Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 1 Disorders of The Ear
Lecture 1 Disorders of The Ear
Uploaded by
drunkenwukongCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ENT Toronto Notes 2006Document52 pagesENT Toronto Notes 2006Jacklyn Yek100% (1)
- Untitled15 PDFDocument22 pagesUntitled15 PDFElizabeth LeonNo ratings yet
- Ear Emergencies: Thomas Morrissey and John B. LissowayDocument11 pagesEar Emergencies: Thomas Morrissey and John B. LissowayFajriah SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- 43959-Article Text-42180-1-10-20090702Document6 pages43959-Article Text-42180-1-10-20090702lailatul husnaNo ratings yet
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa : Most CommonDocument2 pagesPseudomonas Aeruginosa : Most CommonSoojung Nam100% (1)
- Otitis Exter Na: Jennifer WippermanDocument9 pagesOtitis Exter Na: Jennifer Wippermandifa fatayaNo ratings yet
- Ear Pathology22Document34 pagesEar Pathology22nagham hamdanNo ratings yet
- Otitis Externa: Journal ReadingDocument22 pagesOtitis Externa: Journal ReadingRizka FadilahNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument98 pagesOtitis MediaLody Lean CruzNo ratings yet
- 18 Head and NeckDocument23 pages18 Head and NeckMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Ears and HearingDocument22 pagesAssessing The Ears and HearingGrace RamosNo ratings yet
- Otitis EksternaDocument9 pagesOtitis EksternaKoas PatoNo ratings yet
- Ryan Martin Ko, M.DDocument54 pagesRyan Martin Ko, M.DDhaval Makwana100% (2)
- 01 Congenital Diseases of The External and Middle Ear-1Document39 pages01 Congenital Diseases of The External and Middle Ear-1cabdinuux32No ratings yet
- Ear DisorderDocument61 pagesEar DisorderSakthi DeviNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE TEACHING On Otitis Media FinalDocument33 pagesPRACTICE TEACHING On Otitis Media FinalAjit ThangeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Disorders of The Eyes and EarsDocument42 pagesChapter 15 Disorders of The Eyes and Earskelsey jacksonNo ratings yet
- Chronic Otitis Media (Mesotympanitis. Epitympanitis) - Otogenous Intracranial ComplicationsDocument53 pagesChronic Otitis Media (Mesotympanitis. Epitympanitis) - Otogenous Intracranial Complicationssimi yNo ratings yet
- Ear InfectionDocument8 pagesEar InfectionArt Christian Ramos100% (1)
- Med 3, Chloe SaadeDocument53 pagesMed 3, Chloe Saadeanon_767794134No ratings yet
- ENT - Diseases of The External Ear, Middle Ear and MastoidDocument7 pagesENT - Diseases of The External Ear, Middle Ear and MastoidChristian LantanoNo ratings yet
- Otitis: MSN 3 - Week 7B Ns - Lani Natalia Watania, S.Kep., M.KepDocument21 pagesOtitis: MSN 3 - Week 7B Ns - Lani Natalia Watania, S.Kep., M.KepDeviNo ratings yet
- Surgeryii: I. Benign Conditions of The Head and NeckDocument13 pagesSurgeryii: I. Benign Conditions of The Head and NeckALIMBOYOGUEN RexorNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument32 pagesOtitis MediaRiya GautamNo ratings yet
- External Otitis (Otitis Externa)Document16 pagesExternal Otitis (Otitis Externa)Amit MartinNo ratings yet
- Krishna Reddy OTALGIA AND TINNITUS FinalDocument14 pagesKrishna Reddy OTALGIA AND TINNITUS FinalSiva ramaNo ratings yet
- Illustrator File Edit Select Effect View Window HelpDocument8 pagesIllustrator File Edit Select Effect View Window HelpHaizel BieberNo ratings yet
- Management of Diseases of Ear, Nose and ThroatDocument16 pagesManagement of Diseases of Ear, Nose and ThroatSaurabh LamkhadeNo ratings yet
- Penyebab Otalgia 2010 PDFDocument11 pagesPenyebab Otalgia 2010 PDFnotpentingNo ratings yet
- Penyebab Otalgia 2010Document11 pagesPenyebab Otalgia 2010siska tiaraNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument11 pagesOtitis MediaAnkita BramheNo ratings yet
- 6 +Assessing+Ears+and+NoseDocument55 pages6 +Assessing+Ears+and+Nosejapheth agoncilloNo ratings yet
- Ear InfectionDocument20 pagesEar InfectionJohn Kenneth AranicoNo ratings yet
- Acute Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument19 pagesAcute Suppurative Otitis MediaRajesh Sharma100% (1)
- Lecture 2 Ent.Document70 pagesLecture 2 Ent.kiprotich weldonNo ratings yet
- Current Concepts in The Pathogenesis and Treatment of Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument31 pagesCurrent Concepts in The Pathogenesis and Treatment of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Mediafurqon alNo ratings yet
- OtitisDocument25 pagesOtitisjoselyn cabreraNo ratings yet
- Disorders of EarDocument37 pagesDisorders of Earmalika.hirachan007No ratings yet
- ENTssssssDocument15 pagesENTsssssssurg absiteNo ratings yet
- COM FinalDocument10 pagesCOM FinalCeelin RoblesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Patients With Eye, Nose, and Throat (ENT)Document8 pagesNursing Management of Patients With Eye, Nose, and Throat (ENT)محمد سعد طه احمدNo ratings yet
- Ayu Jurnal Inggris OEDocument22 pagesAyu Jurnal Inggris OEAyu Putri HaryantiNo ratings yet
- Ear BulletsDocument3 pagesEar BulletsDonaJeanNo ratings yet
- HEARING DISORDERS-2 AutosavedDocument45 pagesHEARING DISORDERS-2 AutosavedDanella RicañaNo ratings yet
- DT Otitis MediaDocument21 pagesDT Otitis MediaDio PutraNo ratings yet
- EaracheDocument5 pagesEaracheclubsanatateNo ratings yet
- Expose On EntDocument20 pagesExpose On EntDUCHELNo ratings yet
- OtomycosisDocument18 pagesOtomycosisaku arthanaNo ratings yet
- CASE ANALYSIS - Chronic TympanomastoiditisDocument5 pagesCASE ANALYSIS - Chronic TympanomastoiditisTerry Mae Atilazal SarciaNo ratings yet
- CANINE-Medical Management of Chronic Otitis in DogsDocument11 pagesCANINE-Medical Management of Chronic Otitis in Dogstaner_soysuren100% (2)
- Lecture 2.1-External Ear Disorders-Ashadi Prasetyo (2017) PDFDocument71 pagesLecture 2.1-External Ear Disorders-Ashadi Prasetyo (2017) PDFAnonymous XFDJfsGviNo ratings yet
- Early Otorrhea RatesDocument26 pagesEarly Otorrhea RatesRhea Andrea UyNo ratings yet
- Discharge From The Ear: Otitis Externa and Acute Otitis MediaDocument2 pagesDischarge From The Ear: Otitis Externa and Acute Otitis MediaHendrikus HaluanNo ratings yet
- Drugs and Substance AbuseDocument75 pagesDrugs and Substance Abuseseline sherylNo ratings yet
- Ears&MouthDocument76 pagesEars&Mouthrichelley08No ratings yet
- Externa Otitis FinalDocument11 pagesExterna Otitis Finalmalika.hirachan007No ratings yet
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM)Document31 pagesChronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM)Mimo HemadNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Hearing and Balance DisordersDocument9 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Hearing and Balance Disordersxhemhae100% (1)
- A Concept Map On External OtitisDocument9 pagesA Concept Map On External OtitisJoe RealNo ratings yet
- Otitis Media (Acute) : Middle Ear DisordersDocument6 pagesOtitis Media (Acute) : Middle Ear DisordersFernando BudimanNo ratings yet
- Ear Discharge HandoutDocument9 pagesEar Discharge HandoutPorori BookshopNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 Environmental EmergenciesDocument5 pagesLecture 12 Environmental EmergenciesdrunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- BSPH Student-Submitted Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesBSPH Student-Submitted Exam QuestionsdrunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Dreaded Red EyeDocument8 pagesLecture 3 Dreaded Red EyedrunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 The Dizzy PatientDocument6 pagesLecture 2 The Dizzy PatientdrunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Intro To CNS DrugsDocument4 pagesLecture 1 Intro To CNS DrugsdrunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Antidepressants Mood Stabalizers 1 2Document7 pagesLecture 3 Antidepressants Mood Stabalizers 1 2drunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Celiac DiseaseDocument7 pagesCeliac DiseasedrunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Energearadionics RatesDocument163 pagesEnergearadionics RatesRoberta & Thomas NormanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of HearingDocument45 pagesPhysiology of HearingJP SouaidNo ratings yet
- OTO Alex ProgDocument54 pagesOTO Alex ProgCharm MeelNo ratings yet
- Strahlenfolter - REMOTE NEURAL MONITORING - Greatdreams-ComDocument15 pagesStrahlenfolter - REMOTE NEURAL MONITORING - Greatdreams-ComFred_Blanke100% (2)
- Auditory Pathways: Anatomy and Physiology: Handbook of Clinical Neurology March 2015Document24 pagesAuditory Pathways: Anatomy and Physiology: Handbook of Clinical Neurology March 2015florensiaNo ratings yet
- Accessing Hearing and Spoken LanguageDocument46 pagesAccessing Hearing and Spoken Languagesu lynnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology 4th Edition Solomon Test BankDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology 4th Edition Solomon Test Bankmenaionemperilgtod26100% (29)
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 NOTESDocument13 pagesClass 11 Biology Chapter 21 NOTESYashica PradhanNo ratings yet
- ENT Sakshi AroraDocument477 pagesENT Sakshi AroraTimothy Jalam100% (1)
- Price List of Hasc Hearing Aids (Rexton) W.E.F. 1/6/2012: Arena Digital FamilyDocument6 pagesPrice List of Hasc Hearing Aids (Rexton) W.E.F. 1/6/2012: Arena Digital FamilyPaulo DantasNo ratings yet
- Sensory Systems: Vision Hearing Taste Smell Equilibrium Somatic SensesDocument54 pagesSensory Systems: Vision Hearing Taste Smell Equilibrium Somatic SensesTiara RaraNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Balance/Equilibrium: Departemen Fisiologi FK UsuDocument20 pagesPhysiology of Balance/Equilibrium: Departemen Fisiologi FK UsuSonia P SNo ratings yet
- ReversedIpsilateralAcousticReflexPattern BaslDocument9 pagesReversedIpsilateralAcousticReflexPattern BaslSarah fadlainiNo ratings yet
- G Oster - Auditory Beats in The BrainDocument19 pagesG Oster - Auditory Beats in The BrainCeci_SunshineNo ratings yet
- Brain 1963 PENFIELD 595 696Document102 pagesBrain 1963 PENFIELD 595 696Leroy FinkleNo ratings yet
- Clinical Discussion EarDocument90 pagesClinical Discussion EarMuhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- Assr, Vemp, VNG, OaeDocument8 pagesAssr, Vemp, VNG, OaeSuprit Sn100% (1)
- Buku BPPV EditDocument30 pagesBuku BPPV EditalvinoNo ratings yet
- Temporal Bone and EarDocument76 pagesTemporal Bone and EarGuo YageNo ratings yet
- Auricular TherapyDocument19 pagesAuricular Therapyneedurheed90100% (1)
- Special Senses Hearing and EquilibriumDocument17 pagesSpecial Senses Hearing and EquilibriumMompati Letsweletse100% (1)
- Expediente Sanitario Nombre Producto Registro Sanitario Vencimiento Modalidad Estado Registro ObservacionesDocument4 pagesExpediente Sanitario Nombre Producto Registro Sanitario Vencimiento Modalidad Estado Registro ObservacionesFuneRales GaMezNo ratings yet
- Hiperakusis 2015Document20 pagesHiperakusis 2015Abdur ShamilNo ratings yet
- Q2 1st SUMMATIVE TESTS 2022 2023Document10 pagesQ2 1st SUMMATIVE TESTS 2022 2023Marjorie De Vera100% (1)
- Main PDFDocument4 pagesMain PDFNadya Dwi PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Hearing Conservation ProgramDocument11 pagesHearing Conservation ProgramaryzalNo ratings yet
- Menieres-Slides 061213Document50 pagesMenieres-Slides 061213ajikwaNo ratings yet
- Cochlear ImplantDocument33 pagesCochlear ImplantNithiyah DevarajuNo ratings yet
Lecture 1 Disorders of The Ear
Lecture 1 Disorders of The Ear
Uploaded by
drunkenwukongOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 1 Disorders of The Ear
Lecture 1 Disorders of The Ear
Uploaded by
drunkenwukongCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 1:Disorders of the Ear
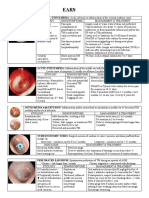
What is Otitis Externa inflammation and edema of the ear canal
skin.
What is function of Cerumen Cerumen helps protect the canal by forming
an acidic coat that helps prevent infection.
Predisposing factors for Otitis Externa = absence of cerumen, excessive cleaning of
ears, water, trauma to ear canal.
Common pathogen causing otitis externa = ● Pseudomonas and Staphylococcus.
● Aspergillus and Candida.
Compara to bacterial otitis externa, fungal ITCHY
otitis externa pts have what complaint?
Treatments of externa otitis Bacterial = cleaning the ear canal of any
debris and instilling antibiotic drops with or
without steroids
Fungal = cleaning out debris and instilling
drops(2% acetic acid or some antifungals)
What professions have Auricular Hematoma wrestlers and boxers
What is Auricular Hematoma fluctuant swelling with loss of normal auricular
landmarks.
What is complication of auricular hematoma Caudiflower ear
Treatment of auricular hematoma incision and drainage of the hematoma with
dental cotton rolls on the opposite sides of
the affected ear
Patients who present with dry cough which Ears
has not responded to usual measures should
have their ___ checked.
What drug is used to remove live bug from LIDOCAINE
ear canal? Not saline
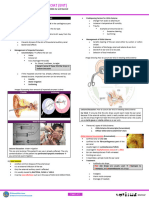
Cerumen impaction = cerumen obstruction
Is Qtip good at helping cerumen impaction? NO, further push cerumen impaction further
Body parts at high risk for frost bite Ears, nose and cheeks
Treatment consists of quickly warming the ear
Treatment of frost bite ?
with gauze soaked in saline at 38-40 degrees
C.
What is Bullous Myringitis
painful inflammatory bullae on the tympanic
membrane.
Must distinguish Bullous Myringitis from ?
otitis externa and herpes zoster oticus.
What is Most common infection for which
children are seen in a physician’s office. Acute otitis media
Pathogen causing acute otitis media Strep pneumoniae, H. influenza and
Moraxella catarrhalis.
What are 3 criteria for acute otitis media ● acute onset
● presence of middle ear effusion
● signs of middle ear inflammation
(fever, pain, erythema of tympanic
membrane)
Erythema of the TM without middle effusion is myringitis or tympanitis
________
What is Standard of care for treatment of not to treat with antibiotics on first visit but to
AOM in children older than 2 years treat pain and observe.
___ # decibel loss or more in hearing
40 decibel loss
bilaterally mandates referral by ENT for
polyethylene tube(PE tubes) placement.
Treatment for otitis meida with effusion
What is Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media the presence of persistent purulent otorrhea
through a perforated tympanic membrane or
Tympanostomy tube.
Symptoms of chronic suppurative otitis media hearing loss, tinnitus, increasing pain, vertigo,
or facial palsy
Treatment of chronic suppurative otitis media culture and sensitivity of the discharge to get
most appropriate antibiotic selection.
Chronic otitis media can lead to infection of Mastoid = mastoiditis
___
SKIM
What are signs of Traumatic Tympanic
Membrane Perforations sudden pain which subsides quickly and
bloody otorrhea, severe vertigo can occur but
resolves quickly. Hearing loss and tinnitus
may be present.
Treatment of traumatic tympanic membrane
perforation ● Perforation will heal spontaneously
over several days to weeks
● keeping the ear dry and ototopical
antibiotics if infection is suspected.
What is Barotrauma and Barotitis ● sudden changes in middle ear
pressure while flying or scuba diving.
● This causes an accumulation of
serous fluid in the middle ear.
Treatment of barotrauma and barotitis ? Fluid is normally resorbed over several weeks
but Autoinflation maneuvers (popping the
ears) may hasten recovery.
What is drug of choice of acute otitis media ? Amoxicillin
What vaccine decreases the number of cases Influenza vaccine
of AOM in children 6-24 months.
All traumatic perforations of the TM require audiologic
___ evaluation to rule out sensorineural
hearing loss.
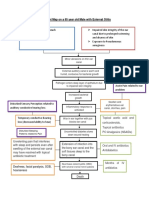
What is Conductive Hearing Loss when there is a failure of normal propagation
of acoustic energy through the conducting
portions of the ear
What is Sensorineural Hearing Loss dysfunction of the inner ear, which may be
caused by a failure of the generation of nerve
signals in the cochlea by the cochlea hair
cells or propagation of electrical signals along
the cochlear division of CN VIII.
What is Central Hearing Loss ischemic or traumatic brain injury leading to
hearing loss
Medications leading to hearing loss
What is Otosclerosis
sclerotic fixation of the stapes.
● hearing-aid, or surgery.
Treatment of Otosclerosis
● Surgery is stapedectomy and
placement of prosthesis. Procedure
has 95% success rate
All-inclusive term to describe the process of
What is Presbycusis
hearing loss related to aging.
High pitch or low pitch voice is lost first in
higher pitched tones(women & children voice)
Presbycusis ?
● Acoustic neuroma (vestibular
What is Acoustic Neuroma
schwannoma) is a benign tumor from
the Schwann cells of CN VIII.
Acoustic Neuroma
What are symptoms of Acoustic Neuroma asymmetric hearing loss and tinnitus.
Neurofibromatosis can be associated with
Acoustic Neuroma
Sound above # decibels is dangerous for 90
ear?
You might also like
- ENT Toronto Notes 2006Document52 pagesENT Toronto Notes 2006Jacklyn Yek100% (1)
- Untitled15 PDFDocument22 pagesUntitled15 PDFElizabeth LeonNo ratings yet
- Ear Emergencies: Thomas Morrissey and John B. LissowayDocument11 pagesEar Emergencies: Thomas Morrissey and John B. LissowayFajriah SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- 43959-Article Text-42180-1-10-20090702Document6 pages43959-Article Text-42180-1-10-20090702lailatul husnaNo ratings yet
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa : Most CommonDocument2 pagesPseudomonas Aeruginosa : Most CommonSoojung Nam100% (1)
- Otitis Exter Na: Jennifer WippermanDocument9 pagesOtitis Exter Na: Jennifer Wippermandifa fatayaNo ratings yet
- Ear Pathology22Document34 pagesEar Pathology22nagham hamdanNo ratings yet
- Otitis Externa: Journal ReadingDocument22 pagesOtitis Externa: Journal ReadingRizka FadilahNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument98 pagesOtitis MediaLody Lean CruzNo ratings yet
- 18 Head and NeckDocument23 pages18 Head and NeckMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Ears and HearingDocument22 pagesAssessing The Ears and HearingGrace RamosNo ratings yet
- Otitis EksternaDocument9 pagesOtitis EksternaKoas PatoNo ratings yet
- Ryan Martin Ko, M.DDocument54 pagesRyan Martin Ko, M.DDhaval Makwana100% (2)
- 01 Congenital Diseases of The External and Middle Ear-1Document39 pages01 Congenital Diseases of The External and Middle Ear-1cabdinuux32No ratings yet
- Ear DisorderDocument61 pagesEar DisorderSakthi DeviNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE TEACHING On Otitis Media FinalDocument33 pagesPRACTICE TEACHING On Otitis Media FinalAjit ThangeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Disorders of The Eyes and EarsDocument42 pagesChapter 15 Disorders of The Eyes and Earskelsey jacksonNo ratings yet
- Chronic Otitis Media (Mesotympanitis. Epitympanitis) - Otogenous Intracranial ComplicationsDocument53 pagesChronic Otitis Media (Mesotympanitis. Epitympanitis) - Otogenous Intracranial Complicationssimi yNo ratings yet
- Ear InfectionDocument8 pagesEar InfectionArt Christian Ramos100% (1)
- Med 3, Chloe SaadeDocument53 pagesMed 3, Chloe Saadeanon_767794134No ratings yet
- ENT - Diseases of The External Ear, Middle Ear and MastoidDocument7 pagesENT - Diseases of The External Ear, Middle Ear and MastoidChristian LantanoNo ratings yet
- Otitis: MSN 3 - Week 7B Ns - Lani Natalia Watania, S.Kep., M.KepDocument21 pagesOtitis: MSN 3 - Week 7B Ns - Lani Natalia Watania, S.Kep., M.KepDeviNo ratings yet
- Surgeryii: I. Benign Conditions of The Head and NeckDocument13 pagesSurgeryii: I. Benign Conditions of The Head and NeckALIMBOYOGUEN RexorNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument32 pagesOtitis MediaRiya GautamNo ratings yet
- External Otitis (Otitis Externa)Document16 pagesExternal Otitis (Otitis Externa)Amit MartinNo ratings yet
- Krishna Reddy OTALGIA AND TINNITUS FinalDocument14 pagesKrishna Reddy OTALGIA AND TINNITUS FinalSiva ramaNo ratings yet
- Illustrator File Edit Select Effect View Window HelpDocument8 pagesIllustrator File Edit Select Effect View Window HelpHaizel BieberNo ratings yet
- Management of Diseases of Ear, Nose and ThroatDocument16 pagesManagement of Diseases of Ear, Nose and ThroatSaurabh LamkhadeNo ratings yet
- Penyebab Otalgia 2010 PDFDocument11 pagesPenyebab Otalgia 2010 PDFnotpentingNo ratings yet
- Penyebab Otalgia 2010Document11 pagesPenyebab Otalgia 2010siska tiaraNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument11 pagesOtitis MediaAnkita BramheNo ratings yet
- 6 +Assessing+Ears+and+NoseDocument55 pages6 +Assessing+Ears+and+Nosejapheth agoncilloNo ratings yet
- Ear InfectionDocument20 pagesEar InfectionJohn Kenneth AranicoNo ratings yet
- Acute Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument19 pagesAcute Suppurative Otitis MediaRajesh Sharma100% (1)
- Lecture 2 Ent.Document70 pagesLecture 2 Ent.kiprotich weldonNo ratings yet
- Current Concepts in The Pathogenesis and Treatment of Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument31 pagesCurrent Concepts in The Pathogenesis and Treatment of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Mediafurqon alNo ratings yet
- OtitisDocument25 pagesOtitisjoselyn cabreraNo ratings yet
- Disorders of EarDocument37 pagesDisorders of Earmalika.hirachan007No ratings yet
- ENTssssssDocument15 pagesENTsssssssurg absiteNo ratings yet
- COM FinalDocument10 pagesCOM FinalCeelin RoblesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Patients With Eye, Nose, and Throat (ENT)Document8 pagesNursing Management of Patients With Eye, Nose, and Throat (ENT)محمد سعد طه احمدNo ratings yet
- Ayu Jurnal Inggris OEDocument22 pagesAyu Jurnal Inggris OEAyu Putri HaryantiNo ratings yet
- Ear BulletsDocument3 pagesEar BulletsDonaJeanNo ratings yet
- HEARING DISORDERS-2 AutosavedDocument45 pagesHEARING DISORDERS-2 AutosavedDanella RicañaNo ratings yet
- DT Otitis MediaDocument21 pagesDT Otitis MediaDio PutraNo ratings yet
- EaracheDocument5 pagesEaracheclubsanatateNo ratings yet
- Expose On EntDocument20 pagesExpose On EntDUCHELNo ratings yet
- OtomycosisDocument18 pagesOtomycosisaku arthanaNo ratings yet
- CASE ANALYSIS - Chronic TympanomastoiditisDocument5 pagesCASE ANALYSIS - Chronic TympanomastoiditisTerry Mae Atilazal SarciaNo ratings yet
- CANINE-Medical Management of Chronic Otitis in DogsDocument11 pagesCANINE-Medical Management of Chronic Otitis in Dogstaner_soysuren100% (2)
- Lecture 2.1-External Ear Disorders-Ashadi Prasetyo (2017) PDFDocument71 pagesLecture 2.1-External Ear Disorders-Ashadi Prasetyo (2017) PDFAnonymous XFDJfsGviNo ratings yet
- Early Otorrhea RatesDocument26 pagesEarly Otorrhea RatesRhea Andrea UyNo ratings yet
- Discharge From The Ear: Otitis Externa and Acute Otitis MediaDocument2 pagesDischarge From The Ear: Otitis Externa and Acute Otitis MediaHendrikus HaluanNo ratings yet
- Drugs and Substance AbuseDocument75 pagesDrugs and Substance Abuseseline sherylNo ratings yet
- Ears&MouthDocument76 pagesEars&Mouthrichelley08No ratings yet
- Externa Otitis FinalDocument11 pagesExterna Otitis Finalmalika.hirachan007No ratings yet
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM)Document31 pagesChronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM)Mimo HemadNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Hearing and Balance DisordersDocument9 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Hearing and Balance Disordersxhemhae100% (1)
- A Concept Map On External OtitisDocument9 pagesA Concept Map On External OtitisJoe RealNo ratings yet
- Otitis Media (Acute) : Middle Ear DisordersDocument6 pagesOtitis Media (Acute) : Middle Ear DisordersFernando BudimanNo ratings yet
- Ear Discharge HandoutDocument9 pagesEar Discharge HandoutPorori BookshopNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 Environmental EmergenciesDocument5 pagesLecture 12 Environmental EmergenciesdrunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- BSPH Student-Submitted Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesBSPH Student-Submitted Exam QuestionsdrunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Dreaded Red EyeDocument8 pagesLecture 3 Dreaded Red EyedrunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 The Dizzy PatientDocument6 pagesLecture 2 The Dizzy PatientdrunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Intro To CNS DrugsDocument4 pagesLecture 1 Intro To CNS DrugsdrunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Antidepressants Mood Stabalizers 1 2Document7 pagesLecture 3 Antidepressants Mood Stabalizers 1 2drunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Celiac DiseaseDocument7 pagesCeliac DiseasedrunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Energearadionics RatesDocument163 pagesEnergearadionics RatesRoberta & Thomas NormanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of HearingDocument45 pagesPhysiology of HearingJP SouaidNo ratings yet
- OTO Alex ProgDocument54 pagesOTO Alex ProgCharm MeelNo ratings yet
- Strahlenfolter - REMOTE NEURAL MONITORING - Greatdreams-ComDocument15 pagesStrahlenfolter - REMOTE NEURAL MONITORING - Greatdreams-ComFred_Blanke100% (2)
- Auditory Pathways: Anatomy and Physiology: Handbook of Clinical Neurology March 2015Document24 pagesAuditory Pathways: Anatomy and Physiology: Handbook of Clinical Neurology March 2015florensiaNo ratings yet
- Accessing Hearing and Spoken LanguageDocument46 pagesAccessing Hearing and Spoken Languagesu lynnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology 4th Edition Solomon Test BankDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology 4th Edition Solomon Test Bankmenaionemperilgtod26100% (29)
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 NOTESDocument13 pagesClass 11 Biology Chapter 21 NOTESYashica PradhanNo ratings yet
- ENT Sakshi AroraDocument477 pagesENT Sakshi AroraTimothy Jalam100% (1)
- Price List of Hasc Hearing Aids (Rexton) W.E.F. 1/6/2012: Arena Digital FamilyDocument6 pagesPrice List of Hasc Hearing Aids (Rexton) W.E.F. 1/6/2012: Arena Digital FamilyPaulo DantasNo ratings yet
- Sensory Systems: Vision Hearing Taste Smell Equilibrium Somatic SensesDocument54 pagesSensory Systems: Vision Hearing Taste Smell Equilibrium Somatic SensesTiara RaraNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Balance/Equilibrium: Departemen Fisiologi FK UsuDocument20 pagesPhysiology of Balance/Equilibrium: Departemen Fisiologi FK UsuSonia P SNo ratings yet
- ReversedIpsilateralAcousticReflexPattern BaslDocument9 pagesReversedIpsilateralAcousticReflexPattern BaslSarah fadlainiNo ratings yet
- G Oster - Auditory Beats in The BrainDocument19 pagesG Oster - Auditory Beats in The BrainCeci_SunshineNo ratings yet
- Brain 1963 PENFIELD 595 696Document102 pagesBrain 1963 PENFIELD 595 696Leroy FinkleNo ratings yet
- Clinical Discussion EarDocument90 pagesClinical Discussion EarMuhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- Assr, Vemp, VNG, OaeDocument8 pagesAssr, Vemp, VNG, OaeSuprit Sn100% (1)
- Buku BPPV EditDocument30 pagesBuku BPPV EditalvinoNo ratings yet
- Temporal Bone and EarDocument76 pagesTemporal Bone and EarGuo YageNo ratings yet
- Auricular TherapyDocument19 pagesAuricular Therapyneedurheed90100% (1)
- Special Senses Hearing and EquilibriumDocument17 pagesSpecial Senses Hearing and EquilibriumMompati Letsweletse100% (1)
- Expediente Sanitario Nombre Producto Registro Sanitario Vencimiento Modalidad Estado Registro ObservacionesDocument4 pagesExpediente Sanitario Nombre Producto Registro Sanitario Vencimiento Modalidad Estado Registro ObservacionesFuneRales GaMezNo ratings yet
- Hiperakusis 2015Document20 pagesHiperakusis 2015Abdur ShamilNo ratings yet
- Q2 1st SUMMATIVE TESTS 2022 2023Document10 pagesQ2 1st SUMMATIVE TESTS 2022 2023Marjorie De Vera100% (1)
- Main PDFDocument4 pagesMain PDFNadya Dwi PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Hearing Conservation ProgramDocument11 pagesHearing Conservation ProgramaryzalNo ratings yet
- Menieres-Slides 061213Document50 pagesMenieres-Slides 061213ajikwaNo ratings yet
- Cochlear ImplantDocument33 pagesCochlear ImplantNithiyah DevarajuNo ratings yet