Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gati Retrogrades 1716305758733479199
Gati Retrogrades 1716305758733479199
Uploaded by
108maridevi108Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gati Retrogrades 1716305758733479199
Gati Retrogrades 1716305758733479199
Uploaded by
108maridevi108Copyright:
Available Formats
Om gurave nama om gurava omg ogurave nama, o ram gurave nama o raven, o rave
nama, o rave nama om gurave nama arya. So what we are doing now is on the
request of the PJSE Jagannath batch, we will be doing some things called focused
topics. Our first topic that we are taking up is based on the request of Vina Shadav. It
is Richard Briggs. And as you can see in that joining picture, the. What is
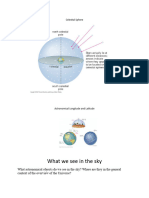
retrogradation? Retrogradation is the movement of a planet as viewed from Earth or
what we are calling a geocentric movement. This is not a heliocentric movement.
Because in heliocentric movements there are no retrogrades. There are no
retrogrades in the heliocentric movement. So this is something very, very important
to understand. We are in a geocentric movement. So our basic understanding is, I do
not know whether I can use a pen in this drawing tools. Yeah. So what I am talking
about is, you see, so we call something, you know, something important to know is
Sansar. Yeah. Sansara is what we call Earth plane. And that is what is called Bhuloka.
Right. And in Bhuloka we have. How are we seeing everything in this Bhuloka, what
we call a geocentric view. This geocentric view is the view of Samsara. That is,
everything is going around the earth. So the earth is the focus. So this is the Samsara
view. So this is Bhuloka. Now, in a. In a heliocentric view, what happens in a
heliocentric view is that there are no retrogrades. And we call that Sannyasa. And
that is seen from the sun. So it is called Satya Loka. So these are two very, very
extreme viewpoints. Bhu Loka is the 7th or this is the 7th Loka. This is the 7th.
Whereas the heliocentric view is the first or the topmost of the Brahmanokas. And
this is the 7th point. So now these are different viewpoints in Jyotish and
retrogradation. The concept of retrogradation or how we see planets retrograding is
from the earth. Like for example, here we are seeing Mercury as compared to the
sun. You know, as compared to the sun. We see, instead of moving in the direction,
the sun is moving in this direction, you can see from the Earth. When we observe, the
sun is actually moving in this direction. Right? Whereas we find that, look, this
mercury at this, this planet Mercury is now moving in the retrograde direction. And
now here it becomes direct. And then it goes here. And then you can see this is all
direct. Whereas from here the retrograde motion has again started. So at this point,
this is the retrograde motion. But you see out here, if you see the turning points, they
are here. At this point, it looks as if it is stationary. These are stationary points. And
this is called slow retrogradation. So there are two points of slow retrogradation. One
point of very powerful retrograde.
Transcribed by Transkriptor 1/1
You might also like
- O Level Space Physics NotesDocument40 pagesO Level Space Physics Noteslolshedo100% (2)
- Retrograde PlanetsDocument3 pagesRetrograde Planetsddeepuk100% (1)
- Astronomy BasicsDocument35 pagesAstronomy BasicsShivam VinothNo ratings yet
- Aspects Phases Key Planetary PairsDocument33 pagesAspects Phases Key Planetary PairsSundar Balakrishnan100% (2)
- Togel Sound Light and Rays and The Six LampsDocument55 pagesTogel Sound Light and Rays and The Six LampsSean Griffin100% (5)
- An Introduction To Planetary PeriodsDocument7 pagesAn Introduction To Planetary PeriodsFernando Luis OrtizNo ratings yet
- Husserl at The Limits of Phenomenology: Including Texts by Edmund HusserlDocument11 pagesHusserl at The Limits of Phenomenology: Including Texts by Edmund HusserlAnonymous WwvfsME9100% (1)
- The Retrograde Guidebook: An All-in-One Astrology Guide to the Cycles of Planetary Retrograde and How They Affect Your Emotions, Decisions, and RelationshipsFrom EverandThe Retrograde Guidebook: An All-in-One Astrology Guide to the Cycles of Planetary Retrograde and How They Affect Your Emotions, Decisions, and RelationshipsNo ratings yet
- Rotation and RevolutionDocument31 pagesRotation and Revolutionma antoniette miguelNo ratings yet
- Observing Reflection PaperDocument3 pagesObserving Reflection PaperHikage23No ratings yet
- (Croatian) 05-11 Binary Stars 09 41 (DownSub - Com)Document9 pages(Croatian) 05-11 Binary Stars 09 41 (DownSub - Com)Davor MaracicNo ratings yet
- ASTRONOMYDocument5 pagesASTRONOMYRomel SenaNo ratings yet
- Nadi SutrasDocument6 pagesNadi SutrasRavi Goyal100% (2)
- The Faces, or Phases, of the Moon - Astronomy Book for Kids | Children's Astronomy BooksFrom EverandThe Faces, or Phases, of the Moon - Astronomy Book for Kids | Children's Astronomy BooksNo ratings yet
- Moon Does Not Rotate Around It AxisDocument6 pagesMoon Does Not Rotate Around It Axisarfanansary100% (2)
- Document (Recovered)Document15 pagesDocument (Recovered)Lester PapadulosNo ratings yet
- The Significance of DakshinayanaDocument10 pagesThe Significance of Dakshinayanacharan74No ratings yet
- Retro Gradation and AccelerationDocument15 pagesRetro Gradation and AccelerationandrewduttaNo ratings yet
- Stationary Planets in Transit: WarningDocument7 pagesStationary Planets in Transit: Warningpramodc22No ratings yet
- 2 OsDocument6 pages2 OsACU PLUNGERNo ratings yet
- GravityDocument1 pageGravityapi-242193509No ratings yet
- Earth Science 1Document38 pagesEarth Science 1DaisyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 How Earth and Sky Work-Effects of Latitude: Sphere Is An Imaginary Sphere With TheDocument10 pagesChapter 3 How Earth and Sky Work-Effects of Latitude: Sphere Is An Imaginary Sphere With TheLukman AididNo ratings yet
- Role Play EngDocument64 pagesRole Play Engsumita bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Tropical or Sidereal ZodiacDocument2 pagesTropical or Sidereal ZodiacSrikanth SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Vedic Astrology Lesson - 3: The Anticlockwise Solar SystemDocument3 pagesVedic Astrology Lesson - 3: The Anticlockwise Solar SystemNagendra KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Our Universe Class 8Document10 pagesOur Universe Class 8shihabnittNo ratings yet
- Ira Sevaya at Sri PadaDocument3 pagesIra Sevaya at Sri PadaAnonymous xifNvNNo ratings yet
- Retrograde Planets-A Different ViewDocument2 pagesRetrograde Planets-A Different ViewGPFanNo ratings yet
- How To Read TransitsDocument6 pagesHow To Read TransitsRavi Goyal100% (2)
- SpaceDocument9 pagesSpacetrical27 tricalNo ratings yet
- Transit of PlanetsDocument74 pagesTransit of Planetsnitkol100% (5)
- Astronomy PaperDocument4 pagesAstronomy Paperapi-253195322No ratings yet
- Lec 30Document28 pagesLec 30AshutoshBhattNo ratings yet
- LPDocument11 pagesLPKria Undag LacangNo ratings yet
- Riding Session 6Document11 pagesRiding Session 6Cooper GrosscupNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Progressions and DirectionsDocument15 pagesAn Introduction To Progressions and DirectionsMNo ratings yet
- A Brief Note On Retrograde Planets by Prof CDocument8 pagesA Brief Note On Retrograde Planets by Prof CJatinder SandhuNo ratings yet
- Astronomical Phenomena - EditedDocument79 pagesAstronomical Phenomena - EditedRIZALINA BATANNo ratings yet
- No Magnetic Declination On The Flat Earth PART 2 The Northern PartDocument7 pagesNo Magnetic Declination On The Flat Earth PART 2 The Northern PartJava ContrataqueNo ratings yet
- Universe in MotionDocument1 pageUniverse in Motionhello itsme100% (1)
- Remaking Your Life: The Outer Planets in Motion: by Sesh Venugopal, USADocument15 pagesRemaking Your Life: The Outer Planets in Motion: by Sesh Venugopal, USASaptarishisAstrologyNo ratings yet
- Brock Planetary Declination SDocument6 pagesBrock Planetary Declination SDositheus Seth100% (2)
- BhriguDocument3 pagesBhriguHoracio TackanooNo ratings yet
- Shadows and The MoonDocument5 pagesShadows and The MoonBhaktha vatsalaNo ratings yet
- Astro Jyoti 3Document2 pagesAstro Jyoti 3Karan MittalNo ratings yet
- All GroupDocument9 pagesAll GroupMhmmd FasyaNo ratings yet
- Retro PlanetsDocument11 pagesRetro Planetsbharikrishnan17701100% (1)
- Astronomy For AstrologyDocument7 pagesAstronomy For AstrologyVaradarajanNo ratings yet
- The Sun, Earth and MoonDocument10 pagesThe Sun, Earth and MoonOJO BEATS FREE MUSICNo ratings yet
- Five New ProgressionsDocument13 pagesFive New Progressionsezequielrasanchez100% (1)
- Rotation Is A Term That Describes TheDocument7 pagesRotation Is A Term That Describes TheBelizeandreams AllenNo ratings yet
- 8 Step MeditationDocument30 pages8 Step MeditationFirstLook100% (3)
- Progressions DirectionsDocument15 pagesProgressions DirectionsTTamara29No ratings yet
- Togel Sound Light and Rays and The Six LampsDocument35 pagesTogel Sound Light and Rays and The Six LampsJosh Carswell100% (2)
- AYANMSADocument4 pagesAYANMSAAJITNo ratings yet
- IHMoontraces OCRDocument67 pagesIHMoontraces OCRmadaswsNo ratings yet
- Universe Solar System AstrologyDocument22 pagesUniverse Solar System AstrologyjssastryNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Space Lesson (Autosaved)Document26 pagesUnit 11 Space Lesson (Autosaved)JOVELYN JOY CABUELLONo ratings yet
- Phases of The MoonDocument9 pagesPhases of The MoonMarcus Skookumchuck VanniniNo ratings yet
- Kepler's LawsDocument15 pagesKepler's LawsAngelica DulvaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper of Physical ScienceDocument2 pagesReaction Paper of Physical ScienceCyrill Kristoffer Q. AustriaNo ratings yet
- Plasma PhysicsDocument17 pagesPlasma Physicsanb243No ratings yet
- Lecture7 Stellar EvolutionDocument4 pagesLecture7 Stellar EvolutionKeshav AggarwalNo ratings yet
- PhySci LAS Qrtr2 8thweek RevisedDocument7 pagesPhySci LAS Qrtr2 8thweek RevisedpaulNo ratings yet
- Black Holes - Volker PerlickDocument110 pagesBlack Holes - Volker PerlickRafael SimõesNo ratings yet
- I. Preliminaries: Lesson: Universe and Solar SystemDocument17 pagesI. Preliminaries: Lesson: Universe and Solar SystemCecilia ReyesNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Quarter 2: Module 2Document9 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Quarter 2: Module 2Maria Kriselle ApuhinNo ratings yet
- Option D - AstrophysicsDocument20 pagesOption D - AstrophysicsMM DomìN8RNo ratings yet
- New MONDDocument7 pagesNew MONDVernonNo ratings yet
- KP Horary Table 1 249 - CompressDocument5 pagesKP Horary Table 1 249 - CompressHarish RajuNo ratings yet
- Formation of The Universe Student SheetDocument2 pagesFormation of The Universe Student SheetDubu Dubu DahyunieeNo ratings yet
- Harvard Astrophysics BookDocument151 pagesHarvard Astrophysics Bookakadvance100% (1)
- Full Chapter The General Theory of Relativity A Mathematical Approach 1St Edition Farook Rahaman PDFDocument53 pagesFull Chapter The General Theory of Relativity A Mathematical Approach 1St Edition Farook Rahaman PDFstephen.inoue766100% (4)
- Dark Energy - WikipediaDocument22 pagesDark Energy - Wikipediasamer menNo ratings yet
- Plasma (Physics)Document14 pagesPlasma (Physics)Shubham BansalNo ratings yet
- Astrophysics Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesAstrophysics Lesson PlanwanaimranNo ratings yet
- KPP - 03 - Arjuna JEE 2024Document2 pagesKPP - 03 - Arjuna JEE 2024Kurosaki JotaroNo ratings yet
- Tese Pedro Carrilho 63431Document46 pagesTese Pedro Carrilho 63431Shibu lalNo ratings yet
- CV ArnabDocument1 pageCV ArnabRon H LetwinskiNo ratings yet
- Stars FormationDocument13 pagesStars Formationjyotirmoy21No ratings yet
- The Dark Reality of Cosmic Space Exploring The UnseenDocument7 pagesThe Dark Reality of Cosmic Space Exploring The UnseenVandan PatelNo ratings yet
- Relativity108b Schwarzschild Metric InterpretationDocument96 pagesRelativity108b Schwarzschild Metric InterpretationAbhinav RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Gravitational-Wave Astronomy Is An Emerging Branch of ObservationalDocument11 pagesGravitational-Wave Astronomy Is An Emerging Branch of ObservationaliuhalsdjvauhNo ratings yet
- Black Hole TheoryDocument14 pagesBlack Hole TheoryraflyNo ratings yet
- Planetisimal TheoryDocument3 pagesPlanetisimal Theorymakoy29826578No ratings yet
- Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and The Fate of The UniverseDocument25 pagesDark Matter, Dark Energy, and The Fate of The UniverseVishvaksen ChintamaneniNo ratings yet
- BAC Blanc 2Document2 pagesBAC Blanc 2Hocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet