Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsCircuits Circuit Symbols
Circuits Circuit Symbols
Uploaded by
Budi LindrawatiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Electricity Separate With AnswersDocument112 pagesElectricity Separate With AnswersMitra BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Electricity For Grade 6Document4 pagesNotes On Electricity For Grade 6Robert Hooke100% (1)
- Student Exploration: Circuit BuilderDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Circuit BuilderRico Gurley100% (1)
- Electricity SeparateDocument61 pagesElectricity SeparatePham TuNo ratings yet
- Electricity CombinedDocument58 pagesElectricity CombinedMitra BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Q1 W2 Series and Parallel CircuitDocument7 pagesQ1 W2 Series and Parallel CircuitLouis Miguel LauritoNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Circuit BuilderDocument6 pagesStudent Exploration: Circuit BuilderMinchae ParkNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled Documentstephaunrose69No ratings yet
- 2022 01 05 VI Science 1Document4 pages2022 01 05 VI Science 1KITE GLOBALNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism Test ReviewDocument41 pagesElectricity and Magnetism Test ReviewYao LinNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and Circuits NotesDocument9 pagesElectric Current and Circuits Notes13srivastava.nimishaNo ratings yet
- Written Test 1 - SolutionDocument3 pagesWritten Test 1 - SolutionNajwa LolyPopNo ratings yet
- Constructing A Series Circuit - PPTDocument19 pagesConstructing A Series Circuit - PPTLepoldo Jr. RazaNo ratings yet
- Circuits PhET LAb ActivityDocument11 pagesCircuits PhET LAb ActivityTim MahoneyNo ratings yet
- Chapters 20 and 21: Physical Science Unit 7 - Electricity and MagnetismDocument21 pagesChapters 20 and 21: Physical Science Unit 7 - Electricity and MagnetismPatry sanchezNo ratings yet
- Workshop AssignmentDocument10 pagesWorkshop AssignmentBernabasNo ratings yet
- Measuring Current and Voltage: Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument3 pagesMeasuring Current and Voltage: Series and Parallel CircuitsaarhusNo ratings yet
- P503 - CircuitsDocument53 pagesP503 - Circuitstai057482No ratings yet
- GTCH PBL Exit Ticket PacketDocument6 pagesGTCH PBL Exit Ticket Packetapi-534908130No ratings yet
- G6 Answer Key Physiccs WSDocument21 pagesG6 Answer Key Physiccs WSMohammed HussainNo ratings yet
- 7th - Physics - Electric Current and Its Effect - Assignment 1 - BirjotDocument2 pages7th - Physics - Electric Current and Its Effect - Assignment 1 - Birjotjai gopalNo ratings yet
- Part 1: Answer The Following Questions (20 Points) : Manuel CusicanquiDocument3 pagesPart 1: Answer The Following Questions (20 Points) : Manuel CusicanquiAlexander RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Science-5-Q3-W4 Exam MondayDocument4 pagesScience-5-Q3-W4 Exam MondayDavon MacabacyaoNo ratings yet
- Eto Na Talaga. Todo Na ToDocument6 pagesEto Na Talaga. Todo Na ToMaria Gella PerezNo ratings yet
- COT ElectricityDocument23 pagesCOT ElectricityArlene Tuyor Agunod0% (1)
- Electricity Practice TestDocument4 pagesElectricity Practice Testashleysykes2No ratings yet
- Serries ParallelDocument13 pagesSerries ParallelNoel SeniegoNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits NotesDocument5 pagesElectricity and Circuits NotesThwayyiba PKNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism PresentationDocument58 pagesElectricity and Magnetism PresentationnowarabdullaaNo ratings yet
- Types of Electrical CircuitsDocument9 pagesTypes of Electrical CircuitsJoel Christian Salentes100% (1)
- Electromagnetism Assignment #1 CircuitsDocument6 pagesElectromagnetism Assignment #1 CircuitsJanaarthNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Circuits: Vocabulary: Ammeter, Circuit, Current, Electron, Ohmmeter, Ohm's Law, Parallel CircuitDocument11 pagesStudent Exploration: Circuits: Vocabulary: Ammeter, Circuit, Current, Electron, Ohmmeter, Ohm's Law, Parallel CircuitKoral Agan100% (1)
- Electronics For Absolute BeginnersDocument17 pagesElectronics For Absolute Beginnersvladadj_1603No ratings yet
- Symbols and CircuitsDocument11 pagesSymbols and CircuitsJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- Batteries & Bulbs: Open CircuitDocument7 pagesBatteries & Bulbs: Open CircuitVinujah SukumaranNo ratings yet
- 8.09 Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument1 page8.09 Series and Parallel CircuitsSonika NagiNo ratings yet
- ELT1010 AssignmentDocument2 pagesELT1010 AssignmentEd PawliwNo ratings yet
- LAS Q 1 WEEK 3 Ste 9Document6 pagesLAS Q 1 WEEK 3 Ste 9KimmmiNo ratings yet
- National 4 Electricity and Energy HomeworkDocument22 pagesNational 4 Electricity and Energy Homeworkkibafim771No ratings yet
- Lesson 02Document7 pagesLesson 02abdeldjalildaraniunivNo ratings yet
- 5.02 Electric CircuitsDocument21 pages5.02 Electric Circuitsfouad alkasehNo ratings yet
- Circuit ElectrcityDocument23 pagesCircuit Electrcityapi-246410374No ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument1 pageCurrent ElectricityPratiti samantaNo ratings yet
- (Class 6) CH - Electricity and CircuitsDocument3 pages(Class 6) CH - Electricity and CircuitsSnigdha GoelNo ratings yet
- Elec EBDocument38 pagesElec EBAngleNo ratings yet
- 2 Electric Circuits NoteDocument3 pages2 Electric Circuits Noteapi-266021217No ratings yet
- Portfolio in ScienceDocument13 pagesPortfolio in ScienceMarkLesterEstrellaMabagos100% (1)
- 5) Drawing CircuitsDocument3 pages5) Drawing CircuitsKaren J LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 LabDocument6 pagesUnit 8 Labzia mooreNo ratings yet
- Current and VolatageDocument19 pagesCurrent and VolatageJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 ExercisesDocument6 pagesUnit 9 Exercisesyooh9814No ratings yet
- Drawing Circuits-SERIES PARALLELDocument2 pagesDrawing Circuits-SERIES PARALLELmvinytsky1No ratings yet
- Electricity Mastery BookletDocument34 pagesElectricity Mastery Bookletapi-422428700No ratings yet
- SNC1D Electricity Test 4 PDFDocument4 pagesSNC1D Electricity Test 4 PDFRadha RamineniNo ratings yet
- 6 ElectricityDocument24 pages6 ElectricityBisini PraveenNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 23 Current&VoltageInCircuitsDocument31 pagesIGCSE 23 Current&VoltageInCircuitsleena100% (1)
- SS9A - Parallel and Series CircuitsDocument3 pagesSS9A - Parallel and Series CircuitsImranHashmiNo ratings yet
- 33 Cellsand BatteriesDocument6 pages33 Cellsand BatteriesNicole LouiseNo ratings yet
- Bee 18esee02l Lab ManualDocument43 pagesBee 18esee02l Lab ManualGemechu TayeNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Balancing Act 1Document4 pagesBalancing Act 1Budi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Electron Energy LevelDocument1 pageElectron Energy LevelBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Sound 7Document2 pagesSound 7Budi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Current ProblemsDocument1 pageCurrent ProblemsBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Projectiles MotionDocument1 pageProjectiles MotionBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- The Human Heart System AnswersDocument2 pagesThe Human Heart System AnswersBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Day 58 HomeworkDocument1 pageDay 58 HomeworkBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Current and Charge WorksheetDocument2 pagesCurrent and Charge WorksheetBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- A2 Extended Writing PracticeDocument116 pagesA2 Extended Writing PracticeBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Using Moments WorksheetsDocument5 pagesUsing Moments WorksheetsBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Current ProblemsDocument1 pageCurrent ProblemsBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Review PH2Document1 pageReview PH2Budi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Potential Difference Calculations WorksheetDocument1 pagePotential Difference Calculations WorksheetBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Transformer Equation AnswersDocument2 pagesTransformer Equation AnswersBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- BU2+GCSE-Biology - Digestion-WorksheetDocument2 pagesBU2+GCSE-Biology - Digestion-WorksheetBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Transformer Power EquationsDocument2 pagesTransformer Power EquationsBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans (Multiple Choice) QPDocument12 pagesGas Exchange in Humans (Multiple Choice) QPBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Food DietDocument4 pagesFood DietBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
Circuits Circuit Symbols
Circuits Circuit Symbols
Uploaded by
Budi Lindrawati0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesOriginal Title
circuits-circuit-symbols
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesCircuits Circuit Symbols
Circuits Circuit Symbols
Uploaded by
Budi LindrawatiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
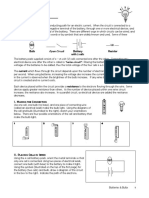
Basic:
1. Draw the symbols for:
a) A bulb
b) A cell
c) A battery
d) A voltmeter
e) An ammeter
f) A fuse
g) An LDR
h) A thermistor
i) A resistor
j) A variable resistor
k) An LED
l) A switch
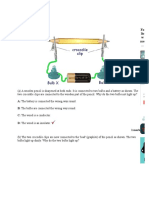
2. Look at each of the circuit
diagrams to the right.
Label each one as either a
series or parallel circuit. If
the circuit is parallel,
write how many different
routes there are around
the circuit.
Medium:
1) Draw a series circuit with two cells, a bulb and an ammeter.
2) Draw a series circuit with a cell an open switch and a motor.
3) Draw a series circuit with a cell, a closed switch, a motor and a bulb.
4) Draw a circuit with two cells, and three bulbs in parallel with the cells.
5) Draw a circuit with one cell, and with a bulb and voltmeter in parallel with
each other.
Parts of a circuit will only work if there is a complete circuit for the current to
flow. If there is a break in the circuit then it’s not complete.
Current also prefers to take the path of least resistance.
Hard:
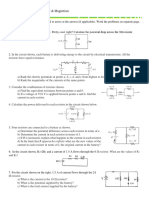
1) Bulb A is unscrewed. Which
bulbs are on and which bulbs
are off? Explain why.
2) Bulb D is unscrewed. Which
bulbs are on and which bulbs
are off? Explain why.
3) Bulb E is unscrewed. Which
bulbs are on and which bulbs
are off? Explain why.
4) Would bulb 2 be lit when the
switch is open? Explain why.
5) Would bulb 1 be lit when the
switch is open? Explain why.
6) Would bulb 1 be lit when the
switch is closed? Explain why.
You might also like
- Electricity Separate With AnswersDocument112 pagesElectricity Separate With AnswersMitra BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Electricity For Grade 6Document4 pagesNotes On Electricity For Grade 6Robert Hooke100% (1)
- Student Exploration: Circuit BuilderDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Circuit BuilderRico Gurley100% (1)
- Electricity SeparateDocument61 pagesElectricity SeparatePham TuNo ratings yet
- Electricity CombinedDocument58 pagesElectricity CombinedMitra BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Q1 W2 Series and Parallel CircuitDocument7 pagesQ1 W2 Series and Parallel CircuitLouis Miguel LauritoNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Circuit BuilderDocument6 pagesStudent Exploration: Circuit BuilderMinchae ParkNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled Documentstephaunrose69No ratings yet
- 2022 01 05 VI Science 1Document4 pages2022 01 05 VI Science 1KITE GLOBALNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism Test ReviewDocument41 pagesElectricity and Magnetism Test ReviewYao LinNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and Circuits NotesDocument9 pagesElectric Current and Circuits Notes13srivastava.nimishaNo ratings yet
- Written Test 1 - SolutionDocument3 pagesWritten Test 1 - SolutionNajwa LolyPopNo ratings yet
- Constructing A Series Circuit - PPTDocument19 pagesConstructing A Series Circuit - PPTLepoldo Jr. RazaNo ratings yet
- Circuits PhET LAb ActivityDocument11 pagesCircuits PhET LAb ActivityTim MahoneyNo ratings yet
- Chapters 20 and 21: Physical Science Unit 7 - Electricity and MagnetismDocument21 pagesChapters 20 and 21: Physical Science Unit 7 - Electricity and MagnetismPatry sanchezNo ratings yet
- Workshop AssignmentDocument10 pagesWorkshop AssignmentBernabasNo ratings yet
- Measuring Current and Voltage: Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument3 pagesMeasuring Current and Voltage: Series and Parallel CircuitsaarhusNo ratings yet
- P503 - CircuitsDocument53 pagesP503 - Circuitstai057482No ratings yet
- GTCH PBL Exit Ticket PacketDocument6 pagesGTCH PBL Exit Ticket Packetapi-534908130No ratings yet
- G6 Answer Key Physiccs WSDocument21 pagesG6 Answer Key Physiccs WSMohammed HussainNo ratings yet
- 7th - Physics - Electric Current and Its Effect - Assignment 1 - BirjotDocument2 pages7th - Physics - Electric Current and Its Effect - Assignment 1 - Birjotjai gopalNo ratings yet
- Part 1: Answer The Following Questions (20 Points) : Manuel CusicanquiDocument3 pagesPart 1: Answer The Following Questions (20 Points) : Manuel CusicanquiAlexander RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Science-5-Q3-W4 Exam MondayDocument4 pagesScience-5-Q3-W4 Exam MondayDavon MacabacyaoNo ratings yet
- Eto Na Talaga. Todo Na ToDocument6 pagesEto Na Talaga. Todo Na ToMaria Gella PerezNo ratings yet
- COT ElectricityDocument23 pagesCOT ElectricityArlene Tuyor Agunod0% (1)
- Electricity Practice TestDocument4 pagesElectricity Practice Testashleysykes2No ratings yet
- Serries ParallelDocument13 pagesSerries ParallelNoel SeniegoNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits NotesDocument5 pagesElectricity and Circuits NotesThwayyiba PKNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism PresentationDocument58 pagesElectricity and Magnetism PresentationnowarabdullaaNo ratings yet
- Types of Electrical CircuitsDocument9 pagesTypes of Electrical CircuitsJoel Christian Salentes100% (1)
- Electromagnetism Assignment #1 CircuitsDocument6 pagesElectromagnetism Assignment #1 CircuitsJanaarthNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Circuits: Vocabulary: Ammeter, Circuit, Current, Electron, Ohmmeter, Ohm's Law, Parallel CircuitDocument11 pagesStudent Exploration: Circuits: Vocabulary: Ammeter, Circuit, Current, Electron, Ohmmeter, Ohm's Law, Parallel CircuitKoral Agan100% (1)
- Electronics For Absolute BeginnersDocument17 pagesElectronics For Absolute Beginnersvladadj_1603No ratings yet
- Symbols and CircuitsDocument11 pagesSymbols and CircuitsJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- Batteries & Bulbs: Open CircuitDocument7 pagesBatteries & Bulbs: Open CircuitVinujah SukumaranNo ratings yet
- 8.09 Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument1 page8.09 Series and Parallel CircuitsSonika NagiNo ratings yet
- ELT1010 AssignmentDocument2 pagesELT1010 AssignmentEd PawliwNo ratings yet
- LAS Q 1 WEEK 3 Ste 9Document6 pagesLAS Q 1 WEEK 3 Ste 9KimmmiNo ratings yet
- National 4 Electricity and Energy HomeworkDocument22 pagesNational 4 Electricity and Energy Homeworkkibafim771No ratings yet
- Lesson 02Document7 pagesLesson 02abdeldjalildaraniunivNo ratings yet
- 5.02 Electric CircuitsDocument21 pages5.02 Electric Circuitsfouad alkasehNo ratings yet
- Circuit ElectrcityDocument23 pagesCircuit Electrcityapi-246410374No ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument1 pageCurrent ElectricityPratiti samantaNo ratings yet
- (Class 6) CH - Electricity and CircuitsDocument3 pages(Class 6) CH - Electricity and CircuitsSnigdha GoelNo ratings yet
- Elec EBDocument38 pagesElec EBAngleNo ratings yet
- 2 Electric Circuits NoteDocument3 pages2 Electric Circuits Noteapi-266021217No ratings yet
- Portfolio in ScienceDocument13 pagesPortfolio in ScienceMarkLesterEstrellaMabagos100% (1)
- 5) Drawing CircuitsDocument3 pages5) Drawing CircuitsKaren J LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 LabDocument6 pagesUnit 8 Labzia mooreNo ratings yet
- Current and VolatageDocument19 pagesCurrent and VolatageJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 ExercisesDocument6 pagesUnit 9 Exercisesyooh9814No ratings yet
- Drawing Circuits-SERIES PARALLELDocument2 pagesDrawing Circuits-SERIES PARALLELmvinytsky1No ratings yet
- Electricity Mastery BookletDocument34 pagesElectricity Mastery Bookletapi-422428700No ratings yet
- SNC1D Electricity Test 4 PDFDocument4 pagesSNC1D Electricity Test 4 PDFRadha RamineniNo ratings yet
- 6 ElectricityDocument24 pages6 ElectricityBisini PraveenNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 23 Current&VoltageInCircuitsDocument31 pagesIGCSE 23 Current&VoltageInCircuitsleena100% (1)
- SS9A - Parallel and Series CircuitsDocument3 pagesSS9A - Parallel and Series CircuitsImranHashmiNo ratings yet
- 33 Cellsand BatteriesDocument6 pages33 Cellsand BatteriesNicole LouiseNo ratings yet
- Bee 18esee02l Lab ManualDocument43 pagesBee 18esee02l Lab ManualGemechu TayeNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Balancing Act 1Document4 pagesBalancing Act 1Budi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Electron Energy LevelDocument1 pageElectron Energy LevelBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Sound 7Document2 pagesSound 7Budi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Current ProblemsDocument1 pageCurrent ProblemsBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Projectiles MotionDocument1 pageProjectiles MotionBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- The Human Heart System AnswersDocument2 pagesThe Human Heart System AnswersBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Day 58 HomeworkDocument1 pageDay 58 HomeworkBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Current and Charge WorksheetDocument2 pagesCurrent and Charge WorksheetBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- A2 Extended Writing PracticeDocument116 pagesA2 Extended Writing PracticeBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Using Moments WorksheetsDocument5 pagesUsing Moments WorksheetsBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Current ProblemsDocument1 pageCurrent ProblemsBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Review PH2Document1 pageReview PH2Budi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Potential Difference Calculations WorksheetDocument1 pagePotential Difference Calculations WorksheetBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Transformer Equation AnswersDocument2 pagesTransformer Equation AnswersBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- BU2+GCSE-Biology - Digestion-WorksheetDocument2 pagesBU2+GCSE-Biology - Digestion-WorksheetBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Transformer Power EquationsDocument2 pagesTransformer Power EquationsBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans (Multiple Choice) QPDocument12 pagesGas Exchange in Humans (Multiple Choice) QPBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Food DietDocument4 pagesFood DietBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet