Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics MCQ 0625/23 Octnov 23
Physics MCQ 0625/23 Octnov 23
Uploaded by
tamanhnguyen2101Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Ultimate Guide To Drum Programming - EDMProdDocument32 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Drum Programming - EDMProdSteveJones100% (4)
- Past Paper IGCSE 2023 22Document8 pagesPast Paper IGCSE 2023 22David ThydetNo ratings yet
- Past Papers IGCSE 2022 22Document10 pagesPast Papers IGCSE 2022 22David ThydetNo ratings yet
- Past Papers IGCSE 2023 22Document8 pagesPast Papers IGCSE 2023 22David ThydetNo ratings yet
- Past Papers IGCSE 2022 23Document10 pagesPast Papers IGCSE 2022 23David ThydetNo ratings yet
- Point Pattern Analysis: Using Spatial Inferential StatisticsDocument34 pagesPoint Pattern Analysis: Using Spatial Inferential StatisticskimhoaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/01Document18 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/01Aditya RaoNo ratings yet
- Nurture - 20,27 July - Paper-2 - 27-08-20Document22 pagesNurture - 20,27 July - Paper-2 - 27-08-20VhhhhNo ratings yet
- Past Papers IGCSE 2022 21Document8 pagesPast Papers IGCSE 2022 21David ThydetNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge Ordinary LevelMadonna Hany naeemNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23shabanaNo ratings yet
- Bukit View Secondary Prelim 2021 PhysicsDocument47 pagesBukit View Secondary Prelim 2021 PhysicsChristian AjaNo ratings yet
- Physics 8b Midterm 1 Practice TestDocument6 pagesPhysics 8b Midterm 1 Practice TestPooja ParekhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Statistics and Probability (Calculator)Document20 pagesUnit 1 - Statistics and Probability (Calculator)ezNo ratings yet
- Chap00 OverviewDocument22 pagesChap00 OverviewMuhammad HamzaNo ratings yet
- Past Paper Non Calc Higher MathsDocument24 pagesPast Paper Non Calc Higher Mathsmontymorton631No ratings yet
- Physical Quantities, Units and Measurements: Practice Question Week-1Document24 pagesPhysical Quantities, Units and Measurements: Practice Question Week-1Muhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- As Physics May 9Document24 pagesAs Physics May 9Tayyaba Mumtaz KhanNo ratings yet
- P1 Chapter 5::: Straight Line GraphsDocument40 pagesP1 Chapter 5::: Straight Line GraphsPrince YugNo ratings yet
- 02 BasicProbabilityTheory PDFDocument27 pages02 BasicProbabilityTheory PDFCarlos RiveraNo ratings yet
- Paper-2 With Solution: Nurture - 24-JuneDocument26 pagesPaper-2 With Solution: Nurture - 24-JuneVhhhhNo ratings yet
- June 2016 QP - Paper 2 Edexcel Physics AS-LevelDocument19 pagesJune 2016 QP - Paper 2 Edexcel Physics AS-LevelSolace HusseinNo ratings yet
- Past Papers IGCSE 2022 41Document8 pagesPast Papers IGCSE 2022 41David ThydetNo ratings yet
- 2022 Jan Unit 1 New - PhysicsDocument28 pages2022 Jan Unit 1 New - PhysicsABDULLAH SHAHZADNo ratings yet
- Set 1Document27 pagesSet 1Ai HooiNo ratings yet
- 64ac51911b52b Edexcel As... Physics Question Paper 1 June 2023 PDFDocument32 pages64ac51911b52b Edexcel As... Physics Question Paper 1 June 2023 PDFDharshaan GopaulNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Final January 2008: GCE Physics (6732/01)Document12 pagesMark Scheme Final January 2008: GCE Physics (6732/01)sfbdhaedbdzNo ratings yet
- Past Papers IGCSE 2023 23Document8 pagesPast Papers IGCSE 2023 23David ThydetNo ratings yet
- Explanation Sat Practice Test 4 Digital by MR Mohamed AbdallahDocument26 pagesExplanation Sat Practice Test 4 Digital by MR Mohamed AbdallahнуркызNo ratings yet
- 0625 s20 QP 11...Document20 pages0625 s20 QP 11...Saeed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Paper-2 With Solution: Nurture - AllDocument29 pagesPaper-2 With Solution: Nurture - AllHdhhdhNo ratings yet
- Nuiviber: FfiffiDocument12 pagesNuiviber: FfiffiThero SethapeloNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document47 pagesCH 01Samuel ThembaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Change in TandemDocument5 pages1.1 Change in Tandemjakeya0No ratings yet
- Solution: Introduction To Deep LearningDocument20 pagesSolution: Introduction To Deep LearningAkshay KumbarwarNo ratings yet
- North Sydney Boys 2023 4U Trials & SolutionsDocument30 pagesNorth Sydney Boys 2023 4U Trials & Solutionsramyasatchi02No ratings yet
- 2023 North Sydney Boys High School - X2 - QuestionsDocument11 pages2023 North Sydney Boys High School - X2 - Questionsmariamarsbar17No ratings yet
- PHYSICS MechanicsDocument329 pagesPHYSICS MechanicsPeng GengNo ratings yet
- Paper - 2 With Solution: Nurture - 13-JulyDocument22 pagesPaper - 2 With Solution: Nurture - 13-JulyVhhhhNo ratings yet
- 8PH0 02 RmsDocument18 pages8PH0 02 RmsLwincho LayNo ratings yet
- 3 Curvilinear MotionDocument50 pages3 Curvilinear Motiongarhgelh100% (1)
- Physics: Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: Physics On The GoDocument24 pagesPhysics: Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: Physics On The GoMuhammad Saif AmirNo ratings yet
- Paper-1 With Solution: Jee Advanced PatternDocument24 pagesPaper-1 With Solution: Jee Advanced PatternIshaan jainNo ratings yet
- Fall Final Review TIPERs Solutions 2019Document8 pagesFall Final Review TIPERs Solutions 2019SoulArcher23No ratings yet
- 0s2 9MA0 32 Mechanics Mock Set 2 PDF 1Document20 pages0s2 9MA0 32 Mechanics Mock Set 2 PDF 1ayeshamq13No ratings yet
- G. Gradients and Areas of Graphs in Context (H)Document19 pagesG. Gradients and Areas of Graphs in Context (H)ashwithanumandlaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 20240304v5Document33 pagesLecture 1 20240304v5ReedusNo ratings yet
- Physics - 01Document25 pagesPhysics - 01Raiyan IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - brute-force algorithms (part 2) - miscellaneousDocument14 pagesLecture 4 - brute-force algorithms (part 2) - miscellaneousUmama ZafranNo ratings yet
- 0 PreliminariesDocument27 pages0 Preliminariesyvonnetsai0306No ratings yet
- Rotational Motion Key ConceptsDocument1 pageRotational Motion Key ConceptsHEIDI ROSE MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Past Papers IGCSE 2023 21Document8 pagesPast Papers IGCSE 2023 21David ThydetNo ratings yet
- Mathematics A: Pearson Edexcel GCSEDocument24 pagesMathematics A: Pearson Edexcel GCSElinuxuser userNo ratings yet
- OperationswithdecimalsDocument8 pagesOperationswithdecimalsEdzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Mathematics 1MA0 Mock Paper 2HDocument23 pagesEdexcel GCSE Mathematics 1MA0 Mock Paper 2Hzo zNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE A Maths Higher Paper 2 June 2022Document24 pagesEdexcel IGCSE A Maths Higher Paper 2 June 2022rogerNo ratings yet
- Learning Target: I Can Solve and Graph Linear Inequalities Using Different PropertiesDocument43 pagesLearning Target: I Can Solve and Graph Linear Inequalities Using Different PropertiesCheryll Ann CerbitoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Topics: Projectiles in M1: - Gun Shot, Canons, FireworksDocument5 pagesTeaching Topics: Projectiles in M1: - Gun Shot, Canons, Fireworkswill bellNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationChryssa EconomouNo ratings yet
- CV12 SE Ch01 Sec1 1 Page4to12Document9 pagesCV12 SE Ch01 Sec1 1 Page4to12lillian.albassamNo ratings yet
- Hots Advance MiraeDocument36 pagesHots Advance MiraeHabibie BoilerNo ratings yet
- Ax88796B With Ali M3602 Mcu Reference Schematic IndexDocument4 pagesAx88796B With Ali M3602 Mcu Reference Schematic IndexdistefanoNo ratings yet
- Leadership in Virtual TeamsDocument13 pagesLeadership in Virtual TeamsBrandon ManuelNo ratings yet
- B1.1-Self-Study Đã Sài XongDocument5 pagesB1.1-Self-Study Đã Sài XongVy CẩmNo ratings yet
- Real Exam 22.03.2024 (With Answers) - UpdatedDocument12 pagesReal Exam 22.03.2024 (With Answers) - Updatedtd090404No ratings yet
- Before Reading: An Encyclopedia EntryDocument6 pagesBefore Reading: An Encyclopedia EntryĐào Nguyễn Duy TùngNo ratings yet
- Solved Examples: Axes-Zz and - YyDocument8 pagesSolved Examples: Axes-Zz and - YyDeepak SahNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource PlanningDocument20 pagesEnterprise Resource Planningapi-3831939No ratings yet
- Synopsis and ReflectionDocument2 pagesSynopsis and ReflectionArfaida LadjaNo ratings yet
- Ruq Abdominal PainDocument55 pagesRuq Abdominal PainriphqaNo ratings yet
- PDF Medical Management of Thyroid Disease 3Rd Ed 3Rd Edition David S Cooper Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Medical Management of Thyroid Disease 3Rd Ed 3Rd Edition David S Cooper Ebook Full Chapterrebecca.baez273100% (5)
- Squirrels of Indian SubcontinentDocument14 pagesSquirrels of Indian SubcontinentAkshay MotiNo ratings yet
- Infosys Verification FormDocument6 pagesInfosys Verification Formamanueljoseph1310No ratings yet
- Renesas Application Note AN1340Document6 pagesRenesas Application Note AN1340Rip_BarNo ratings yet
- Neuromusic IIIDocument3 pagesNeuromusic IIIJudit VallejoNo ratings yet
- Testable Concepts in MCQDocument188 pagesTestable Concepts in MCQrami100% (1)
- Tide Times and Tide Chart For Dammam PDFDocument8 pagesTide Times and Tide Chart For Dammam PDFAnonymous g5nMjONo ratings yet
- Market Analysis On Tata IndicaDocument47 pagesMarket Analysis On Tata Indicasnehasis nandyNo ratings yet
- DLL - Co.q2 Science IVDocument16 pagesDLL - Co.q2 Science IVAllyn MadeloNo ratings yet
- Dolomite in Manila Bay A Big HitDocument3 pagesDolomite in Manila Bay A Big HitJoanaPauline FloresNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)Document16 pagesLab 5 Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)Programming CodingNo ratings yet
- HP Scanjet Pro 2500 F1 Flatbed Scanner: DatasheetDocument2 pagesHP Scanjet Pro 2500 F1 Flatbed Scanner: DatasheetKarkittykatNo ratings yet
- Colonialism and Imperialism by Usman KhanDocument2 pagesColonialism and Imperialism by Usman KhanUSMANNo ratings yet
- Adetunji CVDocument5 pagesAdetunji CVAdetunji AdegbiteNo ratings yet
- Marketing Approach To Promoting Banking ServicesDocument8 pagesMarketing Approach To Promoting Banking Servicessubbaiah aNo ratings yet
- Automated Guided VehicleDocument14 pagesAutomated Guided VehicleSRI RAMNo ratings yet
- Architecture in EthDocument4 pagesArchitecture in Ethmelakumikias2No ratings yet
- 107 Hand Tool Field Maintenance v0311Document8 pages107 Hand Tool Field Maintenance v0311rabbit_39No ratings yet
- AC S08 Week 08Document3 pagesAC S08 Week 08ERICK BORJA DELGADONo ratings yet
Physics MCQ 0625/23 Octnov 23
Physics MCQ 0625/23 Octnov 23
Uploaded by
tamanhnguyen2101Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics MCQ 0625/23 Octnov 23
Physics MCQ 0625/23 Octnov 23
Uploaded by
tamanhnguyen2101Copyright:
Available Formats
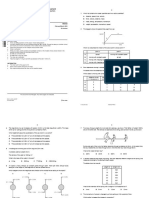
2
1 How many of the quantities shown are scalars?
mass momentum density energy
™
Cambridge IGCSE A 1 B 2 C 3 D 4
PHYSICS 0625/23 2 A train is on a straight track. The graph shows how a quantity y varies with time.
Paper 2 Multiple Choice (Extended) October/November 2023
45 minutes y
You must answer on the multiple choice answer sheet.
*2430101011*
You will need: Multiple choice answer sheet
Soft clean eraser
Soft pencil (type B or HB is recommended)
0
0 time
INSTRUCTIONS
• There are forty questions on this paper. Answer all questions. Which statements can be true?
• For each question there are four possible answers A, B, C and D. Choose the one you consider correct
and record your choice in soft pencil on the multiple choice answer sheet.
1 The train is stationary and y represents the distance from the last station.
• Follow the instructions on the multiple choice answer sheet.
• Write in soft pencil. 2 The train is moving and y represents the distance from the last station.
• Write your name, centre number and candidate number on the multiple choice answer sheet in the
spaces provided unless this has been done for you. 3 The train is stationary and y represents the speed of the train.
• Do not use correction fluid.
4 The train is moving and y represents the speed of the train.
• Do not write on any bar codes.
• You may use a calculator. A 1 and 2 B 1 and 4 C 2 and 3 D 3 and 4
• Take the weight of 1.0 kg to be 9.8 N (acceleration of free fall = 9.8 m / s2).
3 The diagram shows a speed–time graph for a moving object.
INFORMATION
• The total mark for this paper is 40.
• Each correct answer will score one mark.
• Any rough working should be done on this question paper. speed
0
0 time
Which description of the object’s motion is correct?
A decreasing acceleration
B decreasing speed
C constant acceleration
This document has 20 pages. Any blank pages are indicated.
D constant speed
IB23 11_0625_23/4RP
© UCLES 2023 [Turn over
© UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23
3 4
4
4 The mass of air hitting the blades of a wind turbine each second is 1.5 × 10 kg. 6 A uniform rod rests on a pivot at its centre. The rod is not attached to the pivot. Forces are then
applied to the rod in four different ways, as shown. The weight of the rod can be ignored.
The speed of the air is 4.0 m / s.
Which diagram shows the rod in equilibrium?
The density of air is 1.2 kg / m3.
A B
100 N 100 N
100 N 100 N
C D
Which row gives the volume of the air hitting the blades each second and the kinetic energy of 100 N 100 N
the air hitting the blades each second?
volume of air kinetic energy
each second / m3 each second / J
100 N 100 N 100 N
A 13 000 72 000
B 13 000 120 000
7 A car of mass 1200 kg is travelling along a straight horizontal road.
C 18 000 72 000
Which impulse is needed to accelerate the car from 5.0 m / s to 10 m / s?
D 18 000 120 000
A 6000 N s B 12 000 N s C 15 000 N s D 18 000 N s
5 An object moves in a circle at constant speed.
Which statement about the force needed on the object is correct?
A A force away from the centre of the circle keeps the object moving in the circle.
B A force in the direction of motion of the object keeps it moving in the circle.
C A force towards the centre of the circle keeps the object moving in the circle.
D No force is needed to keep the object moving at constant speed in the circle.
© UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23 [Turn over © UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23
5 6
8 A mass bounces up and down on a steel spring. The diagram shows the mass and the spring at 10 A microwave oven is rated at 900 watts.
different points during the motion.
Which statement correctly describes the meaning of this value?
A 900 joules are transferred every second.
B 900 amperes are transferred every second.
C 900 volts are transferred every second.
highest mass mass
point moving moving D 900 ohms are transferred every second.
down up
11 An object is immersed in a liquid of density ρ. The pressure at this depth due to the liquid is p.
The gravitational field strength is g.
lowest
What is the equation for the depth h of the object beneath the surface?
point
ρg p pg
A h = pρ g B h= C h= D h=
At which point is the least energy in the gravitational potential store of the mass and at which p ρg ρ
point is the most energy in the elastic store of the spring?
least energy in most energy in 12 A sealed bottle of constant volume contains air.
gravitational potential the elastic store
store of the mass of the spring The air in the bottle is heated by the Sun.
A mass moving down mass moving up What is the effect on the average speed of the air particles in the bottle and the average distance
between them?
B mass moving down lowest point
C lowest point mass moving up average distance
average speed
between air
D lowest point lowest point of air particles
particles
A decreases decreases
9 A boy uses a rope to pull an object of mass m up a slope.
B decreases stays the same
The rope is parallel to the slope.
C increases increases
The tension in the rope is constant and of value F. D increases stays the same
The object moves a distance d along the slope and rises through a height h.
How much work is done by the boy?
A F×d
B F×h
C m×g×h×d
D m × g × h2
© UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23 [Turn over © UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23
7 8
13 In an experiment to investigate the relationship between the volume of a sample of air and its 15 Four containers each contain water.
pressure, the volume of the sample is decreased and its pressure is measured continuously.
More water at the same temperature is added to each container.
Curve X on the graph shows the results that would be expected for a fixed mass of air at constant
temperature. Curve Y shows the results that are obtained in this particular experiment. From which container does water now evaporate more slowly than it did before?
X A B C D
pressure
0
0 volume 16 A cupboard is placed in front of a heater. Air can move through a gap under the cupboard.
Which row shows two possible reasons why curve Y is different from curve X?
1 2
wall
A the temperature of the air increases air leaks into the container
as the volume is decreased as the volume is decreased
cupboard
B the temperature of the air increases air leaks out of the container heater
as the volume is decreased as the volume is decreased
C the temperature of the air decreases air leaks into the container
as the volume is decreased as the volume is decreased air moves through gap
D the temperature of the air decreases air leaks out of the container
as the volume is decreased as the volume is decreased
floor
Which row describes the temperature and the direction of movement of the air in the gap?
14 A student splashes water on to her face. Here are three statements about the effects.
P The water uses energy to evaporate. air temperature air direction
Q The water gains energy from the student. A cool away from the heater
R The face of the student cools. B cool towards the heater
C warm away from the heater
Which statements are correct?
D warm towards the heater
A P and Q only B P and R only C Q and R only D P, Q and R
© UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23 [Turn over © UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23
9 10
17 Light diffracts when it enters a telescope. This causes the image to blur slightly. The amount of 19 The diagram shows the effect of a prism on white light.
diffraction depends on the diameter of the hole through which the light enters the telescope and
the wavelength of the light. Some light is reflected on striking the prism and some is refracted and dispersed to form a
spectrum.
Which combination for diameter and wavelength will result in the sharpest image (least blurring)?
reflected
diameter wavelength light
A large long
B large short
C small long
white spectrum
D small short light
What happens if monochromatic light is used instead of white light?
18 The diagram shows a transverse wave.
A The light changes colour as it passes through the prism.
S
B The light forms a brighter spectrum.
P R C There is no reflected light.
Q
D There is no dispersion of the emerging light.
20 The diagram shows a ray of light incident on a plane mirror.
Which row identifies the amplitude and the wavelength of the wave?
mirror
amplitude wavelength
A P R
35q
B P S
C Q R
D Q S The angle between the ray and the mirror is 35°.
The ray is reflected by the mirror.
What is the angle of reflection?
A 35° B 55° C 70° D 110°
© UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23 [Turn over © UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23
11 12
21 A thin converging lens in a camera produces a real image on a photo-sensitive surface, as 25 The diagram shows an electric circuit.
shown.
At which position is the image of the top of the object formed?
thin converging lens A
top
A B
object In which direction do free electrons flow around this circuit and what quantity does the ammeter
measure?
D C
quantity measured
direction of electron flow
photo-sensitive by the ammeter
surface
A anticlockwise charge passing each point
in the circuit per unit time
22 Light is travelling through air. It strikes a glass block at an angle of incidence of 45°. The glass B anticlockwise total charge passing
has a refractive index of 1.4. through the ammeter
What is the angle of refraction of the light as it enters the glass? C clockwise charge passing each point
in the circuit per unit time
A 29° B 30° C 32° D 82°
D clockwise total charge passing
through the ammeter
23 Which row gives approximate values for the speed of sound in copper, water and air?
speed of sound in copper speed of sound in water speed of sound in air 26 Which substances both contain large concentrations of free electrons?
m/s m/s m/s
A aluminium and glass
A 4500 1500 350 B copper and water
B 350 4500 1500 C copper and nylon
C 1500 4500 350 D silver and gold
D 4500 350 1500
27 A resistance wire of length L melts and has to be replaced with a wire of the same material and
the same resistance. The only wire available has twice the diameter of the broken wire.
24 Which metal can be attracted by a magnet?
A zinc Which length of this wire should be used?
B lead A L B L C 2L D 4L
4 2
C iron
D copper
© UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23 [Turn over © UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23
13 14
28 A teacher wishes to show the production of electrostatic charges. 30 The diagram shows a light-dependent resistor (LDR) connected in a potential divider circuit.
She holds a rod and rubs it with a cotton cloth. A copper rod, a glass rod, a plastic rod and a steel
rod are available.
V
Which two rods would both be suitable to use?
A a copper rod and a glass rod
B a glass rod and a plastic rod
C a plastic rod and a copper rod
D a plastic rod and a steel rod
The brightness of the light falling on the LDR is increased.
29 Two resistors, with resistances R1 and R2, are used as a potential divider. Which row shows what happens to the resistance of the LDR and what happens to the reading
on the voltmeter?
resistance of LDR reading on voltmeter
R1 V1
A decreases decreases
B decreases increases
C increases decreases
R2 V2
D increases increases
31 A simple a.c. generator has a coil rotating in a magnetic field.
What is the relationship between R1, R2 and potential differences V1 and V2?
A R1 × R2 = V1 × V2 What happens to the peak electromotive force (e.m.f.) and to the frequency of the a.c. output
when the coil is rotated faster?
B R1 × V1 = R2 × V2
peak e.m.f. frequency
R1
C = V1 × V2
R2 A greater greater
R1 V 1 B greater no change
D =
R2 V 2
C no change greater
D no change no change
© UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23 [Turn over © UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23
15 16
32 A current passes along a wire placed between the poles of a permanent magnet. 34 The scattering of α-particles by a thin gold foil provides evidence for the nuclear model of the
atom.
The wire experiences a force due to the magnetic field.
Two α-particles of the same energy are incident on a nucleus of gold.
Which diagram shows the correct paths followed by the α-particles as they pass close to the
nucleus?
N S A B
path of D-particle
What will change the direction of this force?
A increasing the current
B reversing the current
C increasing the strength of the magnetic field gold nucleus
D using an electromagnet with the same polarity as the permanent magnet
C D
33 What is a transformer used for?
A changing a direct current into an alternating current
B changing the magnitude of an alternating voltage
C reducing the frequency of an alternating current
D switching off the current in a circuit when there is a fault
35 The half-life of carbon-14 is 5700 years.
An object containing carbon-14 has a count rate of 100 counts / minute when it is first formed. The
graph shows how the count rate decreases over time.
Which point on the graph corresponds to a time 11 400 years after the formation of the object?
100
count rate
A
counts / minute
B
C
D
0
0 time
© UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23 [Turn over © UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23
17 18
36 Why are beta-particles deflected more strongly than alpha-particles when they enter an electric 39 The nearest star to the Sun is about four light-years away from the Earth.
field?
A student makes three statements about the star.
A Beta-particles have less mass than alpha-particles.
1 Light from the star takes about four years to reach the Earth.
B Beta-particles are negatively charged.
2 Light from the Sun takes about four years to travel to the star and back to the Earth.
C Beta-particles have lower velocities than alpha-particles.
3 The star is outside our galaxy.
D Beta-particles have more ionising power than alpha-particles.
Which statements are correct?
37 Which statement describes how nuclear energy is released by fission in a nuclear power station? A 1, 2 and 3 B 1 and 3 only C 1 only D 2 and 3 only
A Atoms join together to make molecules.
B Heavy nuclei split into lighter nuclei. 40 A planet orbits the Sun with orbital period T. The average radius of the orbit is r.
C Light nuclei join together to form heavier nuclei. What is the average orbital speed of the planet?
D Molecules break down into atoms. 2πr T πr
A 2πrT B C D
T 2πr 2T
38 The diagram shows a star S and the initial arrangement of three planets, X, Y and Z.
Z
NOT TO
Y
SCALE
X
clockwise S
Each planet orbits clockwise in a circle about S.
The time for one orbit of Y is three times the time taken for one orbit of X.
The time for one orbit of Z is twice the time taken for one orbit of Y.
Starting from the initial arrangement, which diagram shows the positions of the planets after X
has made one complete orbit?
A B C D
Z Z
X X X X
S Y S Y Y S Y S
Z Z
© UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23 [Turn over © UCLES 2023 0625/23/O/N/23
You might also like
- The Ultimate Guide To Drum Programming - EDMProdDocument32 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Drum Programming - EDMProdSteveJones100% (4)
- Past Paper IGCSE 2023 22Document8 pagesPast Paper IGCSE 2023 22David ThydetNo ratings yet
- Past Papers IGCSE 2022 22Document10 pagesPast Papers IGCSE 2022 22David ThydetNo ratings yet
- Past Papers IGCSE 2023 22Document8 pagesPast Papers IGCSE 2023 22David ThydetNo ratings yet
- Past Papers IGCSE 2022 23Document10 pagesPast Papers IGCSE 2022 23David ThydetNo ratings yet
- Point Pattern Analysis: Using Spatial Inferential StatisticsDocument34 pagesPoint Pattern Analysis: Using Spatial Inferential StatisticskimhoaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/01Document18 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/01Aditya RaoNo ratings yet
- Nurture - 20,27 July - Paper-2 - 27-08-20Document22 pagesNurture - 20,27 July - Paper-2 - 27-08-20VhhhhNo ratings yet
- Past Papers IGCSE 2022 21Document8 pagesPast Papers IGCSE 2022 21David ThydetNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge Ordinary LevelMadonna Hany naeemNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23shabanaNo ratings yet
- Bukit View Secondary Prelim 2021 PhysicsDocument47 pagesBukit View Secondary Prelim 2021 PhysicsChristian AjaNo ratings yet
- Physics 8b Midterm 1 Practice TestDocument6 pagesPhysics 8b Midterm 1 Practice TestPooja ParekhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Statistics and Probability (Calculator)Document20 pagesUnit 1 - Statistics and Probability (Calculator)ezNo ratings yet
- Chap00 OverviewDocument22 pagesChap00 OverviewMuhammad HamzaNo ratings yet
- Past Paper Non Calc Higher MathsDocument24 pagesPast Paper Non Calc Higher Mathsmontymorton631No ratings yet
- Physical Quantities, Units and Measurements: Practice Question Week-1Document24 pagesPhysical Quantities, Units and Measurements: Practice Question Week-1Muhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- As Physics May 9Document24 pagesAs Physics May 9Tayyaba Mumtaz KhanNo ratings yet
- P1 Chapter 5::: Straight Line GraphsDocument40 pagesP1 Chapter 5::: Straight Line GraphsPrince YugNo ratings yet
- 02 BasicProbabilityTheory PDFDocument27 pages02 BasicProbabilityTheory PDFCarlos RiveraNo ratings yet
- Paper-2 With Solution: Nurture - 24-JuneDocument26 pagesPaper-2 With Solution: Nurture - 24-JuneVhhhhNo ratings yet
- June 2016 QP - Paper 2 Edexcel Physics AS-LevelDocument19 pagesJune 2016 QP - Paper 2 Edexcel Physics AS-LevelSolace HusseinNo ratings yet
- Past Papers IGCSE 2022 41Document8 pagesPast Papers IGCSE 2022 41David ThydetNo ratings yet
- 2022 Jan Unit 1 New - PhysicsDocument28 pages2022 Jan Unit 1 New - PhysicsABDULLAH SHAHZADNo ratings yet
- Set 1Document27 pagesSet 1Ai HooiNo ratings yet
- 64ac51911b52b Edexcel As... Physics Question Paper 1 June 2023 PDFDocument32 pages64ac51911b52b Edexcel As... Physics Question Paper 1 June 2023 PDFDharshaan GopaulNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Final January 2008: GCE Physics (6732/01)Document12 pagesMark Scheme Final January 2008: GCE Physics (6732/01)sfbdhaedbdzNo ratings yet
- Past Papers IGCSE 2023 23Document8 pagesPast Papers IGCSE 2023 23David ThydetNo ratings yet
- Explanation Sat Practice Test 4 Digital by MR Mohamed AbdallahDocument26 pagesExplanation Sat Practice Test 4 Digital by MR Mohamed AbdallahнуркызNo ratings yet
- 0625 s20 QP 11...Document20 pages0625 s20 QP 11...Saeed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Paper-2 With Solution: Nurture - AllDocument29 pagesPaper-2 With Solution: Nurture - AllHdhhdhNo ratings yet
- Nuiviber: FfiffiDocument12 pagesNuiviber: FfiffiThero SethapeloNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document47 pagesCH 01Samuel ThembaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Change in TandemDocument5 pages1.1 Change in Tandemjakeya0No ratings yet
- Solution: Introduction To Deep LearningDocument20 pagesSolution: Introduction To Deep LearningAkshay KumbarwarNo ratings yet
- North Sydney Boys 2023 4U Trials & SolutionsDocument30 pagesNorth Sydney Boys 2023 4U Trials & Solutionsramyasatchi02No ratings yet
- 2023 North Sydney Boys High School - X2 - QuestionsDocument11 pages2023 North Sydney Boys High School - X2 - Questionsmariamarsbar17No ratings yet
- PHYSICS MechanicsDocument329 pagesPHYSICS MechanicsPeng GengNo ratings yet
- Paper - 2 With Solution: Nurture - 13-JulyDocument22 pagesPaper - 2 With Solution: Nurture - 13-JulyVhhhhNo ratings yet
- 8PH0 02 RmsDocument18 pages8PH0 02 RmsLwincho LayNo ratings yet
- 3 Curvilinear MotionDocument50 pages3 Curvilinear Motiongarhgelh100% (1)
- Physics: Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: Physics On The GoDocument24 pagesPhysics: Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: Physics On The GoMuhammad Saif AmirNo ratings yet
- Paper-1 With Solution: Jee Advanced PatternDocument24 pagesPaper-1 With Solution: Jee Advanced PatternIshaan jainNo ratings yet
- Fall Final Review TIPERs Solutions 2019Document8 pagesFall Final Review TIPERs Solutions 2019SoulArcher23No ratings yet
- 0s2 9MA0 32 Mechanics Mock Set 2 PDF 1Document20 pages0s2 9MA0 32 Mechanics Mock Set 2 PDF 1ayeshamq13No ratings yet
- G. Gradients and Areas of Graphs in Context (H)Document19 pagesG. Gradients and Areas of Graphs in Context (H)ashwithanumandlaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 20240304v5Document33 pagesLecture 1 20240304v5ReedusNo ratings yet
- Physics - 01Document25 pagesPhysics - 01Raiyan IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - brute-force algorithms (part 2) - miscellaneousDocument14 pagesLecture 4 - brute-force algorithms (part 2) - miscellaneousUmama ZafranNo ratings yet
- 0 PreliminariesDocument27 pages0 Preliminariesyvonnetsai0306No ratings yet
- Rotational Motion Key ConceptsDocument1 pageRotational Motion Key ConceptsHEIDI ROSE MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Past Papers IGCSE 2023 21Document8 pagesPast Papers IGCSE 2023 21David ThydetNo ratings yet
- Mathematics A: Pearson Edexcel GCSEDocument24 pagesMathematics A: Pearson Edexcel GCSElinuxuser userNo ratings yet
- OperationswithdecimalsDocument8 pagesOperationswithdecimalsEdzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Mathematics 1MA0 Mock Paper 2HDocument23 pagesEdexcel GCSE Mathematics 1MA0 Mock Paper 2Hzo zNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE A Maths Higher Paper 2 June 2022Document24 pagesEdexcel IGCSE A Maths Higher Paper 2 June 2022rogerNo ratings yet
- Learning Target: I Can Solve and Graph Linear Inequalities Using Different PropertiesDocument43 pagesLearning Target: I Can Solve and Graph Linear Inequalities Using Different PropertiesCheryll Ann CerbitoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Topics: Projectiles in M1: - Gun Shot, Canons, FireworksDocument5 pagesTeaching Topics: Projectiles in M1: - Gun Shot, Canons, Fireworkswill bellNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationChryssa EconomouNo ratings yet
- CV12 SE Ch01 Sec1 1 Page4to12Document9 pagesCV12 SE Ch01 Sec1 1 Page4to12lillian.albassamNo ratings yet
- Hots Advance MiraeDocument36 pagesHots Advance MiraeHabibie BoilerNo ratings yet
- Ax88796B With Ali M3602 Mcu Reference Schematic IndexDocument4 pagesAx88796B With Ali M3602 Mcu Reference Schematic IndexdistefanoNo ratings yet
- Leadership in Virtual TeamsDocument13 pagesLeadership in Virtual TeamsBrandon ManuelNo ratings yet
- B1.1-Self-Study Đã Sài XongDocument5 pagesB1.1-Self-Study Đã Sài XongVy CẩmNo ratings yet
- Real Exam 22.03.2024 (With Answers) - UpdatedDocument12 pagesReal Exam 22.03.2024 (With Answers) - Updatedtd090404No ratings yet
- Before Reading: An Encyclopedia EntryDocument6 pagesBefore Reading: An Encyclopedia EntryĐào Nguyễn Duy TùngNo ratings yet
- Solved Examples: Axes-Zz and - YyDocument8 pagesSolved Examples: Axes-Zz and - YyDeepak SahNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource PlanningDocument20 pagesEnterprise Resource Planningapi-3831939No ratings yet
- Synopsis and ReflectionDocument2 pagesSynopsis and ReflectionArfaida LadjaNo ratings yet
- Ruq Abdominal PainDocument55 pagesRuq Abdominal PainriphqaNo ratings yet
- PDF Medical Management of Thyroid Disease 3Rd Ed 3Rd Edition David S Cooper Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Medical Management of Thyroid Disease 3Rd Ed 3Rd Edition David S Cooper Ebook Full Chapterrebecca.baez273100% (5)
- Squirrels of Indian SubcontinentDocument14 pagesSquirrels of Indian SubcontinentAkshay MotiNo ratings yet
- Infosys Verification FormDocument6 pagesInfosys Verification Formamanueljoseph1310No ratings yet
- Renesas Application Note AN1340Document6 pagesRenesas Application Note AN1340Rip_BarNo ratings yet
- Neuromusic IIIDocument3 pagesNeuromusic IIIJudit VallejoNo ratings yet
- Testable Concepts in MCQDocument188 pagesTestable Concepts in MCQrami100% (1)
- Tide Times and Tide Chart For Dammam PDFDocument8 pagesTide Times and Tide Chart For Dammam PDFAnonymous g5nMjONo ratings yet
- Market Analysis On Tata IndicaDocument47 pagesMarket Analysis On Tata Indicasnehasis nandyNo ratings yet
- DLL - Co.q2 Science IVDocument16 pagesDLL - Co.q2 Science IVAllyn MadeloNo ratings yet
- Dolomite in Manila Bay A Big HitDocument3 pagesDolomite in Manila Bay A Big HitJoanaPauline FloresNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)Document16 pagesLab 5 Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)Programming CodingNo ratings yet
- HP Scanjet Pro 2500 F1 Flatbed Scanner: DatasheetDocument2 pagesHP Scanjet Pro 2500 F1 Flatbed Scanner: DatasheetKarkittykatNo ratings yet
- Colonialism and Imperialism by Usman KhanDocument2 pagesColonialism and Imperialism by Usman KhanUSMANNo ratings yet
- Adetunji CVDocument5 pagesAdetunji CVAdetunji AdegbiteNo ratings yet
- Marketing Approach To Promoting Banking ServicesDocument8 pagesMarketing Approach To Promoting Banking Servicessubbaiah aNo ratings yet
- Automated Guided VehicleDocument14 pagesAutomated Guided VehicleSRI RAMNo ratings yet
- Architecture in EthDocument4 pagesArchitecture in Ethmelakumikias2No ratings yet
- 107 Hand Tool Field Maintenance v0311Document8 pages107 Hand Tool Field Maintenance v0311rabbit_39No ratings yet
- AC S08 Week 08Document3 pagesAC S08 Week 08ERICK BORJA DELGADONo ratings yet