Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reading 29 - Income Tax
Reading 29 - Income Tax
Uploaded by
maimaitaan1202010 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageOriginal Title
Reading 29_ Income Tax
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageReading 29 - Income Tax
Reading 29 - Income Tax
Uploaded by
maimaitaan120201Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
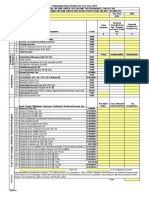
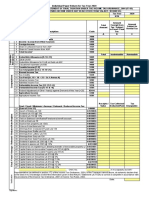
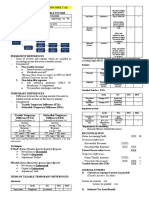
Accounting profit vs Taxable income
income tax payable
Income tax expense = taxes payable + ΔDTL –
ΔDTA
Deferred tax assets vs Deferred tax liabilities
Permanent/Temporary difference
Effective tax rate
Tax loss carry forward
■Timing of revenue and expense recognition
in IS and tax return differ
1. Differences Between Accounting ■Certain revenues and expenses are
Profit and Taxable Income recognized in IS but never on tax return or
vice-versa.
■ Assets and/or liabilities have different
carrying amounts and tax bases.
■ Gain or loss recognition in IS differs from
the tax return
■ Tax losses from prior periods may offset
future taxable income
■ Financial statement adjustments may not
affect equally the tax and accounting return or
may be recognized in different periods
Current Tax Assets and Liabilities Differences in accounting and tax
7. Comparison of IFRS and USGAAP
Under IFRS, deferred tax assets and liabilities
are always classified as non-current.
6. Presentation and Disclosure
Under US GAAP, however, deferred tax assets
Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities and liabilities are classified on the balance
sheet as current and noncurrent based on the
Deferred taxes as well as income taxes should always be classification of the underlying asset or liability
recognized on the income statement of an entity unless it pertains
to:
■ Taxes or deferred taxes charged directly to equity, or
■ A possible provision for deferred taxes relates to a business
2.1 Determining the Tax Base of an Asset
combination 2. Determining the Base of Assets and
5. Recognition and Measurement of Liabilities 2.2 Determining the Tax Base of a Liability
5.1 Recognition of a Valuation Allowance Current and Deferred Tax
Reading 29: Income Tax 2.3 Changes in Income Tax Rates Floating Topic
5.2 Recognition of Current and Deferred Tax
Charged Directly to Equity
Permanent differences are differences
between tax and financial reporting of
there is uncertainty as to the probability of
revenue (expenses) that will not be reversed
future taxable profits => only recognized to
at some future date
the extent of the available taxable temporary
differences
IFRS provides an exemption (that is, deferred tax is not provided on
the temporary difference) for the initial recognition of an asset or
generate future taxable profits before the
liability in a transaction that:
unused tax losses and/or credits expire
a) is not a business combination (e.g., joint ventures, branches and
assessing the probability that sufficient unconsolidated investments);
Determine whether the past tax losses were a 4. Unused Tax Losses and Tax Credits
taxable profit will be generated in the future and b) affects neither accounting profit nor taxable profit at the time
result of specific circumstances that are
of the transaction.
unlikely to be repeated;
4.1 Taxable Temporary Differences => Result
Discover if tax planning opportunities are in DTL US GAAP does not provide an exemption for these circumstances
available to the entity that will result in future
4.2 Deductible temporary differences = >
profits.
result in DTA
3. Temporary and Permanent
Differences Between Taxable and
Accounting Profit
4.3 Business Combinations and Deferred
Taxes
■The parent is in a position to control the
timing of the future reversal of the temporary
difference, and
DTL: unless both of the following criterion are ■ It is probable that the temporary difference
satisfied will not reverse in the future.
4.4 Investments in Subsidiaries, Branches,
Associates and Interests in Joint Ventures
■ The temporary difference will reverse in the
future, and
DTA if the following criteria are ■ Sufficient taxable profits exist against which
satisfied the temporary difference can be used.
You might also like
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (17)
- Practical Wisdom - The Right Way To Do The Right Thing - PDFDocument5 pagesPractical Wisdom - The Right Way To Do The Right Thing - PDFChauhan RadhaNo ratings yet
- Service-manual-SG Emachines E725 E525 031809Document236 pagesService-manual-SG Emachines E725 E525 031809andhrimnirNo ratings yet
- Toshiba Case 3Document4 pagesToshiba Case 3Deta Detade100% (1)
- CREATE Zalamea Briefing + RRsDocument76 pagesCREATE Zalamea Briefing + RRsGerryNo ratings yet
- "Individual Paper Return For Tax Year 2021: SignatureDocument25 pages"Individual Paper Return For Tax Year 2021: SignatureWaqas MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Individual Paper Return For Tax Year 2020: SignatureDocument26 pagesIndividual Paper Return For Tax Year 2020: SignaturejamalNo ratings yet
- In Come Tax Return Form 2019Document48 pagesIn Come Tax Return Form 2019Mirza Naseer AbbasNo ratings yet
- Appendix 7b - Rror-SagfDocument1 pageAppendix 7b - Rror-SagfEdwin Siruno LopezNo ratings yet
- GST Handwritten Notes Charts Etc 30032018Document90 pagesGST Handwritten Notes Charts Etc 30032018Prasad Rao60% (5)
- Module 3 ACCTDocument16 pagesModule 3 ACCTFathimath NoohaNo ratings yet
- IAS 12 BinderDocument20 pagesIAS 12 BinderUmer Shah100% (1)
- IND AS 12 Income TaxesDocument5 pagesIND AS 12 Income TaxesPavan Kumar PurohitNo ratings yet
- FR - Ias 12Document1 pageFR - Ias 12Zubair JallohNo ratings yet
- Business Expenses Worksheet 2020Document2 pagesBusiness Expenses Worksheet 2020Dendi MonNo ratings yet
- 2 - CIT - Tax AdjustmentsDocument56 pages2 - CIT - Tax AdjustmentsMaricarmen SilvaNo ratings yet
- FBR Tax FilingDocument48 pagesFBR Tax FilingMuhammad Waqas Hanif100% (2)
- Individual Paper Return For Tax Year 2019: SignatureDocument10 pagesIndividual Paper Return For Tax Year 2019: SignatureEngr Saad Bin SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Manual Return 2023Document28 pagesManual Return 2023arsalanghuralgtNo ratings yet
- Individual Paper Returnfor Tax Year 2022Document25 pagesIndividual Paper Returnfor Tax Year 2022abdul karimNo ratings yet
- US Internal Revenue Service: fct1 - 1996Document2 pagesUS Internal Revenue Service: fct1 - 1996IRSNo ratings yet
- Salary Tds Computation Sheet Sec 192bDocument1 pageSalary Tds Computation Sheet Sec 192bpradhan13No ratings yet
- BIR Form No. 1600Document2 pagesBIR Form No. 1600Lorraine Steffany BanguisNo ratings yet
- Manage Taxes - 8Document1 pageManage Taxes - 8I'm RangaNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement HauajwbwbajsjajaDocument1 pageAcknowledgement HauajwbwbajsjajaAnkush ManhasNo ratings yet
- IA2 Income TaxesDocument1 pageIA2 Income TaxesJoey Mhey BenicoNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Calculator 2018-2019Document1 pageIncome Tax Calculator 2018-2019Muhammad Hanif SuchwaniNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 6Document9 pagesProblem Set 6Jade BilisNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard 22Document23 pagesAccounting Standard 22Rida TaarnnumNo ratings yet
- Indian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruDocument1 pageIndian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruDupati K VeerappaNo ratings yet
- FRA - 10-Income TaxesDocument35 pagesFRA - 10-Income Taxeskmayank0723No ratings yet
- 2021 GeneralDocument8 pages2021 GeneralWajiha HaroonNo ratings yet
- Indian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruDocument1 pageIndian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruDIVYANSHU SHEKHARNo ratings yet
- US Internal Revenue Service: f943 - 1995Document4 pagesUS Internal Revenue Service: f943 - 1995IRSNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement Niket Panjiier Army LucknowDocument1 pageAcknowledgement Niket Panjiier Army Lucknowbeauty kumariNo ratings yet
- MODIFIED - TIMTA Annexes For CREATE FAs of 20 June 2021Document14 pagesMODIFIED - TIMTA Annexes For CREATE FAs of 20 June 2021Sunshine PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- US Internal Revenue Service: fct1 - 2000Document2 pagesUS Internal Revenue Service: fct1 - 2000IRSNo ratings yet
- US Internal Revenue Service: fct1 - 1997Document2 pagesUS Internal Revenue Service: fct1 - 1997IRSNo ratings yet
- Indian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruDocument2 pagesIndian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruHussain YadavNo ratings yet
- Manual ReturnDocument26 pagesManual ReturnMuhammad Arsalan TariqNo ratings yet
- Accounting of Taxation in Accordance With ITO 1984 (IAS-12)Document35 pagesAccounting of Taxation in Accordance With ITO 1984 (IAS-12)Gazi Md. Ifthakhar HossainNo ratings yet
- Income Taxes: Basic ConceptsDocument7 pagesIncome Taxes: Basic ConceptsTrisha Mae Mendoza MacalinoNo ratings yet
- IAS 12 - Income Taxes - Measurement - Permanent DifferencesDocument4 pagesIAS 12 - Income Taxes - Measurement - Permanent DifferencesReenestus DumeniNo ratings yet
- 9 M - 28-Dec-2020 - 917355441Document1 page9 M - 28-Dec-2020 - 917355441Arihant SatpathyNo ratings yet
- Performa Income StatementDocument1 pagePerforma Income StatementAhsan JamalNo ratings yet
- Handout - Deferred Tax Asset (March 8, 2024)Document30 pagesHandout - Deferred Tax Asset (March 8, 2024)atty.francis.angelo.lopezNo ratings yet
- Form BDocument2 pagesForm BPower MuruganNo ratings yet
- US Internal Revenue Service: f943 - 1996Document4 pagesUS Internal Revenue Service: f943 - 1996IRSNo ratings yet
- 2020 09 13 10 56 29 221 - 1599974789221 - XXXPR9253X - AcknowledgementDocument1 page2020 09 13 10 56 29 221 - 1599974789221 - XXXPR9253X - Acknowledgementraoanagha27No ratings yet
- Ack Fy 2019-20Document1 pageAck Fy 2019-20Prashant MoreNo ratings yet
- Itr Ay 21-22Document6 pagesItr Ay 21-22sagarsavla110No ratings yet
- ITR AY 21-22Document1 pageITR AY 21-22rishi0184parkashNo ratings yet
- 2020 07 31 16 05 55 486 - 1596191755486 - XXXPK8367X - AcknowledgementDocument1 page2020 07 31 16 05 55 486 - 1596191755486 - XXXPK8367X - AcknowledgementSiva Jyothi KNo ratings yet
- Indian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruDocument8 pagesIndian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, Bengalurubhashkar yadavNo ratings yet
- Indian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruDocument2 pagesIndian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruHussain YadavNo ratings yet
- Instructions For Filling in Return Form & Wealth Statement Form Sr. InstructionDocument15 pagesInstructions For Filling in Return Form & Wealth Statement Form Sr. InstructionTausif ArshadNo ratings yet
- Indian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruDocument1 pageIndian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruMadhan Kumar BobbalaNo ratings yet
- Ack Ahipk1805e 2021-22 452077740280322Document1 pageAck Ahipk1805e 2021-22 452077740280322b.ramanareddy7226No ratings yet
- Farm Expenses Worksheet 2021Document2 pagesFarm Expenses Worksheet 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- MacroDocument2 pagesMacrominnie.patittaNo ratings yet
- Pas 12: Accounting For Income TaxDocument2 pagesPas 12: Accounting For Income TaxKiana FernandezNo ratings yet
- RACS Itr 2020-2021Document1 pageRACS Itr 2020-2021Lakshay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Current Trends of Farm Power Sources inDocument6 pagesCurrent Trends of Farm Power Sources inNakul DevaiahNo ratings yet
- Chapter Outline For FTSDocument1 pageChapter Outline For FTSBalvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Astaro Security Gateway enDocument4 pagesAstaro Security Gateway enmaxbyzNo ratings yet
- Special Conditions of Contract (SCC) : Section - VDocument16 pagesSpecial Conditions of Contract (SCC) : Section - VAnonymous 7ZYHilDNo ratings yet
- Cesabb 300 B 400Document8 pagesCesabb 300 B 400BeyzaNo ratings yet
- EF4e Intplus Filetest 3bDocument7 pagesEF4e Intplus Filetest 3bjeanneramazanovaNo ratings yet
- 5 Leadership LessonsDocument2 pages5 Leadership LessonsnyniccNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Customer Attitude, Preference and Satisfaction Level of Mutual Fund InvestmentDocument109 pagesAnalysis of Customer Attitude, Preference and Satisfaction Level of Mutual Fund Investmentlalitgitam80% (5)
- Advancement ProposalDocument2 pagesAdvancement ProposalJEFFERSON GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Sro 565-2006Document44 pagesSro 565-2006Abdullah Jathol100% (1)
- Public Sector Accounting Tutorial (Ain)Document2 pagesPublic Sector Accounting Tutorial (Ain)Ain FatihahNo ratings yet
- Anh Văn Chuyên NgànhDocument7 pagesAnh Văn Chuyên Ngành19150004No ratings yet
- Characteristics Finite Element Methods in Computational Fluid Dynamics - J. Iannelli (Springer, 2006) WW PDFDocument744 pagesCharacteristics Finite Element Methods in Computational Fluid Dynamics - J. Iannelli (Springer, 2006) WW PDFsanaNo ratings yet
- Example 12: Design of Panel Walls: SolutionDocument2 pagesExample 12: Design of Panel Walls: SolutionSajidAliKhanNo ratings yet
- (IMechE Conference Transactions) PEP (Professional Engineering Publishers) - Power Station Maintenance - Professional Engineering Publishing (2000) PDFDocument266 pages(IMechE Conference Transactions) PEP (Professional Engineering Publishers) - Power Station Maintenance - Professional Engineering Publishing (2000) PDFAlexanderNo ratings yet
- 0508 First Language Arabic: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 SeriesDocument5 pages0508 First Language Arabic: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 SeriessCience 123No ratings yet
- Score:: 1 Out of 1.00 PointDocument12 pagesScore:: 1 Out of 1.00 PointDiscord YtNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics Module 3 Q1Document21 pagesApplied Economics Module 3 Q1Jefferson Del Rosario100% (1)
- Project WorkDocument6 pagesProject WorkNurbek YaxshimuratovNo ratings yet
- Alim Knit (BD) LTD.: Recommended Process Flow DiagramDocument1 pageAlim Knit (BD) LTD.: Recommended Process Flow DiagramKamrul HasanNo ratings yet
- Strand A Ilp Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesStrand A Ilp Lesson PlanyoNo ratings yet
- Midas - NFX - 2022R1 - Release NoteDocument10 pagesMidas - NFX - 2022R1 - Release NoteCristian Camilo Londoño PiedrahítaNo ratings yet
- Tiger Grey Card CopyrightDocument2 pagesTiger Grey Card Copyrightsabo6181No ratings yet
- Gs Survey & Engineers: Tax InvoiceDocument2 pagesGs Survey & Engineers: Tax InvoiceShivendra KumarNo ratings yet
- GSM System Fundamental TrainingDocument144 pagesGSM System Fundamental Trainingmansonbazzokka100% (2)
- University of Michigan Dissertation ArchiveDocument6 pagesUniversity of Michigan Dissertation ArchiveBuyResumePaperUK100% (1)