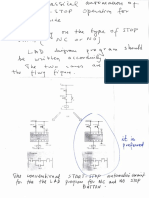
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Immer
Immer
Uploaded by
Tehe Saglam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesOriginal Title
immer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesImmer
Immer
Uploaded by
Tehe SaglamCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Academic Analysis of "immer.
txt": A Deep Dive into the German Word "immer"
The provided text, "immer.txt", is a detailed lexicographical entry exploring the multifaceted nature of
the German word "immer". While the specific dictionary source remains unconfirmed, the structure an
d depth suggest it originates from a comprehensive resource like the Deutsches Wörterbuch by Jacob a
nd Wilhelm Grimm.
Exploring the Entry:
The entry systematically dissects the various meanings and applications of "immer", providing a rich u
nderstanding of its nuanced usage. The analysis unfolds as follows:
1. Foundational Information:
Headword: The entry centers on the word "immer", providing its pronunciation as "‘imer’".
Source Identification: References to specific texts and locations suggest the utilization of aut
hentic sources to illustrate the word's contextual usage.
Frequency and Contextualization: The entry emphasizes the word's prevalence in the Germ
an language and its frequent appearance in compound forms like "immerfortgehend" (continuo
usly) and "immerzu" (constantly).
2. Temporal Applications (1a):
This section delves into the temporal functions of "immer", particularly its role in expressing continuit
y and duration.
Subcategories of Temporal Usage:
o α (Continuous Actions): This category focuses on the uninterrupted and persistent na
ture of relatively short actions. Examples highlight its usage to depict ongoing movem
ent or activity.
o β (Extended Durations): Here, the focus shifts to longer durations, ongoing states, an
d consistent processes or developments. "Immer" often carries the connotation of "con
tinuously" or "permanently" in this context.
o γ (Stable Characteristics): This category explores how "immer" depicts stable, reliab
le, or typical characteristics, procedures, and behaviors. It often implies meanings like
"usually", "regularly", or "constantly".
o δ (Temporal Emphasis): This section examines how "immer" provides temporal emp
hasis or differentiation, especially when referencing the past (with nuances like "still"
or "until now") and the future (often in phrases like "forever"). It also includes the neg
ation "immer nicht", signifying "not yet" or "still not".
3. Repetition and Frequency (1b):
This section analyzes how "immer" signifies repeated or frequent occurrences.
Key Points:
o Emphasis on Repetition: The entry emphasizes the repetitive nature of actions, often
in correlation with "often" or specifying conditions for the repetition.
o Negation and Exceptions: It includes the negation "immer nicht", meaning "never" o
r "in no case", highlighting exceptions to the repetitive nature.
o Regular Intervals: The less frequent usage of "immer" for actions repeating at regula
r, usually longer, intervals is also explored.
4. Categorical Usage (2):
This section explores the use of "immer" to express something fundamental or inherent, often in sente
ntious statements or with a logical/systematic definition.
Key Points:
o Inherent Qualities: The entry underscores the word's function in asserting inherent q
ualities or characteristics of entities or concepts.
o Scientific Regularities: Examples demonstrate the use of "immer" in natural science
contexts to describe observed regularities and laws, emphasizing its role in expressing
consistent phenomena.
5. Relative Indeterminacy or Arbitrariness (3):
This section examines how "immer" can express relative arbitrariness or indefiniteness.
Subcategories:
o a (Indefinite Pronouns/Adverbs): This category focuses on the combination of "imm
er" with pronouns or adverbs like "was", "wer", "wann", or "wo(hin)" to convey a sen
se of "whatever", "whoever", etc., indicating a lack of specific limitations.
o b (Indefinite Maximum/Optimum): The entry explains how "immer" is used to deno
te an indefinite maximum or optimum, often in phrases like "so viel (nur) immer" to e
xpress an unbounded or limitless quantity or degree.
6. Usage with Comparatives (4):
This section delves into the use of "immer" before comparatives to indicate continuous increase or inte
nsification.
Key Points:
o Continuous Intensification: The entry highlights common phrases like "immer weite
r und weiter" or "mehr und immer mehr" to emphasize ongoing intensification or prog
ression.
o Correlation and Proportionality: It mentions the correlation with "je mehr" and the
construction "immer — immer" to express a proportional relationship where one elem
ent increases or intensifies in relation to another.
7. Particle Usage (5):
The final section explores the function of "immer" as a particle with various modal functions, includin
g concession, affirmation, exhortation, and general emphasis.
Subcategories:
o a (Concessive): This category explores the concessive or admitting function of "imme
r", often contrasted with "aber" or "doch" to acknowledge a point while introducing a
contrasting statement.
o b (Affirmative/Intensifying): The entry explains the affirmative or intensifying funct
ion, often in phrases like "doch immer" or "immer und immer", to express certainty or
strengthen a statement.
o c (Exhortation/Permission): This section examines the use of "immer" in requests or
encouragements, often with imperatives and phrases like "nur immer", to express per
mission, encouragement, or sometimes challenge.
o d (General Intensifier): The entry discusses the general intensifying function of "im
mer", especially for expressing rejection, irritation, or surprise, often with the nuance
of "constantly" or "always".
Conclusion:
The lexicographical entry for "immer" provides a comprehensive and insightful analysis of the word's
diverse applications in the German language. By exploring its temporal, repetitive, categorical, compar
ative, and modal functions, the entry equips readers with a deeper understanding of the nuanced meani
ngs and expressive capabilities of "immer" within various contexts.
Category 3: The Realm of Indeterminacy
This category explores how "immer" introduces a sense of indefiniteness or arbitrariness into expressi
ons. Two key subcategories emerge:
a) Indefinite Pronouns and Adverbs:
Syntactic Structure: "Immer" combines with interrogative pronouns or adverbs like "was" (w
hat), "wer" (who), "wann" (when), or "wo(hin)" (where/to) to create expressions of open-
endedness or inclusivity.
Semantic Function: This construction conveys a lack of specific limitations or restrictions. F
or example, "Was immer du tust" translates to "Whatever you do", encompassing all possible a
ctions without specifying any particular one.
Academic Implications: This usage of "immer" proves valuable in academic discourse when
discussing hypothetical scenarios, general principles, or open-ended questions. For instance, a
researcher might say, "Welche Methode immer Sie wählen, stellen Sie sicher, dass sie zuverläs
sig ist" ("Whichever method you choose, ensure its reliability"), emphasizing the importance o
f reliability regardless of the specific methodological approach.
b) Indefinite Maximum/Optimum:
Expression of Limitlessness: "Immer" functions to denote an indefinite maximum or optimu
m, often appearing in phrases like "so viel (nur) immer" (as much as possible) or "so gut imme
r möglich" (as well as possible).
Semantic Nuance: This usage emphasizes an unbounded or limitless quantity or degree, sugg
esting an open-ended potential or capacity.
Academic Relevance: In academic contexts, this construction proves useful when discussing t
heoretical limits, ideal scenarios, or striving for excellence. For example, a professor might en
courage students by saying, "Streben Sie immer nach dem besten Ergebnis" ("Always strive fo
r the best possible outcome"), highlighting the pursuit of continuous improvement without sett
ing a defined upper limit.
Category 4: Intensification and Comparatives
This category analyzes the function of "immer" when paired with comparatives to express continuous i
ncrease or intensification.
Syntactic Position: "Immer" typically precedes the comparative adjective or adverb, forming
constructions like "immer größer" (ever larger) or "immer schneller" (ever faster).
Semantic Contribution: "Immer" signifies an ongoing process of intensification or progressi
on, implying that the quality or action described continues to increase without reaching a defin
ed endpoint.
Common Phrases: The entry highlights frequent expressions such as "immer weiter und weit
er" (further and further) and "mehr und immer mehr" (more and more), emphasizing the conti
nuous and often exponential nature of the intensification.
Proportionality and Correlation: The construction "immer — immer" expresses a proportio
nal relationship where one element increases or intensifies in relation to another. Additionally,
the correlation with "je mehr" (the more) further reinforces this sense of proportional intensific
ation.
Academic Significance: In academic writing and discourse, this usage of "immer" proves val
uable when describing trends, developments, or processes that exhibit continuous growth or in
tensification. For example, a historian might write, "Die Bevölkerung der Stadt wuchs immer
schneller" ("The city's population grew ever faster"), highlighting the accelerating rate of popu
lation growth over time.
You might also like
- Pie MethodDocument1 pagePie MethodbdskrabNo ratings yet
- Flying High 2 Student Book High Res PDFDocument84 pagesFlying High 2 Student Book High Res PDFRoza Zerraf50% (2)
- Categorical Logic: BEDANA, Joy Gabrielle A. 1C - 2010-019022Document11 pagesCategorical Logic: BEDANA, Joy Gabrielle A. 1C - 2010-019022Gabe BedanaNo ratings yet
- Logic NotesDocument38 pagesLogic Notesfarrukh khanNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - PresentationDocument17 pagesWeek 3 - Presentationsokratis98salNo ratings yet
- Paragraph WritingDocument35 pagesParagraph WritingMahadi HasanNo ratings yet
- AP English Language Midterm ReviewDocument8 pagesAP English Language Midterm Reviewerykah722No ratings yet
- Oratio TermsDocument3 pagesOratio TermsenzoNo ratings yet
- Aspect, Tense, SituationsDocument6 pagesAspect, Tense, SituationsgratielageorgianastoicaNo ratings yet
- NotetakingDocument40 pagesNotetakinganna.soroka1811No ratings yet
- RehabilitationDocument13 pagesRehabilitationapi-439825848No ratings yet
- Quintilian - Rhetorical TermsDocument3 pagesQuintilian - Rhetorical TermsIliya GramatikoffNo ratings yet
- Grammar For TeacherDocument2 pagesGrammar For TeacherhumblereadersNo ratings yet
- Judgement and Preposition-RevisedDocument14 pagesJudgement and Preposition-RevisedLeixter Win BalingaoNo ratings yet
- Word Order: The SubjectDocument4 pagesWord Order: The SubjectFouzia Jamal GorejaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8: The Academic Paragraph: Do Not Write: But RatherDocument7 pagesLesson 8: The Academic Paragraph: Do Not Write: But RatherBrahim Cr7No ratings yet
- Group 5 Semantic: Presented By: Hanaul Mubarokah Shofi Nisa Aulia Saharani Sanayatul FarhahDocument31 pagesGroup 5 Semantic: Presented By: Hanaul Mubarokah Shofi Nisa Aulia Saharani Sanayatul FarhahMuzayyinatul MushafiyyahNo ratings yet
- Copia de Guía InglésDocument6 pagesCopia de Guía Inglésvictoria ArzaveNo ratings yet
- English ConnectorsDocument50 pagesEnglish ConnectorsJuan Carlos Rodriguez100% (1)
- ABOUTDocument3 pagesABOUTHaha HahaNo ratings yet
- Text As Connected DiscourseDocument69 pagesText As Connected DiscourseIvy Mae SagangNo ratings yet
- ClauseDocument5 pagesClauseFred Ryan Canoy DeañoNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Sense Relations, Identity and Similarity of SenseDocument10 pagesUnit 10 Sense Relations, Identity and Similarity of Sensemhhhrm07No ratings yet
- Kifle Assign't - 1Document6 pagesKifle Assign't - 1abezuloveNo ratings yet
- Unity and CoherenceDocument9 pagesUnity and CoherenceRania FarranNo ratings yet
- Features of Academic WritingDocument50 pagesFeatures of Academic WritingJaymar ReponteNo ratings yet
- How To Write Scientific Texts in EnglishDocument66 pagesHow To Write Scientific Texts in EnglishNguyễn Hoàng ĐăngNo ratings yet
- Makalah B.Inggris RixwanDocument8 pagesMakalah B.Inggris Rixwanrixwanpebri4No ratings yet
- Letran Logic Lecture 3Document3 pagesLetran Logic Lecture 3panchojrNo ratings yet
- Part I. Essentials of GrammarDocument4 pagesPart I. Essentials of GrammarIX-B angkatan 21No ratings yet
- LK 1.1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri (Modul 6 - Profesional)Document7 pagesLK 1.1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri (Modul 6 - Profesional)Arman DullahNo ratings yet
- Beaver Clark - AlwaysonlyDocument38 pagesBeaver Clark - AlwaysonlyChano HerreraNo ratings yet
- Report Writing SummaryDocument3 pagesReport Writing SummaryFadhil FawwazNo ratings yet
- Distinguishes Between and Among Patterns of Development in Writing Across DisciplinesDocument41 pagesDistinguishes Between and Among Patterns of Development in Writing Across DisciplinesAries SungaNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 PPT - English - Q3 - W5Document73 pagesGrade 6 PPT - English - Q3 - W5Cynthia Lee CampanerNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing SkillsDocument2 pagesReading and Writing SkillsJhoanna ValdezNo ratings yet
- 11191-Article Text-13217-1-10-20180125Document25 pages11191-Article Text-13217-1-10-20180125Anh Thư NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Transition WordsDocument6 pagesTransition Wordspeiling87100% (1)
- Analytical ExpositionDocument9 pagesAnalytical ExpositionChairani MufidahNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing (Reviewer For Grade 11)Document13 pagesReading and Writing (Reviewer For Grade 11)Den89% (9)
- Principles and Methods of Analysis of Communicative - Pragmatic Features of Complete SentencesDocument4 pagesPrinciples and Methods of Analysis of Communicative - Pragmatic Features of Complete SentencesResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- Types of ParagraphDocument11 pagesTypes of ParagraphOrlando Mendez100% (2)
- RDG Journal 9Document5 pagesRDG Journal 9api-383958067No ratings yet
- Expository Paragraph WritingDocument17 pagesExpository Paragraph WritingSarah LNo ratings yet
- Analytical ExpositionDocument5 pagesAnalytical ExpositionDharWin d'Wing-Wing d'AriestBoyzNo ratings yet
- Written Expression Second Year - Semester Two: 2.2. Types of EssaysDocument20 pagesWritten Expression Second Year - Semester Two: 2.2. Types of EssaysAya ChentoufNo ratings yet
- Developing Topic Sentence & ParagraphDocument31 pagesDeveloping Topic Sentence & ParagraphNur HayatiNo ratings yet
- APA & Style ComboDocument43 pagesAPA & Style ComboasolivaresNo ratings yet
- Paragraph WritingDocument4 pagesParagraph Writingsamsoum1No ratings yet
- Motion Verb Constructions, Frames, and Profiling: PreprintDocument31 pagesMotion Verb Constructions, Frames, and Profiling: PreprintZhannaNo ratings yet
- Unit I Paragraph, Paragraph Coherence 1.1 ParagraphDocument6 pagesUnit I Paragraph, Paragraph Coherence 1.1 Paragraphhernanda chossaNo ratings yet
- Common Errors in Technical WritingDocument6 pagesCommon Errors in Technical WritingEmrico Cabahug100% (1)
- English10 q4 CLAS3 Giving The Expanded Extended Definition of Words Final-Carissa-CalalinDocument13 pagesEnglish10 q4 CLAS3 Giving The Expanded Extended Definition of Words Final-Carissa-CalalinSophia Erika LargoNo ratings yet
- Sentence ConstructionDocument4 pagesSentence Constructionspacehd931No ratings yet
- Reference: Civil Engineering 2010Document21 pagesReference: Civil Engineering 2010Dandy Hendro KusumoNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheets Phil 8Document7 pagesCheat Sheets Phil 8Marcos GómezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 08Document4 pagesLecture 08sanamkhaan929No ratings yet
- Root Locus RulesDocument2 pagesRoot Locus RulesTehe SaglamNo ratings yet
- Midterm Study ProblemDocument4 pagesMidterm Study ProblemTehe SaglamNo ratings yet
- İndustri̇al Automati̇on - 11 (Yeni)Document20 pagesİndustri̇al Automati̇on - 11 (Yeni)Tehe SaglamNo ratings yet
- (I) Assume N(S) 0 and Find The Transfer Function Y(s) /R(S) - (Ii) Assume R(S) 0 and Find The Transfer Function Y(s) /N(S)Document6 pages(I) Assume N(S) 0 and Find The Transfer Function Y(s) /R(S) - (Ii) Assume R(S) 0 and Find The Transfer Function Y(s) /N(S)Tehe SaglamNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2: Bed-Kitchen-Know-Big-Read-Free-CheapDocument3 pagesQuiz 2: Bed-Kitchen-Know-Big-Read-Free-CheapSheyma.M.No ratings yet
- Year 1 English Yearly PlanDocument11 pagesYear 1 English Yearly PlanYONG HUEI BING Moe100% (1)
- Form 2 General English Worksheet For Unit 2 (KEY No Cover)Document5 pagesForm 2 General English Worksheet For Unit 2 (KEY No Cover)Jing jiangovo (F3E陸雅靜20)No ratings yet
- ApostropheDocument10 pagesApostrophemonetNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Midterm ExamDocument4 pagesOral Communication Midterm ExamJayson CastilloNo ratings yet
- Keep Memory Alive. Lesson - AnthologyDocument22 pagesKeep Memory Alive. Lesson - AnthologySofia Aguayo GranadosNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap On Tap Theo Tung UnitDocument77 pagesBai Tap On Tap Theo Tung UnitNguyen Lan AnhNo ratings yet
- Types of Speech DeliveryDocument27 pagesTypes of Speech Deliverykevin kovhgNo ratings yet
- Language Acquisition TheoriesDocument13 pagesLanguage Acquisition TheoriesMinh NgọcNo ratings yet
- Use of Definite Article: The: 1. Articles-A, An, TheDocument2 pagesUse of Definite Article: The: 1. Articles-A, An, TheVritika ShorieNo ratings yet
- Portofolio Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument19 pagesPortofolio Makalah Bahasa Inggriskarini fathiyaNo ratings yet
- Test Tasks For Reading: Presented by Lesley Nayeli Chávez Velázquez March 2020Document19 pagesTest Tasks For Reading: Presented by Lesley Nayeli Chávez Velázquez March 2020api-511296445No ratings yet
- English Grade 7 Comprehension, Language Punctuation ExerciseDocument9 pagesEnglish Grade 7 Comprehension, Language Punctuation ExerciseLumko NguboNo ratings yet
- ID Penggunaan Diksi Dalam Karangan Berita SDocument18 pagesID Penggunaan Diksi Dalam Karangan Berita Srin rinNo ratings yet
- Notes To Hildegard Von Bingen's 'Lingua Ignota'Document41 pagesNotes To Hildegard Von Bingen's 'Lingua Ignota'Richter, Joannes100% (1)
- A1 Primera UnidadDocument8 pagesA1 Primera UnidadAndrea Reyes TelloNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm MidtermDocument4 pagesOral Comm MidtermLealyn Dimaano OrdinarioNo ratings yet
- Occupations Vocabulary Esl Unscramble The Words Worksheets For Kids PDFDocument10 pagesOccupations Vocabulary Esl Unscramble The Words Worksheets For Kids PDFLeonardoSouzaNo ratings yet
- The Influence of The English Language On The Russian Youth SlangDocument10 pagesThe Influence of The English Language On The Russian Youth SlangВасилий БоровцовNo ratings yet
- عرب الجزيرة العراقيةDocument34 pagesعرب الجزيرة العراقيةJeremiahNo ratings yet
- Stereo Love by Edward MayaDocument1 pageStereo Love by Edward MayaJuanARNo ratings yet
- Assessing Your Communication CompetenceDocument4 pagesAssessing Your Communication CompetenceCristina DziubaNo ratings yet
- JipbsiDocument11 pagesJipbsiBaby LionNo ratings yet
- 10 - 03 - 21 - Wednesday Imperative Verbs WorksheetDocument4 pages10 - 03 - 21 - Wednesday Imperative Verbs Worksheetpriscila.baila5No ratings yet
- Polysemy in The Semantic Field of Movement in The English LanguageDocument14 pagesPolysemy in The Semantic Field of Movement in The English Languagesv32611No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Grade 2 - Articles - A and An 1 August 2022Document3 pagesLesson Plan Grade 2 - Articles - A and An 1 August 2022desliani surentu100% (1)
- Sow English Year 5 2024 - 2025 SKSGDocument12 pagesSow English Year 5 2024 - 2025 SKSGg-78229557No ratings yet
- Voca-Book (Ruby Sparks)Document46 pagesVoca-Book (Ruby Sparks)Анастасия ВознесенскаяNo ratings yet
- 7-3 Critisise Auditor's ReportDocument42 pages7-3 Critisise Auditor's Reportsixun zhouNo ratings yet