Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Work Sheet For Remadials 3rd Round
Work Sheet For Remadials 3rd Round
Uploaded by
Markos Kebede0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Work Sheet for Remadials 3rd Round
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesWork Sheet For Remadials 3rd Round
Work Sheet For Remadials 3rd Round
Uploaded by
Markos KebedeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Mizan Tepi University
College of Natural and Computational Science
Department of Physics
Physics Work Sheet for Remedial Students Round III
I. Choose the best answer from the given alternatives
1. What physical quantity is responsible for keeping satellites in orbit around celestial bodies?
A. Gravitational force. C. Electrostatic force.
B. Magnetic force. D. Frictional force.
2. What factor determines the speed at which a satellite orbits a celestial body?
A. The satellite's size.
B. The satellite's shape.
C. The satellite's distance from the celestial body.
D. The satellite's color.
3. When a force acts perpendicular to the direction of an object's motion, how does this affect
the work done by the force?
A. Work done is increased C. Work done is zero
B. Work done is decreased D. Work done is negative
4. If a system moving with initial velocity is subjected to applied force and displaced to a
displacement of a change occurs only its speed. The work done on this system is
A. Equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the system
B. Different from the change in the kinetic energy of the system
C. Equal to the change in the potential energy of the system
D. Independent of each types of energy
5. If a force of 400 N is applied to lift a box vertically upwards by a distance of 10 meters, what
is the work done against gravity?
A. B. C. D.
6. When a force is applied in the direction opposite to the displacement, the work done is:
A. Positive B. Negative C. Zero D. unknown
7. Which of the following statements is true about work done by a variable force?
A. It is always constant
B. It is equal to the area under the force vs. distance graph
C. It is only dependent on the initial and final positions
D. It does not depend on the magnitude of the force
8. A object is initially at rest. a constant force of is applied to the object for a
distance of . Calculate the final velocity of the object.
A. √ m/ s B. √ m/ s C. m/ s D. √ m/ s
9. A 500 g ball is dropped from a height of 10 meters. What is its velocity just before hitting the
ground, neglecting air resistance?
A. m/ s B. m/ s C. √ m/ s D. √ m/ s
10. A block of mass 2 kg is pushed up a frictionless incline with an initial speed of 5 m/s. If the
incline makes an angle of 30 degrees with the horizontal, what is the vertical height the block
reaches before it comes to a stop?
A. B. C. D.
11. A spring with a spring constant of 200 N/m is compressed by 0.1 meters. What is the work
done in compressing the spring
A. B. C. D.
12. Two ice skaters of equal mass, one moving at and the other at in opposite
direction, collides head-on and stick together. What is their final velocity after the collision?
A. m/ s B. m/ s C. m/ s D. √ m/ s
13. A 1 kg ball moving to the right at 4 m/s collides elastically with a stationary 2 kg ball on a
frictionless surface. What are the final velocities of the two balls after the collision?
A. C.
B. D.
14. A mass moving at collides with a mass moving at in the opposite
direction. If the collision is perfectly elastic, what are their final velocities after the collision?
A. C.
B. D.
15. A 6 kg mass moving at 4 m/s collides with a 3 kg mass moving at 6 m/s in the same direction.
If the collision is completely inelastic, what is their final velocity after the collision?
A. m/ s B. m/ s C. m/ s D. m/ s
16. Which of the following correctly defines the center of mass of an object?
A. The point where the weight of an object is concentrated
B. The point where the density of an object is highest
C. The point where the net force on an object is zero
D. The point where the pressure of an object is highest
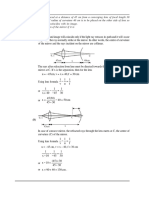
17. A uniform rod of length L and mass M is laying along the x-axis with one end at the origin.
Where is the center of mass of the rod located?
A. C.
B. D.
18. If a system consists of two masses of 3kg and 5kg at positions respectively,
what is the center of mass of the system?
A. B. C. D.
19. Which of the following factors affect the center of mass of an object?
A. Shape and position of the object C. Color of the object
B. area of the object D. temperature of the object
20. A system consists of three masses of located at
respectively. What is the center of mass of the system?
A. B. C. D. )
21. Which of the following is true for a thermally insulated system?
A. It allows heat transfer with the surrounding
B. It doesn’t allow heat transfer with the surrounding
C. It allows transfer of matter
D. It allows transfer of energy
22. The heat required to raise the temperature of of a substance by is . What is
the specific heat capacity of the substance?
A. C.
B. D.
23. What will happen to the, torque and moment of inertia of a rotating objects respectively if the
angular acceleration doubles?
A. Double , halved C. Quadruple, doubled
B. Double, tripled D. Halved, doubled
24. What is the name of the force that acts on an object during simple harmonic motion?
A. Centripetal force C. Restoring force
B. Gravitational force D. Frictional force
25. What is the period of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion related to its mass
and spring constant ?
A. √ C. √
B. √ D. √
26. A mass of 5 kg is attached to a spring with a spring constant of . The mass is pulled
from its equilibrium position and released. What are the values of Period of the
motion, Maximum velocity of the mass and maximum acceleration of the mass respectively?
A. C.
B. D.
27. Which of the following is a characteristic of damped oscillation?
A. The amplitude of the oscillation remains constant over time.
B. The amplitude of the oscillation increases over time.
C. The amplitude of the oscillation decreases over time.
D. The frequency of the oscillation increases over time
28. What is the primary difference between damped and forced oscillation?
A. Damped oscillation occurs naturally, while forced oscillation requires an external
driving force.
B. Damped oscillation has constant amplitude, while forced oscillation has a varying
amplitude.
C. Damped oscillation always dies out over time, while forced oscillation continues
indefinitely.
D. Damped oscillation has a single natural frequency, while forced oscillation has multiple
frequencies
29. Which type of wave involves the oscillation of particles perpendicular to the direction of
wave propagation?
A. Longitudinal wave C. Electromagnetic wave
B. Transverse wave D. All
30. Which of these is an example of a longitudinal wave?
A. Light B. Radio C. Sound D. Laser
31. Choose the one which contradicts the relation between the thermal expansion coefficients (if
is linear expansion, is areal expansion, and is volume expansion).
A. B. C. D.
32. The boiling point of water is ______.
A. 0 K B. 100 K C. 373 K D. 273K
33. Which wave type has both electric and magnetic field components that are perpendicular to
each other and the direction of propagation?
A. Mechanical wave C. Electromagnetic wave
B. Matter wave D. Gravitational wave
II. Essay type questions
34. List, explain and compare the four wave behaviors.
35. List and explain
A. The effect of heat on materials
B. The first three laws of thermodynamics
36. Compare and contrast the following terms
A. Temperature and heat D. Center of mass and moment of inertia
B. Work and heat E. Torque and angular momentum
C. Energy, work and power F. Elastic and in elastic collision
You might also like
- Diagnostic Test Science 8Document3 pagesDiagnostic Test Science 8Santisas Zai96% (24)
- John Vincent T. Villamor First Prelim in Conceptual PhysicsDocument5 pagesJohn Vincent T. Villamor First Prelim in Conceptual PhysicsJVVillamor100% (1)
- 1st Summative Test in Science 8Document3 pages1st Summative Test in Science 8Dhanessa Condes88% (40)
- General Summative For Quarter 2Document3 pagesGeneral Summative For Quarter 2Archie NeilNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument69 pagesEngineering MechanicsMaria Angelica Pantila100% (4)
- Grade 8 Science ExamDocument4 pagesGrade 8 Science Exammedrondur89% (9)
- De-Broglie HypothesisDocument19 pagesDe-Broglie HypothesisAmanda BoltonNo ratings yet
- Phys 1011 Final SAMPLEDocument10 pagesPhys 1011 Final SAMPLEJonah the mixerNo ratings yet
- MaayohonDocument22 pagesMaayohonkingds2006No ratings yet
- 1stQ-G8-Test-Questions LATESTDocument5 pages1stQ-G8-Test-Questions LATESTMich100% (1)
- 2ND Periodic Exam SHSDocument7 pages2ND Periodic Exam SHSshirley cortezNo ratings yet
- QUestions On Classical Physics (Them 1)Document27 pagesQUestions On Classical Physics (Them 1)davididosa40No ratings yet
- Science 9Document4 pagesScience 9Danna Mae BarteNo ratings yet
- Questions On Force and Newton's Law of MotionDocument7 pagesQuestions On Force and Newton's Law of MotionZee AmanuelNo ratings yet
- Science 9 SummativeDocument2 pagesScience 9 SummativeJAMES TrinidadNo ratings yet
- 1ST Quarterly Examination in Science 8 (2023-2024)Document11 pages1ST Quarterly Examination in Science 8 (2023-2024)Jonalyn ViernesNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet For Grade 9Document4 pagesPhysics Worksheet For Grade 9Kassahun100% (1)
- g8 Summative Test Science 1st QTRDocument6 pagesg8 Summative Test Science 1st QTRMaria Ysabel AbillonNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: 2 Periodical Test in General Physics 1 Grade 12 STEMDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: 2 Periodical Test in General Physics 1 Grade 12 STEMLanz ManaloNo ratings yet
- Jimma University Ques - All ModelDocument39 pagesJimma University Ques - All ModelYohannes TeferiNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 11 Unit 4 WorksheetDocument14 pagesPhysics Grade 11 Unit 4 Worksheetsample nameNo ratings yet
- Q2 Pointers 2Document3 pagesQ2 Pointers 2Angelica Maye DuquiatanNo ratings yet
- Physics G - 11 Dynamics Worksheet 1Document8 pagesPhysics G - 11 Dynamics Worksheet 1abdiasfaw7152No ratings yet
- Gen Physics 2nd QuarterDocument5 pagesGen Physics 2nd QuarterJoriel CruzNo ratings yet
- Test-Questions-Physics IDocument7 pagesTest-Questions-Physics INheszie Cortez MendozaNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Physical ScienceDocument2 pagesSummative Test Physical ScienceBrendick AbellaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8Document3 pagesGrade 8Windy C. RomeroNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa City Administration Education Bureau Addis Abeba Grade 12 Physics Model Examinations GINBOT 2013/MAY 2021Document9 pagesAddis Ababa City Administration Education Bureau Addis Abeba Grade 12 Physics Model Examinations GINBOT 2013/MAY 2021dmc constructionNo ratings yet
- Reviewer NAME: - SECTIONDocument2 pagesReviewer NAME: - SECTIONSonny RivasNo ratings yet
- General Physics I Q2 PreDocument1 pageGeneral Physics I Q2 PreMurs H. AsbiNo ratings yet
- A A PHYSICS MODEL EXAM 2011 Model TwoDocument9 pagesA A PHYSICS MODEL EXAM 2011 Model TwoKerod MohamedNo ratings yet
- Genphysics Lec 2nd Exam 2nd SemDocument6 pagesGenphysics Lec 2nd Exam 2nd SemLorenze Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Physics Standard Level Paper 1 Monday 10 May 2010 (Morning) 45 MinutesDocument119 pagesPhysics Standard Level Paper 1 Monday 10 May 2010 (Morning) 45 MinutesNipun RustagiNo ratings yet
- TQs Q1 EXAM SCIENCE 8 2023 2024.editedDocument5 pagesTQs Q1 EXAM SCIENCE 8 2023 2024.editedRaffy AlbiosNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Model 2014 G12Document11 pagesPHYSICS Model 2014 G12Kedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- 4th Summative Test Science 9Document3 pages4th Summative Test Science 9odette carzanoNo ratings yet
- DP2 HL QPDocument26 pagesDP2 HL QPChinmay BhaveNo ratings yet
- DP2 SL QPDocument19 pagesDP2 SL QPChinmay BhaveNo ratings yet
- 4Q Science G9Document3 pages4Q Science G9Kimmy Grace TañoNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Second Quarter ExamDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Second Quarter ExamMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Practice AssessmentKEYDocument4 pagesUnit 11 Practice AssessmentKEYNahom DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 (Momentum) Practice AssessmentDocument4 pagesUnit 10 (Momentum) Practice AssessmentRachel MarshallNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Leomar ExamDocument16 pagesPhysical Science Leomar ExamXtine Rivera - ParungaoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 8 1ST PERIODIC EXAMfinalDocument3 pagesSCIENCE 8 1ST PERIODIC EXAMfinalJeff SuarezNo ratings yet
- 1st QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT IN SCIENCE 8 - SY2022-2023Document4 pages1st QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT IN SCIENCE 8 - SY2022-2023Jessica PingolNo ratings yet
- 2018 General Education Part XIXDocument3 pages2018 General Education Part XIXJessica Mae SalazarNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam in Science With TosDocument7 pagesSample Exam in Science With TosJessavel QuindoyosNo ratings yet
- FINALS - MechanicsDocument4 pagesFINALS - MechanicsMaria Liza Lastima abrinicaNo ratings yet
- Sample ExamDocument2 pagesSample ExamJamoi Ray VedastoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 ScienceDocument4 pagesGrade 8 ScienceRoselyn DechavezNo ratings yet
- Additional Reviewer Grade 9 TalaDocument4 pagesAdditional Reviewer Grade 9 TalaagaltalangNo ratings yet
- Exit Exam 2nd QTR 2010 11 Set ADocument4 pagesExit Exam 2nd QTR 2010 11 Set ArickiegasparNo ratings yet
- GTS Academy PakMCQs PhysicsDocument105 pagesGTS Academy PakMCQs Physicsbsat-f21-242No ratings yet
- Modern Physics SET ADocument6 pagesModern Physics SET AMichael Clyde GurdielNo ratings yet
- ESAS Objectives 2Document15 pagesESAS Objectives 2Jayven VillamaterNo ratings yet
- 1ST Quarter Examination in Sci 8 - 2023-2024Document4 pages1ST Quarter Examination in Sci 8 - 2023-2024Jonathan donanNo ratings yet
- FIRST QUARTER EXAM Science 8Document3 pagesFIRST QUARTER EXAM Science 8JEOSYLYN SUMALPONGNo ratings yet
- PHY101 MIDTERM SOLVED MCQS by JUNAIDDocument19 pagesPHY101 MIDTERM SOLVED MCQS by JUNAIDhs6077074No ratings yet
- Physic ExamsDocument7 pagesPhysic ExamsmeaniwoaniNo ratings yet
- REM PracticeDocument25 pagesREM Practiceyayykedlyy0123No ratings yet
- High-Contrast Gratings For Integrated Optoelectronics: Connie J. Chang-Hasnain and Weijian YangDocument62 pagesHigh-Contrast Gratings For Integrated Optoelectronics: Connie J. Chang-Hasnain and Weijian YangMohit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Phy SoundDocument51 pagesLecture Phy SoundYi Ying HannieNo ratings yet
- Rayleigh Wave - WikipediaDocument5 pagesRayleigh Wave - Wikipediaghhhf gfffhNo ratings yet
- Band-Limited Angular Spectrum Numerical Propagation Method With Selection Scaling of Obervation Window Size and Samole Number PDFDocument6 pagesBand-Limited Angular Spectrum Numerical Propagation Method With Selection Scaling of Obervation Window Size and Samole Number PDFluo wangNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis: FFT, PSD, and Spectrogram Basics (Free Download)Document36 pagesVibration Analysis: FFT, PSD, and Spectrogram Basics (Free Download)ECG CarditekNo ratings yet
- Physics 2022-23Document10 pagesPhysics 2022-23RPNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Week 7 - Harmonic VibrationDocument17 pagesModule 2 Week 7 - Harmonic VibrationNathaniel BaguioNo ratings yet
- Lecture22 Dynamic Soil Properties Part2Document34 pagesLecture22 Dynamic Soil Properties Part2Arun GoyalNo ratings yet
- ECA-unit 3Document25 pagesECA-unit 3srinithaNo ratings yet
- Lissajous-Like Figures With Triangular and Square Waves: J. Flemming, A. HornesDocument4 pagesLissajous-Like Figures With Triangular and Square Waves: J. Flemming, A. Horneshemanta gogoiNo ratings yet
- TP - Physics - Djeffal - Selman (Pohl Penduluum) - 231006 - 223826Document10 pagesTP - Physics - Djeffal - Selman (Pohl Penduluum) - 231006 - 223826oumaimachi70No ratings yet
- Non Diff BeamDocument3 pagesNon Diff BeamSalomon SalomonNo ratings yet
- Optics-02 - Theory (26-38)Document13 pagesOptics-02 - Theory (26-38)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Signature Hole Blast Vibration ControlDocument5 pagesSignature Hole Blast Vibration Controlpartha das sharma67% (3)
- Makalah FisikaDocument10 pagesMakalah FisikaFega RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- E-Marking Notes On Physics HSSC I May 2017Document34 pagesE-Marking Notes On Physics HSSC I May 2017rabiaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4.1 P2 Long QuestionsDocument8 pagesTopic 4.1 P2 Long QuestionsAnthony Felser SutantoNo ratings yet
- Ee 425 - Circuits 2 Problem SetDocument4 pagesEe 425 - Circuits 2 Problem SetIvan Barrion BacarroNo ratings yet
- EC8701 - Antennas and Microwave Engineering (Ripped From Amazon Kindle Ebooks by Sai Seena)Document620 pagesEC8701 - Antennas and Microwave Engineering (Ripped From Amazon Kindle Ebooks by Sai Seena)Suresh100% (1)
- Be 201 Engineering Physics Unit 2Document34 pagesBe 201 Engineering Physics Unit 2dbahBNo ratings yet
- Circular Waveguide FInalDocument8 pagesCircular Waveguide FInaljoel joyNo ratings yet
- Physics: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelDocument28 pagesPhysics: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelAnne Nirmani RodrigoNo ratings yet
- PHY50A-Course Support MaterialDocument22 pagesPHY50A-Course Support MaterialShamma AhmedNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Seismic WavesDocument13 pagesGrade 10 Seismic WavesAzziely-Arah Santiago PabroNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Lesson Plan (Physics)Document9 pagesGrade 8 Science Lesson Plan (Physics)Gerick Dave Monencillo VenderNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Frequency of A Simple Harmonic OscillatorDocument4 pagesFactors Affecting The Frequency of A Simple Harmonic OscillatoradsadasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- SLK G7 Q3wk4 Catubig RevisedDocument12 pagesSLK G7 Q3wk4 Catubig RevisedJen-jen Ybanez BalderasNo ratings yet
- Ft-Ir Spectroscopy Principle, Technique and MathematicsDocument7 pagesFt-Ir Spectroscopy Principle, Technique and MathematicsYisi LrNo ratings yet
- ECAT Unit 7 (Oscillations) - 1Document3 pagesECAT Unit 7 (Oscillations) - 1MScIT2M1012 Jawad TariqNo ratings yet