Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phlebotomy and Specimen Considerations
Phlebotomy and Specimen Considerations
Uploaded by
chayiezen0301Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Niagara PlatformDocument266 pagesNiagara PlatformGabor KomuvesNo ratings yet
- Nollet 2015 - Handbook of Food Analysis PDFDocument1,531 pagesNollet 2015 - Handbook of Food Analysis PDFემილი ონოფრე100% (3)
- Capillary Puncture Equipment and ProcedureDocument3 pagesCapillary Puncture Equipment and ProcedureSieg100% (1)
- PMLS 1 Topic 8.1 TransDocument8 pagesPMLS 1 Topic 8.1 TranslalaNo ratings yet
- ST ND RDDocument3 pagesST ND RDYana DNo ratings yet
- Immuno InflammDocument3 pagesImmuno InflammKrizel Anne DeriNo ratings yet
- 2 Cardio Lecture PDFDocument9 pages2 Cardio Lecture PDFNadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- Cardio FinalsDocument17 pagesCardio FinalsNadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- PhlebotomyDocument5 pagesPhlebotomyFuture TrekingNo ratings yet
- Surgical Instrumentation Program: Training Surgical Planning IQX-FT-003-BUCDocument10 pagesSurgical Instrumentation Program: Training Surgical Planning IQX-FT-003-BUCapi-684047665No ratings yet
- Week 4 - PhlebotomyDocument3 pagesWeek 4 - PhlebotomyJay AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- Planeamiento Cambio de Valvula AorticaDocument10 pagesPlaneamiento Cambio de Valvula Aorticaapi-684047665No ratings yet
- Planeamiento Reemplazo de Valvula Aortica RVMDocument11 pagesPlaneamiento Reemplazo de Valvula Aortica RVMapi-684047665No ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 5Document13 pagesBiology Chapter 5Shahzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- CC Blood CollectionDocument3 pagesCC Blood Collectionlcrujido100% (1)
- PMLS 2 Unit 3Document3 pagesPMLS 2 Unit 3Elyon Jirehel AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Renal System Bat NotesDocument41 pagesRenal System Bat NotesAfk SystemNo ratings yet
- RVM CompressedDocument10 pagesRVM Compressedapi-703195004No ratings yet
- Planemientos RVM 1Document10 pagesPlanemientos RVM 1api-703195004No ratings yet
- Kidney Physiology (Q & A)Document28 pagesKidney Physiology (Q & A)ramadan100% (1)
- Lesson Plan On Prom.Document9 pagesLesson Plan On Prom.Archana PaudelNo ratings yet
- 5 IV CannulationDocument61 pages5 IV CannulationNursing Superintendent (SH)No ratings yet
- Physiology Cardiovascular Physiology NotesDocument13 pagesPhysiology Cardiovascular Physiology Noteshedayatamin44No ratings yet
- Urinary System TransesDocument5 pagesUrinary System Transesadrielvamos28No ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesCirculatory System: Science Reviewermarie parfanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System - AnaphyDocument5 pagesCirculatory System - Anaphy4pxg7jgps8No ratings yet
- The Vascular SystemDocument7 pagesThe Vascular SystemMiguel GumatayNo ratings yet
- IVTherapy 2Document24 pagesIVTherapy 2Ayub PakidingNo ratings yet
- Reintervention in Congenital Heart Disease Due To Pulmonary Stenosis and Tricuspid ValvuloplastyDocument7 pagesReintervention in Congenital Heart Disease Due To Pulmonary Stenosis and Tricuspid Valvuloplastyapi-703195004No ratings yet
- Surgical Instrumentation Program: Training Surgical Planning IQX-FT-003-BUCDocument11 pagesSurgical Instrumentation Program: Training Surgical Planning IQX-FT-003-BUCapi-654112138No ratings yet
- Module 7 Capillary Puncture Equipment AND ProcedureDocument6 pagesModule 7 Capillary Puncture Equipment AND ProcedureHazel Joyce Gonda RoqueNo ratings yet
- Aortic Valve ReplacementDocument4 pagesAortic Valve ReplacementDANI SOFIA BENITEZ SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY-Cardiovascular SystemDocument1 pageBIOLOGY-Cardiovascular SystemSilverNo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory and Diagnostic TestsDocument8 pagesCommon Laboratory and Diagnostic TestsCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- Planeamiento Reemplazo de Valvula Aortica RVMDocument11 pagesPlaneamiento Reemplazo de Valvula Aortica RVMapi-684047665No ratings yet
- Planemientos RVMDocument10 pagesPlanemientos RVMapi-703195004No ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Bypass EssentialsDocument29 pagesCardiopulmonary Bypass EssentialsRafsae Iqbal AkbarNo ratings yet
- Charts RenalDocument26 pagesCharts Renallucymuki1975No ratings yet
- They Perform Need To Be Collected Clinical Responsibilities of Urology Nurses at Both The Basic and Advanced Practice LevelDocument6 pagesThey Perform Need To Be Collected Clinical Responsibilities of Urology Nurses at Both The Basic and Advanced Practice LevelNela IndrianiNo ratings yet
- CVP LinesDocument1 pageCVP LinesshifaNo ratings yet
- Bio Crisis - 2nd DayDocument4 pagesBio Crisis - 2nd DayaryanjimeraNo ratings yet
- Planeamientoo RVMDocument10 pagesPlaneamientoo RVMapi-702934667No ratings yet
- Apheresis PrincipleDocument68 pagesApheresis Principlemelisa asibalNo ratings yet
- Arterial Puncture: ComplicationsDocument17 pagesArterial Puncture: ComplicationsGerly MaglangitNo ratings yet
- L02 - 1 - Hemodialysis-Part 1Document20 pagesL02 - 1 - Hemodialysis-Part 1Tec Mohamed A. MengedNo ratings yet
- L02 1 Hemodialysis-Part 1Document20 pagesL02 1 Hemodialysis-Part 1Tec Mohamed A. MengedNo ratings yet
- Original Article: Rapamycin Combined with α-Cyanoacrylate Contributes to Inhibiting Intimal Hyperplasia in Rat ModelsDocument8 pagesOriginal Article: Rapamycin Combined with α-Cyanoacrylate Contributes to Inhibiting Intimal Hyperplasia in Rat ModelsMariantFomperosaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Cardiology: Rebound HypertensionDocument8 pagesNursing Cardiology: Rebound HypertensionVon R SemillaNo ratings yet
- Planeamiento RVM Sin BombaDocument10 pagesPlaneamiento RVM Sin Bombaapi-702934667No ratings yet
- Hema - General Characteristics of Blood and Hematological TestsDocument5 pagesHema - General Characteristics of Blood and Hematological TestsBSMT Kharylle divine FuentibellaNo ratings yet
- PMLS2 - Familiarization in PhleboDocument3 pagesPMLS2 - Familiarization in PhleboCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- Tadadafilo ExpocisionDocument72 pagesTadadafilo ExpocisionCristhian Gabriel Guevara NuñezNo ratings yet
- Planeamientoo RVM 3Document12 pagesPlaneamientoo RVM 3api-702934667No ratings yet
- Platelet CountDocument2 pagesPlatelet CountSirias_black100% (2)
- Specimen Collection and ProcessingDocument6 pagesSpecimen Collection and ProcessingTan DanielNo ratings yet
- Trans PMLS 1 - Batch 2 and 3.Document23 pagesTrans PMLS 1 - Batch 2 and 3.leexxjannelapatNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculationDocument12 pagesBody Fluids and Circulationadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument1 pagePleural Effusionfahad nokiaNo ratings yet
- HEMADocument72 pagesHEMABOEN YATORNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsFrom EverandAntiarrhythmic DrugsAntoni Martínez-RubioNo ratings yet
- Duplex and Color Doppler Imaging of the Venous SystemFrom EverandDuplex and Color Doppler Imaging of the Venous SystemGerhard H. MostbeckNo ratings yet
- Perfusion for Congenital Heart Surgery: Notes on Cardiopulmonary Bypass for a Complex Patient PopulationFrom EverandPerfusion for Congenital Heart Surgery: Notes on Cardiopulmonary Bypass for a Complex Patient PopulationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- SS 1 Agric Science First Term E-NoteDocument58 pagesSS 1 Agric Science First Term E-Notekanajoseph2009No ratings yet
- El Bazar de Los Malos Sueños Stephen King: Venta: #2415356115 Cant: 1Document4 pagesEl Bazar de Los Malos Sueños Stephen King: Venta: #2415356115 Cant: 1Juan Cervantes LópezNo ratings yet
- Piano Pentatonic Blues Scales - Overview With PicturesDocument8 pagesPiano Pentatonic Blues Scales - Overview With PicturesВладимир Перминов100% (2)
- ACA - Exam - Objectives - Photoshop - CC 2018Document5 pagesACA - Exam - Objectives - Photoshop - CC 2018Jeffrey FarillasNo ratings yet
- Goetze Mechanical Face SealsDocument7 pagesGoetze Mechanical Face SealsDheeraj GoswamiNo ratings yet
- General: Specific: Leading Statement:: TITLE: A Healthy LifestyleDocument2 pagesGeneral: Specific: Leading Statement:: TITLE: A Healthy LifestyleM Arshad M AmirNo ratings yet
- Sailing With Paul - IronsideDocument3 pagesSailing With Paul - IronsideLawrence GarnerNo ratings yet
- God Will Protect His Church God Will Protect His ChurchDocument17 pagesGod Will Protect His Church God Will Protect His ChurchLaura GarciaNo ratings yet
- Maribelle Z. Neri vs. Ryan Roy Yu (Full Text, Word Version)Document11 pagesMaribelle Z. Neri vs. Ryan Roy Yu (Full Text, Word Version)Emir MendozaNo ratings yet
- Project of WCM 19c0h008 Madhu MaamDocument41 pagesProject of WCM 19c0h008 Madhu MaamSourav TiwariNo ratings yet
- # Pembagian Kelas Alkes Per KategoriDocument41 pages# Pembagian Kelas Alkes Per KategoriR.A.R TVNo ratings yet
- En 12245 (2022) (E)Document9 pagesEn 12245 (2022) (E)David Chirinos100% (1)
- WorkshopPLUS-PowerShell For The IT Administrator Part 2 PDFDocument2 pagesWorkshopPLUS-PowerShell For The IT Administrator Part 2 PDFArif MohmmadNo ratings yet
- (GUARANTEED RATE AFFINITY) & (8905 BEAVER FALLS) - UCC1 Financial Statement LIENDocument9 pages(GUARANTEED RATE AFFINITY) & (8905 BEAVER FALLS) - UCC1 Financial Statement LIENHakim-Aarifah BeyNo ratings yet
- Teaching PronunciationDocument6 pagesTeaching PronunciationKathryn LupsonNo ratings yet
- Primary Gingival Squamous Cell CarcinomaDocument7 pagesPrimary Gingival Squamous Cell CarcinomaMandyWilsonNo ratings yet
- The Ape-Man: His Kith and KinDocument128 pagesThe Ape-Man: His Kith and KinamitrupaniNo ratings yet
- Note On F3 SC C2 TransportationDocument4 pagesNote On F3 SC C2 Transportationgan tong hock a.k.a ganosNo ratings yet
- Application DevelopmentDocument14 pagesApplication DevelopmentReema MubarakNo ratings yet
- Santiago City, Isabela: University of La Salette, IncDocument1 pageSantiago City, Isabela: University of La Salette, IncLUCAS, PATRICK JOHNNo ratings yet
- Tools, Materials and Equipment in Nail Care: Learning Activity Sheet Week 1 Quarter 1Document8 pagesTools, Materials and Equipment in Nail Care: Learning Activity Sheet Week 1 Quarter 1Barbara PosoNo ratings yet
- P2P Partnering Success Playbook PDFDocument48 pagesP2P Partnering Success Playbook PDFYesenia RamirezNo ratings yet
- Brandi PPT For BrandingDocument27 pagesBrandi PPT For BrandingShah ParinNo ratings yet
- Comsys 2Document10 pagesComsys 2MarjorieNo ratings yet
- World Red Cross DayDocument17 pagesWorld Red Cross DayAshwani K SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower AshraeDocument18 pagesCooling Tower AshraeMAITREE JHANo ratings yet
- DOMINODocument16 pagesDOMINOBerat DalyabrakNo ratings yet
- TestDocument3 pagesTestPopovska KristinaNo ratings yet
Phlebotomy and Specimen Considerations
Phlebotomy and Specimen Considerations
Uploaded by
chayiezen0301Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Phlebotomy and Specimen Considerations
Phlebotomy and Specimen Considerations
Uploaded by
chayiezen0301Copyright:
Available Formats
CLINICAL CHEMISTRY 1
Source: Book,PPT,Discussion
Types of Blood Specimen
Phlebotomy and Specimen Considerations
Whole blood
Introduction - There is still plasma and cellular component
Pre-Analytical (Sample Processing) - When collected must be put in tube containing
Patient anticoagulant
MD test order - Arterial- for pH and blood gases, tube must have
Collection heparin (syringe only)
Transport - Venous
Analytical (Chemical Analysis) Plasma
Analysis - 90% water, 9% organic compound, 1% dissolved
Data flow gases
Post-Analytical (Data Management) - Liquid portion of anticoagulated blood
Interpretation by MD - The yellowish part in whole blood (anticoagulant)
Diagnosis and treatment - With fibrinogen
Phlebotomy Serum
- Process of collecting blood “to cut vein” - Liquid portion of clotted blood
- 2 main procedures: - Clotting factor is active
Venipuncture- used of needle attached - No fibrinogen
to a collecting device
Capillary puncture- collect through Venipuncture Equipment
skin puncture; micro capillary tube Tourniquet - Made of pliable
-Insert needle types- and lancet- rubber
- Strip with Velcro
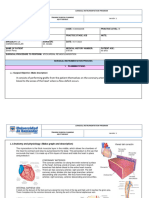
The Vascular System - Locate the patient’s
- Network of arteries, vein and capillaries vein
- Arteries and Vein: - Must not be left for 1
Tunica intima- inner min
Tunica media- middle, thickest Needle - Size: gauge and
Tunica adventia- outer layer bore are inversely
- Capillaries: related
Only have one layer of tissue. - 21 gauge is the
Arteries - Arterial blood in standard for routine
bright res venipuncture
- Oxygenated blood -
- Collected through 90 Evacuated Tube - Multiple sample
degrees. System - Tube holder
- Performed by (barrel/adapter)
physician or RT - Evacuated tubes
Vein - Venous blood is Needle and syringe - Syringe needle
dark red - Syringe
- Deoxygenated blood - Transfer device
Capillaries - Smallest blood Winged Infusion Set - Luer fitting
vessels (Butterfly) (for syringe)
- One cell thick to - Luer adapter
allow for gas and (for ETS)
nutrient exchange Tube and a. Anticoagulant
Tube additives Light blue
Phlebotomy sites (citrate)
- Cephalic- second choice Green
- Median cubital- most preferred site (heparin)
- Basilic vein- least favorable site; near to brachial Lavender
artery, nerves and tendon; do not anchor. (EDTA)
- Other sites: hand vein- small, less anchored, b. Antiglycolytic
painful agents
Gray (sodium
fluoride)
c. Clot Activators
Red (silica)
MA. PATRICIA VILLANUEVA 1
CLINICAL CHEMISTRY 1
Source: Book,PPT,Discussion
Orange Plasma Preparation - Pearl top
(thrombin) Tube - EDTA, thixotropic
d. Thixotropic Gel gel
Gold (serum) - Molecular
Light green diagnostics
(plasma) Fluoride tubes - Gray
Pearl or white - Na fluoride / K
oxalate
Order of Draw - Chemistry
- Reduce the risk of specimen contamination by ESR tubes - Black
microorganisms and additive carry over - Na citrate
- Hematology
ACD tubes - Yellow
- Na3 citrate, citric
acid dextrose
Trace element tubes - Royal blue, tan, light
brown
- Plain Na heparin
- Toxicology
- Tan/Light brown
- K2 EDTA, Na
heparin
- Lead testing
Blood donor bags
Pre-analytic Consideration
Problem sites:
Burns
Blood Culture tubes - Yellow Scars tattoos
- Sodium Polyanethol Damaged veins
Sulfonate SPS Hematoma- cold compress treatment then hot
- Microbiology Edema
Coagulation tubes - Light blue Mastectomy
- Sodium citrate IV Therapy
- Hematology Heparin and Saline Locks
Glass- non additive tube - Red Fistulas
- No additive Procedural Error Risk:
- Chemistry,BB, Hematoma
Serology Iatrogenic anemia
Plastic clot activator tube - Red Infection of the site
- Silica particles Nerve injury
- Chemistry Inadvertent arterial puncture
Serum separator Tubes - Gold plastic/red & Reflux
gray rubber Patient Conditions and Complications:
- Silica particles/ Allergies to supplies and equipment
thixotropic gel Excessive bleeding
- Chemistry Syncope
Plasma separator tube - Light Nausea or vomiting
green/green/gray Obese patients
rubber Pain
- Lithium heparin, Petechiae
thixotropic gel Seizures/convulsion
- Chemistry
Heparin tubes - Green
- Lithium heparin
- Chemistry
EDTA tubes - Lavender/pink
- EDTA
- Hematology and BB
MA. PATRICIA VILLANUEVA 2
CLINICAL CHEMISTRY 1
Source: Book,PPT,Discussion
Capillary Specimen Collection Hemolyzed- destruction of RBC result in
- Blood is collected using lancet or skin puncture. pinkish to red of serum and plasma; affect
Collection site: potassium and enzyme testing
Outer area of heel Icteric- yellowish
Fingers Stopper removal
Earlobe Stopper removal devices
Materials: Face shield
Lancets Splash shield
Warming device Aliquot Preparation
Micro collection tubes - For multiple test in a single specimen
Microhematocrit tubes - Stored at 4 or -20 degrees for 8 hrs.
Sealants
Capillary Order of Draw
Blood gases (heparin)
EDTA
Sodium Heparin
Other additive
Non additive
Indications of Capillary Puncture
Inaccessible veins
Fragile veins
Thrombotic tendencies
POCT
Small blood volume
Prevent injury
Newborn Screening
- Collected by heel puncture.
Specimen Processing
Routine handling
Mixing tubes:
- Invert 3-8 x
Transporting Specimens:
- Plastic bag with logo of biohazard
Delivery time limits:
- 45 minutes after collection
- Centrifuged within 1-2 hour
Special Handling
- Maintained at 37 degrees (heat block)
- Chilled (using crushed ice)
- Wrapped on foil
Specimen Suitability
- Hemolyzed
- Collection in wrong tube
- Failure to follow timing and handling requirements
- Quantity not sufficient
- Clotting in WB or plasma specimen
Centrifugation
- Specimens must be completely clotted within 30-
60 minutes at room temp.
- Visually check:
Lipemic- cloudy, turbid appearance,
presence of lipid and a non-fasting
specimen; interferes with colorimetric
analysis
MA. PATRICIA VILLANUEVA 3
You might also like
- Niagara PlatformDocument266 pagesNiagara PlatformGabor KomuvesNo ratings yet
- Nollet 2015 - Handbook of Food Analysis PDFDocument1,531 pagesNollet 2015 - Handbook of Food Analysis PDFემილი ონოფრე100% (3)
- Capillary Puncture Equipment and ProcedureDocument3 pagesCapillary Puncture Equipment and ProcedureSieg100% (1)
- PMLS 1 Topic 8.1 TransDocument8 pagesPMLS 1 Topic 8.1 TranslalaNo ratings yet
- ST ND RDDocument3 pagesST ND RDYana DNo ratings yet
- Immuno InflammDocument3 pagesImmuno InflammKrizel Anne DeriNo ratings yet
- 2 Cardio Lecture PDFDocument9 pages2 Cardio Lecture PDFNadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- Cardio FinalsDocument17 pagesCardio FinalsNadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- PhlebotomyDocument5 pagesPhlebotomyFuture TrekingNo ratings yet
- Surgical Instrumentation Program: Training Surgical Planning IQX-FT-003-BUCDocument10 pagesSurgical Instrumentation Program: Training Surgical Planning IQX-FT-003-BUCapi-684047665No ratings yet
- Week 4 - PhlebotomyDocument3 pagesWeek 4 - PhlebotomyJay AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- Planeamiento Cambio de Valvula AorticaDocument10 pagesPlaneamiento Cambio de Valvula Aorticaapi-684047665No ratings yet
- Planeamiento Reemplazo de Valvula Aortica RVMDocument11 pagesPlaneamiento Reemplazo de Valvula Aortica RVMapi-684047665No ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 5Document13 pagesBiology Chapter 5Shahzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- CC Blood CollectionDocument3 pagesCC Blood Collectionlcrujido100% (1)
- PMLS 2 Unit 3Document3 pagesPMLS 2 Unit 3Elyon Jirehel AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Renal System Bat NotesDocument41 pagesRenal System Bat NotesAfk SystemNo ratings yet
- RVM CompressedDocument10 pagesRVM Compressedapi-703195004No ratings yet
- Planemientos RVM 1Document10 pagesPlanemientos RVM 1api-703195004No ratings yet
- Kidney Physiology (Q & A)Document28 pagesKidney Physiology (Q & A)ramadan100% (1)
- Lesson Plan On Prom.Document9 pagesLesson Plan On Prom.Archana PaudelNo ratings yet
- 5 IV CannulationDocument61 pages5 IV CannulationNursing Superintendent (SH)No ratings yet
- Physiology Cardiovascular Physiology NotesDocument13 pagesPhysiology Cardiovascular Physiology Noteshedayatamin44No ratings yet
- Urinary System TransesDocument5 pagesUrinary System Transesadrielvamos28No ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesCirculatory System: Science Reviewermarie parfanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System - AnaphyDocument5 pagesCirculatory System - Anaphy4pxg7jgps8No ratings yet
- The Vascular SystemDocument7 pagesThe Vascular SystemMiguel GumatayNo ratings yet
- IVTherapy 2Document24 pagesIVTherapy 2Ayub PakidingNo ratings yet
- Reintervention in Congenital Heart Disease Due To Pulmonary Stenosis and Tricuspid ValvuloplastyDocument7 pagesReintervention in Congenital Heart Disease Due To Pulmonary Stenosis and Tricuspid Valvuloplastyapi-703195004No ratings yet
- Surgical Instrumentation Program: Training Surgical Planning IQX-FT-003-BUCDocument11 pagesSurgical Instrumentation Program: Training Surgical Planning IQX-FT-003-BUCapi-654112138No ratings yet
- Module 7 Capillary Puncture Equipment AND ProcedureDocument6 pagesModule 7 Capillary Puncture Equipment AND ProcedureHazel Joyce Gonda RoqueNo ratings yet
- Aortic Valve ReplacementDocument4 pagesAortic Valve ReplacementDANI SOFIA BENITEZ SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY-Cardiovascular SystemDocument1 pageBIOLOGY-Cardiovascular SystemSilverNo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory and Diagnostic TestsDocument8 pagesCommon Laboratory and Diagnostic TestsCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- Planeamiento Reemplazo de Valvula Aortica RVMDocument11 pagesPlaneamiento Reemplazo de Valvula Aortica RVMapi-684047665No ratings yet
- Planemientos RVMDocument10 pagesPlanemientos RVMapi-703195004No ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Bypass EssentialsDocument29 pagesCardiopulmonary Bypass EssentialsRafsae Iqbal AkbarNo ratings yet
- Charts RenalDocument26 pagesCharts Renallucymuki1975No ratings yet
- They Perform Need To Be Collected Clinical Responsibilities of Urology Nurses at Both The Basic and Advanced Practice LevelDocument6 pagesThey Perform Need To Be Collected Clinical Responsibilities of Urology Nurses at Both The Basic and Advanced Practice LevelNela IndrianiNo ratings yet
- CVP LinesDocument1 pageCVP LinesshifaNo ratings yet
- Bio Crisis - 2nd DayDocument4 pagesBio Crisis - 2nd DayaryanjimeraNo ratings yet
- Planeamientoo RVMDocument10 pagesPlaneamientoo RVMapi-702934667No ratings yet
- Apheresis PrincipleDocument68 pagesApheresis Principlemelisa asibalNo ratings yet
- Arterial Puncture: ComplicationsDocument17 pagesArterial Puncture: ComplicationsGerly MaglangitNo ratings yet
- L02 - 1 - Hemodialysis-Part 1Document20 pagesL02 - 1 - Hemodialysis-Part 1Tec Mohamed A. MengedNo ratings yet
- L02 1 Hemodialysis-Part 1Document20 pagesL02 1 Hemodialysis-Part 1Tec Mohamed A. MengedNo ratings yet
- Original Article: Rapamycin Combined with α-Cyanoacrylate Contributes to Inhibiting Intimal Hyperplasia in Rat ModelsDocument8 pagesOriginal Article: Rapamycin Combined with α-Cyanoacrylate Contributes to Inhibiting Intimal Hyperplasia in Rat ModelsMariantFomperosaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Cardiology: Rebound HypertensionDocument8 pagesNursing Cardiology: Rebound HypertensionVon R SemillaNo ratings yet
- Planeamiento RVM Sin BombaDocument10 pagesPlaneamiento RVM Sin Bombaapi-702934667No ratings yet
- Hema - General Characteristics of Blood and Hematological TestsDocument5 pagesHema - General Characteristics of Blood and Hematological TestsBSMT Kharylle divine FuentibellaNo ratings yet
- PMLS2 - Familiarization in PhleboDocument3 pagesPMLS2 - Familiarization in PhleboCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- Tadadafilo ExpocisionDocument72 pagesTadadafilo ExpocisionCristhian Gabriel Guevara NuñezNo ratings yet
- Planeamientoo RVM 3Document12 pagesPlaneamientoo RVM 3api-702934667No ratings yet
- Platelet CountDocument2 pagesPlatelet CountSirias_black100% (2)
- Specimen Collection and ProcessingDocument6 pagesSpecimen Collection and ProcessingTan DanielNo ratings yet
- Trans PMLS 1 - Batch 2 and 3.Document23 pagesTrans PMLS 1 - Batch 2 and 3.leexxjannelapatNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculationDocument12 pagesBody Fluids and Circulationadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument1 pagePleural Effusionfahad nokiaNo ratings yet
- HEMADocument72 pagesHEMABOEN YATORNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsFrom EverandAntiarrhythmic DrugsAntoni Martínez-RubioNo ratings yet
- Duplex and Color Doppler Imaging of the Venous SystemFrom EverandDuplex and Color Doppler Imaging of the Venous SystemGerhard H. MostbeckNo ratings yet
- Perfusion for Congenital Heart Surgery: Notes on Cardiopulmonary Bypass for a Complex Patient PopulationFrom EverandPerfusion for Congenital Heart Surgery: Notes on Cardiopulmonary Bypass for a Complex Patient PopulationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- SS 1 Agric Science First Term E-NoteDocument58 pagesSS 1 Agric Science First Term E-Notekanajoseph2009No ratings yet
- El Bazar de Los Malos Sueños Stephen King: Venta: #2415356115 Cant: 1Document4 pagesEl Bazar de Los Malos Sueños Stephen King: Venta: #2415356115 Cant: 1Juan Cervantes LópezNo ratings yet
- Piano Pentatonic Blues Scales - Overview With PicturesDocument8 pagesPiano Pentatonic Blues Scales - Overview With PicturesВладимир Перминов100% (2)
- ACA - Exam - Objectives - Photoshop - CC 2018Document5 pagesACA - Exam - Objectives - Photoshop - CC 2018Jeffrey FarillasNo ratings yet
- Goetze Mechanical Face SealsDocument7 pagesGoetze Mechanical Face SealsDheeraj GoswamiNo ratings yet
- General: Specific: Leading Statement:: TITLE: A Healthy LifestyleDocument2 pagesGeneral: Specific: Leading Statement:: TITLE: A Healthy LifestyleM Arshad M AmirNo ratings yet
- Sailing With Paul - IronsideDocument3 pagesSailing With Paul - IronsideLawrence GarnerNo ratings yet
- God Will Protect His Church God Will Protect His ChurchDocument17 pagesGod Will Protect His Church God Will Protect His ChurchLaura GarciaNo ratings yet
- Maribelle Z. Neri vs. Ryan Roy Yu (Full Text, Word Version)Document11 pagesMaribelle Z. Neri vs. Ryan Roy Yu (Full Text, Word Version)Emir MendozaNo ratings yet
- Project of WCM 19c0h008 Madhu MaamDocument41 pagesProject of WCM 19c0h008 Madhu MaamSourav TiwariNo ratings yet
- # Pembagian Kelas Alkes Per KategoriDocument41 pages# Pembagian Kelas Alkes Per KategoriR.A.R TVNo ratings yet
- En 12245 (2022) (E)Document9 pagesEn 12245 (2022) (E)David Chirinos100% (1)
- WorkshopPLUS-PowerShell For The IT Administrator Part 2 PDFDocument2 pagesWorkshopPLUS-PowerShell For The IT Administrator Part 2 PDFArif MohmmadNo ratings yet
- (GUARANTEED RATE AFFINITY) & (8905 BEAVER FALLS) - UCC1 Financial Statement LIENDocument9 pages(GUARANTEED RATE AFFINITY) & (8905 BEAVER FALLS) - UCC1 Financial Statement LIENHakim-Aarifah BeyNo ratings yet
- Teaching PronunciationDocument6 pagesTeaching PronunciationKathryn LupsonNo ratings yet
- Primary Gingival Squamous Cell CarcinomaDocument7 pagesPrimary Gingival Squamous Cell CarcinomaMandyWilsonNo ratings yet
- The Ape-Man: His Kith and KinDocument128 pagesThe Ape-Man: His Kith and KinamitrupaniNo ratings yet
- Note On F3 SC C2 TransportationDocument4 pagesNote On F3 SC C2 Transportationgan tong hock a.k.a ganosNo ratings yet
- Application DevelopmentDocument14 pagesApplication DevelopmentReema MubarakNo ratings yet
- Santiago City, Isabela: University of La Salette, IncDocument1 pageSantiago City, Isabela: University of La Salette, IncLUCAS, PATRICK JOHNNo ratings yet
- Tools, Materials and Equipment in Nail Care: Learning Activity Sheet Week 1 Quarter 1Document8 pagesTools, Materials and Equipment in Nail Care: Learning Activity Sheet Week 1 Quarter 1Barbara PosoNo ratings yet
- P2P Partnering Success Playbook PDFDocument48 pagesP2P Partnering Success Playbook PDFYesenia RamirezNo ratings yet
- Brandi PPT For BrandingDocument27 pagesBrandi PPT For BrandingShah ParinNo ratings yet
- Comsys 2Document10 pagesComsys 2MarjorieNo ratings yet
- World Red Cross DayDocument17 pagesWorld Red Cross DayAshwani K SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower AshraeDocument18 pagesCooling Tower AshraeMAITREE JHANo ratings yet
- DOMINODocument16 pagesDOMINOBerat DalyabrakNo ratings yet
- TestDocument3 pagesTestPopovska KristinaNo ratings yet