Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsCAPD
CAPD
Uploaded by
Berley BrooksCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Practical Medical Oncology Textbook (Antonio Russo, Marc Peeters, Lorena Incorvaia Etc.)Document1,104 pagesPractical Medical Oncology Textbook (Antonio Russo, Marc Peeters, Lorena Incorvaia Etc.)Paolo FassinaNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Notes 1Document3 pagesDialysis Notes 1SarahSigrid88% (24)
- DIALYSISDocument6 pagesDIALYSISJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- CRRT Self Learning PKT 5 - 2015Document25 pagesCRRT Self Learning PKT 5 - 2015pamorales100% (1)
- Dialysis DocumentDocument3 pagesDialysis DocumentLucelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Renal Physiology For MBBSDocument129 pagesLecture Notes On Renal Physiology For MBBSNayyer Khan83% (6)
- What Is DialysisDocument17 pagesWhat Is DialysisnsrimadhavarajaNo ratings yet
- Dialysis 104412Document5 pagesDialysis 104412nidhi100nNo ratings yet
- Dialysismachine2 160121151938Document42 pagesDialysismachine2 160121151938Ebrahim Abd El HadyNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis Gopuy22Document26 pagesHemodialysis Gopuy22Salim AloneNo ratings yet
- Renal Replacement Therapies Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisDocument86 pagesRenal Replacement Therapies Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisSabita Tripathi100% (2)
- Dialysis - Need and Types in Dialysis - 13131Document23 pagesDialysis - Need and Types in Dialysis - 13131muthuNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab 1Document8 pagesBiochem Lab 1Kristine PangahinNo ratings yet
- DialysisDocument34 pagesDialysisdaisy100% (3)
- PDDocument27 pagesPDDebasree sahaNo ratings yet
- DIALISIS BacaDocument4 pagesDIALISIS BacabrokentinjaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Renal Function and TestsDocument63 pagesLESSON 3 Renal Function and TestsFaith TambongNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisDocument57 pagesHemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysisirene joy91% (11)
- Hemodialysis Machine12Document45 pagesHemodialysis Machine12Divya SoundarajanNo ratings yet
- DialysisDocument17 pagesDialysisLALITH SAI KNo ratings yet
- L5 - Kidney FailureDocument15 pagesL5 - Kidney Failurekemi.sklNo ratings yet
- Class 5 (12.07.2022)Document72 pagesClass 5 (12.07.2022)Ãqûã FîggâNo ratings yet
- Dialysis PrescriptionDocument23 pagesDialysis PrescriptionMercy Juliana Jacqualine100% (1)
- Clinical Teaching On HaemodialysisDocument7 pagesClinical Teaching On HaemodialysisAnusha AkhilNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal Dialysis SeminarDocument25 pagesPeritoneal Dialysis SeminardrresmiajithNo ratings yet
- Renal Replacement Therapy HandoutDocument4 pagesRenal Replacement Therapy HandoutAsdzxcNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Notes 1Document3 pagesDialysis Notes 1Kavidu KeshanNo ratings yet
- DialysisDocument63 pagesDialysisDhonat Flash100% (1)
- Dialysis 200819075444Document96 pagesDialysis 200819075444nadeeshashami675No ratings yet
- Paper II - Urine FormationDocument4 pagesPaper II - Urine Formationritik dwivediNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching On HaemodialysisDocument7 pagesClinical Teaching On HaemodialysisAnusha AkhilNo ratings yet
- Dialysis (Hemodialysis and Peritoneal)Document63 pagesDialysis (Hemodialysis and Peritoneal)Qeely100% (2)
- DIALYSIS ReportingDocument10 pagesDIALYSIS ReportingGlenelyn Grace InfanteNo ratings yet
- Iv TherapyDocument15 pagesIv Therapynorhain4.aNo ratings yet
- Dialysis: Navigation SearchDocument48 pagesDialysis: Navigation SearchCalimlim KimNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Dose Prescription: Presented by Dr. UjjawalDocument54 pagesDialysis Dose Prescription: Presented by Dr. UjjawalZH. omg sarNo ratings yet
- RRT - MSDocument57 pagesRRT - MSfrankozed1No ratings yet
- Intravenous TherapyDocument20 pagesIntravenous TherapyFaith Tabangay ManalangNo ratings yet
- CV-5 PH MicrocircDocument34 pagesCV-5 PH Microcircaya najemNo ratings yet
- Dialysis BiologyDocument13 pagesDialysis BiologyDeeptiValunjkarNo ratings yet
- HEMODIALYSI1Document4 pagesHEMODIALYSI1ashi leginNo ratings yet
- Dialysis PresentationDocument21 pagesDialysis PresentationRon Anderson100% (1)
- HEMODIALYSIS FinalDocument8 pagesHEMODIALYSIS Finalvineeta.ashoknagarNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis Seperation ProcessDocument7 pagesHemodialysis Seperation Processchen18111007 KFUEITNo ratings yet
- Dialysis TrainingDocument83 pagesDialysis TrainingJspmani2040No ratings yet
- Continuous Renal Replacement TherapyDocument38 pagesContinuous Renal Replacement Therapyanju rachel joseNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis 1Document25 pagesHemodialysis 1Jasmine KaurNo ratings yet
- HemodialysisDocument19 pagesHemodialysissofi wardatiNo ratings yet
- Extra Corporeal Removal of DrugsDocument25 pagesExtra Corporeal Removal of Drugsyuppie_raj2175No ratings yet
- Dialysis ReviewerDocument66 pagesDialysis ReviewerMarife Joy Loredo Gagarin0% (1)
- Body Fluid DistributionDocument56 pagesBody Fluid DistributionZoya Morani100% (1)
- HemodialysisDocument9 pagesHemodialysisKristine Artes Aguilar100% (2)
- Hemodialysis MachineDocument17 pagesHemodialysis MachineMehdi MohammedNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal DialysisDocument13 pagesPeritoneal DialysisDebasree sahaNo ratings yet
- DialysisDocument9 pagesDialysisfelipeferreiramendesleaoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Faiez Alhmoud Albashir Teaching HospitalDocument76 pagesDr. Faiez Alhmoud Albashir Teaching HospitalDr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- IVFDocument20 pagesIVFAntonette RendalNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Centre: Assignment - 3Document12 pagesDialysis Centre: Assignment - 3grvoneandonlyNo ratings yet
- DIALYSIS ProcedureDocument8 pagesDIALYSIS ProcedureRaman SamraoNo ratings yet
- HemodialysisDocument5 pagesHemodialysisSameer MhatreNo ratings yet
- Bipolar DisorderDocument44 pagesBipolar DisorderBerley BrooksNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument62 pagesAnxiety DisordersBerley BrooksNo ratings yet
- Eating DisordersDocument27 pagesEating DisordersBerley BrooksNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theory and The Discipline of NursingDocument42 pagesNursing Theory and The Discipline of NursingBerley BrooksNo ratings yet
- Florence Nightingale's LegacyDocument23 pagesFlorence Nightingale's LegacyBerley BrooksNo ratings yet
- EstradiolDocument1 pageEstradiol3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2666765722001661 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S2666765722001661 MainJoshua HammedNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAnn Therese C. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Nonconvulsive Status Epilepticus: Validating The Salzburg Criteria Against An Expert EEG ExaminerDocument5 pagesNonconvulsive Status Epilepticus: Validating The Salzburg Criteria Against An Expert EEG ExaminerNathaly LapoNo ratings yet
- Nurnbergprosessen Starter Den 03.07.2021Document3 pagesNurnbergprosessen Starter Den 03.07.2021Gabriel ChiquettoNo ratings yet
- PRM - Ma5 BookletDocument25 pagesPRM - Ma5 BookletVan LabasanoNo ratings yet
- The Small Intestine Channel - Discernment, Sorting, Mental ClarityDocument5 pagesThe Small Intestine Channel - Discernment, Sorting, Mental Clarityلوليتا وردةNo ratings yet
- 2-Preschool Parent QuestionnaireDocument3 pages2-Preschool Parent QuestionnaireION677No ratings yet
- VheeeeDocument50 pagesVheeeeKathlene GamitNo ratings yet
- Ecologic ModelDocument3 pagesEcologic ModelHazel Regencia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Effect of Swedish Massage and Hot Mud With Calotropis Gigantea Application Among Knee Joint Osteoarthritis Cases-A Randomized Control TrialDocument5 pagesEffect of Swedish Massage and Hot Mud With Calotropis Gigantea Application Among Knee Joint Osteoarthritis Cases-A Randomized Control TrialIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Stannard Chapter5Document22 pagesStannard Chapter5Mae ann BalgoaNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank Law National Blood Service Act of 1994Document2 pagesBlood Bank Law National Blood Service Act of 1994Jess DelapazNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Patients With Ventilation DisordersDocument33 pagesNursing Care of Patients With Ventilation DisordersYAMINIPRIYANNo ratings yet
- Staff Doses in Interventional Cardiology and Radiology PurposeDocument7 pagesStaff Doses in Interventional Cardiology and Radiology Purposedian riantiNo ratings yet
- Lam. Pathway Gagal Jantung KongestiDocument2 pagesLam. Pathway Gagal Jantung KongestiMegawati Dwi PutriNo ratings yet
- Gareth Loosle Ot Resume 2018Document2 pagesGareth Loosle Ot Resume 2018api-436257683No ratings yet
- Trindade 2018Document10 pagesTrindade 2018Tales FernandoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Aspects of IVHDocument11 pagesClinical Aspects of IVHsteffiwpNo ratings yet
- Gi MapDocument5 pagesGi MapBethany MosesNo ratings yet
- Measles EpiDocument22 pagesMeasles Epiمحمد صالحNo ratings yet
- Management of C Shaped Canals: 3 Case ReportsDocument3 pagesManagement of C Shaped Canals: 3 Case ReportsTaufiqurrahman Abdul Djabbar100% (1)
- Vaccines 08 00321Document17 pagesVaccines 08 00321Kshitiz Raj ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Obs & GynDocument121 pagesObs & GynSaya K. AkremNo ratings yet
- IMP Scientific Review Clinical Documentation On OsseoSpeed Profile Implants Documentation EN 32670089 USX 1805Document2 pagesIMP Scientific Review Clinical Documentation On OsseoSpeed Profile Implants Documentation EN 32670089 USX 1805Mary SmileNo ratings yet
- KochDocument3 pagesKochJared NyakambaNo ratings yet
- Which Is Not True of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) ?Document241 pagesWhich Is Not True of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) ?Mostafa Kamel TemrazNo ratings yet
- Anestesi Pada Pasien Gangguan GinjalDocument28 pagesAnestesi Pada Pasien Gangguan GinjallovianettesherryNo ratings yet
- Management of ChoriocarcinomaDocument27 pagesManagement of Choriocarcinomaapi-3705046100% (2)
CAPD
CAPD
Uploaded by
Berley Brooks0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views19 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views19 pagesCAPD
CAPD
Uploaded by
Berley BrooksCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 19
Tracy Morrill MSN, RN, CLN
Kathleen Conway MSN, APRN
» Thirteen percent of Americans now have
chronic kidney disease, up 3% over the last
decade, mostly due to higher rates of diabetes
and high blood pressure.
» Kidney disease ranks low on America's radar
screen. But it's a major killer. While many
patients with chronic kidney disease go on to
die of kidney failure, many more of these
patients die of heart disease.
» Kidneys are the dynamic duo of filtration of the
blood.
» The 1 million nephrons in each kidney filter the
blood, form urine and excrete toxins and waste.
» Damage to the nephrons decreases their
filtration capabilities thereby allowing the build
up of toxins and waste which damage blood
vessels and organs.
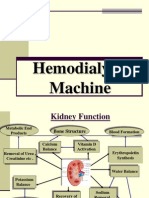
» Describe the structures of the kidney
» Outline the role of the kidneys
» Verbalize understanding of terminology
» Describe types of dialysis including rationales
» Kidneys are paired retroperitoneal structures
that are located betweeen the transverse
processes of T12 to L3.
» They receive approximately 20% of the cardiac
output (the amount of blood pumped by the
heart averages 4-8 LPM)
» The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney
&there is approximately 1-1.25 million in each
kidney
» The glomerulus is a cluster of vessels that acts
as a filter and is connected to a tubule (each
pair makes a nephron)
» The membrane is semi-permeable which
allows waste products and water to pass into
the tubule while retaining RBCs and proteins in
the blood
» Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) – volume of plasma from the
glomerulus into the Bowman’s capsule each minute (ml/min)
» Diffusion – movement of particles from an area of higher
concentration to an area of lesser concentration. Diffusion stops
when equilibrium occurs.
» Osmosis- movement of water across a semipermeable membrane
from an area of lower concentration of solutes to an area of higher
concentration of solutes. Osmosis stops when equilibrium occurs.
» Hydrostatic Pressure – the pressure a solution exerts against the
wall of its container. If the container is permeable, filtration
occurs.
» Isotonic solution – a solution with concentration the same as body
fluid (such as NSS and LR)
» Hypertonic solution – a solution where concentration is greater
than what it is compared to, thereby drawing and retaining water
in the circulation increasing blood volume (such as D5W with
0.45NS, D10, D5NS)
» Hypotonic solution – a solution where the concentration is less
than that with which it is compared. This allows water to shift out
of the capillaries into the tissues, resulting in decreased blood
volume (such as 0.45NS)
» Osmolality – is a term that reflects the number of particles (such as
electrolytes) dissolved in the urine. (dehydration – high osmolality,
volume excess – low osmolality)
» Specific gravity – 1.015-1.025 (lower end dilution, higher end
concentration)
» Creatinine – is an endogenous waste product of skeletal muscle
that is excreted by glomerular filtration and is not appreciably
reabsorbed or secreted by the renal tubules.
» Renin is secreted by the juxtaglomerular cells when
BP decreases.
» An enzyme converts the renin to angiotensin I then
to angiotensin II.
» In return this causes the blood pressure to increase.
» Aldosterone is secreted by the adrenals which
increases NA and water (by releasing ACTH –
adrenocorticotropic hormone) which increase
extracellular volume thereby increasing BP.
» Functions:
˃ Filtration & excretion of metabolic wastes
˃ Regulation of electrolytes
˃ Acid/Base balance
˃ Regulation of blood pressure
˃ Controlling reabsorption of water & maintaining
intravascular volume
˃ Reabsorption of glucose & amino acids
˃ Hormonal function via erythropoetin, calcitrol and
vitamin D activation
» Definition:
˃ Irreversible decline in a person’s kidney
function that is severe enough that without
dialysis or a transplant the patient will die
˃ It is measured by the GFR (the average
glomerular filtration rate is 90-120 ml/min)
˃ GFR below 15ml/min is a sign of renal failure
» Affects more than 1500 people per million in countries
with high prevalence such as US and Japan
» 2/3 receive hemodialysis, ¼ receive transplants, 1/10
receive peritoneal dialysis
» Risk factors include:
˃ Advanced age
˃ Diabetes
˃ HTN
˃ Obesity
˃ HX of renal disease
˃ Smoking
˃ Drug use
˃ Analgesic use
» The leading cause of mortality in
ESRD is cardiovascular disease
» The prognosis is poor for these
patients
» Hemodialysis
˃ This type of dialysis uses a special dialyzer thast acts as an artificial
kidney to clean the blood
˃ The machine pulls blood through diffeerent types of “baths” and
then returns it to the patient
˃ Some patients need fluid removed during the treatment but
others may just need to be “even”
˃ Patient NEEDS a special central line in order to do this type of
dialysis, such as the Quinton or Vaxcell catheters
˃ Instead, a patient may have an AV fistula that will need at least 6-8
weeks to mature once it is surgically created
˃ There is an arterial & venous port for blood to be to pulled from
and returned to the patient
˃ The procedure takes approximately 3-4 hours
˃ The patient needs to go to a facility for treatment on average 3
times a week
˃ It can be exhausting and time consuming
» Peritoneal Dialysis
˃ A catheter is placed in the peritoneal membrane
˃ Fluid is instilled and allowed to dwell then emptied
˃ The procedure is repeated every 4-6 hours per the
provider’s orders
˃ The process of peritoneal dialysis is based on
diffusion and osmosis
˃ CCPD (continuous cycling peritoneal dialysis) is
performed on a machine continuously at night while
the patient sleeps
˃ CAPD (continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis) is
performed without the use of the machine
» You will begin to learn about CAPD (continuous
ambulatory peritoneal dialysis)and the role and
responsibilities of the nurse. This portion of your
training will include viewing four videos that will
give you a base of knowledge for your training.
» The videos have sound so please ensure that you
are using a desk top computer that allows for
sound.
» You may want to use head phones and a computer
in one of the Education computer rooms on the
second floor.
» Please view the following videos in sequence:
A prompt will appear asking if you want to “Open” (yes) or “Save”
(no). You will also need to close each video at the end.
» Introduction-to-Peritoneal-Dialysis video #1 of 4 Time 23:41
» Damage-to-PD-Catheter video #2 of 4 Time 13:07
» Ultra-Bag-Solution-Delivery-system video #3 of 4 Time 11:53
» Transfer-Set-Change-Procedure video #4 of 4 Time 6:27
These videos can also be found on the hospital Intranet, in the
Education and Organization Development site within the Training
Video Library.
REMEMBER:
» You will attend a class that will continue your CAPD
learning.
» The third and final component to your independent
management of CAPD for your patients is a skills
validation by a mentor. Details will be provided to
you during the class.
» All three segments of the training must be
completed.
» Please direct your questions to:
Education Department
Kathleen Conway X 7618
You might also like
- Practical Medical Oncology Textbook (Antonio Russo, Marc Peeters, Lorena Incorvaia Etc.)Document1,104 pagesPractical Medical Oncology Textbook (Antonio Russo, Marc Peeters, Lorena Incorvaia Etc.)Paolo FassinaNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Notes 1Document3 pagesDialysis Notes 1SarahSigrid88% (24)
- DIALYSISDocument6 pagesDIALYSISJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- CRRT Self Learning PKT 5 - 2015Document25 pagesCRRT Self Learning PKT 5 - 2015pamorales100% (1)
- Dialysis DocumentDocument3 pagesDialysis DocumentLucelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Renal Physiology For MBBSDocument129 pagesLecture Notes On Renal Physiology For MBBSNayyer Khan83% (6)
- What Is DialysisDocument17 pagesWhat Is DialysisnsrimadhavarajaNo ratings yet
- Dialysis 104412Document5 pagesDialysis 104412nidhi100nNo ratings yet
- Dialysismachine2 160121151938Document42 pagesDialysismachine2 160121151938Ebrahim Abd El HadyNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis Gopuy22Document26 pagesHemodialysis Gopuy22Salim AloneNo ratings yet
- Renal Replacement Therapies Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisDocument86 pagesRenal Replacement Therapies Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisSabita Tripathi100% (2)
- Dialysis - Need and Types in Dialysis - 13131Document23 pagesDialysis - Need and Types in Dialysis - 13131muthuNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab 1Document8 pagesBiochem Lab 1Kristine PangahinNo ratings yet
- DialysisDocument34 pagesDialysisdaisy100% (3)
- PDDocument27 pagesPDDebasree sahaNo ratings yet
- DIALISIS BacaDocument4 pagesDIALISIS BacabrokentinjaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Renal Function and TestsDocument63 pagesLESSON 3 Renal Function and TestsFaith TambongNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisDocument57 pagesHemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysisirene joy91% (11)
- Hemodialysis Machine12Document45 pagesHemodialysis Machine12Divya SoundarajanNo ratings yet
- DialysisDocument17 pagesDialysisLALITH SAI KNo ratings yet
- L5 - Kidney FailureDocument15 pagesL5 - Kidney Failurekemi.sklNo ratings yet
- Class 5 (12.07.2022)Document72 pagesClass 5 (12.07.2022)Ãqûã FîggâNo ratings yet
- Dialysis PrescriptionDocument23 pagesDialysis PrescriptionMercy Juliana Jacqualine100% (1)
- Clinical Teaching On HaemodialysisDocument7 pagesClinical Teaching On HaemodialysisAnusha AkhilNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal Dialysis SeminarDocument25 pagesPeritoneal Dialysis SeminardrresmiajithNo ratings yet
- Renal Replacement Therapy HandoutDocument4 pagesRenal Replacement Therapy HandoutAsdzxcNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Notes 1Document3 pagesDialysis Notes 1Kavidu KeshanNo ratings yet
- DialysisDocument63 pagesDialysisDhonat Flash100% (1)
- Dialysis 200819075444Document96 pagesDialysis 200819075444nadeeshashami675No ratings yet
- Paper II - Urine FormationDocument4 pagesPaper II - Urine Formationritik dwivediNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching On HaemodialysisDocument7 pagesClinical Teaching On HaemodialysisAnusha AkhilNo ratings yet
- Dialysis (Hemodialysis and Peritoneal)Document63 pagesDialysis (Hemodialysis and Peritoneal)Qeely100% (2)
- DIALYSIS ReportingDocument10 pagesDIALYSIS ReportingGlenelyn Grace InfanteNo ratings yet
- Iv TherapyDocument15 pagesIv Therapynorhain4.aNo ratings yet
- Dialysis: Navigation SearchDocument48 pagesDialysis: Navigation SearchCalimlim KimNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Dose Prescription: Presented by Dr. UjjawalDocument54 pagesDialysis Dose Prescription: Presented by Dr. UjjawalZH. omg sarNo ratings yet
- RRT - MSDocument57 pagesRRT - MSfrankozed1No ratings yet
- Intravenous TherapyDocument20 pagesIntravenous TherapyFaith Tabangay ManalangNo ratings yet
- CV-5 PH MicrocircDocument34 pagesCV-5 PH Microcircaya najemNo ratings yet
- Dialysis BiologyDocument13 pagesDialysis BiologyDeeptiValunjkarNo ratings yet
- HEMODIALYSI1Document4 pagesHEMODIALYSI1ashi leginNo ratings yet
- Dialysis PresentationDocument21 pagesDialysis PresentationRon Anderson100% (1)
- HEMODIALYSIS FinalDocument8 pagesHEMODIALYSIS Finalvineeta.ashoknagarNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis Seperation ProcessDocument7 pagesHemodialysis Seperation Processchen18111007 KFUEITNo ratings yet
- Dialysis TrainingDocument83 pagesDialysis TrainingJspmani2040No ratings yet
- Continuous Renal Replacement TherapyDocument38 pagesContinuous Renal Replacement Therapyanju rachel joseNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis 1Document25 pagesHemodialysis 1Jasmine KaurNo ratings yet
- HemodialysisDocument19 pagesHemodialysissofi wardatiNo ratings yet
- Extra Corporeal Removal of DrugsDocument25 pagesExtra Corporeal Removal of Drugsyuppie_raj2175No ratings yet
- Dialysis ReviewerDocument66 pagesDialysis ReviewerMarife Joy Loredo Gagarin0% (1)
- Body Fluid DistributionDocument56 pagesBody Fluid DistributionZoya Morani100% (1)
- HemodialysisDocument9 pagesHemodialysisKristine Artes Aguilar100% (2)
- Hemodialysis MachineDocument17 pagesHemodialysis MachineMehdi MohammedNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal DialysisDocument13 pagesPeritoneal DialysisDebasree sahaNo ratings yet
- DialysisDocument9 pagesDialysisfelipeferreiramendesleaoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Faiez Alhmoud Albashir Teaching HospitalDocument76 pagesDr. Faiez Alhmoud Albashir Teaching HospitalDr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- IVFDocument20 pagesIVFAntonette RendalNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Centre: Assignment - 3Document12 pagesDialysis Centre: Assignment - 3grvoneandonlyNo ratings yet
- DIALYSIS ProcedureDocument8 pagesDIALYSIS ProcedureRaman SamraoNo ratings yet
- HemodialysisDocument5 pagesHemodialysisSameer MhatreNo ratings yet
- Bipolar DisorderDocument44 pagesBipolar DisorderBerley BrooksNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument62 pagesAnxiety DisordersBerley BrooksNo ratings yet
- Eating DisordersDocument27 pagesEating DisordersBerley BrooksNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theory and The Discipline of NursingDocument42 pagesNursing Theory and The Discipline of NursingBerley BrooksNo ratings yet
- Florence Nightingale's LegacyDocument23 pagesFlorence Nightingale's LegacyBerley BrooksNo ratings yet
- EstradiolDocument1 pageEstradiol3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2666765722001661 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S2666765722001661 MainJoshua HammedNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAnn Therese C. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Nonconvulsive Status Epilepticus: Validating The Salzburg Criteria Against An Expert EEG ExaminerDocument5 pagesNonconvulsive Status Epilepticus: Validating The Salzburg Criteria Against An Expert EEG ExaminerNathaly LapoNo ratings yet
- Nurnbergprosessen Starter Den 03.07.2021Document3 pagesNurnbergprosessen Starter Den 03.07.2021Gabriel ChiquettoNo ratings yet
- PRM - Ma5 BookletDocument25 pagesPRM - Ma5 BookletVan LabasanoNo ratings yet
- The Small Intestine Channel - Discernment, Sorting, Mental ClarityDocument5 pagesThe Small Intestine Channel - Discernment, Sorting, Mental Clarityلوليتا وردةNo ratings yet
- 2-Preschool Parent QuestionnaireDocument3 pages2-Preschool Parent QuestionnaireION677No ratings yet
- VheeeeDocument50 pagesVheeeeKathlene GamitNo ratings yet
- Ecologic ModelDocument3 pagesEcologic ModelHazel Regencia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Effect of Swedish Massage and Hot Mud With Calotropis Gigantea Application Among Knee Joint Osteoarthritis Cases-A Randomized Control TrialDocument5 pagesEffect of Swedish Massage and Hot Mud With Calotropis Gigantea Application Among Knee Joint Osteoarthritis Cases-A Randomized Control TrialIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Stannard Chapter5Document22 pagesStannard Chapter5Mae ann BalgoaNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank Law National Blood Service Act of 1994Document2 pagesBlood Bank Law National Blood Service Act of 1994Jess DelapazNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Patients With Ventilation DisordersDocument33 pagesNursing Care of Patients With Ventilation DisordersYAMINIPRIYANNo ratings yet
- Staff Doses in Interventional Cardiology and Radiology PurposeDocument7 pagesStaff Doses in Interventional Cardiology and Radiology Purposedian riantiNo ratings yet
- Lam. Pathway Gagal Jantung KongestiDocument2 pagesLam. Pathway Gagal Jantung KongestiMegawati Dwi PutriNo ratings yet
- Gareth Loosle Ot Resume 2018Document2 pagesGareth Loosle Ot Resume 2018api-436257683No ratings yet
- Trindade 2018Document10 pagesTrindade 2018Tales FernandoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Aspects of IVHDocument11 pagesClinical Aspects of IVHsteffiwpNo ratings yet
- Gi MapDocument5 pagesGi MapBethany MosesNo ratings yet
- Measles EpiDocument22 pagesMeasles Epiمحمد صالحNo ratings yet
- Management of C Shaped Canals: 3 Case ReportsDocument3 pagesManagement of C Shaped Canals: 3 Case ReportsTaufiqurrahman Abdul Djabbar100% (1)
- Vaccines 08 00321Document17 pagesVaccines 08 00321Kshitiz Raj ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Obs & GynDocument121 pagesObs & GynSaya K. AkremNo ratings yet
- IMP Scientific Review Clinical Documentation On OsseoSpeed Profile Implants Documentation EN 32670089 USX 1805Document2 pagesIMP Scientific Review Clinical Documentation On OsseoSpeed Profile Implants Documentation EN 32670089 USX 1805Mary SmileNo ratings yet
- KochDocument3 pagesKochJared NyakambaNo ratings yet
- Which Is Not True of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) ?Document241 pagesWhich Is Not True of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) ?Mostafa Kamel TemrazNo ratings yet
- Anestesi Pada Pasien Gangguan GinjalDocument28 pagesAnestesi Pada Pasien Gangguan GinjallovianettesherryNo ratings yet
- Management of ChoriocarcinomaDocument27 pagesManagement of Choriocarcinomaapi-3705046100% (2)