Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amacr 2
Amacr 2
Uploaded by
nyandasteven2050Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Scientific Glass ExcelDocument13 pagesScientific Glass ExcelSakshi ShardaNo ratings yet
- AP Macro Cheat SheetDocument23 pagesAP Macro Cheat SheetGabriel Jimenez100% (7)
- AP Macro Cheat Sheet Good To Have For The ExamDocument24 pagesAP Macro Cheat Sheet Good To Have For The ExamLilith PersephoneNo ratings yet
- AP Macroeconomics - Models & Graphs Study GuideDocument22 pagesAP Macroeconomics - Models & Graphs Study GuideLynn Hollenbeck Breindel100% (2)
- Yarn Faults: Types Causes RemediesDocument20 pagesYarn Faults: Types Causes Remediesஹரி கிருஷ்ணன் வாசு71% (7)
- Questions Macroeconomics (With Answers) : 2 Money and InflationDocument3 pagesQuestions Macroeconomics (With Answers) : 2 Money and InflationMuhazzam MaazNo ratings yet
- Answer Macroeconomics: 2 Money and InflationDocument3 pagesAnswer Macroeconomics: 2 Money and InflationsamNo ratings yet
- Part IIIDocument47 pagesPart IIICoutinhoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Monetary and Fiscal PolicyDocument25 pagesLecture 8 Monetary and Fiscal PolicyThao Nguyen TranNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Monetary On Aggregate DemandDocument14 pagesThe Influence of Monetary On Aggregate DemandNgọc ÁnhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Review QuestionsDocument21 pagesChapter 12 Review QuestionsBrahim BelkadiNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy On Aggregate DemandDocument41 pagesThe Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy On Aggregate DemandPutri Aprilia ManembuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 InflationDocument25 pagesChapter 9 InflationĐỉnh Kout NamNo ratings yet
- ETP Econ Lecture Note 34 Winter 2012Document31 pagesETP Econ Lecture Note 34 Winter 2012Shubhika PantNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Economic Growth: DefinitionsDocument4 pages2.5 Economic Growth: DefinitionsAryan KalyanamNo ratings yet
- Copy of AP MACRO - GRAPHS GUIDEDocument2 pagesCopy of AP MACRO - GRAPHS GUIDEM KNo ratings yet
- Liquidity Preference TheoryDocument34 pagesLiquidity Preference Theorygoldenguy90100% (2)
- 09 - Fiscal and Monetary PoliciesDocument59 pages09 - Fiscal and Monetary PoliciesMinh PhươngNo ratings yet
- Putting The Market Togethere: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDocument21 pagesPutting The Market Togethere: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyKatherine Asis NatinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Money Growth and InflationDocument41 pagesLecture 6 Money Growth and InflationLê Thiên Giang 2KT-19No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics I: Aggregate Demand II: Applying The IS-LM ModelDocument27 pagesMacroeconomics I: Aggregate Demand II: Applying The IS-LM Model우상백No ratings yet
- Macro 2 Chap 3Document46 pagesMacro 2 Chap 3ngant21401cNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy On Aggregate DemandDocument25 pagesThe Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy On Aggregate DemandWening RestiyaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document49 pagesChapter 3Trang ĐoànNo ratings yet
- 9 - Monetary and Fiscal PolicyDocument40 pages9 - Monetary and Fiscal PolicyChi NguyenNo ratings yet
- InflationDocument25 pagesInflationAarti YadavNo ratings yet
- Monetary PolicyDocument11 pagesMonetary PolicydrezatullahhaqmalNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics: Assignment 04Document11 pagesMacro Economics: Assignment 04Areesha NafeesNo ratings yet
- Fiscal and Monetary PolicyDocument34 pagesFiscal and Monetary Policyvenkataswamynath channa100% (4)
- Lecture 8 Relationship Between Money and Goods MarketDocument27 pagesLecture 8 Relationship Between Money and Goods MarketAvinash PrashadNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Economics Chapter 6Document15 pagesFundamentals of Economics Chapter 6faraz aijazNo ratings yet
- Macro Session On AD-AS ModelDocument53 pagesMacro Session On AD-AS Modelsaty16No ratings yet
- 5 - General Equilibrium and AD-As ModelDocument55 pages5 - General Equilibrium and AD-As ModelMendese KamalaNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy On Aggregate DemandDocument38 pagesThe Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy On Aggregate DemandLuthfia ZulfaNo ratings yet
- 05) Money MarketDocument56 pages05) Money MarketNaina GoyalNo ratings yet
- Session 12 Fiscal PolicyDocument36 pagesSession 12 Fiscal PolicySourabh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Short-Run Economic Fluctuations: Economic Activity Fluctuates From Year To YearDocument49 pagesShort-Run Economic Fluctuations: Economic Activity Fluctuates From Year To YearDinda Cici AuliaNo ratings yet
- Mock 2 Paper 2 AnswerDocument5 pagesMock 2 Paper 2 AnswerL MyNo ratings yet
- Macro Lecture ch16 Fiscal and Monetary PolicyDocument33 pagesMacro Lecture ch16 Fiscal and Monetary PolicyKatherine Sauer100% (1)
- 2.2.1 The Characteristics of ADDocument25 pages2.2.1 The Characteristics of AD18kchohanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Exchange Rate Determination PDFDocument65 pagesChapter 7. Exchange Rate Determination PDFKim NgânNo ratings yet
- Money Growth and InflationDocument30 pagesMoney Growth and InflationopshoraNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Chapter 34cDocument8 pagesMacroeconomics Chapter 34cThiha Kaung SettNo ratings yet
- 6 - Aggregate Demand and SupplyDocument62 pages6 - Aggregate Demand and SupplyMạnh Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- Interest Rates PresentationDocument29 pagesInterest Rates PresentationFitri RajabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Money Growth and InflationDocument35 pagesLecture 7 - Money Growth and InflationY Nguyen Ngoc Nhu QTKD-1TC-18No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-03-05 at 8.09.02 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2024-03-05 at 8.09.02 PMemmanuelkakayayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 (Principle of Economic)Document42 pagesChapter 14 (Principle of Economic)izatul akmal maisarahNo ratings yet
- Interest RatesDocument62 pagesInterest RatesclementNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand Aggregate SupplyDocument26 pagesAggregate Demand Aggregate Supplycompudoc11No ratings yet
- PDF For SEBI Economics ISLMDocument41 pagesPDF For SEBI Economics ISLMSaraswathi Putra KamalNo ratings yet
- Money Growth and Inflation: Week 7Document22 pagesMoney Growth and Inflation: Week 7Dewi Ushriyah UlyaNo ratings yet
- Low .BDocument13 pagesLow .Bsteven msusaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Price IndexDocument8 pagesConsumer Price IndexNguyễn Long VũNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy Lecture - PGP 26Document23 pagesFiscal Policy Lecture - PGP 26Parth BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Unit2 Study GuideDocument3 pagesUnit2 Study Guide高瑞韩No ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document29 pagesChapter 8Tafirenyika SundeNo ratings yet
- Fiscal PolicyDocument25 pagesFiscal PolicyAlexNo ratings yet
- ICERDocument13 pagesICEROussama ChaoukiNo ratings yet
- Chap 34Document76 pagesChap 34Jia Wei MiaoNo ratings yet
- Notes - Introduction To Hearing ImpairmentDocument66 pagesNotes - Introduction To Hearing Impairmentnyandasteven2050No ratings yet
- Non Exchange RevenueDocument44 pagesNon Exchange Revenuenyandasteven2050No ratings yet
- MacroeconomicsDocument308 pagesMacroeconomicsnyandasteven2050No ratings yet
- Public Sector Finances SourcesDocument21 pagesPublic Sector Finances Sourcesnyandasteven2050No ratings yet
- LAW of Contract 1 2023Document9 pagesLAW of Contract 1 2023nyandasteven2050No ratings yet
- Custom Hand Grips For RevolverDocument13 pagesCustom Hand Grips For RevolverfrankieitalianNo ratings yet
- This Is An Auto-Generated Purchase Order Based On Online Tender DecisionDocument2 pagesThis Is An Auto-Generated Purchase Order Based On Online Tender DecisionTUff LabNo ratings yet
- 18 International Capital BudgetingDocument49 pages18 International Capital BudgetingBrijesh Chauhan100% (1)
- Gini Coefficient: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument3 pagesGini Coefficient: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchTeodoro Miguel Carlos IsraelNo ratings yet
- Infant and Child Mortality: Mothers and Infants, As Well As The Effectiveness ofDocument3 pagesInfant and Child Mortality: Mothers and Infants, As Well As The Effectiveness ofhendraNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Service Sector in The Indian Economy: Dr.D.AmuthaDocument10 pagesThe Role of The Service Sector in The Indian Economy: Dr.D.AmuthaHitesh ManglaniNo ratings yet
- Pol 223 Main TextDocument147 pagesPol 223 Main TextDaramola Olanipekun EzekielNo ratings yet
- SAP Revenue Accounting and Reporting in SAP S 4HANA 2020 1637339074Document48 pagesSAP Revenue Accounting and Reporting in SAP S 4HANA 2020 1637339074Fatima Zohra BoughlalNo ratings yet
- Principle Acct. Ii - Chapter FourDocument22 pagesPrinciple Acct. Ii - Chapter Fourbereket nigussieNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Fundamentals of Economics 6th Edition William BoyesDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Fundamentals of Economics 6th Edition William Boyesforeliftperiople.ttyox100% (47)
- Some Et Any ExercicesDocument1 pageSome Et Any ExercicesJean-Loïc HANNAISNo ratings yet
- Duplicated RecordsDocument12 pagesDuplicated RecordsOğuzhan DaşkayaNo ratings yet
- Full Economics 10Th Edition Boyes Test Bank Online PDF All ChapterDocument64 pagesFull Economics 10Th Edition Boyes Test Bank Online PDF All Chaptermauraanaviolat284100% (6)
- Struktur Organisasi BTN KCS Makassar TMT Januari 2022Document1 pageStruktur Organisasi BTN KCS Makassar TMT Januari 2022sriwahyuningsih7656No ratings yet
- AP Macro WorkbookDocument346 pagesAP Macro WorkbookLynn Hollenbeck Breindel100% (5)
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA FATA TerbaruDocument2 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA FATA TerbaruFata JualanNo ratings yet
- MayaSavings SoA 2023AUGDocument1 pageMayaSavings SoA 2023AUGChrissandra BolarNo ratings yet
- Invoice 20211130121017 CBN30105841121Document1 pageInvoice 20211130121017 CBN30105841121Fadhil RachmanNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics 12th Edition Michael Parkin Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesMacroeconomics 12th Edition Michael Parkin Solutions ManualDanielCarterrdcz100% (56)
- PO 062 PT. Riau Indo PasifikDocument4 pagesPO 062 PT. Riau Indo PasifikhkbpsimpangpadangduriNo ratings yet
- Demand ForecastingDocument26 pagesDemand Forecastingnuraini9332No ratings yet
- Las Melc 3 QTR 3 English 8 Odbulaong 1Document5 pagesLas Melc 3 QTR 3 English 8 Odbulaong 1Celso Abel Jr. PontillasNo ratings yet
- ECO558Document26 pagesECO558Nur Adriana binti Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- AppliedEconomics Q3 M3 Market-StructureDocument25 pagesAppliedEconomics Q3 M3 Market-Structure•LAZY SHEEP•No ratings yet
- Module For Managerial Accounting-Job Order CostingDocument17 pagesModule For Managerial Accounting-Job Order CostingMary De JesusNo ratings yet
- 'KGHN Fot Flag Iffkd Øhmk Ladqy: Shaheed Vijay Singh Pathik Sports ComplexDocument26 pages'KGHN Fot Flag Iffkd Øhmk Ladqy: Shaheed Vijay Singh Pathik Sports ComplexSurendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Managerial Economics Applications Strategies and Tactics 13th EditionDocument6 pagesTest Bank For Managerial Economics Applications Strategies and Tactics 13th EditionJamesJohnsonqxcej100% (28)
- SS 80-100 1072Document1 pageSS 80-100 1072Rodrigo SantosNo ratings yet
Amacr 2
Amacr 2
Uploaded by
nyandasteven2050Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amacr 2
Amacr 2
Uploaded by
nyandasteven2050Copyright:
Available Formats
Answer Macroeconomics
2 Money and inflation
01 Money 1
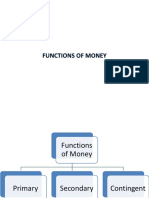
Functions of money:
Medium of exchange
Unit of account
Store of value
02 Money 2
/ Motives for holding money:
Transactions motive / dependent on income
Precautionary motive / dependent on income
Speculative motive / dependent on interest rates
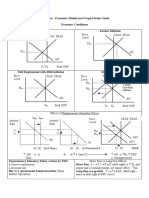
03 Money market
Interest rates (r)
Supply 2 Supply 1
r2
r1
Demand
Money
Interest rates rise.
AMACR2.DOC Page 1 (of 3) 2 Money and inflation 09/06/2016
04 Money market, GDP and inflation
Interest rates (r) Price level (PL) Aggregate supply
Supply 1 Supply 2
r1 PL 2
PL 1 Aggregate
demand 2
Demand
Aggregate demand 1
Money GDP
1 2
Money supply rises Interest rates fall Aggregate demand (investment) rises
GDP and the price level rise
05 Money creation 1
1 1 1
Money = 5000 * 1 - (1 - r) = 5000 * r = 5000 * 0.2 = 25000
06 Money creation 2
Cash ratio rises: Money multiplier decreases.
Reserve ratio falls: Money multiplier increases.
07 Inflation 1
Shoeleather costs (= costs of holding less cash)
Menu costs (= costs of changing prices)
In the case of unexpected inflation:
Arbitrary change in the redistribution of income and wealth
People with nominal assets (liabilities) lose (gain).
AMACR2.DOC Page 2 (of 3) 2 Money and inflation 09/06/2016
08 Inflation 2
Price level (PL)
Aggregate supply 2
Aggregate
supply 1
PL 2
PL 1
GDP
The price level rises, GDP falls (Stagflation).
09 Price level
108.2 - 105.0
Increase in prices = 105.0 * 100 = 3.05 %
10 Quantity theory of money
M*V=Q*P
If velocity of money and real output (full employment) are constant, a rise in the money
supply will cause an increase in the price level.
Back to questions. Click here!
AMACR2.DOC Page 3 (of 3) 2 Money and inflation 09/06/2016
You might also like
- Scientific Glass ExcelDocument13 pagesScientific Glass ExcelSakshi ShardaNo ratings yet
- AP Macro Cheat SheetDocument23 pagesAP Macro Cheat SheetGabriel Jimenez100% (7)
- AP Macro Cheat Sheet Good To Have For The ExamDocument24 pagesAP Macro Cheat Sheet Good To Have For The ExamLilith PersephoneNo ratings yet
- AP Macroeconomics - Models & Graphs Study GuideDocument22 pagesAP Macroeconomics - Models & Graphs Study GuideLynn Hollenbeck Breindel100% (2)
- Yarn Faults: Types Causes RemediesDocument20 pagesYarn Faults: Types Causes Remediesஹரி கிருஷ்ணன் வாசு71% (7)
- Questions Macroeconomics (With Answers) : 2 Money and InflationDocument3 pagesQuestions Macroeconomics (With Answers) : 2 Money and InflationMuhazzam MaazNo ratings yet
- Answer Macroeconomics: 2 Money and InflationDocument3 pagesAnswer Macroeconomics: 2 Money and InflationsamNo ratings yet
- Part IIIDocument47 pagesPart IIICoutinhoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Monetary and Fiscal PolicyDocument25 pagesLecture 8 Monetary and Fiscal PolicyThao Nguyen TranNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Monetary On Aggregate DemandDocument14 pagesThe Influence of Monetary On Aggregate DemandNgọc ÁnhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Review QuestionsDocument21 pagesChapter 12 Review QuestionsBrahim BelkadiNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy On Aggregate DemandDocument41 pagesThe Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy On Aggregate DemandPutri Aprilia ManembuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 InflationDocument25 pagesChapter 9 InflationĐỉnh Kout NamNo ratings yet
- ETP Econ Lecture Note 34 Winter 2012Document31 pagesETP Econ Lecture Note 34 Winter 2012Shubhika PantNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Economic Growth: DefinitionsDocument4 pages2.5 Economic Growth: DefinitionsAryan KalyanamNo ratings yet
- Copy of AP MACRO - GRAPHS GUIDEDocument2 pagesCopy of AP MACRO - GRAPHS GUIDEM KNo ratings yet
- Liquidity Preference TheoryDocument34 pagesLiquidity Preference Theorygoldenguy90100% (2)
- 09 - Fiscal and Monetary PoliciesDocument59 pages09 - Fiscal and Monetary PoliciesMinh PhươngNo ratings yet
- Putting The Market Togethere: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDocument21 pagesPutting The Market Togethere: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyKatherine Asis NatinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Money Growth and InflationDocument41 pagesLecture 6 Money Growth and InflationLê Thiên Giang 2KT-19No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics I: Aggregate Demand II: Applying The IS-LM ModelDocument27 pagesMacroeconomics I: Aggregate Demand II: Applying The IS-LM Model우상백No ratings yet
- Macro 2 Chap 3Document46 pagesMacro 2 Chap 3ngant21401cNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy On Aggregate DemandDocument25 pagesThe Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy On Aggregate DemandWening RestiyaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document49 pagesChapter 3Trang ĐoànNo ratings yet
- 9 - Monetary and Fiscal PolicyDocument40 pages9 - Monetary and Fiscal PolicyChi NguyenNo ratings yet
- InflationDocument25 pagesInflationAarti YadavNo ratings yet
- Monetary PolicyDocument11 pagesMonetary PolicydrezatullahhaqmalNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics: Assignment 04Document11 pagesMacro Economics: Assignment 04Areesha NafeesNo ratings yet
- Fiscal and Monetary PolicyDocument34 pagesFiscal and Monetary Policyvenkataswamynath channa100% (4)
- Lecture 8 Relationship Between Money and Goods MarketDocument27 pagesLecture 8 Relationship Between Money and Goods MarketAvinash PrashadNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Economics Chapter 6Document15 pagesFundamentals of Economics Chapter 6faraz aijazNo ratings yet
- Macro Session On AD-AS ModelDocument53 pagesMacro Session On AD-AS Modelsaty16No ratings yet
- 5 - General Equilibrium and AD-As ModelDocument55 pages5 - General Equilibrium and AD-As ModelMendese KamalaNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy On Aggregate DemandDocument38 pagesThe Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy On Aggregate DemandLuthfia ZulfaNo ratings yet
- 05) Money MarketDocument56 pages05) Money MarketNaina GoyalNo ratings yet
- Session 12 Fiscal PolicyDocument36 pagesSession 12 Fiscal PolicySourabh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Short-Run Economic Fluctuations: Economic Activity Fluctuates From Year To YearDocument49 pagesShort-Run Economic Fluctuations: Economic Activity Fluctuates From Year To YearDinda Cici AuliaNo ratings yet
- Mock 2 Paper 2 AnswerDocument5 pagesMock 2 Paper 2 AnswerL MyNo ratings yet
- Macro Lecture ch16 Fiscal and Monetary PolicyDocument33 pagesMacro Lecture ch16 Fiscal and Monetary PolicyKatherine Sauer100% (1)
- 2.2.1 The Characteristics of ADDocument25 pages2.2.1 The Characteristics of AD18kchohanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Exchange Rate Determination PDFDocument65 pagesChapter 7. Exchange Rate Determination PDFKim NgânNo ratings yet
- Money Growth and InflationDocument30 pagesMoney Growth and InflationopshoraNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Chapter 34cDocument8 pagesMacroeconomics Chapter 34cThiha Kaung SettNo ratings yet
- 6 - Aggregate Demand and SupplyDocument62 pages6 - Aggregate Demand and SupplyMạnh Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- Interest Rates PresentationDocument29 pagesInterest Rates PresentationFitri RajabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Money Growth and InflationDocument35 pagesLecture 7 - Money Growth and InflationY Nguyen Ngoc Nhu QTKD-1TC-18No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-03-05 at 8.09.02 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2024-03-05 at 8.09.02 PMemmanuelkakayayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 (Principle of Economic)Document42 pagesChapter 14 (Principle of Economic)izatul akmal maisarahNo ratings yet
- Interest RatesDocument62 pagesInterest RatesclementNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand Aggregate SupplyDocument26 pagesAggregate Demand Aggregate Supplycompudoc11No ratings yet
- PDF For SEBI Economics ISLMDocument41 pagesPDF For SEBI Economics ISLMSaraswathi Putra KamalNo ratings yet
- Money Growth and Inflation: Week 7Document22 pagesMoney Growth and Inflation: Week 7Dewi Ushriyah UlyaNo ratings yet
- Low .BDocument13 pagesLow .Bsteven msusaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Price IndexDocument8 pagesConsumer Price IndexNguyễn Long VũNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy Lecture - PGP 26Document23 pagesFiscal Policy Lecture - PGP 26Parth BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Unit2 Study GuideDocument3 pagesUnit2 Study Guide高瑞韩No ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document29 pagesChapter 8Tafirenyika SundeNo ratings yet
- Fiscal PolicyDocument25 pagesFiscal PolicyAlexNo ratings yet
- ICERDocument13 pagesICEROussama ChaoukiNo ratings yet
- Chap 34Document76 pagesChap 34Jia Wei MiaoNo ratings yet
- Notes - Introduction To Hearing ImpairmentDocument66 pagesNotes - Introduction To Hearing Impairmentnyandasteven2050No ratings yet
- Non Exchange RevenueDocument44 pagesNon Exchange Revenuenyandasteven2050No ratings yet
- MacroeconomicsDocument308 pagesMacroeconomicsnyandasteven2050No ratings yet
- Public Sector Finances SourcesDocument21 pagesPublic Sector Finances Sourcesnyandasteven2050No ratings yet
- LAW of Contract 1 2023Document9 pagesLAW of Contract 1 2023nyandasteven2050No ratings yet
- Custom Hand Grips For RevolverDocument13 pagesCustom Hand Grips For RevolverfrankieitalianNo ratings yet
- This Is An Auto-Generated Purchase Order Based On Online Tender DecisionDocument2 pagesThis Is An Auto-Generated Purchase Order Based On Online Tender DecisionTUff LabNo ratings yet
- 18 International Capital BudgetingDocument49 pages18 International Capital BudgetingBrijesh Chauhan100% (1)
- Gini Coefficient: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument3 pagesGini Coefficient: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchTeodoro Miguel Carlos IsraelNo ratings yet
- Infant and Child Mortality: Mothers and Infants, As Well As The Effectiveness ofDocument3 pagesInfant and Child Mortality: Mothers and Infants, As Well As The Effectiveness ofhendraNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Service Sector in The Indian Economy: Dr.D.AmuthaDocument10 pagesThe Role of The Service Sector in The Indian Economy: Dr.D.AmuthaHitesh ManglaniNo ratings yet
- Pol 223 Main TextDocument147 pagesPol 223 Main TextDaramola Olanipekun EzekielNo ratings yet
- SAP Revenue Accounting and Reporting in SAP S 4HANA 2020 1637339074Document48 pagesSAP Revenue Accounting and Reporting in SAP S 4HANA 2020 1637339074Fatima Zohra BoughlalNo ratings yet
- Principle Acct. Ii - Chapter FourDocument22 pagesPrinciple Acct. Ii - Chapter Fourbereket nigussieNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Fundamentals of Economics 6th Edition William BoyesDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Fundamentals of Economics 6th Edition William Boyesforeliftperiople.ttyox100% (47)
- Some Et Any ExercicesDocument1 pageSome Et Any ExercicesJean-Loïc HANNAISNo ratings yet
- Duplicated RecordsDocument12 pagesDuplicated RecordsOğuzhan DaşkayaNo ratings yet
- Full Economics 10Th Edition Boyes Test Bank Online PDF All ChapterDocument64 pagesFull Economics 10Th Edition Boyes Test Bank Online PDF All Chaptermauraanaviolat284100% (6)
- Struktur Organisasi BTN KCS Makassar TMT Januari 2022Document1 pageStruktur Organisasi BTN KCS Makassar TMT Januari 2022sriwahyuningsih7656No ratings yet
- AP Macro WorkbookDocument346 pagesAP Macro WorkbookLynn Hollenbeck Breindel100% (5)
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA FATA TerbaruDocument2 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA FATA TerbaruFata JualanNo ratings yet
- MayaSavings SoA 2023AUGDocument1 pageMayaSavings SoA 2023AUGChrissandra BolarNo ratings yet
- Invoice 20211130121017 CBN30105841121Document1 pageInvoice 20211130121017 CBN30105841121Fadhil RachmanNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics 12th Edition Michael Parkin Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesMacroeconomics 12th Edition Michael Parkin Solutions ManualDanielCarterrdcz100% (56)
- PO 062 PT. Riau Indo PasifikDocument4 pagesPO 062 PT. Riau Indo PasifikhkbpsimpangpadangduriNo ratings yet
- Demand ForecastingDocument26 pagesDemand Forecastingnuraini9332No ratings yet
- Las Melc 3 QTR 3 English 8 Odbulaong 1Document5 pagesLas Melc 3 QTR 3 English 8 Odbulaong 1Celso Abel Jr. PontillasNo ratings yet
- ECO558Document26 pagesECO558Nur Adriana binti Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- AppliedEconomics Q3 M3 Market-StructureDocument25 pagesAppliedEconomics Q3 M3 Market-Structure•LAZY SHEEP•No ratings yet
- Module For Managerial Accounting-Job Order CostingDocument17 pagesModule For Managerial Accounting-Job Order CostingMary De JesusNo ratings yet
- 'KGHN Fot Flag Iffkd Øhmk Ladqy: Shaheed Vijay Singh Pathik Sports ComplexDocument26 pages'KGHN Fot Flag Iffkd Øhmk Ladqy: Shaheed Vijay Singh Pathik Sports ComplexSurendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Managerial Economics Applications Strategies and Tactics 13th EditionDocument6 pagesTest Bank For Managerial Economics Applications Strategies and Tactics 13th EditionJamesJohnsonqxcej100% (28)
- SS 80-100 1072Document1 pageSS 80-100 1072Rodrigo SantosNo ratings yet