Professional Documents
Culture Documents
W7 Topic 5D. Market Structure Summary
W7 Topic 5D. Market Structure Summary
Uploaded by
mathisfun.malaysia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOriginal Title
W7 Topic 5D. Market structure summary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesW7 Topic 5D. Market Structure Summary
W7 Topic 5D. Market Structure Summary
Uploaded by
mathisfun.malaysiaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Market Structure Overview
Why study market structure?
Every firm exists to maximize profits.
PROFITS = TR – TC
TR = P X Q
Each firm must set the profit maximizing P and Q.
1. To set the profit maximizing P and Q, each firm must understand the characteristics of
the market structure that it is operating in.
2. Then it can set the profit maximising P and Q.
3. Is the market structure good for society even though a firm can make profits?
4. Are there special features in each market structure?
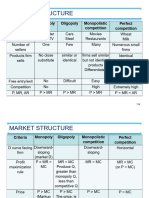
1. ASSUMPTIONS / CHARACTERISTICS
- What are the assumptions?
- Compare the assumptions
Perfect Monopoly Monopolistic Oligopoly
Competition Competition
1 No of firms Many Sole/ only 1 Many Few large
sellers
2 Type of product Homogeneous Unique/ Differentiated Homogeneous
Differentiated
No substitute
3 Entry barriers No Yes No Yes
4 Pricing Price taker Price maker Price maker Price maker
5 Perfect Information Yes No No No
2. PROFIT MAXIMISATION
Price and Quantity decision
Perfect Monopoly Monopolistic Oligopoly
Competition Competition
A Pricing
1 Demand curve Horizontal Downward Downward Downward
Perfectly sloping sloping. sloping.
elastic More elastic Kinked
than monopoly
2 Market power Price taker Price maker Price maker Price marker
3 Price and revenue P=MR P>MR P>MR P>MR
B Quantity MC =MR MC =MR MC =MR MC=MR
P = MC
3. IS THE MARKET STRUCTURE GOOD FOR SOCIETY?
Perfect Monopoly Monopolistic Oligopoly
Competition Competition
1 Allocative efficient Yes. NO NO NO
P=MC P>MC P>MC P>MC
2 Productive efficient Yes. No. No. No.
P=min ATC P>min ATC P>min ATC P>min ATC
4. SPECIAL FEATURES
1. PC - SHUTDOWN RULE (P < AVC)
2. MONOPOLY - ENTRY BARRIERS
- PRICE DISCRIMINATION
3. MC - PRODUCT DIFFERENTIATION
4. OLIGOPOLY - INTER-DEPENDENT RELATIONSHIP
- COLLABORATION
You might also like
- Business Plan Done On Juice ProcessingDocument25 pagesBusiness Plan Done On Juice Processingbernabas93% (54)
- Chapter 3 Test Bank For Management Information Systems LaudonDocument40 pagesChapter 3 Test Bank For Management Information Systems Laudonmira chehab100% (3)
- Hupseng CompletedDocument23 pagesHupseng CompletedHii Nian Tin80% (5)
- Essentials of Contemporary Management: Final Exam Project Prof. Dr. Rania El-Reedy Reham Samir Alaa Sobhy Rana SamirDocument16 pagesEssentials of Contemporary Management: Final Exam Project Prof. Dr. Rania El-Reedy Reham Samir Alaa Sobhy Rana SamirMohamed Raheem100% (1)
- 4 Market StructuresDocument34 pages4 Market StructuresPamelaMariePatawaranNo ratings yet
- LBS Casebook 2010-2011Document58 pagesLBS Casebook 2010-2011Archibald_Moore100% (3)
- Solutions Manual Compensation 9th Edition MilkovichDocument13 pagesSolutions Manual Compensation 9th Edition MilkovichJeeta Sarkar0% (1)
- Chapter 8 MEDocument61 pagesChapter 8 MEHaryadi WidodoNo ratings yet
- Ape 11 2 15 Oli Monocomp For Real Part 1Document10 pagesApe 11 2 15 Oli Monocomp For Real Part 1Kris ANo ratings yet
- FqN1EX3p PDFDocument41 pagesFqN1EX3p PDFjxh6mw58j9No ratings yet
- Current NewsDocument22 pagesCurrent NewsShivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document24 pagesChapter 10prabhuthalaNo ratings yet
- Market Structure - ComparisionDocument4 pagesMarket Structure - Comparision23070977No ratings yet
- Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive MarketsDocument21 pagesManaging in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive MarketsAngelyn SamandeNo ratings yet
- Market 学生版Document29 pagesMarket 学生版405242027No ratings yet
- Monopoly and OligopolyDocument32 pagesMonopoly and OligopolySanchit MiglaniNo ratings yet
- Unit IIIDocument67 pagesUnit IIIprinceNo ratings yet
- Perfect CompetitionDocument53 pagesPerfect CompetitionDattsdNo ratings yet
- Lect17 Mon CompDocument40 pagesLect17 Mon CompRahm TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Monopolistc Competition 3Document10 pagesMonopolistc Competition 3Abid SunnyNo ratings yet
- Eco 1 - Monopolistic Compt (2021) - ClassDocument46 pagesEco 1 - Monopolistic Compt (2021) - ClassGururaj GrampurohitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Market StructureDocument36 pagesChapter 6 Market StructureChen Yee KhooNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic CompetitionDocument37 pagesMonopolistic CompetitionIshika ShahNo ratings yet
- Market Competition Actual1123Document27 pagesMarket Competition Actual1123oshimo.tokuNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic Competition: A2 MicroDocument29 pagesMonopolistic Competition: A2 MicroAjayGuptaNo ratings yet
- MonopolyDocument27 pagesMonopolyAri TamaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 (MC and Oligopoly - Revised)Document16 pagesUnit 5 (MC and Oligopoly - Revised)Vanshi PulasariaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledBhebz Erin Mae0% (1)
- Monopolist C IDocument10 pagesMonopolist C Iragib rahmanNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Perfect CompetitionDocument18 pagesUnit II - Perfect CompetitionSam Ebenezer .SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Monopolies Look For The Answers To These QuestionsDocument20 pagesChapter 15 Monopolies Look For The Answers To These QuestionsshamsaNo ratings yet
- CH - 6 Market Structure - FinalDocument48 pagesCH - 6 Market Structure - FinalAkhil JosephNo ratings yet
- Review Assignment 1 Market Structure Archetypes: - Defining Your Market - Perfect Competition - MonopolyDocument28 pagesReview Assignment 1 Market Structure Archetypes: - Defining Your Market - Perfect Competition - MonopolyKarl LuzungNo ratings yet
- I Mcom Bus EcoDocument39 pagesI Mcom Bus Ecokirthi nairNo ratings yet
- 15 MonopolyDocument45 pages15 Monopolymubeen yaminNo ratings yet
- Eco 1 - Monopolistic ComptDocument67 pagesEco 1 - Monopolistic ComptYAKKALA VENKATA SANDEEPNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10. Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly: N N N N N N N NDocument7 pagesChapter 10. Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly: N N N N N N N NBasanta K SahuNo ratings yet
- CH 17Document23 pagesCH 17debesayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - 16Document20 pagesChapter 15 - 16Zubeda SaraNo ratings yet
- Non Competitive MarketsDocument7 pagesNon Competitive Marketsyodel23957No ratings yet
- Perfect Competition - PPTDocument27 pagesPerfect Competition - PPTShrawani DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Chương 4 EngDocument61 pagesChương 4 EngVĩnh Tân TrầnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13Document12 pagesLecture 13CHAMP TAHA OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- Busi - Eco - PPT 3Document31 pagesBusi - Eco - PPT 3jana.aparna1981No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Business EconomicsDocument15 pagesLecture 4 Business EconomicsTayyaba JawedNo ratings yet
- Monopoly MonopolisticDocument30 pagesMonopoly MonopolisticDr. Sameer KulkarniNo ratings yet
- MonopolyDocument50 pagesMonopolyVishwa Srikanth100% (1)
- MonopolisticDocument25 pagesMonopolisticDharshini RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Micro Ch15 PresentationDocument31 pagesMicro Ch15 PresentationZakaria SakibNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document40 pagesUnit 7unstopable 7 rodiesNo ratings yet
- MONOPOLY Market Spring 2022Document50 pagesMONOPOLY Market Spring 2022Abid SunnyNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic Competition PresentationDocument17 pagesMonopolistic Competition PresentationMarjan Arbab0% (1)
- Chapter 10 - Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly - OnlineDocument30 pagesChapter 10 - Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly - OnlineAudryssa YuanwieNo ratings yet
- Types of Market and Its Price Determination-1Document28 pagesTypes of Market and Its Price Determination-1Pratik BhoirNo ratings yet
- Summary of Market StructuresDocument3 pagesSummary of Market StructuresyvettedeocampoNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic KrugmanDocument22 pagesMonopolistic Krugmanmoshiur.29056No ratings yet
- R16 The Firm and Market Structures PDFDocument37 pagesR16 The Firm and Market Structures PDFROSHNINo ratings yet
- Reading 9 - The Firm & Market StructuresDocument34 pagesReading 9 - The Firm & Market StructuresAllen AravindanNo ratings yet
- 12 - Econ 190.2 - Market Failure PDFDocument29 pages12 - Econ 190.2 - Market Failure PDFErielle SibayanNo ratings yet
- 1.11 Market StructuresDocument37 pages1.11 Market StructuresChristina CarinoNo ratings yet
- Market Structure 1: Perfect Competition and MonopolyDocument30 pagesMarket Structure 1: Perfect Competition and Monopolyshubh suriNo ratings yet
- Discussion A 6Document39 pagesDiscussion A 6anupamsaha107No ratings yet
- Market Structure: MonopolyDocument26 pagesMarket Structure: MonopolySHEKHAR SHUKLANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Market Structures AND Pricing Policies: Unit Iii Part-IDocument39 pagesIntroduction To Market Structures AND Pricing Policies: Unit Iii Part-Igoyal_khushbu88No ratings yet
- Perfectly Competitive Markets: - Many Firms Offering Identical Products, - So Each Firm Has Little Influence Over Price - Price TakersDocument41 pagesPerfectly Competitive Markets: - Many Firms Offering Identical Products, - So Each Firm Has Little Influence Over Price - Price TakersBhaskar PriyadarshiNo ratings yet
- Journal ReviewDocument9 pagesJournal ReviewYat's YinaNo ratings yet
- Banking Industry-Final Report Group 18Document14 pagesBanking Industry-Final Report Group 18Pranav KumarNo ratings yet
- Brand Audit ReportDocument17 pagesBrand Audit ReportRegie RivaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: Background of The StudyDocument32 pagesChapter-1: Background of The StudyPHANTOM 017No ratings yet
- Types of MonopoliesDocument8 pagesTypes of MonopoliesMuzna AijazNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan FinalDocument15 pagesMarketing Plan Finalapi-301056313No ratings yet
- AQA Business IG Year 2Document239 pagesAQA Business IG Year 2Trinh LinhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document28 pagesChapter 12mathewpaul007100% (1)
- Management Fest: A Malgamat Ion of Talent, K Now Ledge & Innovat IonDocument25 pagesManagement Fest: A Malgamat Ion of Talent, K Now Ledge & Innovat IonDikhita MajheeNo ratings yet
- Square Pharma ReportDocument15 pagesSquare Pharma ReportrasfaqurNo ratings yet
- Vertical and HorizonntalDocument5 pagesVertical and HorizonntalFarooqChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Causes and Effects of Examination Malpractice in Secondary SchoolsDocument8 pagesCauses and Effects of Examination Malpractice in Secondary SchoolsAdiuku Kelechi WhitneyNo ratings yet
- Business Plan: Bulacan Ecumenical SchoolDocument16 pagesBusiness Plan: Bulacan Ecumenical SchoolNikkinicole Jawod CubitaNo ratings yet
- CA - 2 Abuse of Dominant Position Competition LawDocument7 pagesCA - 2 Abuse of Dominant Position Competition Lawchaitanya mahendruNo ratings yet
- Case Assignment Questions ALL PDFDocument26 pagesCase Assignment Questions ALL PDFMiscue JoNo ratings yet
- Innovation Agile Project Management and Firm Performance in - 2019 - Socio EconDocument14 pagesInnovation Agile Project Management and Firm Performance in - 2019 - Socio EconAmin HilaliNo ratings yet
- Journal Soewarno Dayasaing OrgperformDocument8 pagesJournal Soewarno Dayasaing Orgperformannisa nurawaliaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Foreign TradeDocument2 pagesModule 2 - Foreign TradejessafesalazarNo ratings yet
- Disposable Diaper Industry: Case AnalysisDocument8 pagesDisposable Diaper Industry: Case AnalysisaabfjabfuagfuegbfNo ratings yet
- Give An Example of A Government-Created Monopoly. Is Creating This Monopoly Necessarily Bad Public Policy? ExplainDocument8 pagesGive An Example of A Government-Created Monopoly. Is Creating This Monopoly Necessarily Bad Public Policy? ExplainMasri Abdul Lasi100% (1)
- CV Felix MunozDocument9 pagesCV Felix MunozAndri YantoNo ratings yet
- Cbmec 2 (Chapter 10 Reviewer)Document8 pagesCbmec 2 (Chapter 10 Reviewer)Shiella marie VillaNo ratings yet
- This Document Presents The Case Study of BRL Hardy: Globalizing An Australian Wine Company (REF), Performed by Group 6Document12 pagesThis Document Presents The Case Study of BRL Hardy: Globalizing An Australian Wine Company (REF), Performed by Group 6george_eldhoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Marketing Environment BIM SMC-TUDocument24 pagesUnit 2 Marketing Environment BIM SMC-TUAnjana RamjaliNo ratings yet