Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsENGG2500 Energy Storage
ENGG2500 Energy Storage
Uploaded by
epicsmurfc2Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Koritarov Grid-Scale Energy Storage FinalDocument53 pagesKoritarov Grid-Scale Energy Storage FinalsaishankarlNo ratings yet
- Electric System For Opel AmperaDocument24 pagesElectric System For Opel AmperaLuca TrottaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Sources and Photovoltaics: AE1M13EZFDocument26 pagesElectrochemical Sources and Photovoltaics: AE1M13EZFalessio8No ratings yet
- LECTURE 3 Energy Storage TechnologiesDocument55 pagesLECTURE 3 Energy Storage Technologieswing fatt hiewNo ratings yet
- Written AssayDocument3 pagesWritten AssayDuroxNo ratings yet
- Electricity Storage Review 2016Document24 pagesElectricity Storage Review 2016tahirprofessionalNo ratings yet
- BatteriesDocument44 pagesBatteriesAnas SakrNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage Technologies in Renewable EnergyDocument28 pagesEnergy Storage Technologies in Renewable Energyjitendra jhaNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Systems IIIDocument34 pagesPhotovoltaic Systems IIIObada Ar-ruzziNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage TechnologiesDocument27 pagesEnergy Storage TechnologiesNew king IndiaNo ratings yet
- The Need of Energy Storage With The Various Energy SystemDocument3 pagesThe Need of Energy Storage With The Various Energy Systemskjdkmq518No ratings yet
- Storage PresentationDocument43 pagesStorage PresentationHafeez Khan TareenNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Notes 19ee3dcepgDocument70 pagesUnit-4 Notes 19ee3dcepghandekashyapNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy ResourcesDocument51 pagesRenewable Energy ResourcesVeerabhadrayya C KNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage SystemDocument22 pagesEnergy Storage Systemmikkumar5No ratings yet
- MEIHAPER Modulo 5 3 Julio ViolaDocument45 pagesMEIHAPER Modulo 5 3 Julio ViolaRodolfo QuadrossNo ratings yet
- Proton Exchange Membrane Water ElectrolyzerDocument64 pagesProton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzerabhijay1987100% (2)
- ME165-1 - Week-10.2 Energy Storage TechDocument39 pagesME165-1 - Week-10.2 Energy Storage Techarsenic_94No ratings yet
- JPS78-156 - A Multifunctional Energy Storage SystemDocument8 pagesJPS78-156 - A Multifunctional Energy Storage Systemcarlosalberto.camargoNo ratings yet
- Fuel CellsDocument5 pagesFuel CellsSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- DC Vessel System BookDocument54 pagesDC Vessel System BookSuzanne WatsonNo ratings yet
- Webinar 6 of 6 EnglishDocument41 pagesWebinar 6 of 6 EnglishBrzata PticaNo ratings yet
- EAT Jan-10-IIIDocument17 pagesEAT Jan-10-IIISiddharth PantNo ratings yet
- 18CHO101T UNIT 5 Energy StorageDocument34 pages18CHO101T UNIT 5 Energy StorageHruday CoolkidNo ratings yet
- Concepts - Boilers, Renewable EnergyDocument10 pagesConcepts - Boilers, Renewable EnergyCrooks, Gene Emmanuel P.No ratings yet
- Sdarticle 15Document12 pagesSdarticle 15Desu MihretuNo ratings yet
- Enrgy System and Its AnalysisDocument58 pagesEnrgy System and Its AnalysisLikith Gowda MNo ratings yet
- 22 Solar Cell Challenges and New DevelopmentsDocument22 pages22 Solar Cell Challenges and New DevelopmentsPatrice ETEMENo ratings yet
- A Homopolar Inductor Motor/Generator and Six-Step Drive Flywheel Energy Storage SystemDocument31 pagesA Homopolar Inductor Motor/Generator and Six-Step Drive Flywheel Energy Storage SystemAnup M UpadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Module-2 Energy Systems & AnalysisDocument46 pagesModule-2 Energy Systems & Analysisrushi C SNo ratings yet
- Town Power ManagementDocument19 pagesTown Power ManagementgrahamtownNo ratings yet
- EE535: Renewable Energy: Systems, Technology & Economics: Solar Plant EngineeringDocument20 pagesEE535: Renewable Energy: Systems, Technology & Economics: Solar Plant Engineeringzabiruddin786No ratings yet
- Exhaust Gas Heat Recovery Power GenerationDocument52 pagesExhaust Gas Heat Recovery Power GenerationabhinavkarthickNo ratings yet
- Ret Solved Question PaperDocument17 pagesRet Solved Question Papersavita.nimbolkar83No ratings yet
- Apresentação Sistemas de Acumulação de Energia PDFDocument23 pagesApresentação Sistemas de Acumulação de Energia PDFcarlosalbertocamargoNo ratings yet
- Balancing Cost and Performance in A PV/Wind/Battery Hybrid Power SystemDocument5 pagesBalancing Cost and Performance in A PV/Wind/Battery Hybrid Power SystemKhubaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy Generation, Utilization and ConsrevationDocument132 pagesElectrical Energy Generation, Utilization and Consrevationvarunflyhigh50% (2)
- Integrated Variable Speed DrivesDocument14 pagesIntegrated Variable Speed DrivesulatbookNo ratings yet
- HybridPowerSystems 2Document43 pagesHybridPowerSystems 2Nithin BasavaNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis Assignment: Syed Ahsan Ali (EE-12092)Document4 pagesPower System Analysis Assignment: Syed Ahsan Ali (EE-12092)ahsan aliNo ratings yet
- Wipo Idb Ip Ryd 07 2Document65 pagesWipo Idb Ip Ryd 07 2RASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Various Forms of Energy and The Law of Conservation of EnergyDocument16 pagesVarious Forms of Energy and The Law of Conservation of EnergydownloadsahuNo ratings yet
- MSC Project Thesis PresentationDocument21 pagesMSC Project Thesis Presentationmamudu francisNo ratings yet
- PROJECT PROPOSAL - Flow CellDocument17 pagesPROJECT PROPOSAL - Flow CellazamshafiqNo ratings yet
- Lec 23Document30 pagesLec 23Mayank SathoneNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage System 2Document23 pagesEnergy Storage System 2Alamgir Kabir ShuvoNo ratings yet
- To Meet Automotive Power NeedsDocument14 pagesTo Meet Automotive Power Needslkhandelwal_3No ratings yet
- Non Conventional Sources OF EnergyDocument9 pagesNon Conventional Sources OF EnergyAnutosh BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Report About: Steam Power PlantDocument13 pagesFeasibility Report About: Steam Power Plantjsmith84No ratings yet
- JPS19-227 - Lead Acid Batteries For Load-Levelling ApplicatiDocument4 pagesJPS19-227 - Lead Acid Batteries For Load-Levelling Applicaticarlosalberto.camargoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Moodle Lecture 1Document9 pagesUNIT 1 Moodle Lecture 1aryanNo ratings yet
- SOLAR POWER SYSTEM RoanDocument34 pagesSOLAR POWER SYSTEM RoanroanNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage Part1Document22 pagesEnergy Storage Part1Mohamed AliNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage SystemsDocument26 pagesEnergy Storage SystemsTU_MTECH_ENV11No ratings yet
- Emergency Power For Amateur Radio Stations SoCal ERC Aug 2010Document40 pagesEmergency Power For Amateur Radio Stations SoCal ERC Aug 2010bsaylor123No ratings yet
- Parabolic Trough Technology DevelopmentDocument1 pageParabolic Trough Technology DevelopmentGabriela VazNo ratings yet
- Jagannathan (Jug) Venkatesh CSE 291 - Smart Grid Seminar: System Energy Efficiency Lab Seelab - Ucsd.eduDocument52 pagesJagannathan (Jug) Venkatesh CSE 291 - Smart Grid Seminar: System Energy Efficiency Lab Seelab - Ucsd.eduGokul VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Marine Electrics Made Simple or How to Keep the Batteries ChargedFrom EverandMarine Electrics Made Simple or How to Keep the Batteries ChargedNo ratings yet
ENGG2500 Energy Storage
ENGG2500 Energy Storage
Uploaded by
epicsmurfc20 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageENGG2500 Energy Storage
ENGG2500 Energy Storage
Uploaded by
epicsmurfc2Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
ENGG2500 Energy Storage –
Pumped Storage –
- Huge amount of potential energy
- Turn around efficiencies >80%
- Most cost effective form of bulk energy storage
- Uses water that could be used elsewhere, which can also affect eco systems downriver
- And takes up a relatively large amount of land
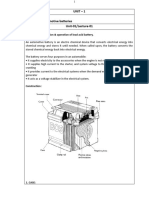
Batteries –
- Anode – negative terminal highly conductive aluminium or coper
- Cathode - positive terminal, typically copper or aluminium coated with lithium-ion
chemistry
- Battery Management System
o Controller that manages charging/discharging, temperature
- C-rate
o Rate a battery can discharge power
- Capacity
o Measured in ampere-hours – amount of energy in the battery
- State of Charge (SoC) – amount of energy left
- Cycle – process of discharging then charging
- Depth of Discharge (DoD) – how much of battery capacity is used
- Energy Density – how much energy relative to mass and volume
- Energy Storage System – complete battery pack system. I.e., cells, electronics, mechanical
housing etc
- Parallel or series
- Things have changed
o Costs are down
o Performance is up
o Lead acid no longer popular in off-grid or transport
o Batteries have been tested in laboratories with energy densities that rival diesel
o Commercially available topologies, have 0 – 80% charge times of 6 minutes
Flywheels –
- In the electrical grid rotating masses were the first used and still the most common today
- Kinetic rotational energy storage
Compressed air storage –
Use a compressor to inject air into reservoir to sink energy
Use compressed air to drive a turbine to source energy
You might also like
- Koritarov Grid-Scale Energy Storage FinalDocument53 pagesKoritarov Grid-Scale Energy Storage FinalsaishankarlNo ratings yet
- Electric System For Opel AmperaDocument24 pagesElectric System For Opel AmperaLuca TrottaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Sources and Photovoltaics: AE1M13EZFDocument26 pagesElectrochemical Sources and Photovoltaics: AE1M13EZFalessio8No ratings yet
- LECTURE 3 Energy Storage TechnologiesDocument55 pagesLECTURE 3 Energy Storage Technologieswing fatt hiewNo ratings yet
- Written AssayDocument3 pagesWritten AssayDuroxNo ratings yet
- Electricity Storage Review 2016Document24 pagesElectricity Storage Review 2016tahirprofessionalNo ratings yet
- BatteriesDocument44 pagesBatteriesAnas SakrNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage Technologies in Renewable EnergyDocument28 pagesEnergy Storage Technologies in Renewable Energyjitendra jhaNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Systems IIIDocument34 pagesPhotovoltaic Systems IIIObada Ar-ruzziNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage TechnologiesDocument27 pagesEnergy Storage TechnologiesNew king IndiaNo ratings yet
- The Need of Energy Storage With The Various Energy SystemDocument3 pagesThe Need of Energy Storage With The Various Energy Systemskjdkmq518No ratings yet
- Storage PresentationDocument43 pagesStorage PresentationHafeez Khan TareenNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Notes 19ee3dcepgDocument70 pagesUnit-4 Notes 19ee3dcepghandekashyapNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy ResourcesDocument51 pagesRenewable Energy ResourcesVeerabhadrayya C KNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage SystemDocument22 pagesEnergy Storage Systemmikkumar5No ratings yet
- MEIHAPER Modulo 5 3 Julio ViolaDocument45 pagesMEIHAPER Modulo 5 3 Julio ViolaRodolfo QuadrossNo ratings yet
- Proton Exchange Membrane Water ElectrolyzerDocument64 pagesProton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzerabhijay1987100% (2)
- ME165-1 - Week-10.2 Energy Storage TechDocument39 pagesME165-1 - Week-10.2 Energy Storage Techarsenic_94No ratings yet
- JPS78-156 - A Multifunctional Energy Storage SystemDocument8 pagesJPS78-156 - A Multifunctional Energy Storage Systemcarlosalberto.camargoNo ratings yet
- Fuel CellsDocument5 pagesFuel CellsSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- DC Vessel System BookDocument54 pagesDC Vessel System BookSuzanne WatsonNo ratings yet
- Webinar 6 of 6 EnglishDocument41 pagesWebinar 6 of 6 EnglishBrzata PticaNo ratings yet
- EAT Jan-10-IIIDocument17 pagesEAT Jan-10-IIISiddharth PantNo ratings yet
- 18CHO101T UNIT 5 Energy StorageDocument34 pages18CHO101T UNIT 5 Energy StorageHruday CoolkidNo ratings yet
- Concepts - Boilers, Renewable EnergyDocument10 pagesConcepts - Boilers, Renewable EnergyCrooks, Gene Emmanuel P.No ratings yet
- Sdarticle 15Document12 pagesSdarticle 15Desu MihretuNo ratings yet
- Enrgy System and Its AnalysisDocument58 pagesEnrgy System and Its AnalysisLikith Gowda MNo ratings yet
- 22 Solar Cell Challenges and New DevelopmentsDocument22 pages22 Solar Cell Challenges and New DevelopmentsPatrice ETEMENo ratings yet
- A Homopolar Inductor Motor/Generator and Six-Step Drive Flywheel Energy Storage SystemDocument31 pagesA Homopolar Inductor Motor/Generator and Six-Step Drive Flywheel Energy Storage SystemAnup M UpadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Module-2 Energy Systems & AnalysisDocument46 pagesModule-2 Energy Systems & Analysisrushi C SNo ratings yet
- Town Power ManagementDocument19 pagesTown Power ManagementgrahamtownNo ratings yet
- EE535: Renewable Energy: Systems, Technology & Economics: Solar Plant EngineeringDocument20 pagesEE535: Renewable Energy: Systems, Technology & Economics: Solar Plant Engineeringzabiruddin786No ratings yet
- Exhaust Gas Heat Recovery Power GenerationDocument52 pagesExhaust Gas Heat Recovery Power GenerationabhinavkarthickNo ratings yet
- Ret Solved Question PaperDocument17 pagesRet Solved Question Papersavita.nimbolkar83No ratings yet
- Apresentação Sistemas de Acumulação de Energia PDFDocument23 pagesApresentação Sistemas de Acumulação de Energia PDFcarlosalbertocamargoNo ratings yet
- Balancing Cost and Performance in A PV/Wind/Battery Hybrid Power SystemDocument5 pagesBalancing Cost and Performance in A PV/Wind/Battery Hybrid Power SystemKhubaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy Generation, Utilization and ConsrevationDocument132 pagesElectrical Energy Generation, Utilization and Consrevationvarunflyhigh50% (2)
- Integrated Variable Speed DrivesDocument14 pagesIntegrated Variable Speed DrivesulatbookNo ratings yet
- HybridPowerSystems 2Document43 pagesHybridPowerSystems 2Nithin BasavaNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis Assignment: Syed Ahsan Ali (EE-12092)Document4 pagesPower System Analysis Assignment: Syed Ahsan Ali (EE-12092)ahsan aliNo ratings yet
- Wipo Idb Ip Ryd 07 2Document65 pagesWipo Idb Ip Ryd 07 2RASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Various Forms of Energy and The Law of Conservation of EnergyDocument16 pagesVarious Forms of Energy and The Law of Conservation of EnergydownloadsahuNo ratings yet
- MSC Project Thesis PresentationDocument21 pagesMSC Project Thesis Presentationmamudu francisNo ratings yet
- PROJECT PROPOSAL - Flow CellDocument17 pagesPROJECT PROPOSAL - Flow CellazamshafiqNo ratings yet
- Lec 23Document30 pagesLec 23Mayank SathoneNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage System 2Document23 pagesEnergy Storage System 2Alamgir Kabir ShuvoNo ratings yet
- To Meet Automotive Power NeedsDocument14 pagesTo Meet Automotive Power Needslkhandelwal_3No ratings yet
- Non Conventional Sources OF EnergyDocument9 pagesNon Conventional Sources OF EnergyAnutosh BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Report About: Steam Power PlantDocument13 pagesFeasibility Report About: Steam Power Plantjsmith84No ratings yet
- JPS19-227 - Lead Acid Batteries For Load-Levelling ApplicatiDocument4 pagesJPS19-227 - Lead Acid Batteries For Load-Levelling Applicaticarlosalberto.camargoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Moodle Lecture 1Document9 pagesUNIT 1 Moodle Lecture 1aryanNo ratings yet
- SOLAR POWER SYSTEM RoanDocument34 pagesSOLAR POWER SYSTEM RoanroanNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage Part1Document22 pagesEnergy Storage Part1Mohamed AliNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage SystemsDocument26 pagesEnergy Storage SystemsTU_MTECH_ENV11No ratings yet
- Emergency Power For Amateur Radio Stations SoCal ERC Aug 2010Document40 pagesEmergency Power For Amateur Radio Stations SoCal ERC Aug 2010bsaylor123No ratings yet
- Parabolic Trough Technology DevelopmentDocument1 pageParabolic Trough Technology DevelopmentGabriela VazNo ratings yet
- Jagannathan (Jug) Venkatesh CSE 291 - Smart Grid Seminar: System Energy Efficiency Lab Seelab - Ucsd.eduDocument52 pagesJagannathan (Jug) Venkatesh CSE 291 - Smart Grid Seminar: System Energy Efficiency Lab Seelab - Ucsd.eduGokul VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Marine Electrics Made Simple or How to Keep the Batteries ChargedFrom EverandMarine Electrics Made Simple or How to Keep the Batteries ChargedNo ratings yet