Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsMode of Inheritance
Mode of Inheritance
Uploaded by
Rachid HissaneCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- AP Biology 2020 Practice Exam 2 FRQ PreviewDocument30 pagesAP Biology 2020 Practice Exam 2 FRQ Preview(22) Bahar Baturoglu100% (3)
- Urinalysis Case StudiesDocument11 pagesUrinalysis Case Studiesdandooshe38% (13)
- Medical Genetics 4th Edition Jorde Test BankDocument4 pagesMedical Genetics 4th Edition Jorde Test BankOdettesNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 10th Edition Lewis Test BankDocument24 pagesHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 10th Edition Lewis Test BankPalma Gibson100% (31)
- TestDaily分享 HL paper1Document18 pagesTestDaily分享 HL paper1gary gazaNo ratings yet
- SCI 111 Multiple Choice QuestionDocument15 pagesSCI 111 Multiple Choice QuestionShaira Jane Villareal AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 For GeneticsDocument5 pagesHomework 2 For GeneticsYunyoung KimNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Sec30 Answers KeyDocument9 pagesAssignment - Sec30 Answers KeyGiselle EleazarNo ratings yet
- GM Review2 HZDocument14 pagesGM Review2 HZfjewuqfheuwqfyqgf23fNo ratings yet
- Krok 1 Stomatology 2006Document21 pagesKrok 1 Stomatology 2006helloNo ratings yet
- Genetics - PYQs and Concept Maps-AKDocument92 pagesGenetics - PYQs and Concept Maps-AKSaiNagaVignesh BandhamNo ratings yet
- Krok 1 Stomatology 2007Document21 pagesKrok 1 Stomatology 2007helloNo ratings yet
- Dev psych-ACTIVITY-Module-4Document7 pagesDev psych-ACTIVITY-Module-4Anne SanchezNo ratings yet
- 4102600920398609Document61 pages4102600920398609sadhanalahemanthNo ratings yet
- SL 4 Test Questions GeneticsDocument16 pagesSL 4 Test Questions GeneticsAllison Khoo100% (1)
- 3rd Year Bcqs Hhhpathology-2Document38 pages3rd Year Bcqs Hhhpathology-2Hira PanhwerNo ratings yet
- k1 Stom F EngDocument19 pagesk1 Stom F EngAdnaneNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Bio 112-Molecular Biology and GeneticsDocument15 pagesFinal Examination Bio 112-Molecular Biology and GeneticsPrince-SimonJohnMwanza100% (1)
- Multiple Choice: Choose Best (2.5 Points Each, 80Document7 pagesMultiple Choice: Choose Best (2.5 Points Each, 80Florence BamigbolaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of The Living World 4th Edition George Johnson DownloadDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of The Living World 4th Edition George Johnson Downloadariadnemarthaauva100% (27)
- Genetics Vocabulary Worksheet 1 AnswersDocument2 pagesGenetics Vocabulary Worksheet 1 AnswersRyleigh SmithNo ratings yet
- Q. & A. Chap 05Document14 pagesQ. & A. Chap 05umamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Genbio2 ModuleDocument47 pagesGenbio2 ModuleAlbert Rosete100% (1)
- Genetics Questions To PrepareDocument6 pagesGenetics Questions To PrepareJohn Osborne100% (1)
- QUESTION BANK 2007 From UT HoustonDocument44 pagesQUESTION BANK 2007 From UT HoustonMindy Lee80% (5)
- Presentation 6,7,8,9,10-1Document96 pagesPresentation 6,7,8,9,10-1hgetachew208No ratings yet
- HL Paper1Document11 pagesHL Paper1Alexis OkosunNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology Principleofinheritanceandvariation tp01Document4 pages12 Biology Principleofinheritanceandvariation tp01Dec veenNo ratings yet
- Inheritance, Variation and Evolution MCQs Set 3Document2 pagesInheritance, Variation and Evolution MCQs Set 3melindahofmannNo ratings yet
- The Language of Genetics Punnett Squares Inheritance Patterns & Human Pedigrees DisordersDocument51 pagesThe Language of Genetics Punnett Squares Inheritance Patterns & Human Pedigrees DisordersehshonorsbioNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Past Exam MC QuestionsDocument14 pagesTopic 3 Past Exam MC QuestionsAhmad FarhatNo ratings yet
- Genetic Final ExamDocument58 pagesGenetic Final ExamTrần Đăng0% (1)
- Genetics and TeratologyDocument21 pagesGenetics and Teratologypandem soniya0% (1)
- Variation and GeneticsDocument11 pagesVariation and GeneticsTasawar Hussain DayoNo ratings yet
- Quiz BankDocument12 pagesQuiz Banknadim1241335No ratings yet
- Chapter 18: Evolutionary Changes in PopulationsDocument11 pagesChapter 18: Evolutionary Changes in PopulationsRCRIIINo ratings yet
- CB27 - Principles of Inheritance and Variation (Modified)Document8 pagesCB27 - Principles of Inheritance and Variation (Modified)Kaziranga English AcademyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument9 pagesChapter-5 Principles of Inheritance and VariationbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 3rd Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesGen Bio 2 3rd Quarter ExamAl SultanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GeneticsDocument6 pagesChapter 5 GeneticsMohamed Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- 01.14.02 Principles of Genetics - Overview of Genetic PathologyDocument9 pages01.14.02 Principles of Genetics - Overview of Genetic PathologyMikmik DGNo ratings yet
- Pathology - Female Reproductive MCQ's - MedPrepOnlineDocument19 pagesPathology - Female Reproductive MCQ's - MedPrepOnlineTony Dawa75% (4)
- 2-Gen-Sept-14-Inheritance of Complex Disorders Handout WeissbeckerDocument4 pages2-Gen-Sept-14-Inheritance of Complex Disorders Handout Weissbeckern-gorNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science 9Document3 pagesIntegrated Science 9jrm.tinoyNo ratings yet
- Heredity and VarationDocument7 pagesHeredity and VarationSwayam Tiwari ANDHNo ratings yet
- TestDaily分享 SL paper1Document24 pagesTestDaily分享 SL paper1gary gazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GeneticsDocument6 pagesChapter 5 GeneticsMohamed Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sample Mult Choice Qs 2018Document7 pagesSample Mult Choice Qs 2018yusrawasim147No ratings yet
- 2012, 25th AprilDocument11 pages2012, 25th Aprilgaruda nusantaraNo ratings yet
- BS Part 6Document7 pagesBS Part 6Lea Fe Comilang ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Wongs Nursing Care of Infants and Children 10th Edition Hockenberry Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Wongs Nursing Care of Infants and Children 10th Edition Hockenberry Test Bank PDFsophiafostercqcv100% (11)
- Gen Bio 2 G12Document3 pagesGen Bio 2 G12Janet BarcimoNo ratings yet
- Genetics Complete UnitDocument60 pagesGenetics Complete Unitchannel of dhyanaNo ratings yet
- Wongs Nursing Care of Infants and Children 10th Edition Hockenberry Test BankDocument14 pagesWongs Nursing Care of Infants and Children 10th Edition Hockenberry Test BankNicoleRoweanbtc100% (9)
- Chapter 5 Principle of Inheritance AndvariationDocument23 pagesChapter 5 Principle of Inheritance AndvariationJhanvi BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Medical Biology and Genetics II-1-1Document6 pagesMedical Biology and Genetics II-1-1Shoshka AliNo ratings yet
- (Student) Chapter 1 - Genetic Inheritance & Genetic ControlDocument24 pages(Student) Chapter 1 - Genetic Inheritance & Genetic ControlDanish Fitri RoslanNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 Genetics To EvolutionDocument12 pagesGen Bio 2 Genetics To EvolutionLeonard CubeloNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument5 pagesMCQvijay kamal meenaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Genetics - MendelismDocument15 pagesBIOLOGY Genetics - Mendelismmoviiiieee2021No ratings yet
- Evo Genetics TestDocument4 pagesEvo Genetics Testapi-545046625No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide To Genetic Diseases, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide To Genetic Diseases, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Plasma Protein DisordersDocument10 pagesInvestigation of Plasma Protein DisordersJosiah BimabamNo ratings yet
- Vii. Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument4 pagesVii. Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Metabolism - Disposal of NitrogenDocument16 pagesAmino Acid Metabolism - Disposal of NitrogenJanelle SumidoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation: Kidney Stone SymptomsDocument16 pagesClinical Presentation: Kidney Stone SymptomsangelynchristabellaNo ratings yet
- 1778 Uralyt U 1331882845Document5 pages1778 Uralyt U 1331882845James HornerNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument55 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic DisordersGlormina Asprec AvenaNo ratings yet
- Minnesota Urolith Center: Canine Cystine UrolithsDocument2 pagesMinnesota Urolith Center: Canine Cystine UrolithsC LNo ratings yet
- Kidney - Renal Stones and HomeopathyDocument4 pagesKidney - Renal Stones and HomeopathyAnonymous dpxYTENo ratings yet
- Clinical FirstDocument342 pagesClinical FirstYasmeen AtiehNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Urine and Body Fluids: Ammonium BiurateDocument2 pagesAnalysis of Urine and Body Fluids: Ammonium BiurateMLSNo ratings yet
- Digestion & Absorption ProteinsDocument44 pagesDigestion & Absorption ProteinsPutri Indah NirmalasariNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument189 pagesGeneticstolgaonayNo ratings yet
- 2011Document87 pages2011Bridget QuansahNo ratings yet
- Inherited Overflow Metabolic Overflow RenalDocument11 pagesInherited Overflow Metabolic Overflow RenalChrissa Mae Tumaliuan CatindoyNo ratings yet
- 1 Slide Urinary Crystals: Formed by The Precipitation of Urine SolutesDocument3 pages1 Slide Urinary Crystals: Formed by The Precipitation of Urine SolutesEveryday FundayNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan Semester 4-5 Maret 2022Document21 pagesPembahasan Semester 4-5 Maret 2022Angger SatriaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Kidney StoneDocument36 pagesCase Study On Kidney Stonemanojkumar200624No ratings yet
- Enzyme Deficiencies - CompiledDocument2 pagesEnzyme Deficiencies - CompiledparkerNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic Disorders: Learning ObjectivesDocument12 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic Disorders: Learning ObjectivesJonalyn LumantasNo ratings yet
- Batu GinjalDocument29 pagesBatu Ginjalarim100% (1)
- Ap Biology 2020 Practice Exam 2 FRQDocument30 pagesAp Biology 2020 Practice Exam 2 FRQEric ChiangNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis 2Document9 pagesUrinalysis 2Dawn GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 Metabolic Disorders HODocument23 pagesChapter 08 Metabolic Disorders HOFrances FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Krok1 PreparedDocument322 pagesKrok1 PreparedGMP EuropeNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Disorders 01Document41 pagesMetabolic Disorders 01Brent LagartoNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument9 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic DisordersXyleene Jency Bien IINo ratings yet
- Amino Acidss & AminoacidopathiesDocument55 pagesAmino Acidss & AminoacidopathiesMustafa KhandgawiNo ratings yet
- MCQ Blok 11Document10 pagesMCQ Blok 11Jefri SoniNo ratings yet
Mode of Inheritance
Mode of Inheritance
Uploaded by
Rachid Hissane0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Mode of inheritance
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesMode of Inheritance
Mode of Inheritance
Uploaded by
Rachid HissaneCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
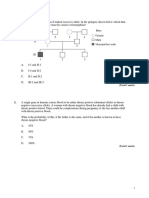
B.
Epistasis
Modes of inheritance C. Complete dominance
D. Complementarity
Click for The explanation video E. Codominance
Cystinuria in humans shows itself in form of
Codominance (complete dominance)
Definition: Both genes are fully expressed. cystine stones in kidneys (homozygotes) or
Examples: AB blood type. else an increased rate of cystine in urine
(heterozygotes). Cystinuria is a monogenic
disease. Specify the type of interaction
between cystinuria genes and normal rate of
cystine in urine:
A. Semidominance
B. Epistasis
C. Complete dominance
A person with the fourth blood group (genotype D. Complementarity
IAIB) has in erythrocytes both antigen A E. Codomination
controlled by allele IA and antigen B controlled
by allele IB. This phenomenon is an example Pleiotropy / Polymerism )( بلوة
of the following gene interaction: Definition: One gene affects two or more other
A. Codominance
genes.
B. Complementarity Examples: Marfan syndrome & Hartnup
C. Semidominance disease
D. Polymery
E. Epistasis
An 18-year-old male has been diagnosed with
Marfan syndrome. Examination revealed a
Semi-dominance (Incomplete dominance)
developmental disorder of connective tissue
Definition: Both genes are partially expressed. and eye lens structure, abnormalities of the
Examples: curvy hair form straight and curly cardiovascular system, arachnodactylia. What
hair or Cystinuria.
genetic phenomenon has caused the
development of this disease?
A. Pleiotropy
B. Complementarity
C. Codominance
D. Multiple allelism
E. Incomplete dominance
Hartnup disease is caused by point mutation of
only one gene which results in disturbance of
Cystinuria manifests itself in a human as tryptophane absorption in the bowels and its
cystine stones in the kidneys (homozygous resorption in the renal tubules. It is the reason
individuals) or increased cystine content in the for disorder of both digestive and urination
urine (heterozygous individuals). Cystinuria is systems. What genetic phenomenon is
a monogenic disorder. Determine the type of observed in this case?
interaction between the genes of cystinuria and A. Pleiotropy
normal urine cystine excretion: B. Complementary interaction
A. Semidominance C. Polymery
D. Codominance
E. Semidominance - Deaf parents (DDee and ddEE)
- Human X chromosome
Polymery (Multiple allelism)
Deaf parents with genotypes DDee and ddEE
Definition: increase number of the genes gave birth to a girl with normal hearing.
increase the effect. The bigger the number, the Specify the form of D and E genes interaction:
bigger the effect. A. Complementary interaction
Examples: Pigmentation & height of a person B. Complete dominance
C. Epistasis
Pigmentation intensity of human skin is D. Polymery
controlled by a few independent dominant E. Overdominance
genes. It is known that pigmentation is the more
intensive, the bigger quantity of these genes. Human X chromosome contains a dominant
What is the type of interaction between these gene that is responsible for normal blood
genes? clotting. An autosomal dominant gene plays a
A. Polymery similar role. Lack of any of these genes leads to
B. Pleiotropy the coagulation disorder. The form of
C. Epistasis interaction between these genes is called:
D. Codominance A. Complementarity
E. Complementarity B. Epistasis
C. Polymerism
The height of a person is controlled by several D. Codominance
non-allelic dominant genes. If the number of E. Pleiotropy
this genes is increased, the height of a person
increases as well. What type of interaction Useful recourse:
occurs between these genes?
A. Polymery Telegram group
B. Pleiotropy
C. Epistasis
1. Chromosomes, Chromatids, Chromatin.
D. Codominance
2. Introduction to Heredity.
E. Complementarity
3. Complementary gene action.
Recessive epistasis
Definition: a recessive gene covers or masks a
dominant gene.
Examples: Blood type AB from 0.
A woman with 0 (I) blood group has born a
child with AB blood group. This woman’s
husband has A blood group. What genetic
interaction explains this phenomenon?
A. Recessive epistasis
B. Codominance
C. Polymery
D. Incomplete dominance
E. Complementation
Complementary
Examples:
You might also like
- AP Biology 2020 Practice Exam 2 FRQ PreviewDocument30 pagesAP Biology 2020 Practice Exam 2 FRQ Preview(22) Bahar Baturoglu100% (3)
- Urinalysis Case StudiesDocument11 pagesUrinalysis Case Studiesdandooshe38% (13)
- Medical Genetics 4th Edition Jorde Test BankDocument4 pagesMedical Genetics 4th Edition Jorde Test BankOdettesNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 10th Edition Lewis Test BankDocument24 pagesHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 10th Edition Lewis Test BankPalma Gibson100% (31)
- TestDaily分享 HL paper1Document18 pagesTestDaily分享 HL paper1gary gazaNo ratings yet
- SCI 111 Multiple Choice QuestionDocument15 pagesSCI 111 Multiple Choice QuestionShaira Jane Villareal AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 For GeneticsDocument5 pagesHomework 2 For GeneticsYunyoung KimNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Sec30 Answers KeyDocument9 pagesAssignment - Sec30 Answers KeyGiselle EleazarNo ratings yet
- GM Review2 HZDocument14 pagesGM Review2 HZfjewuqfheuwqfyqgf23fNo ratings yet
- Krok 1 Stomatology 2006Document21 pagesKrok 1 Stomatology 2006helloNo ratings yet
- Genetics - PYQs and Concept Maps-AKDocument92 pagesGenetics - PYQs and Concept Maps-AKSaiNagaVignesh BandhamNo ratings yet
- Krok 1 Stomatology 2007Document21 pagesKrok 1 Stomatology 2007helloNo ratings yet
- Dev psych-ACTIVITY-Module-4Document7 pagesDev psych-ACTIVITY-Module-4Anne SanchezNo ratings yet
- 4102600920398609Document61 pages4102600920398609sadhanalahemanthNo ratings yet
- SL 4 Test Questions GeneticsDocument16 pagesSL 4 Test Questions GeneticsAllison Khoo100% (1)
- 3rd Year Bcqs Hhhpathology-2Document38 pages3rd Year Bcqs Hhhpathology-2Hira PanhwerNo ratings yet
- k1 Stom F EngDocument19 pagesk1 Stom F EngAdnaneNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Bio 112-Molecular Biology and GeneticsDocument15 pagesFinal Examination Bio 112-Molecular Biology and GeneticsPrince-SimonJohnMwanza100% (1)
- Multiple Choice: Choose Best (2.5 Points Each, 80Document7 pagesMultiple Choice: Choose Best (2.5 Points Each, 80Florence BamigbolaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of The Living World 4th Edition George Johnson DownloadDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of The Living World 4th Edition George Johnson Downloadariadnemarthaauva100% (27)
- Genetics Vocabulary Worksheet 1 AnswersDocument2 pagesGenetics Vocabulary Worksheet 1 AnswersRyleigh SmithNo ratings yet
- Q. & A. Chap 05Document14 pagesQ. & A. Chap 05umamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Genbio2 ModuleDocument47 pagesGenbio2 ModuleAlbert Rosete100% (1)
- Genetics Questions To PrepareDocument6 pagesGenetics Questions To PrepareJohn Osborne100% (1)
- QUESTION BANK 2007 From UT HoustonDocument44 pagesQUESTION BANK 2007 From UT HoustonMindy Lee80% (5)
- Presentation 6,7,8,9,10-1Document96 pagesPresentation 6,7,8,9,10-1hgetachew208No ratings yet
- HL Paper1Document11 pagesHL Paper1Alexis OkosunNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology Principleofinheritanceandvariation tp01Document4 pages12 Biology Principleofinheritanceandvariation tp01Dec veenNo ratings yet
- Inheritance, Variation and Evolution MCQs Set 3Document2 pagesInheritance, Variation and Evolution MCQs Set 3melindahofmannNo ratings yet
- The Language of Genetics Punnett Squares Inheritance Patterns & Human Pedigrees DisordersDocument51 pagesThe Language of Genetics Punnett Squares Inheritance Patterns & Human Pedigrees DisordersehshonorsbioNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Past Exam MC QuestionsDocument14 pagesTopic 3 Past Exam MC QuestionsAhmad FarhatNo ratings yet
- Genetic Final ExamDocument58 pagesGenetic Final ExamTrần Đăng0% (1)
- Genetics and TeratologyDocument21 pagesGenetics and Teratologypandem soniya0% (1)
- Variation and GeneticsDocument11 pagesVariation and GeneticsTasawar Hussain DayoNo ratings yet
- Quiz BankDocument12 pagesQuiz Banknadim1241335No ratings yet
- Chapter 18: Evolutionary Changes in PopulationsDocument11 pagesChapter 18: Evolutionary Changes in PopulationsRCRIIINo ratings yet
- CB27 - Principles of Inheritance and Variation (Modified)Document8 pagesCB27 - Principles of Inheritance and Variation (Modified)Kaziranga English AcademyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument9 pagesChapter-5 Principles of Inheritance and VariationbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 3rd Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesGen Bio 2 3rd Quarter ExamAl SultanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GeneticsDocument6 pagesChapter 5 GeneticsMohamed Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- 01.14.02 Principles of Genetics - Overview of Genetic PathologyDocument9 pages01.14.02 Principles of Genetics - Overview of Genetic PathologyMikmik DGNo ratings yet
- Pathology - Female Reproductive MCQ's - MedPrepOnlineDocument19 pagesPathology - Female Reproductive MCQ's - MedPrepOnlineTony Dawa75% (4)
- 2-Gen-Sept-14-Inheritance of Complex Disorders Handout WeissbeckerDocument4 pages2-Gen-Sept-14-Inheritance of Complex Disorders Handout Weissbeckern-gorNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science 9Document3 pagesIntegrated Science 9jrm.tinoyNo ratings yet
- Heredity and VarationDocument7 pagesHeredity and VarationSwayam Tiwari ANDHNo ratings yet
- TestDaily分享 SL paper1Document24 pagesTestDaily分享 SL paper1gary gazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GeneticsDocument6 pagesChapter 5 GeneticsMohamed Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sample Mult Choice Qs 2018Document7 pagesSample Mult Choice Qs 2018yusrawasim147No ratings yet
- 2012, 25th AprilDocument11 pages2012, 25th Aprilgaruda nusantaraNo ratings yet
- BS Part 6Document7 pagesBS Part 6Lea Fe Comilang ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Wongs Nursing Care of Infants and Children 10th Edition Hockenberry Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Wongs Nursing Care of Infants and Children 10th Edition Hockenberry Test Bank PDFsophiafostercqcv100% (11)
- Gen Bio 2 G12Document3 pagesGen Bio 2 G12Janet BarcimoNo ratings yet
- Genetics Complete UnitDocument60 pagesGenetics Complete Unitchannel of dhyanaNo ratings yet
- Wongs Nursing Care of Infants and Children 10th Edition Hockenberry Test BankDocument14 pagesWongs Nursing Care of Infants and Children 10th Edition Hockenberry Test BankNicoleRoweanbtc100% (9)
- Chapter 5 Principle of Inheritance AndvariationDocument23 pagesChapter 5 Principle of Inheritance AndvariationJhanvi BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Medical Biology and Genetics II-1-1Document6 pagesMedical Biology and Genetics II-1-1Shoshka AliNo ratings yet
- (Student) Chapter 1 - Genetic Inheritance & Genetic ControlDocument24 pages(Student) Chapter 1 - Genetic Inheritance & Genetic ControlDanish Fitri RoslanNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 Genetics To EvolutionDocument12 pagesGen Bio 2 Genetics To EvolutionLeonard CubeloNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument5 pagesMCQvijay kamal meenaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Genetics - MendelismDocument15 pagesBIOLOGY Genetics - Mendelismmoviiiieee2021No ratings yet
- Evo Genetics TestDocument4 pagesEvo Genetics Testapi-545046625No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide To Genetic Diseases, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide To Genetic Diseases, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Plasma Protein DisordersDocument10 pagesInvestigation of Plasma Protein DisordersJosiah BimabamNo ratings yet
- Vii. Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument4 pagesVii. Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Metabolism - Disposal of NitrogenDocument16 pagesAmino Acid Metabolism - Disposal of NitrogenJanelle SumidoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation: Kidney Stone SymptomsDocument16 pagesClinical Presentation: Kidney Stone SymptomsangelynchristabellaNo ratings yet
- 1778 Uralyt U 1331882845Document5 pages1778 Uralyt U 1331882845James HornerNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument55 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic DisordersGlormina Asprec AvenaNo ratings yet
- Minnesota Urolith Center: Canine Cystine UrolithsDocument2 pagesMinnesota Urolith Center: Canine Cystine UrolithsC LNo ratings yet
- Kidney - Renal Stones and HomeopathyDocument4 pagesKidney - Renal Stones and HomeopathyAnonymous dpxYTENo ratings yet
- Clinical FirstDocument342 pagesClinical FirstYasmeen AtiehNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Urine and Body Fluids: Ammonium BiurateDocument2 pagesAnalysis of Urine and Body Fluids: Ammonium BiurateMLSNo ratings yet
- Digestion & Absorption ProteinsDocument44 pagesDigestion & Absorption ProteinsPutri Indah NirmalasariNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument189 pagesGeneticstolgaonayNo ratings yet
- 2011Document87 pages2011Bridget QuansahNo ratings yet
- Inherited Overflow Metabolic Overflow RenalDocument11 pagesInherited Overflow Metabolic Overflow RenalChrissa Mae Tumaliuan CatindoyNo ratings yet
- 1 Slide Urinary Crystals: Formed by The Precipitation of Urine SolutesDocument3 pages1 Slide Urinary Crystals: Formed by The Precipitation of Urine SolutesEveryday FundayNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan Semester 4-5 Maret 2022Document21 pagesPembahasan Semester 4-5 Maret 2022Angger SatriaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Kidney StoneDocument36 pagesCase Study On Kidney Stonemanojkumar200624No ratings yet
- Enzyme Deficiencies - CompiledDocument2 pagesEnzyme Deficiencies - CompiledparkerNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic Disorders: Learning ObjectivesDocument12 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic Disorders: Learning ObjectivesJonalyn LumantasNo ratings yet
- Batu GinjalDocument29 pagesBatu Ginjalarim100% (1)
- Ap Biology 2020 Practice Exam 2 FRQDocument30 pagesAp Biology 2020 Practice Exam 2 FRQEric ChiangNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis 2Document9 pagesUrinalysis 2Dawn GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 Metabolic Disorders HODocument23 pagesChapter 08 Metabolic Disorders HOFrances FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Krok1 PreparedDocument322 pagesKrok1 PreparedGMP EuropeNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Disorders 01Document41 pagesMetabolic Disorders 01Brent LagartoNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument9 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic DisordersXyleene Jency Bien IINo ratings yet
- Amino Acidss & AminoacidopathiesDocument55 pagesAmino Acidss & AminoacidopathiesMustafa KhandgawiNo ratings yet
- MCQ Blok 11Document10 pagesMCQ Blok 11Jefri SoniNo ratings yet