Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Economic Issues
Economic Issues
Uploaded by
examhack00Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Economic Issues
Economic Issues
Uploaded by
examhack00Copyright:
Available Formats
Stages of business cycle
1. Growth- When gdp is rising, low unemployement and high living standards.
2. Boom- Caused due to too much spending. Prices rise and shortage of skilled workers. High
business costs.
3. Recession- Too little spending. Gdp starts to fall. Fall of demand. Unemployment rises.
4. Slump- Long drawn out recession. High unemployment and prices fall. Many businesses fail
to survive.
A boom often leads to recession or slump.
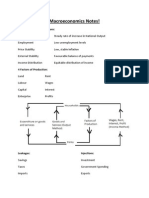
Impact on business of changes in employment, inflation and GDP
1. Changes in employment level- Will affect the ability of companies to recruit employees.
Los of income causes decrease in demand except inferior good.
2. Rising inflation – This may result in increase of business cost. Fall in demand. Ppl have
less money left.
3. Increasing GDP – Means that the economy is growing .Increase in sales.
Inflation – Increase in average price level of goods and services.
Unemployement- When people who are willing to work are not able to find a job.
GDP – Total value of output of good and services in a country.
Economic growth – When a countries gdp increases
Balance of payement – Records difference between a countries export and import.
Government economic objectives-
1. Low inflation – They want this as (problems of rapid inflation)
- Inflation causes real income to fall
- Real income – Is the value in terms of what can be bought of an income
- Prices of good of foreign products is cheaper, causes unemployement in
country.
- Business wont expand
2. Low unemployment – Problems with unemployement
- Unemployed ppl don’t produce good
- Government pays unemployement fees
3. Economic growth- It is said to grow when gdp of a country increases
Problems with no eco growth
- Few workers are needed
- Standard of living decreases
- Business wont expand as ppl have less income
4. Balance of payment-Difference between a countries export and import
- Price of a country’s currency against other currencies – exchange rate
Value of import>value of exports – trade depriations
Value of export> Trade of import – Trade value appreciations
Government economic policies
Fiscal policy
Income tax it's the tax on peoples income
increase in income tax = lower disposable income
reduces sales
profit tax is a tax on profit of business
businesses won't expand
people wont create business as government takes a lot of their income
indirect taxes
GST, VAT
Price of goods increase
Wages of employees decrease
Import tariffs and quotas
Monetary policy
Is the change in interest rate by the government or central bank
Supply side policy
Policies to make economy more efficient. Tries to increase competiveness of industry
Privatisation- aim to use profit as incentive
Improve training and education-
Increase competiveness reducing government control and monopolies
You might also like
- Solow EconomicHistoryEconomics 1985Document5 pagesSolow EconomicHistoryEconomics 1985SYED NAZMUS SAKIBNo ratings yet
- DuraPro Group1Document14 pagesDuraPro Group1Swati Sucharita DasNo ratings yet
- Economic Issues Topic 27 Notes o Level.Document8 pagesEconomic Issues Topic 27 Notes o Level.alisafatimaaNo ratings yet
- Economic Issues IGCSE Business NotesDocument5 pagesEconomic Issues IGCSE Business NotesHiNo ratings yet
- 6.1 External Influences On Business ActivityDocument4 pages6.1 External Influences On Business ActivitySana GargNo ratings yet
- Nguyễn Thị Huyền-24A7511485Document3 pagesNguyễn Thị Huyền-24A7511485Thị Huyền NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Economic Issues IGCSE (Business Studies)Document4 pagesEconomic Issues IGCSE (Business Studies)an4No ratings yet
- Topic 6 - External Influences On BusinessDocument11 pagesTopic 6 - External Influences On BusinesstandmacgmNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Economic IssuesDocument4 pages6.1 Economic IssuesannabellNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-05-21 at 11.51.36 PMDocument64 pagesScreenshot 2023-05-21 at 11.51.36 PMFahad FayyazNo ratings yet
- 6.1 - Government Economic Policies and ObjectivesDocument4 pages6.1 - Government Economic Policies and ObjectivesTYDK MediaNo ratings yet
- Business - External Influences On Business ActivityDocument9 pagesBusiness - External Influences On Business ActivityBeejayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 - Economic Issues Update 2Document20 pagesChapter 27 - Economic Issues Update 2Amour PartekaNo ratings yet
- Economic Crises NoteDocument9 pagesEconomic Crises NoteAdetunbi TolulopeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 - Economic IssuesDocument14 pagesChapter 27 - Economic IssuesKhoa DaoNo ratings yet
- Bs Notes 6Document19 pagesBs Notes 6Engineers UniqueNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Business IssueDocument4 pages6.1 Business IssueFaiz AijazNo ratings yet
- Inflation and Deflation (Econs) NotesDocument6 pagesInflation and Deflation (Econs) Notesstudent 1No ratings yet
- Chap 6 External Influences On Business ActivityDocument18 pagesChap 6 External Influences On Business ActivityDennisNo ratings yet
- Economic IssuesDocument9 pagesEconomic Issuessamikshakumar2009No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Government and Economic Influences On BusinessDocument8 pagesChapter 4: Government and Economic Influences On Businessseanc939No ratings yet
- 5.1-Government Economic PolicyDocument4 pages5.1-Government Economic PolicyMahnoor ArshadNo ratings yet
- .1 - Government Economic Policy: The Macroeconomic AimsDocument3 pages.1 - Government Economic Policy: The Macroeconomic AimsMarisa VetterNo ratings yet
- Economic GrowthDocument4 pagesEconomic GrowthSyed Abdullah NabilNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Economics ProperDocument17 pagesUnit 2 Economics ProperkirstinroseNo ratings yet
- Govt N Economic Influences On BusinessesDocument8 pagesGovt N Economic Influences On BusinessesRuvarasheNo ratings yet
- Ext Influences On Bus ActDocument11 pagesExt Influences On Bus Actattackdfg2002No ratings yet
- Economics Notes From IGCSE AIDDocument50 pagesEconomics Notes From IGCSE AIDAejaz MohamedNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Chapter 24 Government Economic Objectives: and PoliciesDocument59 pages6.1 Chapter 24 Government Economic Objectives: and PoliciesHaritika ChhatwalNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 (CH 27,28,29)Document8 pagesUnit 6 (CH 27,28,29)Wassim AlwanNo ratings yet
- Apuntes Macroeconomía PDFDocument52 pagesApuntes Macroeconomía PDFIsidro Suarez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Economic IssuesDocument5 pagesEconomic Issuesedwin lisutsaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - External Economic Influences On Business ActivityDocument10 pagesChapter 7 - External Economic Influences On Business ActivityJamie HillNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Inflation & UnemploymentDocument30 pagesTopic 3 - Inflation & UnemploymentKhairul AfiqNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Notes!: 5 Macroeconomic ObjectivesDocument7 pagesMacroeconomics Notes!: 5 Macroeconomic ObjectivesHarry JobanputraNo ratings yet
- GR 10 Govt. (Macro) Eco PoliciesDocument4 pagesGR 10 Govt. (Macro) Eco PoliciesAditi JaysonNo ratings yet
- Section 2 - Macroeconomics Complete PackDocument18 pagesSection 2 - Macroeconomics Complete PackBinh Minh DuongNo ratings yet
- 6 - External Influnces On BusinessDocument8 pages6 - External Influnces On BusinessHussainnaailmohmed 11No ratings yet
- CHP 26Document7 pagesCHP 26evelynNo ratings yet
- Economic Issues PDFDocument10 pagesEconomic Issues PDFFathik FouzanNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Aims of GovernmentDocument8 pagesMacroeconomics Aims of Governmentwayandragon247No ratings yet
- Inflation Note Form 5Document4 pagesInflation Note Form 5Sandya PriyadarshaniNo ratings yet
- A: Economic and Business Cycles GDP Expenditure ApproachDocument57 pagesA: Economic and Business Cycles GDP Expenditure ApproachPavan LuckyNo ratings yet
- Econ2 NotesDocument8 pagesEcon2 NoteshuuihsduidhuiNo ratings yet
- A Trade Deficit Is About An Imbalance Between A Country's Savings andDocument3 pagesA Trade Deficit Is About An Imbalance Between A Country's Savings andK62 Kiểm Toán CLCNo ratings yet
- Government As ProducerDocument56 pagesGovernment As ProducerrowobelangNo ratings yet
- Importance of Economic EnvironmentDocument3 pagesImportance of Economic Environmentகப்பல்ஹசன்நபிNo ratings yet
- Government Macroeconomic AimsDocument14 pagesGovernment Macroeconomic Aimsv8qrf2w9zdNo ratings yet
- G 12 Economcs 15Document12 pagesG 12 Economcs 15Abdallah HassanNo ratings yet
- Business NotesDocument89 pagesBusiness NoteskutlwanofredrickNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Circular Flow Grade 10Document15 pagesTopic 3 Circular Flow Grade 10DJAY TIDO-KNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics 1Document21 pagesMacroeconomics 1IneshkaNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Business Studies 0450 Theory v5 RemovedDocument5 pagesCaie Igcse Business Studies 0450 Theory v5 RemovedSwagata DebnathNo ratings yet
- Business NotesDocument3 pagesBusiness Notes2011050No ratings yet
- Chapter 2A - PESTDocument3 pagesChapter 2A - PESTvickyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document7 pagesAssignment 2Philly Mc DonnellNo ratings yet
- STEEPLE Analysis - External EnvironmentDocument16 pagesSTEEPLE Analysis - External Environment2011050No ratings yet
- Year 10 Economics + Legal Topic NotesDocument25 pagesYear 10 Economics + Legal Topic NotesAndrea CATANZARITINo ratings yet
- MECO 121 Chapter 6 NotesDocument5 pagesMECO 121 Chapter 6 NotesHaider EjazNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document14 pagesModule 6Tin ZamudioNo ratings yet
- Government Aims and PoliciesDocument7 pagesGovernment Aims and PoliciesRoseNo ratings yet
- Xi-Poe English Medium Notes - Sigma FT HomelanderDocument91 pagesXi-Poe English Medium Notes - Sigma FT Homelanderkk1573738No ratings yet
- Assignment BBA 1 POM by Shubhankar Mridha Student Id - 211001101252 1 Sem. 1. What Is Government Expenditure Multiplier ? AnsDocument6 pagesAssignment BBA 1 POM by Shubhankar Mridha Student Id - 211001101252 1 Sem. 1. What Is Government Expenditure Multiplier ? AnsBAPPA PRODUCTIONNo ratings yet
- Marketing Notes - Chapter 1Document30 pagesMarketing Notes - Chapter 1Mohadissa Hussain ZadaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 - Capital Structure - Basic ConceptsDocument15 pagesLecture 16 - Capital Structure - Basic ConceptsNhân TrịnhNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Stochastic ProcessDocument2 pagesLecture On Stochastic ProcessMauro MLRNo ratings yet
- Business 9 Week 1 2nd Term Chapter 1 Part 3Document17 pagesBusiness 9 Week 1 2nd Term Chapter 1 Part 3cecilia capiliNo ratings yet
- Assigment 2 Investment Analysis PBS 21101107 AzdzharulnizzamDocument6 pagesAssigment 2 Investment Analysis PBS 21101107 AzdzharulnizzamAzdzharulnizzam AlwiNo ratings yet
- 078-1Document34 pages078-1jesssamuelNo ratings yet
- Internal Rate of Return IRR Calculation - Example - Decision RuleDocument2 pagesInternal Rate of Return IRR Calculation - Example - Decision Ruleakram1978No ratings yet
- FMI7e ch03Document49 pagesFMI7e ch03Saleem MirraniNo ratings yet
- Fin 622 Mcqs and RefDocument69 pagesFin 622 Mcqs and RefEngr Imtiaz Hussain GilaniNo ratings yet
- MIS at Tata MotorsDocument1 pageMIS at Tata MotorsMahadev SubramaniNo ratings yet
- Security Analysis and Portfolio Management Blown Up SyllabusDocument5 pagesSecurity Analysis and Portfolio Management Blown Up SyllabusRupa H GowdaNo ratings yet
- Supply ResearchDocument11 pagesSupply ResearchSara AbidNo ratings yet
- Angus Maddison - The West and The Rest in The World Economy - 1000-2030Document22 pagesAngus Maddison - The West and The Rest in The World Economy - 1000-2030Odair Michelli JuniorNo ratings yet
- Priyanka Divecha Black BookDocument42 pagesPriyanka Divecha Black Bookyogesh DivechaNo ratings yet
- Market Structures and Price-Output DeterminationDocument40 pagesMarket Structures and Price-Output DeterminationHartin StylesNo ratings yet
- Vertical and Horizontal IntegrationDocument12 pagesVertical and Horizontal IntegrationSunil SinghNo ratings yet
- Launching A New ProductDocument22 pagesLaunching A New ProductNayomi Ekanayake0% (1)
- Stock ValuationDocument18 pagesStock ValuationDianne MadridNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 (29) Practice Test: The Monetary System: Multiple ChoiceDocument11 pagesChapter 16 (29) Practice Test: The Monetary System: Multiple ChoiceRaymund GatocNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Foreign Direct Investment On Human Capital Enhancement in Developing CountriesDocument12 pagesThe Impact of Foreign Direct Investment On Human Capital Enhancement in Developing CountriesDanh Nhật HoàNo ratings yet
- Economics Dissertation StructureDocument7 pagesEconomics Dissertation StructurePayToDoPaperCanada100% (1)
- Deficit Financing Concept MeaningDocument11 pagesDeficit Financing Concept Meaningashishjoshi850% (1)
- 11 May 2020 EconomicsDocument32 pages11 May 2020 EconomicsErkin GasimzadeNo ratings yet
- Ias 2Document16 pagesIas 2Kazi93_thefatNo ratings yet
- 103-Managerial Economics: Books RecommendedDocument1 page103-Managerial Economics: Books Recommendedpmsoni007No ratings yet