Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsCH 11
CH 11
Uploaded by
Protul BaruaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Grade 11-Latent HeatDocument13 pagesGrade 11-Latent HeatjenardNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of MatterDocument79 pagesThermal Properties of MatterHafiza JaweriaNo ratings yet
- 14.change of State - PureDocument5 pages14.change of State - Purebaokopo185No ratings yet
- Heating Substances COMPLETEDocument13 pagesHeating Substances COMPLETEMaliq MorrisNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 SummaryDocument6 pagesChap 4 SummaryAzaizulAhmadNo ratings yet
- Heating Substances COMPLETEDocument13 pagesHeating Substances COMPLETEMariah CampbellNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium: Chapter Summary / Chap. 4/ HeatDocument6 pages4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium: Chapter Summary / Chap. 4/ HeatkhodijahaminNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Answer Specific Latent Heat Module 2021Document12 pages4.3 Answer Specific Latent Heat Module 2021黎珮琴No ratings yet
- Thermal ConceptsDocument72 pagesThermal ConceptsARTY &lNo ratings yet
- Specific Heat LF and LVDocument7 pagesSpecific Heat LF and LVYash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry SynopsisDocument4 pagesCalorimetry Synopsissreevaishnava01No ratings yet
- 3.1 Lesson 4 - Specific Latent HeatDocument39 pages3.1 Lesson 4 - Specific Latent HeatMvKhoa Gixer100% (1)
- Calorimetry PDFDocument3 pagesCalorimetry PDFPrudhvi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Discussion For Physics Lab On Latent HeatDocument2 pagesDiscussion For Physics Lab On Latent HeatNyomie CoxNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings: Session 3Document10 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings: Session 3swarup.kadam17No ratings yet
- JC Thermal Properties and TemperatureDocument15 pagesJC Thermal Properties and TemperatureTooba ZahidNo ratings yet
- Heat QuantitiyDocument32 pagesHeat QuantitiyMagued MikhaelNo ratings yet
- Change of StateDocument16 pagesChange of StateMichaelNo ratings yet
- Understanding Specific Latent HeatDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Specific Latent HeatNoraidah Harun100% (1)
- Physics Heat-EnglishDocument2 pagesPhysics Heat-EnglishGoogle AccountNo ratings yet
- Heat and Heat TransferDocument32 pagesHeat and Heat Transferdreambiggere22No ratings yet
- Physics - Thermal Properties of MatterDocument4 pagesPhysics - Thermal Properties of Matterhmatara8No ratings yet
- Week 11 Heat TransferDocument27 pagesWeek 11 Heat TransfertaiwoothnielNo ratings yet
- 8 Nibqis PKEZpp FDPWDUqDocument24 pages8 Nibqis PKEZpp FDPWDUqmrockzedzNo ratings yet
- Larry D. Buban, PH.D Science Education - Physics Cas - WvsuDocument49 pagesLarry D. Buban, PH.D Science Education - Physics Cas - WvsuHannah Grace Romano ViceralNo ratings yet
- Thermal Equilibrium: TemperatureDocument21 pagesThermal Equilibrium: TemperatureFadlan RoslanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties CSEC Physics 2020Document34 pagesThermal Properties CSEC Physics 2020Mariah CampbellNo ratings yet
- Section 1 Phy SyllabusDocument3 pagesSection 1 Phy SyllabusSHarves AUdiNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry 2023Document10 pagesCalorimetry 2023Yatharth TiwariNo ratings yet
- HW Chemistry 3may2024Document3 pagesHW Chemistry 3may2024rabiotadrien068No ratings yet
- Assignment No 3 (O2)Document2 pagesAssignment No 3 (O2)qazi nisarNo ratings yet
- Mod 5Document17 pagesMod 5S M AkashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HeatDocument30 pagesChapter 4 HeatSIP190004 STUDENTNo ratings yet
- 2223 Grade 10 Chemistry Chapter 6 NotesDocument21 pages2223 Grade 10 Chemistry Chapter 6 NotesAhmad RaghebNo ratings yet
- PM TB Solutions C11Document6 pagesPM TB Solutions C11Vishwajeet Ujhoodha100% (8)
- Thermal PropertiesDocument6 pagesThermal PropertiesMordecai ChimedzaNo ratings yet
- Heat (Add Science) OkDocument35 pagesHeat (Add Science) OkJaswardi Anwar Bin Md Yaacob� IPGKKBNo ratings yet
- G9-Chem-Matter 1-NotesDocument11 pagesG9-Chem-Matter 1-NotesvijahatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Heat & TemperatureDocument18 pagesLesson 6 Heat & TemperatureRonnie AbsalonNo ratings yet
- Heat 4.1 Understanding Thermal EquilibriumDocument16 pagesHeat 4.1 Understanding Thermal EquilibriumAz MYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Lesson 3 PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Lesson 3 PDFLOK AI TENG MoeNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument63 pagesThermodynamicsJerome Javier100% (1)
- Thermal Energy Ad Heat Thermal EquilibriumDocument6 pagesThermal Energy Ad Heat Thermal EquilibriumAmrita KaurNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet1Document4 pagesTutorial Sheet1Lê HảiNo ratings yet
- PHASE CHANGE Hand OutDocument8 pagesPHASE CHANGE Hand Outjoel rosalNo ratings yet
- Melting Boiling and EvaporationDocument19 pagesMelting Boiling and EvaporationAnmol MalgotraNo ratings yet
- Heating and Cooling Curve of A SubstanceDocument62 pagesHeating and Cooling Curve of A SubstanceIan Alfred Brimbuela100% (1)
- TP5 - Heat Capacity & Latent Heat 1Document5 pagesTP5 - Heat Capacity & Latent Heat 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of MatterDocument4 pagesThermal Properties of MatterPeter KachouhNo ratings yet
- Thermo Matter PropertiesDocument3 pagesThermo Matter PropertiesdetNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Phase ChangesDocument27 pagesIntermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Phase ChangesJubel Andrea SalungaNo ratings yet
- ThermalDocument48 pagesThermalChris RosarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 IGCSE - ActualDocument7 pagesChapter 2 IGCSE - ActualNajia UmarNo ratings yet
- Specific Heat CapacityDocument12 pagesSpecific Heat Capacitytanvir.md.ahsanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document9 pagesLesson 6Zed QuinoNo ratings yet
- Heat As Energy TransferDocument22 pagesHeat As Energy TransferNiño Gerard JabagatNo ratings yet
- Create By: Basic Physics IIDocument7 pagesCreate By: Basic Physics IIM Umar Said TyhnNo ratings yet
- Specific Latent Heat Power PointDocument14 pagesSpecific Latent Heat Power PointAdamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document33 pagesLecture 2ArabellaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
CH 11
CH 11
Uploaded by
Protul Barua0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Ch 11
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesCH 11
CH 11
Uploaded by
Protul BaruaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
1.
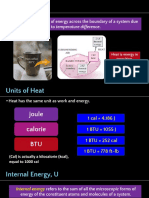
Heat capacity C is the amount of thermal energy required to raise the
temperature of a substance by 1 K (or 10C)
Formula =>
SI Unit => J K-1 or J oC-1
Specific hat capacity c is defined as the amount of thermal energy required
to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by 1 K (or 10C)
Formula =>
SI Unit => J kg-1 K-1 or J kg-1 oC-1
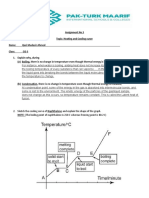
2. (1) At the melting point, the thermal energy absorbed is used to break the
strong bonds between the particles of the solid. Only the total internal
potential energy of the particles is increased. Since none of the thermal
energy supplied is converted to kinetic energy, there is no change in
temperature during melting.
(2) [#pic1]
3. (a) When boiling occurs, the thermal energy given is only used to break the
bonds and intermolecular force between the liquid, hence increasing
internal potential energy. No energy is converted to kinetic energy. So
temperature does not increase.
(b) When condensation occurs, thermal energy is given off from the gas to
form strong bonds and intermolecular force between the gases, hence
decreasing internal potential energy. No energy is converted to kinetic
energy. So temperature does not decrease.
4.
Boiling Evaporation
Occurs at a particular temperature Occurs at any temperature
Relatively fast Relatively slow
Takes place throughout the liquid Takes place only at the liquid surface
Bubbles are formed in the liquid No bubbles are formed in the liquid
Temperature remains constant Temperature may change
External thermal energy source External thermal energy source not
required required
You might also like
- Grade 11-Latent HeatDocument13 pagesGrade 11-Latent HeatjenardNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of MatterDocument79 pagesThermal Properties of MatterHafiza JaweriaNo ratings yet
- 14.change of State - PureDocument5 pages14.change of State - Purebaokopo185No ratings yet
- Heating Substances COMPLETEDocument13 pagesHeating Substances COMPLETEMaliq MorrisNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 SummaryDocument6 pagesChap 4 SummaryAzaizulAhmadNo ratings yet
- Heating Substances COMPLETEDocument13 pagesHeating Substances COMPLETEMariah CampbellNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium: Chapter Summary / Chap. 4/ HeatDocument6 pages4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium: Chapter Summary / Chap. 4/ HeatkhodijahaminNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Answer Specific Latent Heat Module 2021Document12 pages4.3 Answer Specific Latent Heat Module 2021黎珮琴No ratings yet
- Thermal ConceptsDocument72 pagesThermal ConceptsARTY &lNo ratings yet
- Specific Heat LF and LVDocument7 pagesSpecific Heat LF and LVYash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry SynopsisDocument4 pagesCalorimetry Synopsissreevaishnava01No ratings yet
- 3.1 Lesson 4 - Specific Latent HeatDocument39 pages3.1 Lesson 4 - Specific Latent HeatMvKhoa Gixer100% (1)
- Calorimetry PDFDocument3 pagesCalorimetry PDFPrudhvi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Discussion For Physics Lab On Latent HeatDocument2 pagesDiscussion For Physics Lab On Latent HeatNyomie CoxNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings: Session 3Document10 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings: Session 3swarup.kadam17No ratings yet
- JC Thermal Properties and TemperatureDocument15 pagesJC Thermal Properties and TemperatureTooba ZahidNo ratings yet
- Heat QuantitiyDocument32 pagesHeat QuantitiyMagued MikhaelNo ratings yet
- Change of StateDocument16 pagesChange of StateMichaelNo ratings yet
- Understanding Specific Latent HeatDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Specific Latent HeatNoraidah Harun100% (1)
- Physics Heat-EnglishDocument2 pagesPhysics Heat-EnglishGoogle AccountNo ratings yet
- Heat and Heat TransferDocument32 pagesHeat and Heat Transferdreambiggere22No ratings yet
- Physics - Thermal Properties of MatterDocument4 pagesPhysics - Thermal Properties of Matterhmatara8No ratings yet
- Week 11 Heat TransferDocument27 pagesWeek 11 Heat TransfertaiwoothnielNo ratings yet
- 8 Nibqis PKEZpp FDPWDUqDocument24 pages8 Nibqis PKEZpp FDPWDUqmrockzedzNo ratings yet
- Larry D. Buban, PH.D Science Education - Physics Cas - WvsuDocument49 pagesLarry D. Buban, PH.D Science Education - Physics Cas - WvsuHannah Grace Romano ViceralNo ratings yet
- Thermal Equilibrium: TemperatureDocument21 pagesThermal Equilibrium: TemperatureFadlan RoslanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties CSEC Physics 2020Document34 pagesThermal Properties CSEC Physics 2020Mariah CampbellNo ratings yet
- Section 1 Phy SyllabusDocument3 pagesSection 1 Phy SyllabusSHarves AUdiNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry 2023Document10 pagesCalorimetry 2023Yatharth TiwariNo ratings yet
- HW Chemistry 3may2024Document3 pagesHW Chemistry 3may2024rabiotadrien068No ratings yet
- Assignment No 3 (O2)Document2 pagesAssignment No 3 (O2)qazi nisarNo ratings yet
- Mod 5Document17 pagesMod 5S M AkashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HeatDocument30 pagesChapter 4 HeatSIP190004 STUDENTNo ratings yet
- 2223 Grade 10 Chemistry Chapter 6 NotesDocument21 pages2223 Grade 10 Chemistry Chapter 6 NotesAhmad RaghebNo ratings yet
- PM TB Solutions C11Document6 pagesPM TB Solutions C11Vishwajeet Ujhoodha100% (8)
- Thermal PropertiesDocument6 pagesThermal PropertiesMordecai ChimedzaNo ratings yet
- Heat (Add Science) OkDocument35 pagesHeat (Add Science) OkJaswardi Anwar Bin Md Yaacob� IPGKKBNo ratings yet
- G9-Chem-Matter 1-NotesDocument11 pagesG9-Chem-Matter 1-NotesvijahatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Heat & TemperatureDocument18 pagesLesson 6 Heat & TemperatureRonnie AbsalonNo ratings yet
- Heat 4.1 Understanding Thermal EquilibriumDocument16 pagesHeat 4.1 Understanding Thermal EquilibriumAz MYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Lesson 3 PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Lesson 3 PDFLOK AI TENG MoeNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument63 pagesThermodynamicsJerome Javier100% (1)
- Thermal Energy Ad Heat Thermal EquilibriumDocument6 pagesThermal Energy Ad Heat Thermal EquilibriumAmrita KaurNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet1Document4 pagesTutorial Sheet1Lê HảiNo ratings yet
- PHASE CHANGE Hand OutDocument8 pagesPHASE CHANGE Hand Outjoel rosalNo ratings yet
- Melting Boiling and EvaporationDocument19 pagesMelting Boiling and EvaporationAnmol MalgotraNo ratings yet
- Heating and Cooling Curve of A SubstanceDocument62 pagesHeating and Cooling Curve of A SubstanceIan Alfred Brimbuela100% (1)
- TP5 - Heat Capacity & Latent Heat 1Document5 pagesTP5 - Heat Capacity & Latent Heat 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of MatterDocument4 pagesThermal Properties of MatterPeter KachouhNo ratings yet
- Thermo Matter PropertiesDocument3 pagesThermo Matter PropertiesdetNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Phase ChangesDocument27 pagesIntermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Phase ChangesJubel Andrea SalungaNo ratings yet
- ThermalDocument48 pagesThermalChris RosarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 IGCSE - ActualDocument7 pagesChapter 2 IGCSE - ActualNajia UmarNo ratings yet
- Specific Heat CapacityDocument12 pagesSpecific Heat Capacitytanvir.md.ahsanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document9 pagesLesson 6Zed QuinoNo ratings yet
- Heat As Energy TransferDocument22 pagesHeat As Energy TransferNiño Gerard JabagatNo ratings yet
- Create By: Basic Physics IIDocument7 pagesCreate By: Basic Physics IIM Umar Said TyhnNo ratings yet
- Specific Latent Heat Power PointDocument14 pagesSpecific Latent Heat Power PointAdamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document33 pagesLecture 2ArabellaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)