Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Underground Cut Patterns
Underground Cut Patterns
Uploaded by
Hemant KngCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ischebeck Titan Ground Engineering Systems 0523Document32 pagesIschebeck Titan Ground Engineering Systems 0523Thomas GlasbyNo ratings yet
- Dental BursDocument38 pagesDental BursMithra Rajendran100% (1)
- Rock Excavation Methods FinalDocument50 pagesRock Excavation Methods FinalJoanna GamboaNo ratings yet
- Roller Cone TrainingDocument86 pagesRoller Cone TrainingSlim.BNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Demolition PermitDocument1 pageProcedure For Demolition Permitpa3ckblanco100% (1)
- Underground Blasting: by Angesom.gDocument29 pagesUnderground Blasting: by Angesom.gYewuhalashet FisshaNo ratings yet
- Drilling Pattern - 1Document18 pagesDrilling Pattern - 1pranavkumar1961No ratings yet
- Drilling TechniquesDocument11 pagesDrilling Techniquessehrishb01No ratings yet
- Types of Cutting DiesDocument4 pagesTypes of Cutting DiesrheahabyennNo ratings yet
- Stone PDFDocument23 pagesStone PDFSanjuNo ratings yet
- Parameters For The Use of Drill BitsDocument16 pagesParameters For The Use of Drill BitsRaqi IzdiharaNo ratings yet
- Ahmed DrillingDocument5 pagesAhmed DrillingAhmed AmirNo ratings yet
- Ug Drilling PatternDocument30 pagesUg Drilling PatternAlem Anissa100% (1)
- Standard Engineering ReamersDocument5 pagesStandard Engineering Reamersnevin555No ratings yet
- Vol 1 3drillingDocument12 pagesVol 1 3drillingVamshi100% (1)
- Presenter:: Roll No: Class: B.Tech (Part-4) Subject: Underground Metal Mining LabDocument9 pagesPresenter:: Roll No: Class: B.Tech (Part-4) Subject: Underground Metal Mining LabAbhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- 3-2. DTH Button Bits enDocument13 pages3-2. DTH Button Bits enSubhash Kedia0% (1)
- Drill Hole Management Directional JH 1692369056Document30 pagesDrill Hole Management Directional JH 1692369056Hamdan MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Drill Bits - Directional DrillingDocument20 pagesDrill Bits - Directional Drillingahmed1adnan-10100% (1)
- D2 Holes, Coring, Threads (Compatibility Mode)Document19 pagesD2 Holes, Coring, Threads (Compatibility Mode)CIPETIPT Tool RoomNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Underground Metal MiningDocument38 pagesAssignment On Underground Metal MiningAnshul yadavNo ratings yet
- Resharpening of The Twist Drill BitsDocument5 pagesResharpening of The Twist Drill BitsJuanGómezNo ratings yet
- Me II Ch2 DrillingDocument52 pagesMe II Ch2 Drillingdereje mergaNo ratings yet
- Directfilppt PDFDocument24 pagesDirectfilppt PDFmelNo ratings yet
- Various Series of Bits Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageVarious Series of Bits Schematic Diagramthomas.edwardsNo ratings yet
- Leo Workshop: JSW Steels Ltd. Vijayanagara WorksDocument18 pagesLeo Workshop: JSW Steels Ltd. Vijayanagara WorksBinod Kumar PadhiNo ratings yet
- proffesional diamond driller΄s handbook EPIROCDocument52 pagesproffesional diamond driller΄s handbook EPIROCioan100% (1)
- Mandar Failure AnalysisDocument21 pagesMandar Failure Analysisraghavendrajoshi87No ratings yet
- Leo Workshop: JSW Steels Ltd. Vijayanagara WorksDocument16 pagesLeo Workshop: JSW Steels Ltd. Vijayanagara WorksBinod Kumar PadhiNo ratings yet
- Hack SawingDocument15 pagesHack SawingVergara KoyNo ratings yet
- Notes 7Document36 pagesNotes 7Ruben ChirinosNo ratings yet
- Stone Masonry ToolsDocument12 pagesStone Masonry ToolsDauha FaridiNo ratings yet
- Assignment On U Nderground Metal MiningDocument38 pagesAssignment On U Nderground Metal MiningAyush tiwari100% (1)
- ReamersDocument1 pageReamersvikash kumarNo ratings yet
- 01 Drill Bits SeminarDocument80 pages01 Drill Bits SeminarjalalNo ratings yet
- Defining BitsDocument2 pagesDefining BitsahmedNo ratings yet
- Roller BitDocument16 pagesRoller BitRebar KakaNo ratings yet
- Dental Bur and FunctionDocument3 pagesDental Bur and FunctionVony RibeiroNo ratings yet
- A) Hand InstrumentsDocument9 pagesA) Hand InstrumentsMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Caliper (Cal) Log: Mechanical: Caliper Measures Variations in Bore Hole Diameter With Depth, The MeasurementsDocument5 pagesCaliper (Cal) Log: Mechanical: Caliper Measures Variations in Bore Hole Diameter With Depth, The MeasurementsRamy MaamounNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 DrillingDocument12 pagesUnit 5 DrillingManav PatelNo ratings yet
- "V" Cut: Drilling and BlastingDocument14 pages"V" Cut: Drilling and BlastingGen LanggaNo ratings yet
- Bending and Forming of TubingDocument2 pagesBending and Forming of TubingcavnqnNo ratings yet
- 2847-Keys & Driving PinsDocument1 page2847-Keys & Driving PinssyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- 300 000 057 101Document8 pages300 000 057 101Jimmy Junior Blas VenegasNo ratings yet
- Standard Taper Reamers C 01 eDocument2 pagesStandard Taper Reamers C 01 eq5fmdkkk2hNo ratings yet
- Foundry Manual - Part 2Document13 pagesFoundry Manual - Part 2Flop ShowNo ratings yet
- Lab Pos. Teeth PrepDocument17 pagesLab Pos. Teeth Preprugeaelzwea2No ratings yet
- CNC MachiningDocument4 pagesCNC MachiningAdrianNo ratings yet
- GEOLOGYDocument2 pagesGEOLOGYCamille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- Lathe Modelling2Document2 pagesLathe Modelling2Marian DimaNo ratings yet
- Drill Bit TechnologyDocument39 pagesDrill Bit TechnologyMohamed MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Core BoringDocument2 pagesTopic 6 - Core BoringHikaruNo ratings yet
- Welding Assignment PDFDocument2 pagesWelding Assignment PDFBishal MondalNo ratings yet
- Directional & Horizontal DrillingDocument23 pagesDirectional & Horizontal DrillingMuhammad shahbazNo ratings yet
- Cracks Repair in PQCDocument3 pagesCracks Repair in PQCNeeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Shaft SinkingDocument70 pagesShaft SinkingHalo Zeus100% (1)
- Geotechnical Investigation: (Drilling Tools)Document17 pagesGeotechnical Investigation: (Drilling Tools)A Bashir AsalaiNo ratings yet
- Diamond Drillings and Its TypesDocument12 pagesDiamond Drillings and Its TypesPranjal Poudel0% (1)
- Rock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesFrom EverandRock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Metal-Working (Illustrated)From EverandAn Introduction to Metal-Working (Illustrated)Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Script - 1Document2 pagesScript - 1SAMNo ratings yet
- Indicadores Economicos Che Oct. 2014Document1 pageIndicadores Economicos Che Oct. 2014Mari Luz Hermoza MamaniNo ratings yet
- CS1 - 2011 Delegates FolderDocument81 pagesCS1 - 2011 Delegates FolderLászló MéhesNo ratings yet
- Petty Cash FundDocument8 pagesPetty Cash FundApril Rose AlagosNo ratings yet
- Report From C.P & NoidaDocument22 pagesReport From C.P & Noidadeepti singhalNo ratings yet
- x20 Netflix Mix AccountsDocument1 pagex20 Netflix Mix AccountsNathan MachadoNo ratings yet
- MaldivesDocument5 pagesMaldivesHav0c14No ratings yet
- Mali ResumeDocument2 pagesMali Resumeshashikantpatil24No ratings yet
- AOL Time Warner MergeDocument7 pagesAOL Time Warner Mergedipu francyNo ratings yet
- APML 2018 ManifestoDocument6 pagesAPML 2018 ManifestoDawndotcomNo ratings yet
- Chief Engineer Standing Orders - SL Martinique 2015Document3 pagesChief Engineer Standing Orders - SL Martinique 2015024Lita LucianaNo ratings yet
- Kerala State Electricity Board LimitedDocument12 pagesKerala State Electricity Board LimitedPuma PumaNo ratings yet
- Hapag LloydDocument9 pagesHapag LloydzubinpujaraNo ratings yet
- CCE Sustainability Report 15Document63 pagesCCE Sustainability Report 15BradAllenNo ratings yet
- Industrialization: Russia vs. Britain 1850-1914Document3 pagesIndustrialization: Russia vs. Britain 1850-1914Jonathan Cheng50% (2)
- Salary Slip (31837722 February, 2019) PDFDocument1 pageSalary Slip (31837722 February, 2019) PDFUsman AwanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 - Econ 221 - Basic MicroeconomicsDocument3 pagesMODULE 5 - Econ 221 - Basic MicroeconomicsNelly GenosasNo ratings yet
- 12 2 4Document1 page12 2 4AshleyNo ratings yet
- Reportingg ScriptDocument2 pagesReportingg ScriptKRYZLL JAILE PATUALNo ratings yet
- اختبار فرضيتي العجز التوأم والتكافؤ الريكارديDocument23 pagesاختبار فرضيتي العجز التوأم والتكافؤ الريكارديAhmed DanafNo ratings yet
- Krishnaveni Scavenger Retd Benifits TLS and SPFDocument24 pagesKrishnaveni Scavenger Retd Benifits TLS and SPFEso EeplNo ratings yet
- Basel Norms I, II and IIIDocument30 pagesBasel Norms I, II and IIIYashwanth PrasadNo ratings yet
- Barangay Annual Gender and Development (Gad) Plan and Budget FY 2020Document2 pagesBarangay Annual Gender and Development (Gad) Plan and Budget FY 2020Anne En NANo ratings yet
- Phool VMDocument15 pagesPhool VMzayana kadeeja100% (1)
- CHAPTER 3 - ManEcoDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 3 - ManEcoFlorenz Nicole PalisocNo ratings yet
- Ensayo Medio AmbienteDocument2 pagesEnsayo Medio Ambientemrisel76No ratings yet
- The Brigada EskwelaDocument11 pagesThe Brigada Eskwelagladys gomez100% (1)
- Pre Intermediate Progress Test 3Document4 pagesPre Intermediate Progress Test 3Pao NogalesNo ratings yet
- Chemical ContactDocument71 pagesChemical ContactZULIA s.r.o.No ratings yet
Underground Cut Patterns
Underground Cut Patterns
Uploaded by
Hemant KngOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Underground Cut Patterns
Underground Cut Patterns
Uploaded by
Hemant KngCopyright:
Available Formats
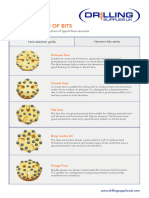
VARIOUS UNDERGROUND CUT PATTERNS
S.No. Name of cut Suitable type of description application Method of mining remark
pattern rock
1 Pyramid cut/ 1.Thick deposits Holes are drilled in horizontal plane w.r.t. face. drifting Its modified
Diamond Holes nearly meet at the centre of face. form is called
cut/double 2.very Hard rock Hole depth is approximately 50-60% of gallery width. cone cut.
wedge cut Consume very less explosive.
2 wedge cut/ 1.Thick deposits Holes are drilled at 45’ with the face plane. Coal mining Bord and pillar method Similar to
v- cut pattern Hole depth is restricted to 50% of drift width. pyramid cut
2.Hard rocks Consume very less explosive.
Suitable for large cross section drifts.
3 Burn cut 1.Hard brittle Parallel holes are drilled perpendicular to face plane. Metal mining Room and pillar method Called
rock Centre hole is charged and is surrounded by 4 empty parallel hole
2.Metallic holes ( large dia holes). cut.
deposits, massive Heavy charging is done.
rock formation Popular cut in underground metalliferous mining.
4 Coromant cut 1.Drifts/tunnels Very sophisticated cut pattern. For drift of very Similar to
of small cross Holes are drilled with help of pusher leg drill, guide small cross section. burn cut.
section in any tube, template and expander. Also called
rock Template is used to mark the hole spot for slot. parallel hole
2. sensitive areas Expander is used to expand the diameter of centre cut.
like river banks, hole.
pond periphery. Guide tube is used to drill 57 mm diameter hole at the
centre of the face.
Group of canter hole and six outer holes is called slot.
Centre hole is left uncharged.
5 Ring cut Moderately hard Holes are drilled in 360’ along a vertical plane. Coal and metal Blasting gallery method
And soft rocks Roof support is done in advance with cable bolting mining Shrinkage stoping
6 Fan cut 1.For laminated Holes are placed at distance such that each hole has drifting
strata to work for itself.
2. soft rock Heavy charging is done in the holes because holes are
independent.
7 Drag cut Laminated strata Suitable for small drifts. For drifting of 15-
Soft rock Holes are drilled parallel but perpendicular to the 20 m.
cleavage plane. Not suitable for
Because of dependency on the cleavage plane, ventilation drifting
direction of the drift changes frequently.
All patterns can be classified in two categories- inclined hole patterns and straight hole patterns.
You might also like
- Ischebeck Titan Ground Engineering Systems 0523Document32 pagesIschebeck Titan Ground Engineering Systems 0523Thomas GlasbyNo ratings yet
- Dental BursDocument38 pagesDental BursMithra Rajendran100% (1)
- Rock Excavation Methods FinalDocument50 pagesRock Excavation Methods FinalJoanna GamboaNo ratings yet
- Roller Cone TrainingDocument86 pagesRoller Cone TrainingSlim.BNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Demolition PermitDocument1 pageProcedure For Demolition Permitpa3ckblanco100% (1)
- Underground Blasting: by Angesom.gDocument29 pagesUnderground Blasting: by Angesom.gYewuhalashet FisshaNo ratings yet
- Drilling Pattern - 1Document18 pagesDrilling Pattern - 1pranavkumar1961No ratings yet
- Drilling TechniquesDocument11 pagesDrilling Techniquessehrishb01No ratings yet
- Types of Cutting DiesDocument4 pagesTypes of Cutting DiesrheahabyennNo ratings yet
- Stone PDFDocument23 pagesStone PDFSanjuNo ratings yet
- Parameters For The Use of Drill BitsDocument16 pagesParameters For The Use of Drill BitsRaqi IzdiharaNo ratings yet
- Ahmed DrillingDocument5 pagesAhmed DrillingAhmed AmirNo ratings yet
- Ug Drilling PatternDocument30 pagesUg Drilling PatternAlem Anissa100% (1)
- Standard Engineering ReamersDocument5 pagesStandard Engineering Reamersnevin555No ratings yet
- Vol 1 3drillingDocument12 pagesVol 1 3drillingVamshi100% (1)
- Presenter:: Roll No: Class: B.Tech (Part-4) Subject: Underground Metal Mining LabDocument9 pagesPresenter:: Roll No: Class: B.Tech (Part-4) Subject: Underground Metal Mining LabAbhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- 3-2. DTH Button Bits enDocument13 pages3-2. DTH Button Bits enSubhash Kedia0% (1)
- Drill Hole Management Directional JH 1692369056Document30 pagesDrill Hole Management Directional JH 1692369056Hamdan MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Drill Bits - Directional DrillingDocument20 pagesDrill Bits - Directional Drillingahmed1adnan-10100% (1)
- D2 Holes, Coring, Threads (Compatibility Mode)Document19 pagesD2 Holes, Coring, Threads (Compatibility Mode)CIPETIPT Tool RoomNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Underground Metal MiningDocument38 pagesAssignment On Underground Metal MiningAnshul yadavNo ratings yet
- Resharpening of The Twist Drill BitsDocument5 pagesResharpening of The Twist Drill BitsJuanGómezNo ratings yet
- Me II Ch2 DrillingDocument52 pagesMe II Ch2 Drillingdereje mergaNo ratings yet
- Directfilppt PDFDocument24 pagesDirectfilppt PDFmelNo ratings yet
- Various Series of Bits Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageVarious Series of Bits Schematic Diagramthomas.edwardsNo ratings yet
- Leo Workshop: JSW Steels Ltd. Vijayanagara WorksDocument18 pagesLeo Workshop: JSW Steels Ltd. Vijayanagara WorksBinod Kumar PadhiNo ratings yet
- proffesional diamond driller΄s handbook EPIROCDocument52 pagesproffesional diamond driller΄s handbook EPIROCioan100% (1)
- Mandar Failure AnalysisDocument21 pagesMandar Failure Analysisraghavendrajoshi87No ratings yet
- Leo Workshop: JSW Steels Ltd. Vijayanagara WorksDocument16 pagesLeo Workshop: JSW Steels Ltd. Vijayanagara WorksBinod Kumar PadhiNo ratings yet
- Hack SawingDocument15 pagesHack SawingVergara KoyNo ratings yet
- Notes 7Document36 pagesNotes 7Ruben ChirinosNo ratings yet
- Stone Masonry ToolsDocument12 pagesStone Masonry ToolsDauha FaridiNo ratings yet
- Assignment On U Nderground Metal MiningDocument38 pagesAssignment On U Nderground Metal MiningAyush tiwari100% (1)
- ReamersDocument1 pageReamersvikash kumarNo ratings yet
- 01 Drill Bits SeminarDocument80 pages01 Drill Bits SeminarjalalNo ratings yet
- Defining BitsDocument2 pagesDefining BitsahmedNo ratings yet
- Roller BitDocument16 pagesRoller BitRebar KakaNo ratings yet
- Dental Bur and FunctionDocument3 pagesDental Bur and FunctionVony RibeiroNo ratings yet
- A) Hand InstrumentsDocument9 pagesA) Hand InstrumentsMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Caliper (Cal) Log: Mechanical: Caliper Measures Variations in Bore Hole Diameter With Depth, The MeasurementsDocument5 pagesCaliper (Cal) Log: Mechanical: Caliper Measures Variations in Bore Hole Diameter With Depth, The MeasurementsRamy MaamounNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 DrillingDocument12 pagesUnit 5 DrillingManav PatelNo ratings yet
- "V" Cut: Drilling and BlastingDocument14 pages"V" Cut: Drilling and BlastingGen LanggaNo ratings yet
- Bending and Forming of TubingDocument2 pagesBending and Forming of TubingcavnqnNo ratings yet
- 2847-Keys & Driving PinsDocument1 page2847-Keys & Driving PinssyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- 300 000 057 101Document8 pages300 000 057 101Jimmy Junior Blas VenegasNo ratings yet
- Standard Taper Reamers C 01 eDocument2 pagesStandard Taper Reamers C 01 eq5fmdkkk2hNo ratings yet
- Foundry Manual - Part 2Document13 pagesFoundry Manual - Part 2Flop ShowNo ratings yet
- Lab Pos. Teeth PrepDocument17 pagesLab Pos. Teeth Preprugeaelzwea2No ratings yet
- CNC MachiningDocument4 pagesCNC MachiningAdrianNo ratings yet
- GEOLOGYDocument2 pagesGEOLOGYCamille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- Lathe Modelling2Document2 pagesLathe Modelling2Marian DimaNo ratings yet
- Drill Bit TechnologyDocument39 pagesDrill Bit TechnologyMohamed MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Core BoringDocument2 pagesTopic 6 - Core BoringHikaruNo ratings yet
- Welding Assignment PDFDocument2 pagesWelding Assignment PDFBishal MondalNo ratings yet
- Directional & Horizontal DrillingDocument23 pagesDirectional & Horizontal DrillingMuhammad shahbazNo ratings yet
- Cracks Repair in PQCDocument3 pagesCracks Repair in PQCNeeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Shaft SinkingDocument70 pagesShaft SinkingHalo Zeus100% (1)
- Geotechnical Investigation: (Drilling Tools)Document17 pagesGeotechnical Investigation: (Drilling Tools)A Bashir AsalaiNo ratings yet
- Diamond Drillings and Its TypesDocument12 pagesDiamond Drillings and Its TypesPranjal Poudel0% (1)
- Rock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesFrom EverandRock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Metal-Working (Illustrated)From EverandAn Introduction to Metal-Working (Illustrated)Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Script - 1Document2 pagesScript - 1SAMNo ratings yet
- Indicadores Economicos Che Oct. 2014Document1 pageIndicadores Economicos Che Oct. 2014Mari Luz Hermoza MamaniNo ratings yet
- CS1 - 2011 Delegates FolderDocument81 pagesCS1 - 2011 Delegates FolderLászló MéhesNo ratings yet
- Petty Cash FundDocument8 pagesPetty Cash FundApril Rose AlagosNo ratings yet
- Report From C.P & NoidaDocument22 pagesReport From C.P & Noidadeepti singhalNo ratings yet
- x20 Netflix Mix AccountsDocument1 pagex20 Netflix Mix AccountsNathan MachadoNo ratings yet
- MaldivesDocument5 pagesMaldivesHav0c14No ratings yet
- Mali ResumeDocument2 pagesMali Resumeshashikantpatil24No ratings yet
- AOL Time Warner MergeDocument7 pagesAOL Time Warner Mergedipu francyNo ratings yet
- APML 2018 ManifestoDocument6 pagesAPML 2018 ManifestoDawndotcomNo ratings yet
- Chief Engineer Standing Orders - SL Martinique 2015Document3 pagesChief Engineer Standing Orders - SL Martinique 2015024Lita LucianaNo ratings yet
- Kerala State Electricity Board LimitedDocument12 pagesKerala State Electricity Board LimitedPuma PumaNo ratings yet
- Hapag LloydDocument9 pagesHapag LloydzubinpujaraNo ratings yet
- CCE Sustainability Report 15Document63 pagesCCE Sustainability Report 15BradAllenNo ratings yet
- Industrialization: Russia vs. Britain 1850-1914Document3 pagesIndustrialization: Russia vs. Britain 1850-1914Jonathan Cheng50% (2)
- Salary Slip (31837722 February, 2019) PDFDocument1 pageSalary Slip (31837722 February, 2019) PDFUsman AwanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 - Econ 221 - Basic MicroeconomicsDocument3 pagesMODULE 5 - Econ 221 - Basic MicroeconomicsNelly GenosasNo ratings yet
- 12 2 4Document1 page12 2 4AshleyNo ratings yet
- Reportingg ScriptDocument2 pagesReportingg ScriptKRYZLL JAILE PATUALNo ratings yet
- اختبار فرضيتي العجز التوأم والتكافؤ الريكارديDocument23 pagesاختبار فرضيتي العجز التوأم والتكافؤ الريكارديAhmed DanafNo ratings yet
- Krishnaveni Scavenger Retd Benifits TLS and SPFDocument24 pagesKrishnaveni Scavenger Retd Benifits TLS and SPFEso EeplNo ratings yet
- Basel Norms I, II and IIIDocument30 pagesBasel Norms I, II and IIIYashwanth PrasadNo ratings yet
- Barangay Annual Gender and Development (Gad) Plan and Budget FY 2020Document2 pagesBarangay Annual Gender and Development (Gad) Plan and Budget FY 2020Anne En NANo ratings yet
- Phool VMDocument15 pagesPhool VMzayana kadeeja100% (1)
- CHAPTER 3 - ManEcoDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 3 - ManEcoFlorenz Nicole PalisocNo ratings yet
- Ensayo Medio AmbienteDocument2 pagesEnsayo Medio Ambientemrisel76No ratings yet
- The Brigada EskwelaDocument11 pagesThe Brigada Eskwelagladys gomez100% (1)
- Pre Intermediate Progress Test 3Document4 pagesPre Intermediate Progress Test 3Pao NogalesNo ratings yet
- Chemical ContactDocument71 pagesChemical ContactZULIA s.r.o.No ratings yet