or not something is in motion
Module 4: Capacitance and Dielectrics
Capacitance- a measure of the capacity of storing electric charge for a given
potential difference
Capacitor- a device that stores electrical energy, particularly electrical potential
energy, in an electric field
Dielectric- an insulating material or an extremely weak conductor of electric
current
Parallel Connection- components linked in parallel are connected via multiple
routes and since the components are connected in parallel, the circuit divides the
current flow
Parallel Plate Capacitor- a type of capacitors which that have an arrangement
of electrodes and insulating material (dielectric).
Polarized Capacitor- a type of capacitor that has implicit polarity, which means it
can only be connected in one way in a circuit.
Resistor- a device that has been intended to block the passage of an electric
current
Series Connection- components linked in series are connected along a single
electrical route and the same amount of current runs through all of its
components.
Standard Capacitor- a capacitor that is built in such a way that its capacitance
value does not fluctuate with temperature and is known to a high degree of
precision.
Terminal Voltage- it is the potential difference across the terminals of a load
when the circuit is turned on
You might also like
- Members' Directory 2023 ICSB FinalDocument228 pagesMembers' Directory 2023 ICSB FinalJoynul Abedin100% (1)
- Masterplan TemplateDocument72 pagesMasterplan TemplateMostafa FawzyNo ratings yet
- Category: Grading Rubric For Storyboard ProjectDocument1 pageCategory: Grading Rubric For Storyboard ProjectRyan EstonioNo ratings yet
- Physics STM 004 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhysics STM 004 ReviewerDrake AlzonaNo ratings yet
- 3RD GRADING - PhysicsDocument2 pages3RD GRADING - PhysicsLJ Princess Mary MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge-It Determines The: Gen. Physics 2 Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesElectric Charge-It Determines The: Gen. Physics 2 Lecture NotesDaryllNo ratings yet
- Technological I-Wps OfficeDocument38 pagesTechnological I-Wps OfficePhilip MiguelNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms in Electrostatics and Electricity and MagnetismDocument4 pagesDefinition of Terms in Electrostatics and Electricity and MagnetismCaca HutajuluNo ratings yet
- Content Basic Terminology Subject Physics Class XII Date 27/03/2020 Subject Teacher Satish PatidarDocument3 pagesContent Basic Terminology Subject Physics Class XII Date 27/03/2020 Subject Teacher Satish PatidarConcepts Classes IndoreNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument7 pagesDefinitionsAnoushka PradhanNo ratings yet
- Name: Werner Jefferson Barrios Zepeda ID: 2012 IT3Document2 pagesName: Werner Jefferson Barrios Zepeda ID: 2012 IT3Jefferson BarriosNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: Coulomb's LawDocument16 pagesElectrostatics: Coulomb's LawTafazzul HazqueelNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSquiz2 1Document2 pagesPHYSICSquiz2 1AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Physics 1.8Document14 pagesPhysics 1.8Priya MalpaniNo ratings yet
- Coulombs Law, Gauss Law, Electric PotentialDocument50 pagesCoulombs Law, Gauss Law, Electric Potentialbryan valle100% (1)
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledJoyce LonzagaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDFDocument19 pagesElectrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDFDipayan DasNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDF PDFDocument19 pagesElectrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDF PDFAryanNo ratings yet
- Basic EE Module 123Document32 pagesBasic EE Module 123Benmark JabayNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Electronics & Comp - SkillDocument44 pagesBasic Electrical Electronics & Comp - SkillPAnkaj BhamareNo ratings yet
- Physics Section D-Electricity and MagnetismDocument10 pagesPhysics Section D-Electricity and MagnetismNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument2 pagesHandoutsShiella BaculpoNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument7 pages3rd Quarter ReviewerJohn Dareen CabelloNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms SummaryDocument3 pagesDefinition of Terms SummaryWenith YapanaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument2 pagesPhysicsAlyssa BihagNo ratings yet
- CoulombsDocument47 pagesCoulombsTrishia LimpinNo ratings yet
- Science Probe 9 Cheat Sheet Ch9-11Document2 pagesScience Probe 9 Cheat Sheet Ch9-11derpNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade - Xii: ElectrostaticsDocument51 pagesPhysics Grade - Xii: Electrostaticskarthikeyan annamalaiNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument7 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsRajender ReddyNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesPhysics 2 ReviewerChickenOn TheRoofNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Energy and Electricity ConservationDocument6 pagesModule 5 - Energy and Electricity ConservationParth KumarNo ratings yet
- Main Topic Ce0053Document49 pagesMain Topic Ce0053JOSHUA MEYER ANGELESNo ratings yet
- Electricity I 1Document9 pagesElectricity I 1Charles Daniel Torre MalolesNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electricity: Circuits 1 Fall 2005 Harding University Jonathan WhiteDocument23 pagesFundamentals of Electricity: Circuits 1 Fall 2005 Harding University Jonathan Whitegobra senNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 (Basic Electrical Terms and Definitions)Document10 pagesLecture 1 (Basic Electrical Terms and Definitions)ayesha khalidNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 (3 Quarter) : Prepared by Engr. Jackielou D. Decena, Ms EceDocument55 pagesGeneral Physics 2 (3 Quarter) : Prepared by Engr. Jackielou D. Decena, Ms EceSpace Monkey100% (1)
- Basic Electrical Terms and DefinitionsDocument6 pagesBasic Electrical Terms and DefinitionsJericho CunananNo ratings yet
- ART INTEGRATED PROJECT - PhysicsDocument6 pagesART INTEGRATED PROJECT - PhysicsShifa SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Class 12 PhysicsDocument1 pageClass 12 PhysicsIshraq KhanNo ratings yet
- Utilities Module 1Document24 pagesUtilities Module 1Camille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- Electric Field: CapacitanceDocument2 pagesElectric Field: CapacitanceAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Electrical Terms and Electrical Units.Document7 pagesDefinition of Electrical Terms and Electrical Units.julianaquino1203No ratings yet
- Electrical Terms (Incomplete)Document1 pageElectrical Terms (Incomplete)Liezel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Electric Circuits - Vocabulary WordsDocument4 pagesElectricity and Electric Circuits - Vocabulary WordsalmolauraaNo ratings yet
- Building Electrical SystemsDocument24 pagesBuilding Electrical SystemsCamille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Electrical TermsDocument8 pagesGlossary of Electrical TermsRafael jei GabisanNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Electricity and Magnetism MidDocument3 pagesGlossary of Electricity and Magnetism MidPadmi RianiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electricity: Physics Dr. AlexanderDocument39 pagesFundamentals of Electricity: Physics Dr. AlexanderPatrickNo ratings yet
- Key Terms OldDocument4 pagesKey Terms Oldklewis1764No ratings yet
- Physics Topic 5 Study GuideDocument8 pagesPhysics Topic 5 Study GuideSai 0235No ratings yet
- 23.1. Properties of Electric Charges: NegativeDocument11 pages23.1. Properties of Electric Charges: NegativeThiện TrầnNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 ReviewerDocument1 pageQuiz 1 ReviewerJOHNWIN NOBLEZANo ratings yet
- GENERAL PHYSICS II - Electric Potential &: Capacitance and CapacitorsDocument11 pagesGENERAL PHYSICS II - Electric Potential &: Capacitance and CapacitorsKarel Cyra CallorinaNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard (I.S.) Fundamental Definitions A.C. QuantitiesDocument3 pagesIndian Standard (I.S.) Fundamental Definitions A.C. QuantitiesPavan KhetrapalNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits: Learn AboutDocument18 pagesElectricity and Circuits: Learn AboutswatitomarNo ratings yet
- Chapter ELECTRICITYDocument21 pagesChapter ELECTRICITYunknown072006No ratings yet
- Modelling Human BodyDocument28 pagesModelling Human BodyDhananjayNo ratings yet
- Emags and Circ1Document14 pagesEmags and Circ1Compl3x CSGONo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrostatics: by Ace FalconDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Electrostatics: by Ace Falconfalconace94No ratings yet
- Electric Field Strengthin An Uniform Electric FieldDocument12 pagesElectric Field Strengthin An Uniform Electric Fieldadhitya2535No ratings yet
- Electrical Terms and UnitsDocument28 pagesElectrical Terms and UnitsMichael PachecoNo ratings yet
- ES191 Electrical and Electronic CircuitsDocument43 pagesES191 Electrical and Electronic CircuitsAbisan ArulananthamNo ratings yet
- Drilled Shaft in Rock Analysis and Design - Part3Document109 pagesDrilled Shaft in Rock Analysis and Design - Part3rshaghayan100% (2)
- United States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitDocument52 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Glutamine USPDocument3 pagesGlutamine USPJai MurugeshNo ratings yet
- Chemical Analysis of Caustic Soda and Caustic Potash (Sodium Hydroxide and Potassium Hydroxide)Document16 pagesChemical Analysis of Caustic Soda and Caustic Potash (Sodium Hydroxide and Potassium Hydroxide)wilfred gomezNo ratings yet
- Below Mentioned Is The List of Mumbai Management CollegesDocument3 pagesBelow Mentioned Is The List of Mumbai Management CollegesManish SainiNo ratings yet
- MPLS Segment RoutingDocument60 pagesMPLS Segment RoutingDúber PérezNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Culture TechniquesDocument22 pagesBasic Cell Culture TechniquestapanagnihotriNo ratings yet
- Koontz, Dean - Fear That ManDocument73 pagesKoontz, Dean - Fear That Mancbirleanu1963No ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection Systems & HoneypotsDocument33 pagesIntrusion Detection Systems & HoneypotsmanahujaNo ratings yet
- Summary of VivekachudamaniDocument3 pagesSummary of VivekachudamaniBr SarthakNo ratings yet
- ATPAR ReviewerDocument25 pagesATPAR ReviewerJohn Paul BuliyatNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmologists in BC 2011 DecDocument14 pagesOphthalmologists in BC 2011 Decbaby_goatNo ratings yet
- 1359 - 1368. TingkahanDocument5 pages1359 - 1368. TingkahanRizal Daujr Tingkahan IIINo ratings yet
- NSTP Barangay ProfileDocument6 pagesNSTP Barangay ProfilealbertNo ratings yet
- Soy Un Discipulo de JesucristoDocument27 pagesSoy Un Discipulo de JesucristoMaggySUDNo ratings yet
- PDF Compiled, Edited and Designed To Resemble The Official Player's Handbook by NersDocument14 pagesPDF Compiled, Edited and Designed To Resemble The Official Player's Handbook by Nerspimolshaha0% (1)
- The Residences at Greenbelt Manila Tower 1-Bedroom For Sale 24DDocument2 pagesThe Residences at Greenbelt Manila Tower 1-Bedroom For Sale 24DJP ReyesNo ratings yet
- Fiber Post Vs Metal PostDocument13 pagesFiber Post Vs Metal PostOdontología UnibeNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document103 pagesBook 1rebeccags1998No ratings yet
- ICBA V1-0 Print MasterDocument88 pagesICBA V1-0 Print MastermeghaliNo ratings yet
- Monteverdi Clorinda e TancrediDocument19 pagesMonteverdi Clorinda e TancrediFelipeCussenNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Introducing Petty Cash Books: Suggested ActivitiesDocument2 pages1.5 Introducing Petty Cash Books: Suggested ActivitiesDonatien Oulaii100% (2)
- Lesson Plan - First Clarinet Lesson Context:: Time Sequencing AssessmentDocument2 pagesLesson Plan - First Clarinet Lesson Context:: Time Sequencing Assessmentapi-454899087No ratings yet
- STS PrelimDocument5 pagesSTS PrelimGomez Agustin LeslieNo ratings yet
- CONCEALEMENTPOLICYDocument15 pagesCONCEALEMENTPOLICYpogsNo ratings yet
- Shur-Lok Design - Manual PDFDocument35 pagesShur-Lok Design - Manual PDFNicola ZorziNo ratings yet
- Route KPL Train Feb Web2Document7 pagesRoute KPL Train Feb Web2Bernard MivilleNo ratings yet