Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abducens Nerve - Cranial Nerve VI Atf
Abducens Nerve - Cranial Nerve VI Atf
Uploaded by
Cathy SolivarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Grossman Baims Cardiac Catheterization Angiography and Intervention 8th Edition Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesGrossman Baims Cardiac Catheterization Angiography and Intervention 8th Edition Ebook PDFjeffrey.nevarez629100% (45)
- Head & Neck Spotters - Final With Answers-1Document78 pagesHead & Neck Spotters - Final With Answers-1Vikram88% (42)
- The Crashing Ventilated Patient Ch.3 (Jairo I. Santanilla, ACEP, 2011) PDFDocument10 pagesThe Crashing Ventilated Patient Ch.3 (Jairo I. Santanilla, ACEP, 2011) PDFPkernNo ratings yet
- 2023.neuroscience - Trans10.posterior Fossa Level Brainstem Cranial Nuclei and NervesDocument7 pages2023.neuroscience - Trans10.posterior Fossa Level Brainstem Cranial Nuclei and NervesstellaNo ratings yet
- Visual PathwayDocument24 pagesVisual PathwayAkshara Eye FoundationNo ratings yet
- Abducens Nerve Cranial Nerve VI AtfDocument4 pagesAbducens Nerve Cranial Nerve VI AtfAfrah AbdulNo ratings yet
- Accessory Nerve: Cranial Nerve XIDocument3 pagesAccessory Nerve: Cranial Nerve XIRubin kasmiNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve III - Oculomotor Nerve - FRCEM SuccessDocument1 pageCranial Nerve III - Oculomotor Nerve - FRCEM SuccessJohn CoxNo ratings yet
- Trochlear Nerve Cranial Nerve IV AtfDocument4 pagesTrochlear Nerve Cranial Nerve IV AtfRishi VermaNo ratings yet
- 117 - Neurology Physiology) Trigeminal Nerve - Cranial Nerve VDocument7 pages117 - Neurology Physiology) Trigeminal Nerve - Cranial Nerve VUssama MDNo ratings yet
- Anatomy AssignmentDocument10 pagesAnatomy AssignmentObansa JohnNo ratings yet
- Neurology - Hypoglossal Nerve - CN XIIDocument3 pagesNeurology - Hypoglossal Nerve - CN XIIRubin kasmiNo ratings yet
- 084 - Neurology Physiology) Medulla Anatomy & FunctionDocument14 pages084 - Neurology Physiology) Medulla Anatomy & Functionice.bear.wolfoNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves. - Sensory Organs - General MedicineDocument100 pagesCranial Nerves. - Sensory Organs - General MedicineHamdi AlaqalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Id - Final MergedDocument152 pagesAnatomy Id - Final MergedCastleKGNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY of Cranial Nerve Oculomotor, Trochlear, AbducensDocument26 pagesANATOMY of Cranial Nerve Oculomotor, Trochlear, AbducensDhita Dewi AlvianeNo ratings yet
- Rongga ObitaDocument27 pagesRongga ObitaFadli LatamaNo ratings yet
- Leavitt 2005Document16 pagesLeavitt 2005qr7bht566gNo ratings yet
- List The Neighboring Anatomical Regions and Structures Related To Each Wall of The OrbitDocument9 pagesList The Neighboring Anatomical Regions and Structures Related To Each Wall of The Orbitkep1313No ratings yet
- Articulo PDFDocument6 pagesArticulo PDFLuisa Vanessa CueroNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument88 pagesCranial NervesAhmed ZakiNo ratings yet
- 115 - Neurology Physiology) Oculomotor Nerve - Cranial Nerve IIIDocument6 pages115 - Neurology Physiology) Oculomotor Nerve - Cranial Nerve IIIUssama MDNo ratings yet
- June 2019Document91 pagesJune 2019watch itNo ratings yet
- Complete Spotters PDFDocument229 pagesComplete Spotters PDFSri Ram Prasath TNo ratings yet
- INICET November 2021Document244 pagesINICET November 2021sonali bhakhoreeNo ratings yet
- Koskas 2013Document15 pagesKoskas 2013Okta Kurniawan SaputraNo ratings yet
- 3rd Cranial NerveDocument7 pages3rd Cranial NerveHuy ThôngNo ratings yet
- (Cranial Nerves - Latest@2022Document95 pages(Cranial Nerves - Latest@2022amanuel melakuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: NeuroembryologyDocument13 pagesLecture 1: NeuroembryologyRaul Docto100% (1)
- Brainstem StrokesDocument4 pagesBrainstem StrokesChandniNo ratings yet
- GRDA Intro Brain Cranial Nerves P1Document16 pagesGRDA Intro Brain Cranial Nerves P1KingNo ratings yet
- BI 232 Lab 9Document17 pagesBI 232 Lab 9Cj LinceNo ratings yet
- Magic Book 150 Sureshots DR NikitaDocument265 pagesMagic Book 150 Sureshots DR Nikitaprateek varshneyNo ratings yet
- Orbit 2Document27 pagesOrbit 2cvmqx7yppdNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument30 pagesCranial NervesNia RwNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument32 pagesAnatomyShashanka PoudelNo ratings yet
- Tutor 16.2 GRACE NASYA (18-091) 4BDocument92 pagesTutor 16.2 GRACE NASYA (18-091) 4BGrace HerlisNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Cranial Nerves - Atlas - Part - 1Document33 pagesLab Manual - Cranial Nerves - Atlas - Part - 1Катерина ЛяшинаNo ratings yet
- Cranial NerveDocument29 pagesCranial NerveCosplay AccountNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Visual Pathway, Field Defects AND Its Lesions.: By-Dr. Ruchi PherwaniDocument43 pagesAnatomy of Visual Pathway, Field Defects AND Its Lesions.: By-Dr. Ruchi Pherwanisafasayed100% (1)
- The Functional Anatomy of The Cranial NervesDocument29 pagesThe Functional Anatomy of The Cranial NervesRăzvan Moțoc100% (1)
- 200F-21 The Brain SVDocument20 pages200F-21 The Brain SVRachel SawhNo ratings yet
- Lecture IIIDocument36 pagesLecture IIIbrittany AcheampongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Anatomical Organization of Cranial Nerves 2009 Manual Therapy For The Cranial NervesDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Anatomical Organization of Cranial Nerves 2009 Manual Therapy For The Cranial NervesDaniela Bustos PéndolaNo ratings yet
- CN FanyDocument24 pagesCN FanymiaNo ratings yet
- El Mejor de Vascular PDFDocument66 pagesEl Mejor de Vascular PDFRoberto RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomi Nervus KranialDocument40 pagesNeuroanatomi Nervus KranialHensy Virginia SolonNo ratings yet
- Visual and Lacrimal AppratusDocument45 pagesVisual and Lacrimal AppratusAzman Bin KadirNo ratings yet
- Quiz Anatomy Part 3 of 3Document56 pagesQuiz Anatomy Part 3 of 3MedShare75% (4)
- III AtfDocument5 pagesIII AtfGavin MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Oculofacial Plastic and Orbital Surgery: Basic and Clinical Science CourseDocument7 pagesOculofacial Plastic and Orbital Surgery: Basic and Clinical Science Coursenuryusri99No ratings yet
- Lecture 6: Cranial Nerves: Objective: To Understand The Organization of Cranial Nerves With RespectDocument30 pagesLecture 6: Cranial Nerves: Objective: To Understand The Organization of Cranial Nerves With Respectcilla235No ratings yet
- Orbital Apex Syndrome. A ReviewDocument10 pagesOrbital Apex Syndrome. A ReviewAndrés Faúndez TeránNo ratings yet
- CNS MCQSDocument24 pagesCNS MCQSSTEVEN OKURUT100% (2)
- Cranial Nerves Atlas Part 2Document26 pagesCranial Nerves Atlas Part 2Катерина ЛяшинаNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves: Romulo U. EsagundeDocument72 pagesCranial Nerves: Romulo U. EsagundeLoisen Nathan DanielNo ratings yet
- 2020OPTICNERVEPRESENTATIONDocument10 pages2020OPTICNERVEPRESENTATIONTendaiNo ratings yet
- MVST IB Head and Neck Anatomy: Ntroduction To The Ranial ErvesDocument4 pagesMVST IB Head and Neck Anatomy: Ntroduction To The Ranial ErvesSaffronMaeNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Notes For DentistsDocument33 pagesOphthalmology Notes For DentistsDr. Mahmoud Tawfik ElSoradyNo ratings yet
- Foramen Structures Conducted Cranial Fossa Cranial Bone Cribriform ForaminaDocument8 pagesForamen Structures Conducted Cranial Fossa Cranial Bone Cribriform ForaminaAchiever FayeNo ratings yet
- 10 - Urological DiordersDocument47 pages10 - Urological Diordersgozali189 biringNo ratings yet
- Tube ThoracostomyDocument17 pagesTube ThoracostomyheiyuNo ratings yet
- Intracranial PressureDocument7 pagesIntracranial PressureGuozhao JiNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker PamphletDocument2 pagesPacemaker Pamphletapi-355079078No ratings yet
- OSCE IV CanulationDocument2 pagesOSCE IV CanulationAmos TalsandekarNo ratings yet
- Undescended Testes (Orchidopexy)Document9 pagesUndescended Testes (Orchidopexy)nuranysha havizNo ratings yet
- Exam C SolDocument10 pagesExam C SolNuhad Bou MoslehNo ratings yet
- 2016 Master Courses Web-2Document16 pages2016 Master Courses Web-2Ioana Camelia TodaNo ratings yet
- Cannistra 2007Document4 pagesCannistra 2007amdreyNo ratings yet
- Limiting Structures: 2 Year/lec3Document7 pagesLimiting Structures: 2 Year/lec3Dr.Haider Saleem AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Dental Auxiliary: Presented By-Sneha Patil (Final Year BDS Student)Document36 pagesDental Auxiliary: Presented By-Sneha Patil (Final Year BDS Student)Mumin RashidNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 4th Edition by Ellis Chapters 12-15-18 Not IncludedDocument11 pagesTest Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 4th Edition by Ellis Chapters 12-15-18 Not Includedcanebrutalfniy66No ratings yet
- Medicine - EKG - Lab Coat PocketsDocument1 pageMedicine - EKG - Lab Coat Pocketsskeebs23No ratings yet
- TEE For ImpellaDocument6 pagesTEE For ImpellaPriya Nair MenonNo ratings yet
- Biomaterials and Implants in Cardiac and Vascular SurgeryDocument9 pagesBiomaterials and Implants in Cardiac and Vascular Surgerytornike kakhetelidzeNo ratings yet
- Hair Transplantation: With Follicular Unit MicrograftsDocument2 pagesHair Transplantation: With Follicular Unit MicrograftsRavvaNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Tokyoguidelines 2018 in The Management of Acute Cholangitis and Acute CholecystitisDocument13 pagesEffectiveness of Tokyoguidelines 2018 in The Management of Acute Cholangitis and Acute CholecystitisIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Ane Publish Ahead of Print 10.1213.ane.0000000000005043Document13 pagesAne Publish Ahead of Print 10.1213.ane.0000000000005043khalisahnNo ratings yet
- Jaundice and AscitesDocument15 pagesJaundice and AscitesJosiah Noella BrizNo ratings yet
- 1 Gastric and Duodenal Peptic Ulcer Disease 1Document30 pages1 Gastric and Duodenal Peptic Ulcer Disease 1rayNo ratings yet
- Articulators in Orthodontics: Theodore D. FreelandDocument12 pagesArticulators in Orthodontics: Theodore D. FreelandJegan KumarNo ratings yet
- Toshiba Medical Ultrasound TransducersDocument6 pagesToshiba Medical Ultrasound Transducersdmseoane100% (1)
- Dexmedetomidine Administration During Brain Tumour Resection andDocument2 pagesDexmedetomidine Administration During Brain Tumour Resection andABRAHAM MANUEL MEDINA LEYTONNo ratings yet
- Fetal and Neonatal Physiology PDFDocument33 pagesFetal and Neonatal Physiology PDFObsaNo ratings yet
- Daftar - Harga - Medika 2021-1Document2 pagesDaftar - Harga - Medika 2021-1riska setyawatiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Kidney Transplantation - Background, History of The Procedure, EpidemiologyDocument14 pagesPediatric Kidney Transplantation - Background, History of The Procedure, EpidemiologyNovi BaliNo ratings yet
- Assessment Question 1. All Are True About Vertebrae Levels EXCEPTDocument13 pagesAssessment Question 1. All Are True About Vertebrae Levels EXCEPTDevsya DodiaNo ratings yet
- Post Partum ComplicationsDocument40 pagesPost Partum ComplicationsMahmoud Abu Al AmrainNo ratings yet
Abducens Nerve - Cranial Nerve VI Atf
Abducens Nerve - Cranial Nerve VI Atf
Uploaded by
Cathy SolivarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abducens Nerve - Cranial Nerve VI Atf
Abducens Nerve - Cranial Nerve VI Atf
Uploaded by
Cathy SolivarCopyright:
Available Formats
AfraTafreeh.
com
Last edited: 9/4/2021
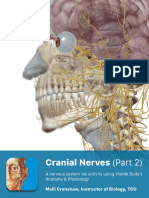
53. ABDUCENS NERVE – CRANIAL NERVE VI
Abducens Nerve: Cranial Nerve VI Medical Editor: Dr. Sarah Abimhamed
OUTLINE
I) ORIGIN OF THE NERVE Location of the Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
II) COURSE OF THE NERVE:
The Anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) originates from
III) STRUCTURES THE NERVE SUPPLIES
IV) CLINICAL CORRELATIONS the basilar artery, it is located near the cranial nerves
V) REVIEW QUESTIONS previously mentioned. Superiorly to AICA are the pontine
VI) REFERENCES branches. So, CN VI runs in between the AICA and the
pontine branches
It is important to know the relation of the artery to CN VI as
I) ORIGIN OF THE NERVE any type of lesion can lead to 6th nerve palsy.
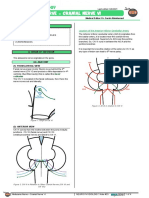
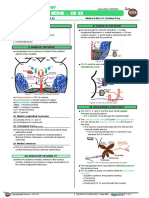
The abducens nerve originates in the pons.
(A) ANATOMY
(1) FROM LATERAL VIEW
Facial nerve proper (motor fibers) move behind the 6th
cranial nerve (CN VI) and produce a little depression in 4th
ventricle (fluid filled cavity) this is called the facial
colliculus
The CN VI is located in the facial colliculus, from there the
nerve moves out and laterally.
Figure 3. AICA in relation to CN VI
Figure 1. Origin of CN VI
(2) ANTERIOR VIEW
CN VI comes from the midline between the pons-medulla
junctions. CN VII (facial nerve) and CN VIII
(vestibulocochlear nerve) are lateral to CN VI.
AfraTafreeh.com
Figure 2. CN VI in Relation to Other Cranial Nerves (CN VII and
CN VIII)
Abducens Nerve – Cranial Nerve VI NEURO PHYSIOLOGY: Note #53. 1 of 4
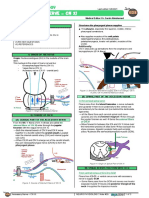
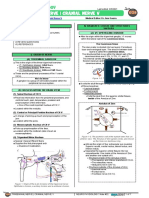
II) COURSE OF THE NERVE: III) STRUCTURES THE NERVE SUPPLIES
From the facial colliculus, the abducens nerve moves out The abducens nerve supplies the Lateral Rectus Muscle of
and up the posterior cranial fossa (on the clivus) enters the eye.
the petrous part of the temporal bone pierces into the
canal (dorello’s canal) with the inferior petrosal sinus (vein) Effects:
enters the cavity of the cavernous sinus runs next to When the abducens stimulates the lateral rectus muscle
the internal carotid artery exits the cavernous sinus it contracts and abducts the eye (lateral rotation of the
enters the superior orbital fissure enters orbital cavity eyeball)
supplies the lateral rectus muscle to produce adduction That is where it gets its name from:
ABDucens nerve ABDuction
Extra ocular muscles and their functions image:
Figure 4. Course of the Abducens Nerve
Figure 6. Extraocular Muscles
To remember which nerve supplies which extraocular
muscles:
LR6, SO4, ATR3
Remember: LR6 (lateral rectus supplied by 6th cranial nerve)
The cavernous sinus is a dural sinus. This is a space SO4 (superior oblique by the 4th cranial nerve)
ATR3 (All The Rest by the 3rd cranial nerve)
between the periosteal layer and the meningeal layer.
In the wall of the cavernous sinus there are 4 nerves
running through it:
AfraTafreeh.com
- CN III (Oculomotor Nerve)
- CN IV (Trochlear Nerve)
- CN V1 (Ophthalmic division of trigeminal nerve)
- CN V2 (Maxillary division of trigeminal nerve.)
But the CN VI through the cavity with the ICA.
Figure 5. Contents of the Cavernous Sinus and its wall
2 of 4 NEURO PHYSIOLOGY: Note #53. Abducens Nerve – Cranial Nerve VI
AfraTafreeh.com
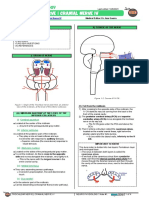
IV) CLINICAL CORRELATIONS CLINICAL EFFECT
All these lesions can result in the Lateral rectus not being
able to contract the eye will look inwards. This is called
Different lesions in different locations along the path of the
unilateral internal strabismus at rest
abducens nerve can result in CN VI Palsy.
If the patient turns their eyes laterally
(1) IN THE BRAIN STEM The visual fields are affected causing diplopia (double
Tumor, blood vessels occlusion/infarction, abscess, multiple vision)
sclerosis can demyelinate the axons of CNS compress
or affect the nucleus of the CN VI
(2) AROUND THE CEREBRAL ARTERY
If AICA develops vasculitis affect the fibers of CN VI
coming from the brain stem
(3) PETROS PART OF THE TEMPORAL BONE
Hematoma in that area high intracranial pressure pull
on CN VI tugging on the nerve at the edge of the bone
can damage it leading to a nerve palsy
(4) CAVERNOUS SINUS
As CN VI runs in the cavernous sinus with ICA, any
Aneurysm or thrombosis of ICA, or infection, or a fissure
can also affect CN VI.
(5) SUPERIOR ORBITAL FISSURE Figure 7. Clinical Effect of CN VI Palsy - Eye showing Unilateral
Internal Strabismus
Trauma in this area damage or fracture the bone
damage the nerve
Which eye movement does the abducens nerve
V) REVIEW QUESTIONS produce?
a. Elevation
Which nerves are located lateral to the abducens
AfraTafreeh.com b. Abduction
nerve?
c. Adduction
a. Trigeminal Nerve & Accessory Nerve
d. Depression
b. Facial Nerve & Glossopharyngeal Nerve
c. Facial Nerve & Vestibulocochlear Nerve
In which of the following would an aneurysm in the
d. Glossopharyngeal Nerve & Vestibulocochlear Nerve
internal carotid artery damage the abducens
nerve?
Which clinically significant artery is located near the
a. Superior Orbital Fissure
abducens nerve?
b. Petros Part of Temporal Bone
a. Basilar Artery
c. Brain Stem
b. Vertebral Artery
d. Cavernous Sinus
c. Posterior Intercostal Cerebellar Artery
d. Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
What is the result of 6th nerve palsy?
a. Unilateral Internal Strabismus At Rest
Which muscle does the abducens nerve supply?
b. Bilateral Internal Strabismus At Rest
a. Superior Oblique
c. Bilateral External Strabismus At Rest
b. Lateral Rectus
d. Unilateral External Strabismus At Rest
c. Inferior Oblique
d. Medial Rectus
What kind of damage to the orbital fissure can affect
the abducens nerve?
Which major artery runs with the abducens nerve in
a. Aneurysm
the cavernous sinus?
b. Trauma
a. Internal Carotid Artery
c. Vasculitis
b. Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
d. Thrombosis
c. External Carotid Artery
d. Pontine branches
CHECK YOUR ANSWERS
Which canal does the abducens nerve pierce
through with the inferior petrosal sinus? VI) REFERENCES
a. Cavernous Canal
b. Clivus Canal
c. Doralo’s Canal
d. Dorello's Canal
Abducens Nerve – Cranial Nerve VI NEURO PHYSIOLOGY: Note #53. 3 of 4
AfraTafreeh.com
AfraTafreeh.com
4 of 4 NEURO PHYSIOLOGY: Note #53. Abducens Nerve – Cranial Nerve VI
AfraTafreeh.com
You might also like
- Grossman Baims Cardiac Catheterization Angiography and Intervention 8th Edition Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesGrossman Baims Cardiac Catheterization Angiography and Intervention 8th Edition Ebook PDFjeffrey.nevarez629100% (45)
- Head & Neck Spotters - Final With Answers-1Document78 pagesHead & Neck Spotters - Final With Answers-1Vikram88% (42)
- The Crashing Ventilated Patient Ch.3 (Jairo I. Santanilla, ACEP, 2011) PDFDocument10 pagesThe Crashing Ventilated Patient Ch.3 (Jairo I. Santanilla, ACEP, 2011) PDFPkernNo ratings yet
- 2023.neuroscience - Trans10.posterior Fossa Level Brainstem Cranial Nuclei and NervesDocument7 pages2023.neuroscience - Trans10.posterior Fossa Level Brainstem Cranial Nuclei and NervesstellaNo ratings yet
- Visual PathwayDocument24 pagesVisual PathwayAkshara Eye FoundationNo ratings yet
- Abducens Nerve Cranial Nerve VI AtfDocument4 pagesAbducens Nerve Cranial Nerve VI AtfAfrah AbdulNo ratings yet
- Accessory Nerve: Cranial Nerve XIDocument3 pagesAccessory Nerve: Cranial Nerve XIRubin kasmiNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve III - Oculomotor Nerve - FRCEM SuccessDocument1 pageCranial Nerve III - Oculomotor Nerve - FRCEM SuccessJohn CoxNo ratings yet
- Trochlear Nerve Cranial Nerve IV AtfDocument4 pagesTrochlear Nerve Cranial Nerve IV AtfRishi VermaNo ratings yet
- 117 - Neurology Physiology) Trigeminal Nerve - Cranial Nerve VDocument7 pages117 - Neurology Physiology) Trigeminal Nerve - Cranial Nerve VUssama MDNo ratings yet
- Anatomy AssignmentDocument10 pagesAnatomy AssignmentObansa JohnNo ratings yet
- Neurology - Hypoglossal Nerve - CN XIIDocument3 pagesNeurology - Hypoglossal Nerve - CN XIIRubin kasmiNo ratings yet
- 084 - Neurology Physiology) Medulla Anatomy & FunctionDocument14 pages084 - Neurology Physiology) Medulla Anatomy & Functionice.bear.wolfoNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves. - Sensory Organs - General MedicineDocument100 pagesCranial Nerves. - Sensory Organs - General MedicineHamdi AlaqalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Id - Final MergedDocument152 pagesAnatomy Id - Final MergedCastleKGNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY of Cranial Nerve Oculomotor, Trochlear, AbducensDocument26 pagesANATOMY of Cranial Nerve Oculomotor, Trochlear, AbducensDhita Dewi AlvianeNo ratings yet
- Rongga ObitaDocument27 pagesRongga ObitaFadli LatamaNo ratings yet
- Leavitt 2005Document16 pagesLeavitt 2005qr7bht566gNo ratings yet
- List The Neighboring Anatomical Regions and Structures Related To Each Wall of The OrbitDocument9 pagesList The Neighboring Anatomical Regions and Structures Related To Each Wall of The Orbitkep1313No ratings yet
- Articulo PDFDocument6 pagesArticulo PDFLuisa Vanessa CueroNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument88 pagesCranial NervesAhmed ZakiNo ratings yet
- 115 - Neurology Physiology) Oculomotor Nerve - Cranial Nerve IIIDocument6 pages115 - Neurology Physiology) Oculomotor Nerve - Cranial Nerve IIIUssama MDNo ratings yet
- June 2019Document91 pagesJune 2019watch itNo ratings yet
- Complete Spotters PDFDocument229 pagesComplete Spotters PDFSri Ram Prasath TNo ratings yet
- INICET November 2021Document244 pagesINICET November 2021sonali bhakhoreeNo ratings yet
- Koskas 2013Document15 pagesKoskas 2013Okta Kurniawan SaputraNo ratings yet
- 3rd Cranial NerveDocument7 pages3rd Cranial NerveHuy ThôngNo ratings yet
- (Cranial Nerves - Latest@2022Document95 pages(Cranial Nerves - Latest@2022amanuel melakuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: NeuroembryologyDocument13 pagesLecture 1: NeuroembryologyRaul Docto100% (1)
- Brainstem StrokesDocument4 pagesBrainstem StrokesChandniNo ratings yet
- GRDA Intro Brain Cranial Nerves P1Document16 pagesGRDA Intro Brain Cranial Nerves P1KingNo ratings yet
- BI 232 Lab 9Document17 pagesBI 232 Lab 9Cj LinceNo ratings yet
- Magic Book 150 Sureshots DR NikitaDocument265 pagesMagic Book 150 Sureshots DR Nikitaprateek varshneyNo ratings yet
- Orbit 2Document27 pagesOrbit 2cvmqx7yppdNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument30 pagesCranial NervesNia RwNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument32 pagesAnatomyShashanka PoudelNo ratings yet
- Tutor 16.2 GRACE NASYA (18-091) 4BDocument92 pagesTutor 16.2 GRACE NASYA (18-091) 4BGrace HerlisNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Cranial Nerves - Atlas - Part - 1Document33 pagesLab Manual - Cranial Nerves - Atlas - Part - 1Катерина ЛяшинаNo ratings yet
- Cranial NerveDocument29 pagesCranial NerveCosplay AccountNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Visual Pathway, Field Defects AND Its Lesions.: By-Dr. Ruchi PherwaniDocument43 pagesAnatomy of Visual Pathway, Field Defects AND Its Lesions.: By-Dr. Ruchi Pherwanisafasayed100% (1)
- The Functional Anatomy of The Cranial NervesDocument29 pagesThe Functional Anatomy of The Cranial NervesRăzvan Moțoc100% (1)
- 200F-21 The Brain SVDocument20 pages200F-21 The Brain SVRachel SawhNo ratings yet
- Lecture IIIDocument36 pagesLecture IIIbrittany AcheampongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Anatomical Organization of Cranial Nerves 2009 Manual Therapy For The Cranial NervesDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Anatomical Organization of Cranial Nerves 2009 Manual Therapy For The Cranial NervesDaniela Bustos PéndolaNo ratings yet
- CN FanyDocument24 pagesCN FanymiaNo ratings yet
- El Mejor de Vascular PDFDocument66 pagesEl Mejor de Vascular PDFRoberto RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomi Nervus KranialDocument40 pagesNeuroanatomi Nervus KranialHensy Virginia SolonNo ratings yet
- Visual and Lacrimal AppratusDocument45 pagesVisual and Lacrimal AppratusAzman Bin KadirNo ratings yet
- Quiz Anatomy Part 3 of 3Document56 pagesQuiz Anatomy Part 3 of 3MedShare75% (4)
- III AtfDocument5 pagesIII AtfGavin MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Oculofacial Plastic and Orbital Surgery: Basic and Clinical Science CourseDocument7 pagesOculofacial Plastic and Orbital Surgery: Basic and Clinical Science Coursenuryusri99No ratings yet
- Lecture 6: Cranial Nerves: Objective: To Understand The Organization of Cranial Nerves With RespectDocument30 pagesLecture 6: Cranial Nerves: Objective: To Understand The Organization of Cranial Nerves With Respectcilla235No ratings yet
- Orbital Apex Syndrome. A ReviewDocument10 pagesOrbital Apex Syndrome. A ReviewAndrés Faúndez TeránNo ratings yet
- CNS MCQSDocument24 pagesCNS MCQSSTEVEN OKURUT100% (2)
- Cranial Nerves Atlas Part 2Document26 pagesCranial Nerves Atlas Part 2Катерина ЛяшинаNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves: Romulo U. EsagundeDocument72 pagesCranial Nerves: Romulo U. EsagundeLoisen Nathan DanielNo ratings yet
- 2020OPTICNERVEPRESENTATIONDocument10 pages2020OPTICNERVEPRESENTATIONTendaiNo ratings yet
- MVST IB Head and Neck Anatomy: Ntroduction To The Ranial ErvesDocument4 pagesMVST IB Head and Neck Anatomy: Ntroduction To The Ranial ErvesSaffronMaeNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Notes For DentistsDocument33 pagesOphthalmology Notes For DentistsDr. Mahmoud Tawfik ElSoradyNo ratings yet
- Foramen Structures Conducted Cranial Fossa Cranial Bone Cribriform ForaminaDocument8 pagesForamen Structures Conducted Cranial Fossa Cranial Bone Cribriform ForaminaAchiever FayeNo ratings yet
- 10 - Urological DiordersDocument47 pages10 - Urological Diordersgozali189 biringNo ratings yet
- Tube ThoracostomyDocument17 pagesTube ThoracostomyheiyuNo ratings yet
- Intracranial PressureDocument7 pagesIntracranial PressureGuozhao JiNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker PamphletDocument2 pagesPacemaker Pamphletapi-355079078No ratings yet
- OSCE IV CanulationDocument2 pagesOSCE IV CanulationAmos TalsandekarNo ratings yet
- Undescended Testes (Orchidopexy)Document9 pagesUndescended Testes (Orchidopexy)nuranysha havizNo ratings yet
- Exam C SolDocument10 pagesExam C SolNuhad Bou MoslehNo ratings yet
- 2016 Master Courses Web-2Document16 pages2016 Master Courses Web-2Ioana Camelia TodaNo ratings yet
- Cannistra 2007Document4 pagesCannistra 2007amdreyNo ratings yet
- Limiting Structures: 2 Year/lec3Document7 pagesLimiting Structures: 2 Year/lec3Dr.Haider Saleem AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Dental Auxiliary: Presented By-Sneha Patil (Final Year BDS Student)Document36 pagesDental Auxiliary: Presented By-Sneha Patil (Final Year BDS Student)Mumin RashidNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 4th Edition by Ellis Chapters 12-15-18 Not IncludedDocument11 pagesTest Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 4th Edition by Ellis Chapters 12-15-18 Not Includedcanebrutalfniy66No ratings yet
- Medicine - EKG - Lab Coat PocketsDocument1 pageMedicine - EKG - Lab Coat Pocketsskeebs23No ratings yet
- TEE For ImpellaDocument6 pagesTEE For ImpellaPriya Nair MenonNo ratings yet
- Biomaterials and Implants in Cardiac and Vascular SurgeryDocument9 pagesBiomaterials and Implants in Cardiac and Vascular Surgerytornike kakhetelidzeNo ratings yet
- Hair Transplantation: With Follicular Unit MicrograftsDocument2 pagesHair Transplantation: With Follicular Unit MicrograftsRavvaNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Tokyoguidelines 2018 in The Management of Acute Cholangitis and Acute CholecystitisDocument13 pagesEffectiveness of Tokyoguidelines 2018 in The Management of Acute Cholangitis and Acute CholecystitisIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Ane Publish Ahead of Print 10.1213.ane.0000000000005043Document13 pagesAne Publish Ahead of Print 10.1213.ane.0000000000005043khalisahnNo ratings yet
- Jaundice and AscitesDocument15 pagesJaundice and AscitesJosiah Noella BrizNo ratings yet
- 1 Gastric and Duodenal Peptic Ulcer Disease 1Document30 pages1 Gastric and Duodenal Peptic Ulcer Disease 1rayNo ratings yet
- Articulators in Orthodontics: Theodore D. FreelandDocument12 pagesArticulators in Orthodontics: Theodore D. FreelandJegan KumarNo ratings yet
- Toshiba Medical Ultrasound TransducersDocument6 pagesToshiba Medical Ultrasound Transducersdmseoane100% (1)
- Dexmedetomidine Administration During Brain Tumour Resection andDocument2 pagesDexmedetomidine Administration During Brain Tumour Resection andABRAHAM MANUEL MEDINA LEYTONNo ratings yet
- Fetal and Neonatal Physiology PDFDocument33 pagesFetal and Neonatal Physiology PDFObsaNo ratings yet
- Daftar - Harga - Medika 2021-1Document2 pagesDaftar - Harga - Medika 2021-1riska setyawatiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Kidney Transplantation - Background, History of The Procedure, EpidemiologyDocument14 pagesPediatric Kidney Transplantation - Background, History of The Procedure, EpidemiologyNovi BaliNo ratings yet
- Assessment Question 1. All Are True About Vertebrae Levels EXCEPTDocument13 pagesAssessment Question 1. All Are True About Vertebrae Levels EXCEPTDevsya DodiaNo ratings yet
- Post Partum ComplicationsDocument40 pagesPost Partum ComplicationsMahmoud Abu Al AmrainNo ratings yet