Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Low Power VLSI
Low Power VLSI
Uploaded by
Amith G NairCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Low Power VLSI
Low Power VLSI
Uploaded by
Amith G NairCopyright:
Available Formats
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
CATEGORY L T P CREDIT
ECT448 LOW POWER VLSI
PEC 2 1 0 3
Preamble: This course aims to impart the basic knowledge in designing of Low power VLSI
Circuits .
Prerequisite: Solid State Devices, VLSI Design, Digital Circuit Design.
Course Outcomes: After the completion of the course the student will be able to
Identify various short channel effects and various sources of power
CO 1
dissipation in MOSFET
CO 2 Apply various power reduction techniques to circuits.
CO 3 Apply various clocked and non clocked design styles for logic implementation.
CO 4 Apply Adiabatic and reversible logic for circuit implementation.
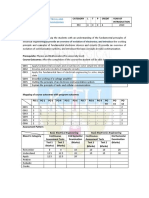
Mapping of course outcomes with program outcomes
PO 1 PO 2 PO 3 PO 4 PO 5 PO 6 PO 7 PO 8 PO 9 PO 10 PO 11 PO 12
CO 1 3 2
CO 2 3 2
CO 3 3 3 2
CO 4 3 3
Assessment Pattern
Continuous End Semester
Bloom’s Category Assessment Tests Examination
1 2
Remember 10 10 10
Understand 20 20 20
Apply 20 20 70
Analyse
Evaluate
Create
Mark distribution
Total Marks CIE ESE ESE Duration
150 50 100 3 hours
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Continuous Internal Evaluation Pattern:
Attendance : 10 marks
Continuous Assessment Test (2 numbers) : 25 marks
Course project/Assignment : 15 marks
End Semester Examination Pattern: There will be two parts; Part A and Part B. Part A
contain 10 questions with 2 questions from each module, having 3 marks for each question.
Students should answer all questions. Part B contains 2 questions from each module of
which student should answer any one. Each question can have maximum 2 sub-divisions
and carry 14 marks. Mark patterns are as per the syllabus with 60% for theory and 40% for
logical/numerical problems, derivation and proof.
Course Level Assessment Questions
Course Outcome 1 (CO1): Identify various short channel effects and various sources of
power dissipation in MOSFET
1. Derive the expression of switching power in static CMOS circuit.
2. Explain impact ionization and Hot electron effect.
3. Explain the various factors causing leakage power in MOSET.
Course Outcome 2 (CO2): Apply various power reduction techniques to circuits.
1. Describe the use of transistor and Gate sizing for power deduction.
2. Describe supply voltage scaling method for power reduction.
3. Apply various power reduction schemes to memory cells..
Course Outcome 3 (CO3) : Apply various clocked and non clocked design styles for logic
implementation
1. Implement XOR gate in domino logic.
2. Implement the function F= [AB+CD] in DCVS.
3. Implement basic gates in nmos and pseudo nmos logic.
Course Outcome 4 (CO4): Apply Adiabatic and reversible logic for circuit implementation.
1. Implement Y=AB using adiabatic logic
2. Explain one stage adiabatic buffer.
3. Implement logic functions using different Reversible logic structures.
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Syllabus
Module 1: Physics of Power dissipation in MOSFET devices
Need for low power circuit design, MIS Structure, Short channel effects-surface scattering, punch
through, velocity saturation, impact ionization Hot electron effects, Drain Induced Barrier
Lowering, Deep submicron transistor design issues.
Module 2: Sources of power dissipation in CMOS-Dynamic Power Dissipation: Charging and
Discharging capacitance power dissipation , Short Circuit Power: Short Circuit Current of
Inverter , Short circuit current dependency with input and output load , Glitching Power, Static
Power Dissipation, Leakage Power Dissipation,
Gate level power analysis : Capacitive, internal and Static power dissipation of gate level circuit.
Module 3: Power Reduction Techniques :Supply voltage Scaling Approaches: Multi VDD
and Dynamic VDD, leakage power reduction Techniques – Transistor stacking,
VTCMOS,MTCMOS, DTCMOS, Power gating, Clock gating for Dynamic power dissipation,
Transistor and Gate Sizing for Dynamic and Leakage Power Reduction.
Module 4: Circuit design style- clocked design style- Basic concept, Domino logic (domino
NAND gate), Differential Current Switch Logic. Non clocked circuit design style-fully
complementary logic. NMOS and pseudo –NMOS logic, differential cascade voltage switch
logic(DCVS)
Module 5: Adiabatic switching – Adiabatic charging, adiabatic amplification, One stage and
two stage adiabatic buffer, Adiabatic logic gates, pulsed power supplies, Reversible logic basic
concepts.
Text Books:
1. Gray Yeap, Practical low power digital VLSI design, Springer, 1998
2. Kaushik Roy, Sharat C Prasad, Low power CMOS VLSI circuit design, Wiley India,
2000
References:
1. Abdellatif Bellaouar, Mohamed I Elmasry, Low power digital VLSI design, Kluwer
Academic, 1995
2. Anatha P Chandrakasan, Robert W Brodersen, Low power digital CMOS Design,
Kluwer Academic, 1995
3. Christian Piguet, Low power CMOS circuits, Taylor & Francis, 2006
4. Kiat Seng Yeo, Kaushik Roy, Low voltage, low power VLSI sub systems, Tata
McGraw Hill, 2004
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Course Contents and Lecture Schedule
No Topic No. of
Lecture
1 Physics of Power dissipation in MOSFET devices
1.1 Need for low power circuit design, MIS Structure. 2
Short channel effects-surface scattering, punch through, velocity saturation,
1.2 3
impact ionization, Hot electron effects, Drain Induced Barrier Lowering.
1.3 Deep submicron transistor design issues. 1
2 Sources of power dissipation in CMOS
Dynamic Power Dissipation: Charging and Discharging capacitance power
2.1 1
dissipation
Short Circuit Power: Short Circuit Current of Inverter , Short circuit current
2.2 2
dependency with input and output load .
2.3 Glitching Power, Static Power Dissipation, Leakage Power Dissipation, 4
Gate level power analysis : Capacitive, internal and Static power dissipation
2.4 2
of gate level circuit.
3 Power Reduction Techniques
3.1 Supply voltage Scaling Approaches: Multi VDD and Dynamic VDD 1
Leakage power reduction Techniques – Transistor stacking
3.2 2
VTCMOS,MTCMOS, DTCMOS
3.3 Power gating, Clock gating for Dynamic power dissipation, 2
3.4 Transistor and Gate Sizing for Dynamic and Leakage Power Reduction 2
4 Circuit design style
4.1 Clocked design style- Basic concept, Domino logic 2
4.2 Differential Current Switch Logic 1
Non clocked circuit design style-fully complementary logic. NMOS and
4.3 pseudo –NMOS logic 2
4.4 Differential Cascade Voltage Switch logic(DCVS) 1
5 Adiabatic switching
5.1 Adiabatic charging, adiabatic amplification,. 3
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
5.2 One stage and two stage adiabatic buffer 2
5.3 Adiabatic logic gates, pulsed power supplies 1
5.4 Reversible logic basic concepts.. 1
Simulation Assignments
Atleast one assignment should be simulation based using any simulation software. It
can be the design of a circuit in any one of the clocked or non clocked style and perform
power analysis. Samples of simulation assignments are given below.
1. Implement NAND gate in conventional CMOS and domino logic and
perform power analysis in each case.
2. Implement any sample logic function in DCVS.
3. Apply threshold voltage scaling method to a logic function implemented
in conventional style and perform power analysis.
Model Question Paper
Model Question Paper
A P J Abdul Kalam Technological University
EIGHTH SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION
BRANCH: ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
COURSE: ECT448 LOW POWER VLSI
Time: 3 Hrs Max. Marks: 100
PART A
Answer All Questions
1. Define the terms (3)
a) DIBL
b) Velocity Saturation
2. Discuss the need for low power VLSI Design (3)
3. Explain the dependency of short circuit current with output load? (3)
4. Explain dynamic power dissipation? (3)
5 Describe leakage power reduction using MTCMOS (3)
6. Define Slack time of logic gate . (3)
7. List the advantages and Disadvantages of Clocked design. (3)
8. Explain the methods to overcome charge sharing problem. (3)
9. Draw the schematic and logic symbol of an Adiabatic amplifier.. (3)
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
10. List the disadvantages of Retractile cascade of Adiabatic logic Gates. (3)
PART B
Answer one question from each module. Each question carries 14 mark
Module I
11(A) Explain the energy band diagram of MIS structure. (8)
11(B) Describe various transistor leakage mechanisms in deep submicron (6)
transistors .
OR
12(A) Explain various short channel effects. (8)
12(B) Explain how the power efficiency of a chip can be measured? (6)
Module II
13(A) Explain how capacitance can be estimated at gate level? (7)
13(B) Explain the formation of glitches in circuits ? Explain various methods (7)
for eliminating the glitches
OR
14(A) Explain the various sources of leakage power in MOSFET (7)
14(B) A 16 bit bus operating in 5V and 66MHz clock rate is driving (7)
capacitance of 2pF/Bit. Each bit is estimated to have a toggling
probability of 0.25 at each clock cycle. Calculate the power
dissipated in operating the bus.
Module III
15(A) Illustrate with examples how low threshold device and high threshold (7)
device can be effectively used for power reduction.
15(B) Explain dynamic supply voltage scaling mechanism for power (7)
reduction.
OR
16(A) Briefly explain dynamic and leakage power reduction using (7)
transistor sizing.
16(B) Illustrate various mechanisms by which power consumption of (7)
6T RAM cells can be reduced.
Module IV
17(A) Implement the function F= [(a+b)(c+d)]’ in NMOS logic and (7)
domino logic.
17(B) Implement the function F= (A+CD) in DCVS logic (7)
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
OR
18(A) Explain how charge sharing problem occur in logic design. How it can (7)
be eliminated?
18(B) Differentiate precharge high and precharge low DCSL. (7)
Module V
19(A) Describe the working of one stage adiabatic buffer. (7)
19(B) Explain pulsed power supply? Describe its importance in adiabatic (7)
logic.
OR
20(A) Describe various reversible gate structures. (7)
20(B) Implement OR and AND function using Fredkin gate. (7)
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
You might also like
- Digital Circuits and SystemsDocument3 pagesDigital Circuits and SystemsAayush JainNo ratings yet
- Electrical Electronics DatabaseDocument588 pagesElectrical Electronics DatabaseUkNo ratings yet
- EC464 Low Power VLSIDocument2 pagesEC464 Low Power VLSIamruth lal.v.No ratings yet
- ALL ECE S4 2019 Scheme Syllabus Ktustudents - inDocument86 pagesALL ECE S4 2019 Scheme Syllabus Ktustudents - inRajagiri CollegeNo ratings yet
- Applied Electronics and InstrumentationDocument192 pagesApplied Electronics and InstrumentationSHINUMMNo ratings yet
- VL9252 Low Power Vlsi Desing 3Document6 pagesVL9252 Low Power Vlsi Desing 3Rakesh Kumar DNo ratings yet
- ANALOG CIRCUITS-Syllabus KtunotesDocument9 pagesANALOG CIRCUITS-Syllabus Ktunotesdrn86686No ratings yet
- Microwave Devices and CircuitsDocument6 pagesMicrowave Devices and Circuitsakhinageorge21No ratings yet
- Analog Circuits SyllabusDocument5 pagesAnalog Circuits SyllabusVilayil jestinNo ratings yet
- Low Power Vlsi Desing123Document4 pagesLow Power Vlsi Desing123Rakesh Kumar DNo ratings yet
- Low Power PrinciplesDocument58 pagesLow Power PrinciplesVishnu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Network Theory Syllabus 2Document12 pagesNetwork Theory Syllabus 2anuNo ratings yet
- Low Power VLSI Design Techniques A ReviewDocument12 pagesLow Power VLSI Design Techniques A Reviewvenkateshprasad1562812No ratings yet
- Vlsi Circuit Design - SyllabusDocument8 pagesVlsi Circuit Design - SyllabusRiyas ANNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Devices For Standard Mos Technologies - Characterisation and ModellingDocument5 pagesHigh Voltage Devices For Standard Mos Technologies - Characterisation and ModellingAnouarNo ratings yet
- Aet306 - KQB KtuqbankDocument8 pagesAet306 - KQB KtuqbankNandu JagguNo ratings yet
- Solid State Devices Syllabus - Ktunotes - inDocument7 pagesSolid State Devices Syllabus - Ktunotes - inNISHIYA VIJAYANNo ratings yet
- Network AnalysisDocument3 pagesNetwork AnalysisDeva Raju TNo ratings yet
- ECE109: Electronics II: 1. Topic P-NDocument2 pagesECE109: Electronics II: 1. Topic P-NMasterMM12No ratings yet
- B.E. 102 2019 II: (Autonomous Institution, Affiliated To Anna University, Chennai) Elayampalayam, Tiruchengode - 637 205Document4 pagesB.E. 102 2019 II: (Autonomous Institution, Affiliated To Anna University, Chennai) Elayampalayam, Tiruchengode - 637 205Mutharasu SNo ratings yet
- LP VLSI SyllabusDocument2 pagesLP VLSI SyllabusPradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Course Outline EDC Dr. HussainDocument6 pagesCourse Outline EDC Dr. Hussainarkhanjee12No ratings yet
- Subject Unit: Course MaterialDocument33 pagesSubject Unit: Course MaterialKavyaNo ratings yet
- AEC Course MaterialDocument144 pagesAEC Course MaterialBruce LeeNo ratings yet
- Final Year BTech Electronics Syllabus 2022-23Document48 pagesFinal Year BTech Electronics Syllabus 2022-23SiddhantNo ratings yet
- 9f55d1 - Introduction To Vlsi DesignDocument4 pages9f55d1 - Introduction To Vlsi DesignAman ShivachhNo ratings yet
- (Ebook PDF) (Ebook PDF) Modeling Nanowire and Double-Gate Junctionless Field-Effect Transistors All ChapterDocument43 pages(Ebook PDF) (Ebook PDF) Modeling Nanowire and Double-Gate Junctionless Field-Effect Transistors All Chaptermitsuopresto100% (15)
- ebook download (eBook PDF) Modeling Nanowire and Double-Gate Junctionless Field-Effect Transistors all chapterDocument43 pagesebook download (eBook PDF) Modeling Nanowire and Double-Gate Junctionless Field-Effect Transistors all chaptereljanaluiso100% (4)
- 1 Low-Voltage Current-Mode Analog Cells Mohit Kumar Iit Bomb Ay 2002Document16 pages1 Low-Voltage Current-Mode Analog Cells Mohit Kumar Iit Bomb Ay 2002jaigodaraNo ratings yet
- RP 5Document34 pagesRP 5Masood AlamNo ratings yet
- Tesi PHD A 2Document163 pagesTesi PHD A 2Joy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- FORTRAN Based ApproachDocument22 pagesFORTRAN Based ApproachGS EKTANo ratings yet
- VL9252 Low Power Vlsi DesingDocument7 pagesVL9252 Low Power Vlsi DesingRakesh Kumar DNo ratings yet
- Vijay BTP Report EndSemDocument46 pagesVijay BTP Report EndSemVijay AjayNo ratings yet
- ALL-ECE S3 2019-Scheme-Syllabus Ktustudents - inDocument68 pagesALL-ECE S3 2019-Scheme-Syllabus Ktustudents - inShakiraNo ratings yet
- Avlsi Mel ZG623Document5 pagesAvlsi Mel ZG6232019ht80591No ratings yet
- ME SyllabusDocument3 pagesME Syllabusaryankamboj025No ratings yet
- Dec50143 Pw2 IzzDocument11 pagesDec50143 Pw2 Izziskandardaniel0063No ratings yet
- Low Power VLSI Design: April 2015Document59 pagesLow Power VLSI Design: April 2015Mahesh Babu MahiNo ratings yet
- PaperDocument10 pagesPaperRMD Academic CoordinatorNo ratings yet
- Low Power Vls I Design Out LookDocument59 pagesLow Power Vls I Design Out LookSumaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionKhilawan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Final MohanDocument272 pagesFinal MohanKatie TaylorNo ratings yet
- 5048 (4)Document4 pages5048 (4)binuaswin057No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument24 pagesUntitled DocumentRami ReddyNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument154 pagesElectronics and Communication EngineeringVinitha SankerNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction and MotivationDocument93 pages1.1 Introduction and MotivationAnand AnajiNo ratings yet
- Low Power Adiabatic Logic Design: G.P.S. Prashanti, N. Navya Sirisha, N. Akhila ReddyDocument7 pagesLow Power Adiabatic Logic Design: G.P.S. Prashanti, N. Navya Sirisha, N. Akhila ReddyprasanthiNo ratings yet
- 2022 Ch0-Course IntroductionDocument10 pages2022 Ch0-Course IntroductionSư LưuNo ratings yet
- M.Tech 2nd SemesterDocument14 pagesM.Tech 2nd SemesterSivaramsharma RupavathamNo ratings yet
- Low Power Techniques in VlsiDocument21 pagesLow Power Techniques in VlsiKool RakeshNo ratings yet
- ME (Updated)Document2 pagesME (Updated)AanjanayshatmaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electrical and ElectronicsDocument11 pagesBasics of Electrical and ElectronicsannpotterNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument55 pagesBasics of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringMeera GeneshNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BeeDocument2 pagesSyllabus BeeMahender NavapetaNo ratings yet
- Mtech VLSI SyllabusDocument37 pagesMtech VLSI SyllabusRavindra vs100% (1)
- EEE2002 Semiconductor Devices and Circuits - Win - 17 - 18Document2 pagesEEE2002 Semiconductor Devices and Circuits - Win - 17 - 18Srirevathi BalapattabiNo ratings yet
- A Study On Adiabatic Logic Circuits For Low Power ApplicationsDocument7 pagesA Study On Adiabatic Logic Circuits For Low Power ApplicationsNoReply ProgramNo ratings yet
- EET285-Dynamic Circuits and SystemsDocument9 pagesEET285-Dynamic Circuits and SystemsDeepa M SNo ratings yet
- Sem 6 VR20 FinalDocument35 pagesSem 6 VR20 FinalNatural DineshNo ratings yet
- Design and Optimization Techniques of High Speed VLSI CircuitDocument310 pagesDesign and Optimization Techniques of High Speed VLSI CircuitHarshvardhanUpadhyayNo ratings yet
- How To Build Your Own PIC-ProgrammerDocument4 pagesHow To Build Your Own PIC-ProgrammerspkmpsNo ratings yet
- 0556 - Seneca Z PC EngDocument16 pages0556 - Seneca Z PC EngSupportNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Partial Discharge Measurement: Application NoteDocument13 pagesMethod Statement For Partial Discharge Measurement: Application Notejmrs7322No ratings yet
- Fuzzy Logic Controlled Ćuk ConverterDocument5 pagesFuzzy Logic Controlled Ćuk ConverterNikolas BekarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A Short Circuit - Open ElectricalDocument5 pagesAnatomy of A Short Circuit - Open ElectricalHerman DamanikNo ratings yet
- PCS VR 16 09007 XDDocument2 pagesPCS VR 16 09007 XDshaker76No ratings yet
- Dell / Compal Confidential: Schematic DocumentDocument4 pagesDell / Compal Confidential: Schematic DocumentAMEN HAG MOSANo ratings yet
- Protection Audit-May-2022 Approved Letter-1Document27 pagesProtection Audit-May-2022 Approved Letter-1ADE MRTNo ratings yet
- Kingbright: 10mm (0.4INCH) DUAL DIGIT Numeric DisplaysDocument6 pagesKingbright: 10mm (0.4INCH) DUAL DIGIT Numeric DisplaysStuxnetNo ratings yet
- 高性能矢量变频器宣传册 英文 (210X285) mm 2023 03 24 20230428060140581Document10 pages高性能矢量变频器宣传册 英文 (210X285) mm 2023 03 24 20230428060140581SaanounNo ratings yet
- PAM410 DS en V02Document2 pagesPAM410 DS en V02Irfan AshrafNo ratings yet
- TPS54528 4.5-V To 18-V Input, 5-A Synchronous Step-Down Converter With Eco-Mode™Document27 pagesTPS54528 4.5-V To 18-V Input, 5-A Synchronous Step-Down Converter With Eco-Mode™Thebat KhamedNo ratings yet
- DVD Camcorder: VP-DC161 (I) /DC161W (I) /DC161WB (I) /DC163 (I) /DC165W (I) /DC165WB (I)Document132 pagesDVD Camcorder: VP-DC161 (I) /DC161W (I) /DC161WB (I) /DC163 (I) /DC165W (I) /DC165WB (I)JohnnyTF1000No ratings yet
- NapajanjeDocument8 pagesNapajanjeМилан ЛукићNo ratings yet
- DTS0068 - PER Measurement PDFDocument5 pagesDTS0068 - PER Measurement PDFDaniel AdebayoNo ratings yet
- Universal Cell Phone Charger Circuit DiagramDocument8 pagesUniversal Cell Phone Charger Circuit Diagramatien_series80% (30)
- BTS3006C ModulesDocument39 pagesBTS3006C ModulesMakarand DereNo ratings yet
- User Guide: For Soundcraft Si Impact ConsoleDocument156 pagesUser Guide: For Soundcraft Si Impact ConsoleBruno DutraNo ratings yet
- Bandpass ManualDocument3 pagesBandpass ManualpratamasryNo ratings yet
- Final Report PDFDocument103 pagesFinal Report PDFsai abhsihekNo ratings yet
- Case 1Document3 pagesCase 1ianiroy13No ratings yet
- Rohde Schwarz LTE PosterDocument2 pagesRohde Schwarz LTE PosterJohn Bofarull GuixNo ratings yet
- En Odm1Document2 pagesEn Odm1Fathi MusaNo ratings yet
- MoserDocument74 pagesMoserSveto SlNo ratings yet
- Item & Description: SR - N o QTYDocument2 pagesItem & Description: SR - N o QTYTARIQ467No ratings yet
- 1 3 1 A Vex Solarhydrogensystem PlainDocument6 pages1 3 1 A Vex Solarhydrogensystem Plainapi-264098583No ratings yet
- 8-1017876 Tyco Informacion General Pedestal FTTXDocument4 pages8-1017876 Tyco Informacion General Pedestal FTTXRony ArguetaNo ratings yet
- ZD50043 Parts Catalog en Us PDFDocument2 pagesZD50043 Parts Catalog en Us PDFEtigraf S.A.No ratings yet