Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12 Standard Costing Solution FT
12 Standard Costing Solution FT
Uploaded by
nsm2zmvnbbCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 7166materials Problems-Standard CostingDocument14 pages7166materials Problems-Standard CostingLumina JulieNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing & Variance AnalysisDocument19 pagesStandard Costing & Variance AnalysisFUNTV5No ratings yet
- 18-10-SA-V1-S1 Solved Problems SC PDFDocument14 pages18-10-SA-V1-S1 Solved Problems SC PDFAlbsNo ratings yet
- Sub-Usage Variance: MaterialDocument1 pageSub-Usage Variance: Materialpatleashish3No ratings yet
- PROBLEMSChap 7 SMDocument27 pagesPROBLEMSChap 7 SMVillena Divina VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsAlbsNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsyanbladeNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsShruti BannerjeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsAfsahNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsShubham NamdevNo ratings yet
- 18 10 SA V1 S1 Solved Problems SC PDFDocument14 pages18 10 SA V1 S1 Solved Problems SC PDFTheVagabond HarshalNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDerrick de los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical Problemskiran shettyNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical Problemsyousuf AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsRuchi pariharNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsNeelima Varma NadimpalliNo ratings yet
- Determination: IntroductionDocument1 pageDetermination: Introductionpatleashish3No ratings yet
- Standard Costing Example SolutionDocument2 pagesStandard Costing Example SolutionVikas KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing With Solutions: SolutionDocument3 pagesStandard Costing With Solutions: Solution777priyankaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial Accounting Canadian 5th Edition Brewer Solutions Manual DownloadDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Managerial Accounting Canadian 5th Edition Brewer Solutions Manual DownloadWm Mcgranahan100% (28)
- Silo - Tips Standard Costing With SolutionsDocument65 pagesSilo - Tips Standard Costing With SolutionsAlbert MuzitiNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing & Variance AnalysisDocument18 pagesStandard Costing & Variance AnalysisMahesh G VNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing 2Document69 pagesStandard Costing 2Jash SanghviNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 AnswerDocument7 pagesTutorial 4 AnswernajihahNo ratings yet
- MCV MPVDocument8 pagesMCV MPVHarsh MittalNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing: 1. Single MaterialDocument7 pagesStandard Costing: 1. Single MaterialManisha KhatriNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting and Decision Making: Submitted ByDocument12 pagesManagement Accounting and Decision Making: Submitted ByKavisha singhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Solutions - Inclass ExercisesDocument12 pagesChapter 10 Solutions - Inclass ExercisesSummerNo ratings yet
- It Will Be Recalled From The Previous Section That A Variance Is The Difference Between Standard Cost and Actual CostDocument4 pagesIt Will Be Recalled From The Previous Section That A Variance Is The Difference Between Standard Cost and Actual CostBisag AsaNo ratings yet
- 1920-1-ACCO 20073 - Solutions To STD Cost ProblemsDocument4 pages1920-1-ACCO 20073 - Solutions To STD Cost ProblemsRaegharp Constantioul100% (1)
- STANDARD COSTING With GP VARIANCE ANALYSIS KEY ANSWERSDocument19 pagesSTANDARD COSTING With GP VARIANCE ANALYSIS KEY ANSWERSaziel caith florentinNo ratings yet
- ItunganDocument8 pagesItunganIjal dhiaulhaqNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing: Cost AccountingDocument15 pagesStandard Costing: Cost Accountingwilson pribadiNo ratings yet
- Board of Studies Academic Chapter 13 Standard Costing Practice Question File 3 1649748588Document29 pagesBoard of Studies Academic Chapter 13 Standard Costing Practice Question File 3 1649748588samueladino876No ratings yet
- Standard Costing (I) - SolutionsDocument3 pagesStandard Costing (I) - Solutions行歌No ratings yet
- Standard Costing With Solution-1Document11 pagesStandard Costing With Solution-1jikuenterprise789No ratings yet
- Ch05 Traditional Overheads Versus Activity-Based CostingDocument15 pagesCh05 Traditional Overheads Versus Activity-Based CostingAndrew ChongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Variance Analysis)Document57 pagesChapter 6 (Variance Analysis)annur azalillahNo ratings yet
- MAF Mixed and Yield Variances (Eng)Document8 pagesMAF Mixed and Yield Variances (Eng)BirukNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 (Individu)Document13 pagesChapter 12 (Individu)Rahmatul MaghfirohNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument16 pagesStandard CostingJash SanghviNo ratings yet
- Soal 1: 1. Computed Equivalent Unit For Production CostDocument10 pagesSoal 1: 1. Computed Equivalent Unit For Production CostRaihan Rohadatul 'AisyNo ratings yet
- HbjhjhjhujuhjDocument14 pagesHbjhjhjhujuhjnjkjhNo ratings yet
- FOH Rate Rp.180.000.000: Jawaban Soal 1: 1. PT. Kopindo Persada RP 6.000 / DLH 30.000 Traditional CostingDocument4 pagesFOH Rate Rp.180.000.000: Jawaban Soal 1: 1. PT. Kopindo Persada RP 6.000 / DLH 30.000 Traditional Costingabd storeNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument11 pagesStandard CostinganishaNo ratings yet
- Item To Classify Standard Actual Type of VarianceDocument7 pagesItem To Classify Standard Actual Type of Variancedavid johnsonNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Personnel and DivisionsDocument37 pagesEvaluating Personnel and DivisionsGaluh Boga KuswaraNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document22 pagesCH 14Rizza Mae EudNo ratings yet
- M11 CHP 10 1 Standard Costs 2011 0524Document58 pagesM11 CHP 10 1 Standard Costs 2011 0524Rose Ann De Guzman67% (3)
- © The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2015. All Rights Reserved. Solutions Manual, Chapter 10 21Document3 pages© The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2015. All Rights Reserved. Solutions Manual, Chapter 10 21RanaNo ratings yet
- Fact Pattern: Example 10.5 (Direct Material Cost Variances)Document9 pagesFact Pattern: Example 10.5 (Direct Material Cost Variances)Saiyed KosinNo ratings yet
- Problem10 18 and 10 20Document9 pagesProblem10 18 and 10 20DhanushaNo ratings yet
- Problem 2 of STD CostingDocument3 pagesProblem 2 of STD CostingBiswajit BNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting Asia Pacific 1st Edition Mowen Solutions ManualDocument29 pagesManagerial Accounting Asia Pacific 1st Edition Mowen Solutions Manualdonaldvioleti7o100% (21)
- Chapter 12Document13 pagesChapter 12mikeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Standard Costing Nov 2020 2Document112 pagesChapter 12 Standard Costing Nov 2020 2Kunal KuvadiaNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance Analysis: 22. A. Total Purchases AP × AQDocument7 pagesStandard Costing and Variance Analysis: 22. A. Total Purchases AP × AQShaira UnggadNo ratings yet
- Analisa Usahatani Produksi Buah Melon Luas 1000 M : Jumlah RP 3.471.500Document6 pagesAnalisa Usahatani Produksi Buah Melon Luas 1000 M : Jumlah RP 3.471.500Agung Dwi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument2 pagesRRLMary Joyce CacoNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Dan StatistikaDocument11 pagesEvaluasi Dan StatistikaAmrita Oza NabillaNo ratings yet
- Downstream Petroleum Sector and Fuel Quality: The Quality of Transport FuelsDocument7 pagesDownstream Petroleum Sector and Fuel Quality: The Quality of Transport Fuelssanjayshah99No ratings yet
- Bid Evaluation GuidelineDocument11 pagesBid Evaluation GuidelineJanith Saumya BandaraNo ratings yet
- Resale Rights - The Alternative: A Must Have Guide For All Resellers and Those in The Making!Document18 pagesResale Rights - The Alternative: A Must Have Guide For All Resellers and Those in The Making!CarlosNo ratings yet
- ExxonMobil Aptitude Test 1Document21 pagesExxonMobil Aptitude Test 1Michael WestNo ratings yet
- Nabus Vs PacsonDocument8 pagesNabus Vs PacsonGladys BantilanNo ratings yet
- Business Plan ENT300 SlaynitizerDocument47 pagesBusiness Plan ENT300 Slaynitizerimran roslan100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Index NumberDocument6 pagesChapter 11 Index Numbersharkfin1403100% (1)
- Holy Family Tender For Lab Items Due On 19-04-2022Document27 pagesHoly Family Tender For Lab Items Due On 19-04-2022Naveed ShahNo ratings yet
- PROCESS COSTING - CW - ExamplesDocument12 pagesPROCESS COSTING - CW - Exampleskushgarg627100% (1)
- Man TparDocument10 pagesMan TparFrederick GbliNo ratings yet
- European Purchase Terms - EnglishDocument21 pagesEuropean Purchase Terms - EnglishgheNo ratings yet
- Ford's Marketing PlanDocument12 pagesFord's Marketing PlanHanna Vanya100% (2)
- Aptitude Shortcuts and General FormulaeDocument6 pagesAptitude Shortcuts and General FormulaeNive AdmiresNo ratings yet
- Fin 121 Answer KeyDocument21 pagesFin 121 Answer KeyDC AranetaNo ratings yet
- Business Understanding of Flower ShopDocument42 pagesBusiness Understanding of Flower ShopMariana Melo RobertoNo ratings yet
- Tesco PLC: A Critical Review On It'S Key Practices People, Marketing, Operations and FinanceDocument21 pagesTesco PLC: A Critical Review On It'S Key Practices People, Marketing, Operations and FinanceNick1No ratings yet
- đề cương thi KTQTDocument51 pagesđề cương thi KTQTHoàng LâmNo ratings yet
- ECONOMICS P1 M18 To J22 C.VDocument428 pagesECONOMICS P1 M18 To J22 C.VsukaNo ratings yet
- Materials Management Business Blueprint V1.0Document27 pagesMaterials Management Business Blueprint V1.0shailNo ratings yet
- Indian Economy Indian Economy: (General Studies)Document152 pagesIndian Economy Indian Economy: (General Studies)LovyNo ratings yet
- MKT 571 Final Exam Answers UpdatedDocument5 pagesMKT 571 Final Exam Answers UpdatedRogue Phoenix100% (4)
- Paper-2 The Government and The Economy (Macroeconomics) Book Chapter (25 To 34) Macroeconomics ObjectiveDocument39 pagesPaper-2 The Government and The Economy (Macroeconomics) Book Chapter (25 To 34) Macroeconomics ObjectiveSharif HossainNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument43 pagesEconomicsAbhishek D. KumarNo ratings yet
- Industrial-Marketing MBADocument111 pagesIndustrial-Marketing MBAGaurav S Jadhav100% (1)
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument62 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysishanaNo ratings yet
- Economical EnvironmentDocument10 pagesEconomical EnvironmentHedayat Ullah100% (1)
- EbayDocument81 pagesEbayJohnny ChanNo ratings yet
- Fashion CycleDocument26 pagesFashion CycleAjinder Deol100% (1)
12 Standard Costing Solution FT
12 Standard Costing Solution FT
Uploaded by
nsm2zmvnbbCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12 Standard Costing Solution FT
12 Standard Costing Solution FT
Uploaded by
nsm2zmvnbbCopyright:
Available Formats
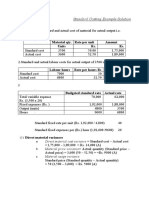
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
Chapter 12: Standard Costing
Solutions
Solution 1:
Source Table
Particulars Standard for Actual Actual
Qty Rate Amount Qty Rate Amount (Rs)
(Rs)
Material 3,00,000 1 3,00,000 2,80,000 0.90 2,52,000
3,00,000 2,52,000
(1) Material Usage Variance = (Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity) × Standard Rate
= (3,00,000 – 2,80,000) × 1 = Rs 20,000 (F)
(2) Material Price Variance = (Standard Rate – Actual Rate ) × Actual Quantity
= (1 – 0.90) × 2,80,000 = Rs 28,000 (F)
(3) Material Cost Variance = Standard Cost – Actual Cost
= (Standard Rate × Standard Quantity) – (Actual Rate ×
Actual Quantity)
= (1 × 3,00,000) – (0.90 × 2,80,000)
= 3,00,000 – 2,52,000 = Rs 48,000 (F)
Verification:
Material Cost Variance = Material Usage Variance + Material Price Variance
= 20,000 (F) + 28,000 (F) = Rs 48,000 (F)
Working Notes:
100 𝑘𝑔
Standard Quantity (SQ) = 2,10,000Kg× 70 𝑘𝑔
= 3,00,000 kg.
𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑀𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑙𝑠 𝑅𝑠.2,52,000
Actual Price per kg = 𝑀𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑈𝑠𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑄𝑡𝑦
= 2,80,000𝑘𝑔 = Rs 0.90 per kg.
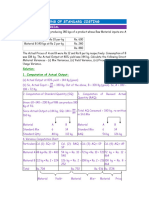
Solution 2:
Source Table
Particulars Standard for Actual Actual
Qty Rate Amount Qty Rate Amount (Rs)
(Rs)
Raw Material 250 × 2 = 500 6 3,000 250 × 1.8 = 8 3,600
450
500 3,000 450 3,600
· Material Usage Variance = (Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity) × Standard
= Rate (500 – 450) × 6 = Rs 300 (F)
· Material Price Variance = (Standard Rate – Actual Rate ) × Actual Quantity
= (6 – 8) × 450 = Rs 900 (A)
· Material Cost Variance = Standard Cost – Actual Cost
= (Standard Rate × Standard Quantity) – (Actual
Rate × Actual Quantity)
= (6 × 500) – (8 × 450) = Rs 600 (A)
Verification:
Material Cost Variance = Material Usage Variance + Material Price Variance
Rs 600 (A) = Rs 300 (F) + Rs 900 (A)
Answer 3:
Source Table
Material Budget Standard Actual
Qty. @ Qty. @ Qty. @
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.1
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
RM 5 kg x 5 x 1000 = 5000 x x - 10 7,14,000
Let Standard price per kg = Rs x/kg
Let Actual price per Kg = Rs x-10/Kg
Material price variance = (SP – AP) x AQ
51,000 = (x – (x-10)) x AQ
5,100 = AQ
So, Actual Qty = 5,100 kgs
Now, Actual cost = 7,14,000
Actual cost = Quantity x Rate
7,14,000 = 5,700 x (x - 10)
140 = x – 10
x = Rs 150
So, standard price = Rs 150
Actual price = Rs 140
(i) Actual quantity = 5,100 kg
Actual price = Rs 140
(ii) Material usage variance = (SQ – AQ) x SP
= (5,000 – 5,100) x 150
= 15,000 (A)
(iii) Cost Variance = (SQ x SR) – (AQ x AR)
= (5,000 x 150) – (5,100 x 140)
= 7,50,000 – 7,14,000
= 36,000 (E)
Source Table
Material Budget Standard Actual
Qty. @ Qty. @ Qty. @
RM 5 kg 150 5 x 1000 = 5000 150 5,100 140 7,14,000
Solution 4:
Source Table
Revised Standard
Materials Standard for Actual Actual Quantity Standard Qty ×
Qty Rate Amount Qty Rate Amount 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑄𝑡𝑦 𝑀𝑖𝑥
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑄𝑡𝑦 𝑀𝑖𝑥
(Kgs.) (Rs.) (Rs.) (Kgs.) (Rs.) (Rs.)
A 3,500 20 70,000 4,500 21 94,500 3,500 ×
7,500
= 3,750
7,000
7,500
B 2,100 10 21,000 1,500 8 12,000 2,100 × 7,000
= 2,250
7,500
1,400 × 7,000
= 1,500
C 1,400 5 7,000 1,500 6 9,000
7,000 98,000 7,500 1,15,500
1. Material Cost Variance = Standard Cost – Actual Cost
= 98,000 – 1,15,000 = Rs. 17,500 (A)
2. Material Price Variance = (Standard Price – Actual Price) × Actual Quantity
A = (20 – 21) × 4,500 = Rs. 4,500 (A)
B = (10 – 8) × 1,500 = Rs. 3,000 (F)
C = (5 – 6) × 1,500 = Rs. 1,500 (A)
Rs. 3,000 (A)
3. Material Usage Variance = (Standard Quantity for Actual Output – Actual Quantity) × Standard Price
A = (3,500 – 4,500) × Rs. 20 =Rs. 20,000 (A)
B = (2,100 – 1,500) × Rs. 10 =Rs. 6,000 (A)
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.2
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
C = (1,400 – 1,500) × Rs. 5 =Rs. 500 (A)
Rs. 14,500 (A)
4. Material Mix Variance = (Revised Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity) × Standard Price
A = (3,750 – 4,500) × Rs. 20 = Rs. 15,000 (A)
B = (2,250 – 1,500) × Rs. 10 = Rs. 7,500 (F)
C = (1,500 – 1,500) × Rs. 5 = Nil
Rs. 7,500 (A)
5. Material Yield Variance = (Standard Yield for Actual Mix – Actual Yield) × Standard Rate
= (6,000 – 5,600) × Rs. 17.5 = Rs. 7,000 (A)
Working Notes:
(i) Total Standard input of raw materials required to produce 5,600 Kgs. of ‘BXE’ are 7,000 Kgs. In 7,000
Kgs. of raw material A, B and C are in proportion of 5 : 3 : 2 or
7,000
A = 10 × 5 = 3,500 Kgs.
7,000
B = 10
× 3 = 2,100 Kgs.
7,000
C = 10
× 2 = 1,400 Kgs.
𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑀𝑖𝑥 𝑅𝑠.98,000
(ii) Standard Rate = 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡
= 5,600 𝐾𝑔
= Rs. 17.50
(iii) For 7,000 Kgs. of standard input the standard output is 5,600 kg. of ‘NXE’
5,600
For 7,500 Kgs. of standard input the standard output is = 7,000 × 7,500 = 6,000 Kgs. of ‘NXE’
Solution 5:
Standard and Actual Cost of 1,000 kgs. of Actual output of GEMCO during April, 1988
Source Table
Materials
Standard Cost for Actual Output Actual Cost Revised Standard
Quantity
Standard Qty ×
Qty. (Kg.) Rate Amount(Rs) Qty. (Kg.) Rate Amount(Rs) 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑄𝑡𝑦 𝑀𝑖𝑥
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑄𝑡𝑦 𝑀𝑖𝑥
(Rs.) (Rs.)
1,250
800 × 1,200
=833.33
A 800 6 4,800 750 7 5,250
B 400 4 1,600 500 5 2,500 400 ×
1,250
=416.67
1,200
1,200 6,400 1,250 7,750
(a) Material Cost Variance = Standard Cost – Actual Cost
= Rs. 6,400 – Rs. 7,750 =Rs. 1,350 (A)
(b) Material Price Variance = (Standard Price – Actual Price) × Actual Quantity
A =(Rs. 6 – Rs. 7) × 750 Kgs. =Rs. 750 (A)
B =(Rs. 4 – Rs. 5) × 500 Kgs. =Rs. 500 (A)
=Rs. 1,250 (A)
(c) Material Usage Variance = (Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity) × Standard Price
A = (800 kgs. – 750 kgs.) × Rs. 6 = Rs. 300 (F)
B = (400 kgs. – 500 kgs.) × Rs. 4 = Rs. 400 (A)
= Rs. 100 (A)
(d) Material Mix Variance = (Revised Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity) × Standard Price
A = (833.33 – 750) × Rs. 6 = Rs. 500.00 (F)
B = (416.67 – 500) × Rs. 4 = Rs. 333.33 (A)
= Rs. 166.67 (F)
(e) Material Yield Variance = (Standard Quantity for Actual Output – Revised Standard Quantity) ×
Standard Price
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.3
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
A = (800 – 833.33) × Rs. 6 = Rs. 200.00 (A)
B = (400 – 416.67) × Rs. 4 = Rs. 66.67 (A)
= Rs. 266.67 (A)
Verification:
Material Cost Variance = Material Price Variance + Material Usage Variance
Rs. 1,350 (A) = Rs. 1,250 (A) + Rs. 100 (A)
Material Usage Variance = Material Mix Variance + Material Yield Variance
Rs. 100 (A) = Rs. 166.67 (F) + Rs. 266.67 (A)
Solution 6:
Source Table
Material Standard for Actual Output Actual
Qty (Kg.) Rate (Rs) Amount (Rs) Qty (Kg.) Rate (Rs) Amount (Rs)
A 800 4 3,200 35 4 140
795 830 4.25 3,378.75
B 1,200 3 3,600 40 3 120
1,150 1,190 2.50 2,875.00
2,000 2,020
Loss 300 320
Output 1,700 6,800 1,700 6,513.75
(a) Material Price Variance = (Standard Price – Actual Price) × Actual Quantity
Material A = (Rs 4 – Rs 4) × 35 kg. + (Rs 4 – Rs 4.25) × 795 kg. = Rs 198.75(A)
Material B = (Rs 3 – Rs 3) × 40 kg. + (Rs 3 – Rs 2.50) × 1,150 kg. = Rs 575 (F)
Rs 376.25 (F)
(b) Material Usage Variance = (Standard Quantity for Actual Output – Actual Quantity) × Standard Price
Material A = (800 – 830) × 4 = Rs 120 (A)
Material B = (1,200 – 1,190) × 3 = Rs 30 (F)
Rs 90 (A)
(c) Material Yield Variance = (Actual Yield – Standard Yield for Actual Mix) × Standard Cost per unit
𝑅𝑠. 6,800
= (1,700 kg. – 1,717* kg.) × 1,700 = Rs 68 (A)
𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡
*Standard Yield = 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝐼𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡
×Actual Input
85 𝐾𝑔.
= 100 𝐾𝑔.
× 2,020 kg. = 1717 kg.
(d) Material Mix Variance = (Revised Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity) × Standard Price
Material A = (808 – 830) × 4 = Rs 88 (A)
Material B = (1,212 – 1,190) × 3 = Rs 66 (F)
Rs 22 (A)
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑄𝑢𝑎𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑀𝑖𝑥.
Revised Standard Quantity = 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑄𝑢𝑎𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑀𝑖𝑥
× Standard Quantity
2,020.
Material A = 2,000
× 800 = 808
2,020.
Material B = 2,000
× 1,200 = 1,212
(e) Total Materials Cost Variance = (Standard Cost – Actual Cost)
= (Rs 6,800 – 6,513.75) = Rs 286.25 (F)
Verification:
Material Cost Variance = Material Price Variance + Material Usage Variance
Rs 286.25 (F) = Rs 376.25 (F) + Rs 90 (A)
Material Usage Variance= Material Mix Variance + Material Yield Variance
Rs 90 (A) = Rs 22 (A) + Rs 68 (A)
Working Notes:
1) For actual (standard) output of 85 kgs. the standard input is 100 kg.
100 𝐾𝑔.
For actual output of 1700 kg the standard = 85 𝐾𝑔. × 1700 kg = 2,000 kg.
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.4
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
2) 2,000 kg. of standard input for an actual output of 1700 kg contains the materials A and B in the
proportion of (40 : 60) i.e. 800 kg of material A and 1200 kg of material B.
3) Material actually consumed for 1700 kg of actual output:
Materials Stock on 1.9.90 Purchases during September 1990 Stock on 30.9.90 Material Consumed
A 35 kg. 800 kg. 5 kg. 830 kg.
B 40 kg. 1,200 kg. 50 kg. 1,190 kg.
𝑅𝑠.3,400
4) Purchase (Actual) Price per kg of Material A = 800 𝐾𝑔.
= Rs. 4.25
𝑅𝑠. 3,000.
Purchase (Actual) Price per kg of Material B = 1,200 𝐾𝑔.
= Rs. 2.50
Solution 7:
Source Table
Standard for Actual Output Actual
Products Qty Rate Amount (Rs.) Qty Rate Amount (Rs.)
A 50 12 600 ? = 40 15 ? = 600
B ? = 50 15 ? = 750 70 20 1,400
100 1,350 110 2,000
Material Usage Variance = (Standard Quantity of Input – Actual Quantity of Input) × Standard Rate
Let x be the Standard Input for Product B
Material B:
- 300 = (x – 70) × 15
- 300 = 15x – 1,050
15x = 750
x = 50
Hence, Standard input for Product B is 50 Kgs.
Material Mix Variance for both product A and B is Rs. 45 Adverse.
Material Mix Variance = Standard Price per unit × (Revised Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity of Input)
Let y be the actual input in Kgs. for Product A
𝑦+70 𝑦+70
- Rs. 45 = (50 × 100 - y)× 12 + (50 × 100 - 70)× 15
- Rs. 45 = [(0.5y + 35) – y] × 12 + [(0.5y + 35) – 70] × 15
- Rs. 45 = (6y + 420 – 12y) + (7.5y + 525 – 1,050)
1.5y = 60
y = 40 kgs.
Variances of Product A:
Material Price Variance = (Standard Price – Actual Price) × Actual Quantity
= (Rs. 12 – Rs. 15) × 40 kgs. = Rs. 120 (A)
Material Usage Variance = (Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity) × Standard Price
= (50 kgs. – 40 kgs.) × Rs. 12 = Rs. 120 (F)
Material Cost Variance = (Standard Cost – Actual Cost)
= (50 kgs. × Rs. 12 – 40 kgs. × Rs. 15) = Nil
Variances of Product B:
Material Price Variance = (Standard Price – Actual Price) × Actual Quantity
= (Rs. 15 – Rs. 20) × 70 kgs. = Rs. 350 (A)
Material Cost Variance = (Standard Cost – Actual Cost)
= (50 kgs. × Rs. 15 – 70 kgs. × Rs. 20) = Rs. 650 (A)
Solution 8:
(i) Material Cost Variance (A + B) = {(SQ × SP) – (AQ × AP)}
₹ 3,625 = (SQ × SP) – ₹ 59,825
(SQ × SP) = ₹ 63,450
(SQA × SPA) + (SQB × SPB) = ₹ 63,450
(940 kg × SPA) + (705 kg × ₹ 30) = ₹ 63,450
940 kg × SPA) + ₹ 21,150 = ₹ 63,450
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.5
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
(940 kg × SPA) = ₹ 42,300
SPA = ₹ 42,300 /940kg
Standard Price of Material-A = ₹ 45
Working Note:
SQ i.e. quantity of inputs to be used to produce actual output
= 1,480 kg/90% = 1,645 kg
SQA = {800 kg /(800+600)}× 1,645kg = 940 kg
SQB = {600 kg / (800+600)} × 1,645kg = 705 kg
(ii) Material Price Variance (A + B) = {(AQ × SP) – (AQ × AP)}
₹ 175 = (AQ × SP) – ₹ 59,825
(AQ × SP) = ₹ 60,000
(AQA × SPA) + (AQB × SPB) = ₹ 60,000
(900 kg × ₹ 45 (from (i) above)) + (AQB × ₹ 30) = ₹ 60,000
₹ 40,500 + (AQB × ₹ 30) = ₹ 60,000
(AQB × ₹ 30) = ₹ 19,500
AQB = 19,500/30 = 650 kg
Actual Quantity of Material B = 650 kg.
(iii) (AQ × AP) = ₹ 59,825
(AQA × APA) + (AQB × APB) = ₹ 59,825
(900 kg × APA) + (650 kg (from (ii) Above ) × ₹ 32.5) = ₹ 59,825
(900 kg × APA) + ₹ 21,125 = ₹ 59,825
(900 kg × APA) = ₹ 38,700
APA = 38,700/ 900 = 43
Actual Price of Material-A = ₹ 43
(iv) Total Actual Quantity of Material-A and Material-B = AQA + AQB
900 kg + 650 kg (from (ii) above) = 1,550 kg
Now,
Revised SQA = {800 kg /(800+600)} × 1,550 kg = 886 kg
Revised SQB = {600 kg / (800+600) } × 1,550 kg = 664 kg
(v) Material Mix Variance (A + B) = {(RSQ × SP) – (AQ × SP)}
= {(RSQA × SPA) + (RSQB × SPB) – 60,000}
= (886 kg (from (iv) above) × ₹ 45 (from (i) above))
+ (664 kg (from (iv) above) × ₹ 30) - ₹ 60,000
= (39,870 + 19,920) – 60,000 = ₹ 210 (A)
Solution 9:
Material Price Variance = (Standard Rate – Actual Rate) × Actual Quantity
9,800 (A) = (40 – 42) × Actual Quantity
(9,800) = -2 Actual Quantity
Actual Quantity = 4,900 Kg.
Solution 10:
Source Table
Chemical Standard for Actual Output Actual Revised Standard Time
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝐻𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑠 𝑀𝑖𝑥
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑆𝑡𝑑. ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑠 𝑀𝑖𝑥
× Std. Hrs
Qty Rate (Rs.) Amount (Rs.) Qty Rate Amount
for Actual output
(Rs.) (Rs.)
A 50 12 600 ? = 40 15 ? = 600 ?=
110
× 50 = 55
100
B 50 15 750 70 ? = 20 ? = 1,400 ?=
110
× 50 = 55
100
100 1,350 110 2,000
1. Material Mix Variance = (Revised Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity) × Standard Price
Chemical A = (55 – 40) × 12 = Rs. 180 (F)
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.6
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
Chemical B = (55 – 70) × 15 = Rs. 225 (A)
Rs. 45 (A)
2. Materials Usage Variance = (Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity) × Standard Price
Chemical A = (50 kg. – 40 kg.) × Rs. 12 = Rs. 120 (F)
Chemical B = (50 kg. – 70 kg.) × Rs. 15 = Rs. 300 (A)
3. Rs. 180 (A)
Materials Price
Variance = (Standard Price – Actual Price) × Actual Quantity
Chemical A = (Rs. 12 – Rs. 15) × 40 kg. = Rs. 120 (A)
Chemical B = (Rs. 15 – Rs. 20) × 70 kg. = Rs. 350 (A)
Rs. 470 (A)
4. Actual Loss of Actual Input
Actual Total Input = 110 kg.
Less: Actual Output = 90 kg.
Actual Loss = 20 kg.
5. Actual Input of Chemical A = 40 kg.
6. Actual Price per kilogram of Chemical B= Rs. 20
Working Notes:
(I) Cost of Standard Mix of Input
Particulars Quantity Price (Rs.) Amount (Rs.)
Chemical A 50 12 600
Chemical B 50 15 750
100 13.5 1,350
Standard Loss 10
90 1,350
(II) Standard Rate of Output = Rs. 1,350/90 kg. = Rs. 15 per kg.
(III) Standard Yield for Actual Input.
Yield Variance = (Actual Yield – Standard Yield for Actual Input) × Standard Cost per unit of Output
Rs. 135 (A) = (90 kg – Standard Yield for actual input) × Rs. 15
Standard Yield for Actual Input = 99 kg.
100 𝑘𝑔.
(IV) Actual input for 99 kg. of output = 90 𝑘𝑔. × 99 kg. = 110 kg.
(V) Actual input of Chemical A = 110 kg. – Actual Input of Chemical B
= 110 kg. – 70 Kg. = 40 Kg.
(VI) Material Cost Variance is Rs. 650 (A).
Hence the Actual Cost of Actual Mix of Chemicals A and B will be Rs. 1,350 + Rs. 650 = Rs. 2,000.
(VII) The Actual Cost of 40 kg. of Chemical A @ Rs. 15 per kg. is Rs. 600.
Thus, the cost of one kg of Chemical B used is (Rs. 2,000 – Rs. 600)/70 kg = Rs. 20 per kg.
Solution 11:
Source Table
Category Standard for Actual Output Actual Revised Std
Quantity
Total Hours Rate Amount Hours Idle Effective Rate Amount 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 ℎ𝑟𝑠 𝑀𝑖𝑥
×
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑆𝑡𝑑. ℎ𝑟𝑠 𝑀𝑖𝑥
Std (Rs.) (Rs.) hours hours (Rs.) (Rs.)
Std. hrs for Actual
Output
Men 400 400 ×
960 1.25 480 520 13 ×2= 49 1.20 624 760
× 480 = 380 hrs
1,000 800
26
=384
960 4×2 760
Women 200 200 × 1,000 0.80 153.6 160 =8 152 0.85 136 800
× 200 = 190 hrs
=192 3×2
Boys 200 200 ×
960 0.70 134.4 120 =6 114 0.65 78 760
× 200 = 190 hrs
1,000 800
=192
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.7
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
800 768 768 800 760 838
Direct Labour Cost Variance = Standard Cost for Actual Output – Actual Cost
= Rs. 768 – Rs. 838 = Rs. 70 (A)
Direct Labour Rate Variance = (Standard Rate – Actual Rate) × Actual Hours Paid for
Men = (Rs. 1.25 – Rs. 1.20) × 520 = Rs. 26 (F)
Women = (Re. 0.80 – Rs. 0.85) × 160 = Rs. 8 (A)
Boys = (Re. 0.70 – Rs. 0.65) × 120 = Rs. 6 (F)
Rs. 24 (F)
Direct Labour Efficiency Variance = (Standard Time for Actual Output – Actual Time Worked) × Standard Rate
Men = (384 – 494) × Rs.1.25 = Rs. 137.50(A)
Women = (192 – 152) × Re. 0.80 = Rs. 32.00 (F)
Boys = (192 – 114) × Re. 0.70 = Rs. 54.60(F)
Rs. 50.90 (A)
Idle Time Variance = Idle hours × Standard Rate
Men = Rs. 26× 1.25 = Rs. 32.50 (A)
Women = Re. 8 × 0.80 = Rs. 6.40 (A)
Boys = Re. 6 × 0.70 = Rs. 4.20 (A)
Rs. 43.10 (A)
Direct Labour Material Variance = (Revised Standard Time – Actual Time Taken) × Standard Rate
Men = (380 – 494) × Rs. 1.25 = Rs. 142.50 (A)
Women = (190 – 152) × Re. 0.80 = Rs. 30.40 (F)
Boys = (190 – 114) × Re. 0.70 = Rs. 53.20 (F)
Rs. 58.90 (A)
Direct Labour Yield Variance = (Standard Output for Actual Time – Actual Output) × Standard Cost per Unit
= (950 – 960) × Re. 0.80 = Rs. 8 (F)
Verification:
Direct Labour Cost Variance = Direct Labour Rate Variance + Idle Time Variance
Rs. 70 (A) = Rs. 24 (F) + Rs. 50.90 (A) + Rs. 43.10 (A)
Direct Labour Efficiency Variance = Direct Labour Material Variance + Direct Labour Yield Variance
Rs. 50.90 (A) = Rs. 58.90 (A) + Rs. 8 (F)
Solution 12:
Source Table
Category Budgeted Standard Actual
hours @ hours @ Paid Idle time Worked @
I II I - II
Skilled 65 x 40 = 2,600 45 2,600/2,000 x 1,800 45 50 x 40 =2,000 50 x 2 = 100 1,900 50
= 2,340
Semi-skilled 20 x 40 = 800 30 800/12,000 x 1,800 30 30 x 40 =1,200 30 x 2 = 60 1,140 35
= 720
Unskilled 15 x 40 = 600 15 600/2,000 x 1,800 = 15 20 x 40 =800 20 x 2 = 40 760 10
540
3,600
I. Labour cost variance = Standard Cost – Actual Cost (Hours paid)
For skilled = (2,340 x 45) – (2,000 x 50) = 5,300 (F)
Semi-skilled = (120 x 30) – (1,200 x 35) = 20,400 (A)
Unskilled = (540 x 15) – (800 x 10) = 100 (F)
15,000 (A)
II. Labour efficiency variance = (SH – AH) x SR
Skilled = (2,340 – 1,900) x 45 = 19,800 (F)
Semi-skilled = (720 – 1140) x 30 = 12,600 (A)
Unskilled = (540 – 760) x 15 = 3,300 (A)
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.8
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
3,900 (F)
III. Labour idle time variance = Idle time x SR
Skilled = (100 x 45) = 4,500 (A)
Semi-skilled = (60 x 30) = 1,800 (A)
Unskilled = (40 x 15) = 600 (A)
6,900 (A)
Solution 13:
Source Table
Standard Hours for Actual Output Actual
Hours Rate Amount No. of Hours Idle time Effective Rate Amount
(Rs.) (Rs.) workers hours (5%) hours (Rs.) (Rs.)
1,040 units × 4 hours =
4,160 6 24,960 10 420 21 399 6.20 2,604
30 1,260 63 1,197 6.00 7,560
60 2,520 126 2,394 5.70 14,364
4,160 24,960 4,200 210 3,990 24,528
Labour Cost Variance = Standard Labour Cost – Actual Labour Cost
= Rs. 24,960 – Rs. 24,528 = Rs. 432 (F)
Labour Rate Variance = (Standard Rate – Actual Rate) × Actual Hours
= (Rs. 6 – Rs. 6.20) × 420 hours + (Rs. 6 – Rs. 6) × 1,260 hours + (Rs. 6 – Rs.5.70) ×
2,520 hours
= Rs. 84 (A) + 756 (F) = Rs. 672 (F)
Labour Efficiency Variance = (Standard hours for Actual Output – Actual Effective hours) × Standard Rate
= (4,160 hours – 3,990 hours) × Rs. 6 = Rs. 1,020 (F)
Labour Idle Time Variance = Standard Rate × Idle Time Hours
= Rs. 6 × 210 hours = Rs. 1,260 (A)
Working Notes:
1) Standard man hours per unit = 25 units is the standard output when 100 workers work for 1 hour. Hence
standard man hours per unit are 4.
Solution 14:
(a) (i) Actual Numbers of Workers in Each Category
Assumed Semi Skilled Workers = L
Total Labour Mix Variance = Total Actual Time Worked (hours) × [Average Standard Rate per hour of Standard
Gang Less: Average Standard Rate per hour of Actual Gang]
10,800 (A) = 4,500 hrs. × [60 – (75 x 180 hrs. x 2L+ 50 x 180 hrs. x L + 40 x 180 hrs. x (25-3L))/ 4,500 hours]
L=7
Semi- Skilled = 7 (as above)
Skilled = 14 (twice of 7)
Unskilled = 4 (balance out of 25)
(ii) Labour Rate Variance = Actual Hours Paid × (Standard Rate – Actual Rate)
Skilled Workers = 2,800 hrs. × (Rs 75 – Rs 80) = Rs 14,000 (A)
Semi- Skilled = 1,400 hrs. × (Rs 50 – Rs 48) = Rs 2,800 (F)
Unskilled Workers = 800 hrs. × (Rs 40 – Rs 42) = Rs 1,600 (A)
Total = Rs 14,000 (A) + Rs 2,800 (F) + Rs 1,600 (A) = Rs 12,800 (A)
(iii) Labour Yield Variance = Average Standard Rate per hour of Standard Gang × {Total Standard Time (hours)
Less Total Actual Time Worked (hours)}
= [Rs 2,86,875/4,781.25 hours] x [4,781.25 hrs.-4,500 hrs.] = Rs 16,875 (F)
Or
= Std. Rate x (Std. Hours – Revised Actual Hours Worked)
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.9
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
Skilled Workers = Rs 75 × (2,295 hrs. – 2,160 hrs.) = Rs 10,125 (F)
Semi-Skilled = Rs 50 × (1,530 hrs. – 1,440 hrs.) = Rs 4,500 (F)
Un Skilled Workers = Rs 40 × (956.25 hrs. – 900 hrs.) = Rs 2,250 (F)
Total = Rs 10,125 (F) + Rs 4,500 (F) + Rs 2,250 (F) = Rs 16,875 (F)
(iii) Labour Efficiency Variance = Std. Rate x (Std. Hours – Actual Hours Worked)
Skilled Workers = Rs 75 × (2,295 hrs. – 2,520 hrs.) = Rs 16,875 (A)
Semi- Skilled = Rs 50 × (1,530 hrs. – 1,260 hrs.) = Rs 13,500 (F)
Un Skilled Workers = Rs 40 × (956.25 hrs. – 720 hrs.) = Rs 9,450 (F)
Total = Rs 16,875 (A) + Rs 13,500 (F) + Rs 9,450 (F) = Rs 6,075 (F)
Working Notes:
Statement Showing “Standard & Actual Cost”
Category Standard for Actual Output Actual Revised Std Quantity
Total Hours Rate Amount Hours Rate Amount 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 ℎ𝑟𝑠 𝑀𝑖𝑥 × Std.Hrs
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑆𝑡𝑑. ℎ𝑟𝑠 𝑀𝑖𝑥
Std (Rs.) (Rs.) (Rs.) (Rs.)
for Actual Output
12Wx200H 2,160
x2295/2400= 14Wx18 2,01,6 [4,500 hours x
Skilled 2,295 75 1,72,125 0= 2,520 80 00 2295/4781.25]
8Wx200hx 1,440
Semi- 2295/2400 7Wx180 [4,500 hours x
skilled = 1,530 50 76,500 = 1,260 48 60,480 1530/4781.25]
5Wx200hx 900
Unskilled 2295/2400 4Wx180 [4,500 hours x
= 956.25 40 38,250 = 720 42 30,240 956.25/4781.25]
4,781.25 60 2,86,875 2,92,320 4,500
Solution 15:
Variable Overhead Cost Variance = (Standard hours for Actual Output × Standard hour) – Actual
Overhead
= (360 × 20 × 1.25) – 9,150 = Rs 150 (A)
Variable Overhead Expenditure Variance = (Standard Rate – Actual Rate) × Actual hours
= (1.25 – 1.3071) × 7,000 = Rs 400 (A)
Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance = (Standard hours for Actual Output – Actual hours) × Standard
Variable OH per hour = (360 × 20 – 7,000) × 1.25 = Rs 250 (F)
Working Notes:
𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝑂𝑣𝑒𝑟ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 𝑅𝑠. 10,000
(a) Variable Overhead Standard Rate per hour = 𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝐻𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑠
= 8,000 ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑠 = Rs 1.25 per hour.
𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝑂𝑣𝑒𝑟ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 𝑅𝑠. 10,000
(b) Variable Overhead Standard Rate per unit = 𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡
= 400 ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑠 = Rs 25 per unit.
(c) 8,000 hours are budgeted for 400 units
8,000 ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑠
One unit requires = 400 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑠 = 20 hour
𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑉𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝑂𝑣𝑒𝑟ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 9,150
(d) Actual Rate = 𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝐻𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑠
= 7,000
= 1.3071
Solution 16:
Workings:
1. Standard cost per unit = Rs 1,20,000/6,000units = Rs 20
2. Standard cost per hour = Rs 1,20,000/6,000units × 2hours = Rs 10
Variable Overhead Cost Variance = (Standard hours for Actual Output × Standard hour) – Actual Overhead
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.10
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
= (Rs 20 × 5,900 units) – Rs 1,22,000 = Rs 4,000 (A)
Variable Overhead Expenditure Variance = (Standard Rate – Actual Rate) × Actual hours
= (Rs 10 x 11,600 hours) – 1,22,000 = Rs 6,000 (A)
Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance = (Standard hours for Actual Output – Actual hours) × Standard Variable
OH per hour
= (2 hours x 5,900 units – 11,600 hours) × Rs 10 = Rs 2,000 (F)
Solution 18:
Fixed Overhead Cost Variance = (Standard Hours for Actual Output × Standard Rate) – Actual Overheads
= (21,220 hours × Rs 6) – 1,42,000 = Rs14,680 (A)
Fixed Overhead Expenditure Variance = (Budgeted Overheads – Actual Overheads)
= (Rs 1,44,000 – Rs 1,42,000) = Rs 2,000 (F)
Fixed Overhead Volume Variance = (Std hours for Actual output × Standard Rate) – Budgeted Overheads
= (21,220 × Rs 6) – Rs 1,44,000 = Rs 16,680 (A)
Fixed Overhead Efficiency Variance = (Standard hours for Actual output – Actual Hours) × Standard Rate
= (21,220 – 20,160) × Rs 6 = Rs 6,360 (F)
Fixed Overhead Capacity Variance = (Actual hours – Budgeted hours) × Standard Rate
= (20,160 – 24,000) × Rs 6 = Rs 23,040 (A)
Fixed Overhead Calendar Variance = (Possible Hours – Budgeted Hours) × Standard Rate
= (23,040 – 24,000) × Rs 6 = Rs 5,760 (A)
Fixed Overhead Reverse Capacity Variance = (Actual hours – Possible hours) × Standard Rate
= (20,160 – 23,040) × Rs 6 = Rs 17,280 (A)
Verification:
Fixed Overhead Cost Variance = Fixed Overhead Expenditure Variance + Fixed Overhead Volume Variance Rs
14,680 (A) = Rs 2,000 (F) + Rs 16,680 (A)
Fixed Overhead Volume Variance = FOH Efficiency Variance + FOH Capacity Variance + FOH Calendar Variance
Rs 16,680 (A) = Rs 6,360 (F) + Rs 17,280 (A) + 5,760 (A)
Working Notes:
Standard Hours for Actual Output = (5,305 Units × 4 Hours) = 21,220
𝑅𝑠. 1,44,000
Standard Rate per Hour = 24,000 ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑠 = Rs 6
Budgeted Hours = (120 Machine Hours × 25 Days × 8 Hours) = 24,000 Hours
Budgeted Overheads = Rs 1,44,000
Actual Hours = (840 Machine Hours × 24 Days) = 20,160 Hours
Actual Overheads = Rs 1,42,000
Possible Hours = (120 Machine Hours × 24 Days × 8 Hours) = 23,040 Hours
Solution 19:
1. Fixed Overhead Cost Variance = (Standard Hours for Actual Output × Standard Rate) – Actual Overheads
= (33,000 hours × Rs 1) – 31,000 = Rs 2,000 (F)
2. Fixed Overhead Expenditure Variance = (Budgeted Overheads – Actual Overheads)
= (Rs 30,000 – Rs 31,000) = Rs 1,000 (A)
3. Fixed Overhead Volume Variance = (Standard hours for Actual output × Standard Rate) – Budgeted
Overheads
= (33,000 × Rs 1) – 30,000 = Rs 3,000 (F)
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.11
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
4. Fixed Overhead Efficiency Variance = (Standard hours for Actual output – Actual Hours) × Standard Rate
= (33,000 – 31,500) × Rs 1 = Rs 1,500 (F)
5. Fixed Overhead Capacity Variance = (Actual hours – Budgeted hours) × Standard Rate
= (31,500 – 30,000) × Rs 1 = Rs 1,500 (F)
6. Fixed Overhead Calendar Variance = (Possible Hours – Budgeted Hours) × Standard Rate
= (32,400 – 30,000) × Rs 1 = Rs 2,400 (F)
7. Fixed Overhead Revised Capacity Variance = (Actual hours – Possible hours) × Standard Rate
= (31,500 – 32,400) × Rs 1 = Rs 900 (A)
Verification:
Fixed Overheads Cost Variance = Fixed Overheads Expenditure Variance + Fixed Overheads Volume Variance
Rs 2,000 (F) = Rs 1,000 (A) + Rs 3,000 (F)
Fixed Overheads Volume Variance = Fixed Overheads Efficiency Variance+Fixed Overheads Capacity Variance
Rs 3,000 (F) = Rs 1,500 (F) + Rs 1,500 (F)
Working Notes:
𝑅𝑠.30,000
● Budgeted Hours = 𝑅𝑠. 1
= 30,000 hours
30,000 𝐻𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑠
● Budgeted Hours per day = 25
= 1,200 hours
30,000 𝐻𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑠
● Standard Hours for Actual Output = 20,000 𝑈𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑠
× 22, 000 = 33,000 hours
● Standard Rate per hour = Rs 1
● Budgeted Overheads = Rs 30,000
● Actual Overheads = Rs 31,000
● Actual Hours = 31,500 hours
Possible hours = 1,200 Hours × 27 Days = 32,400 hours
Solution 21:
Overheads volume variance (in case of fixed overhead):
Standard fixed overheads per unit (SR) : Rs 3,000 (Given)
Actual production: 100 units
Standard production (capacity): 200 units
Fixed Overhead Volume Variance:
= Absorbed overhead – Budgeted Overhead
= (Rs 3,000 × 100 units) – (Rs 3,000 × 200 units) = Rs 3,00,000 – Rs 6,00,000 = Rs 3,00,000 (Adverse)
Overhead expense variances
For variable overhead:
= AQ (SR – AR)
= 100 units (Rs 1,500 – Rs1,500) = Nil
For fixed overhead:
= Budgeted Overhead – Actual Overhead
= (Rs 3,000 × 200 units) – (Total overhead – Variable overhead)
= (Rs 3,000 × 200 units) – (Rs 11,50,000 – Rs 1,500 ×100 units)
= Rs 6,00,000 – (Rs 11,50,000 – Rs 1,50,000)
= Rs 6,00,000 – Rs 10,00,000 = Rs 4,00,000 (Adverse)
Solution 22:
Variable overhead variances:
Variable Overhead Cost Variance = Standard overhead for actual production – Actual Overhead
= (Rs.1,20,000/4,000 units × 3,800 units) – Rs.1,20,000 = Rs.6,000 (A)
Variable Overhead Expenditure Variance = Standard overhead for actual hours × Actual overhead
= (Rs.1,20,000/8,000 hours x 7,800 hours) – 1,20,000 = Rs.3,000 (A)
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.12
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance = (Standard hours for Actual Output – Actual hours) × Standard Variable
OH per hour
= (1,20,000/8,000 hours) x[(8,000 hours/4,000 units x 3,800 units) – 7,800 hours]
= Rs.3,000 (A)
Fixed overhead variances:
Fixed Overhead Cost Variance = (Standard Hours for Actual Output × Standard Rate) – Actual Overheads
= (4,00,000/4,000 units x 3,800 units) – 3,90,000= Rs.10,000 (A)
Fixed Overhead Expenditure Variance = (Budgeted Overheads – Actual Overheads)
= (Rs.4,00,000 – Rs.3,90,000) = Rs.10,000 (F)
Fixed Overhead Volume Variance = (Standard hours for Actual output × Standard Rate) – Budgeted
Overheads
= (Rs.4,00,000/4,000 units x 3,800 units) – Rs.4,00,000 = Rs.20,000 (A)
Fixed Overhead Efficiency Variance = (Standard hours for Actual output – Actual Hours) × Standard
Rate
= [(2 hours x 3,800 units) – 7,800 hours) × Rs.50= Rs.10,000 (A)
Fixed Overhead Capacity Variance = (Actual hours – Budgeted hours) × Standard Rate
= [7,800 hours – 8,000/20 days x 21 days] × Rs.50= Rs.30,000 (A)
Fixed Overhead Calendar Variance = (Possible Hours – Budgeted Hours) × Standard Rate
= Rs.4,00,000/20 days x [20 days – 21 days) = Rs.20,000 (F)
Solution 23:
Working Notes
Fixed Overheads = Budgeted Fixed Overheads = ₹ 12,00,000 ₹ 10
Budgeted Output 1,20,000 units
Fixed Overheads element in Semi-Variable overheads i.e. 60% of ₹ 1,80,000 ₹ 1,08,000
Fixed Overheads =
𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝐹𝑖𝑥𝑒𝑑𝑂𝑣𝑒𝑟ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑𝑠
=
₹ 1,08,000 ₹ 0.90
𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡 1,20,000 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑠
Standard rate of Absorption of Fixed Overheads per units (₹ 10 + ₹ 0.90) ₹ 10.90
Fixed overheads absorbed on 8,000 units @ ₹ 10.90 ₹ 87,200
Budgeted Variable Overheads ₹ 6,00,000
Add: Variable element in Semi-variable overheads 40% of ₹ 1,80,000 ₹ 72,000
Total Budgeted Variable Overheads ₹ 6,72,000
Standard variable Cost per unit =
𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝑂𝑣𝑒𝑟ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑𝑠
=
₹ 6,72,000 ₹ 5.60
𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡 1,20,000 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑠
Standard Variable Overheads for 8,000 units @ ₹ 5.60 ₹ 44,800
Budgeted Annual Fixed Overheads (₹ 12,00,000 + 60% of ₹ 1,80,000) ₹ 13,08,000
Possible Fixed Overheads =
𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝐹𝑖𝑥𝑒𝑑 𝑂𝑣𝑒𝑟ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑𝑠
x Actual days ₹ 1,03,550
𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝐷𝑎𝑦𝑠
₹ 1,09,000
= 20 𝐷𝑎𝑦𝑠
x 19 days
Actual Fixed Overheads (₹ 1,10,000 + 60% of ₹ 19,200) ₹ 1,21,520
Actual Variable Overheads (₹ 48,000 + 40% of ₹ 19,200) ₹ 55,680
Computation of Variances
Overhead Cost Variable = Absorbed Overheads – Actual Overheads
= (₹ 87,200 + ₹ 44,800) – (₹ 1,21,520 + ₹ 55,680)
= ₹ 45,200 (A)
Fixed Overhead cost Variance = Absorbed Fixed Overheads – Actual Fixed Overheads
= ₹ 87,200 – ₹ 1,21,520
= ₹ 34,320 (A)
Variable Overhead Cost Variance = Standard Variable Overheads for Production – Actual Variable Overheads
= ₹ 44,800 – ₹ 55,680
= ₹ 10,880 (A)
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.13
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
Fixed Overhead Volume Variance = Absorbed Fixed Overheads – Budgeted Fixed Overheads
= ₹ 87,200 – ₹ 1,09,000
= ₹ 21,800 (A)
Fixed Overhead Expenditure Variance = Budgeted Fixed Overheads – Actual Fixed Overheads
= ₹ 10.90 × 10,000 units – ₹ 1,21,520
= ₹ 12,520 (A)
Calendar Variance = Possible Fixed Overheads – Budgeted Fixed Overheads
= ₹ 1,03,550 – ₹ 1,09,000
= ₹ 5,450 (A)
OR
Calendar Variance = (Actual days – Budgeted days) x Standard fixed overhead rate per day
Standard fixed overhead rate per day = 1308000/20*12 = ₹ 5450
Fixed Overhead Calendar Variance = (19-20) x 5450 = 5450(A)
Solution 34:
Variable Overhead Variances
● Variable Overhead Cost Variance = (Actual output × Standard Rate Per Unit ) – Actual Overhead
= (8,000 × 0.056) – {480 + (192 × 40%)} = Rs. 108.80 (A)
Fixed Overhead Variances
● Fixed Overhead Cost Variance = (Actual output × Standard Rate Per Unit ) – Actual Overhead
= (8,000 × 0.109) – {1,190 + (192 × 60%)} = Rs. 433.20 (A)
● Fixed Overhead Expenditure Variance = Budgeted Overhead – Actual Overhead
= {12,000/12 + (1,800/12 × 60%]} – 1,305.20 = Rs. 215.20 (A)
● Fixed Overhead Volume Variance = (Actual output × Standard Rate Per Unit) – Budgeted
Overhead
= (8,000 × 0.109) –1,090 = Rs. 218 (A)
● Fixed Overhead Calendar Variance = Possible Fixed Overheads – Budgeted Fixed Overheads
= 1,090 × 19/20 – 1,090 = Rs. 54.50 (A)
Working Notes:
𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑂𝐻 𝑅𝑠. [6,000+(1,800×40%)]
(a) VOH Standard Rate per unit = 𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡 = 1,20,000 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑠
= Rs. 0.056 p.u.
𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝐹𝑂𝐻 𝑅𝑠. [12,000+(1,800×60%)]
(b) FOH Standard Rate per unit = 𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡
= 1,20,000 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑠
= Rs. 0.109 p.u.
Solution 25:
Working:
𝐷𝑖𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑜𝑣𝑒𝑟ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 𝑎𝑡 𝑡𝑤𝑜 𝑙𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑙𝑠 𝑅𝑠.2,10,000−𝑅𝑠.1,80,000
a) Variable overhead rate per unit = 𝐷𝑖𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑠 = 10,000 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑠−8,000 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑠
= Rs 15
b) Fixed overhead = Rs 1,80,000 – (8,000 units x Rs 15) = Rs 60,000
𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑜𝑣𝑒𝑟ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 𝑎𝑏𝑠𝑜𝑟𝑝𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑅𝑠.20
c) Standard hours per unit of production = 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑝𝑒𝑟 ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟
= 𝑅𝑠.4
= 5 hours
𝑉𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝑜𝑣𝑒𝑟ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡 𝑅𝑠. 15
d) Standard variable overhead rate per hour = 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡
= 5 ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑠 = Rs 3
e) Standard fixed overhead rate per hour = Rs 4 – Rs 3 = Rs 1
f) Actual variable overhead = Rs 2,95,000 – Rs 62,500 = Rs 2,32,500
𝑅𝑠.2,32,500
g) Actual variable overhead rate per hour = 74,000 ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑠 = Rs 3.1419
h) Budgeted hours = 12,000 units x 5 hours = 60,000 hours
i) Standard hours for actual production = 15,560 units x 5 hours = 77,800 hours
Variable overhead Efficiency and Expenditure Variance:
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.14
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
Variable overhead Efficiency variance = Standard rate per hour (Standard hours – Actual hours)
= Rs 3 (77,800 hours – 74,000 hours) = Rs 11,400 (F)
Variable overhead Expenditure variance = Actual hours (Std. rate – Actual rate)
= 74,000 hours (Rs 3 – Rs 3.1419)
Fixed Overhead Efficiency and Capacity Variance:
Fixed overhead Efficiency Variance = Standard rate per hour (Standard hours – Actual hours)
= Rs 1 (77,800 hours – 74,000 hours)
= Rs 3,800 (F)
Fixed overhead Capacity Variance = Standard rate per hour (Actual hours – Budgeted hours)
= Rs 1 (74,000 hours – 60,000 hours)
= Rs 74,000 – Rs 60,000 = Rs 14,000 (F)
Solution 26:
Source Table
Particulars Standard for Actual Output Actual
Qty./Hours Rate (Rs.)Amount (Rs.) Qty./Hours Rate (Rs.) Amount(Rs.)
Material 5 × 5,120 = 25,600 4.20 1,07,520 25,700 1,35,000/30,000 = 4.5 1,15,650
Labour 3 × 5,120 = 15,360 3 46,080 15,150 3.20 48,480
Direct Material Variances
Direct Material Cost Variance = Standard Cost – Actual Cost
1,35,000
= 21 × 5,120 – 30,000 × 25,700 = Rs. 8,130 (A)
Direct Material Price Variance = (Standard Price – Actual Price) × Actual Quantity
= (4.2 – 4.5) × 2,570 = Rs. 7,710 (A)
Direct Labour
Direct Material Quantity Variance = (Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity) × Standard
Variances
= Price (5 × 5,120 – 25,700) × 4.2 = Rs. 420 (A)
Direct Labour
Cost Variance
= (Standard Hours for Actual Output × Standard Rate) – (Actual Hours × Actual Rate)
= (5,120 × 3 × 3) – 48,480 = Rs. 2,400 (A)
Direct Labour Rate Variance = (Standard Rate – Actual Rate) × Actual Hours
= (3 – 3.2) × 15,150 = Rs. 3,030 (A)
Direct Labour Efficiency Variance = (Standard Hours for Actual Output – Actual Hours) × Standard Rate
= (5,120 × 3 – 15,150) × 3 = Rs. 630 (F)
Solution 27:
Direct Material Variances:
Source Table
Material Standard for Actual Output Actual
Qty./Hours Rate (Rs.) Amount (Rs.) Qty./Hours Rate (Rs.) Amount (Rs.)
A 12,000 4 48,000 12,500 4.40 55,000
B 18,000 3 54,000 18,000 2.80 50,400
C 90,000 1 90,000 88,500 1.20 1,06,200
1,20,000 1,92,000 1,19,000 2,11,600
Labour 18,000 8 1,44,000 2,500 12 30,000
15,000 8 1,20,000
18,000 1,44,000 17,500 1,50,000
1. Direct Material Cost =(Standard Cost – Actual Cost)
Variance =1,92,000 – 2,11,600 = Rs. 19,600 (A)
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.15
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
2. Direct Material Price Variance = (Standard Price – Actual Price) × Actual Quantity
A =(Rs. 4 – Rs. 4.40) × 12,500 = Rs. 5,000 (A)
B =(Rs. 3 – Rs. 2.80) × 18,000 = Rs. 3,600 (F)
C =(Re. 1 – Rs. 1.20) × 88,500 = Rs. 17,700 (A)
= Rs. 19,100 (A)
3. Direct Material Usage =(Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity) × Standard Price
Variance
A =(12,000 – 12,500) × Rs. 4 = Rs. 2,000 (A)
B =(18,000 – 18,000) × Rs. 3 = Nil
C =(90,000 – 88,500) × Re. 1 = Rs. 1,500 (F)
= Rs. 500 (A)
Direct Labour Variances:
1. Direct Labour Cost Variance =Standard Cost – Actual Cost
=1,44,000 – 1,50,000 = Rs. 6,000 (A)
2. Direct Labour Rate Variance =(Standard Rate per hour – Actual rate per hour) × Actual hours
=(Rs. 8 – Rs. 12) × 2,500 + 15,000 (Rs. 8 – Rs. 8) =Rs. 10,000 (A)
3. Direct Labour Efficiency =(Standard Labour hours – Actual Labour hours) × Standard Rate
Variance
=(18,000 hours – 17,500 hours) × Rs. 800 = Rs. 4,000 (F)
Solution 28:
(i) Material Usage Variance = Std. Price (Std. Quantity – Actual Quantity)
= ₹ 90 (9,000 kg. – 8,900 kg.)
= ₹ 9,000 (Favorable)
(ii) Material Price Variance = Actual Quantity (Std. Price – Actual Price)
= 8,900 kg. (₹ 90 – ₹ 92) = ₹ 17,800 (Adverse)
(iii) Material Cost Variance = Std. Material Cost – Actual Material Cost
= (SQ × SP) – (AQ × AP)
= (9,000 kg. × ₹ 90) – (8,900 kg. × ₹ 92)
= ₹ 8,10,000 – ₹ 8,18,800
= ₹ 8,800 (Adverse)
(iv) Labour Efficiency Variance = Std. Rate (Std. Hours – Actual Hours)
= ₹ 80[(9000/10) x 800hrs. – 7,000 hrs.)
= ₹ 80 (7,200 hrs. – 7,000 hrs.)
= ₹ 16,000 (Favorable)
(v) Labour Rate Variance = Actual Hours (Std. Rate – Actual Rate)
= 7,000 hrs. (₹ 80 – ₹ 84)
= ₹ 28,000 (Adverse)
(vi) Labour Cost Variance = Std. Labour Cost – Actual Labour Cost
= (SH × SR) – (AH × AR)
= (7,200 hrs. × ₹ 80) – (7,000 hrs. × ₹ 84)
= ₹ 5,76,000 – ₹ 5,88,000
= ₹ 12,000 (Adverse)
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.16
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
(vii) Variable Cost Variance = Std. Variable Cost – Actual Variable Cost
= (7,200 hrs. × ₹ 20) – ₹ 1,40,000
= ₹ 4,000 (Adverse)
(viii) Fixed Overhead Cost Variance = Absorbed Fixed Overhead – Actual Fixed Overhead
= (₹ 250/10) x 9000kgs.) – ₹ 2,60,000
= ₹ 2,25,000 – ₹ 2,60,000 = ₹ 35,000 (Adverse)
Solution 29:
Source Table
Particulars Standard for Actual Actual
Qty/ hours Rate Amount (Rs.) Qty/hours Rate Amount (Rs.)
Material 18,000 4 72,000 19,000 4.4 83,600
Labour 4,500 4 18,000 4,950 5 24,750
(a) Standard Cost Card (Per Unit)
Particulars Amount (Rs.)
Direct Material (10 pieces @ Rs. 4 per piece) 40
Direct Labour (2.5 hours @ Rs. 4 per hour) 10
Fixed Overheads (2.5 hours @ Rs. 8 per hour) 20
Total Standard Cost 70
(b) Material Variances:
● Material Cost Variance = Standard Cost of Material for Actual Output – Actual Material Cost
= (1,800 × 10 pieces × Rs. 4) – (Rs. 88,000/20,000) × 19,000
= Rs. 72,000 – Rs. 83,600 = Rs. 11,600 (A)
● Material Price Variance = (Standard Price per piece – Actual Price per piece*) × Actual
Quantity
= (Rs. 4 – Rs. 4.40) × 19,000 pieces = Rs. 7,600 (A)
*Actual Cost of Material per piece = 𝑅𝑠.88,000 = Rs. 4.40
20,000 𝑝𝑖𝑒𝑐𝑒𝑠
● Material Usage Variance = (Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity) × Standard Price
= (18,000 pieces – 19,000 pieces) × Rs. 4 = Rs. 4,000 (A)
Verification:
Total Material Cost Variance = Material Price Variance + Material Usage Variance
Rs. 11,600 (A) = Rs. 7,600 (A) + Rs. 4,000 (A)
Labour Variances:
● Total Labour Cost Variance = Standard Cost of Labour for Actual Output – Actual Labour Cost
= (1,800 × 2.5 hours × Rs. 4) –Rs.24,750
= Rs. 18,000 – Rs. 24,750 =Rs. 6,750 (A)
● Labour Rate Variance = (Standard Rate per hour – Actual Rate per hour) × Actual hours
= (Rs. 4 – Rs. 5) × 4,950 hours = Rs. 4,950 (A)
● Labour Efficiency = (Standard hours – Actual hours) × Standard Rate
Variance = (2.5 hours × 1,800 – 4,950 hours) × Rs. 4
= (4,500 hours – 4,950 hours) × Rs. 4
= 450 hours (A) × Rs. 4 = Rs. 1,800 (A)
Verification:
Total Labour Cost Variance = Labour Rate Variance + Labour Efficiency Variance
Rs. 6,750 (A) = Rs. 4,950 (A) + Rs. 1,800 (A)
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.17
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
Fixed Overhead Variances:
● Total Fixed Overhead = (Overheads recovered on Actual Output – Actual Overheads)
Cost Variance
= (1,800 units × 2.5 hours × Rs. 8 – Rs. 44,000)
= Rs. 36,000 – Rs. 44,000 = Rs. 8,000 (A)
● Fixed Overhead = (Budgeted Fixed Overhead – Actual Fixed Overhead)
Expenditure Variance = Rs. 40,000 – Rs. 44,000 = Rs. 4,000 (A)
● Fixed Overhead Efficiency = (Standard hours for Actual Output – Actual hours) × Standard
Variance Fixed Overhead
= (2.5 hours × 1,800 – 4,950 hours) × Rs. 8
= (4,500 hours – 4,950 hours) × Rs. 8 = Rs. 3,600 (A)
● Fixed Overhead Capacity = (Actual Capacity hours – Budgeted Capacity hours*) ×
Variance Standard Rate per hour
= (Rs. 4,950 – 5,000) × Rs. 8 = Rs. 400 (A)
𝐹𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑦 𝑂𝑣𝑒𝑟ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 𝐵𝑢𝑑𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑅𝑠.40,000
*Budgeted Capacity hours = 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑂𝑣𝑒𝑟ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 𝑝𝑒𝑟 ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟 = 8
= 5,000 hours
Verification:
Total Fixed Overhead Cost = FOH Expenditure Variance + FOH Efficiency Variance + FOH
Variance Capacity Variance
Rs. 8,000 (A) = Rs. 4,000 (A) + Rs. 3,600 (A) + Rs. 400 (A)
Solution 30:
Source Table
Particulars Standard for Actual Actual
Qty/ hours Rate Amount (Rs.) Qty/hours Rate Amount (Rs.)
Material 18,750 × 1.5 = 28,125 6 1,68,750 29,860 5.25 1,56,765
Labour 18,750 × 6 = 1,12,500 5 5,62,500 1,18,125 6 7,08,750
VOH 18,750 × 6 = 1,12,500 4 4,50,000 1,18,125 4.5 5,25,000
(i) Direct Material Usage Variance = (Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity) × Standard Rate
= (28,125 – 29,860) × 6 = Rs. 10,410 (A)
Direct Material Price Variance = (Standard Rate – Actual Rate) × Actual Quantity
= (6 – 5.25) × 29,860 = Rs. 22,395 (F)
(ii) Direct Labour Efficiency Variance = (Standard Hours – Actual Hours) × Standard Rate
= (1,12,500 – 1,12,525) × 5 = Rs. 28,125 (A)
Direct Labour Rate Variance = (Standard Rate – Actual Rate) × Actual Hours
= (6 – 5) × 1,18,125 = Rs. 1,18,125 (A)
(iii) Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance = (Standard Hours for Actual Output – Actual Hours) ×
Standard Variable OH per Hour
= (1,12,500 – 1,18,125) × 4 = Rs. 22,500 (A)
Variable Overhead Expenditure Variance = (Standard Rate – Actual Rate) × Actual Hours
= (4 – 4.4445) × 1,18,125 = Rs. 52,500 (A)
(iv) Fixed Overhead Volume Variance = (Actual Output × Standard Rate) – Budgeted Overhead
= (18,750 × 3) – (20,000 × 3)
= 56,250 – 60,000 = Rs. 3,750 (A)
Fixed Overhead Expenditure Variance =Budgeted Overhead – Actual Overhead
=(20,000 × 3) – 40,000 = Rs. 20,000 (F)
Particulars Budgeted Actual
Quantity Rate Amount (Rs.) Quantity Rate Amount (Rs.)
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.18
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
Sales 20,000 72 14,40,000 18,750 72 13,50,000
(i) Sales Volume Variance = (Actual Quantity – Budgeted Quantity) × Standard Rate
= (18,750 – 20,000) × 72 = Rs. 90,000 (A)
Sales Margin Volume Variance = (Actual Sales Quantity – Standard Sales Quantity) × Standard Profit
= (18,000 – 20,000) × 6 = Rs. 7,500 (A)
Working Notes:
Budgeted Price = Actual Price
∴ Budgeted Margin = Actual Margin
Budgeted Margin = Price – Standard Cost
= 72 – (9 + 30 + 24 + 3)
= Rs. 6
Solution 31:
(i) Statement showing Flexible Budget and its comparison with actual
Flexible budget (at Actual for
Particulars Master Budget standard cost) 72,000 units Variance
Per unit (b)
(80,000 =
units) (a) (a/80,000) (c) = 72,000 × (b) (d) (e) = (d) – (c)
Sales 3,20,000 4.00 2,88,000 2,80,000 8,000 (A)
Less: Direct Material (80,000) (1.00) (72,000) (73,600) 1,600(A)
Direct Wages (1,20,000) (1.50) (1,08,000) (1,04,800) 3,200 (F)
Variable Overhead (40,000) (0.50) (36,000) (37,600) 1,600 (A)
Contribution 80,000 1.00 72,000 64,000 8,000 (A)
Less: Fixed Overhead (40,000) (0.50) (36,000) (39,200) 3,200 (A)
Net Profit 40,000 0.50 36,000 24,800 11,200 (A)
(ii) Calculation of Variances
Source Table
Particulars Standard for Actual Actual
Qty/ hours Rate Amount (Rs.) Qty/hours Rate Amount (Rs.)
Material 72,000 × 1 = 72,000 1.00 72,000 78,400 0.93878 73,600
Labour 72,000 × 1 = 72,000 1.50 1,08,000 70,400 1.48863 1,04,800
VOH 72,000 × 1 = 72,000 0.50 36,000 70,400 0.53409 37,600
Material Variances:
Direct Material Price Variance = (Standard Rate – Actual Rate) × Actual Quantity
= (1.00000 – 0.93878) × 78,400 = Rs. 4,800 (F)
Direct Material Usage Variance = (Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity) × Standard Rate
= (72,000 – 78,400) × 1.0 = Rs. 6,400 (A)
Direct Material Cost Variance = Standard Cost for actual output – Actual Cost
= 72,000 – 73,600 = Rs. 1,600 (A)
Labour Variances
Direct Labour Rate Variance = (Standard Rate – Actual Rate) × Actual Hour
= (1.50000 – 1.48863) × 70,400 = Rs. 800 (F)
Direct Labour Efficiency = (Standard Hour – Actual Hour) × Standard Rate
= (72,000 – 70,400) × 1.50 = Rs. 2,400 (F)
Direct Labour Cost Variance = Standard Cost for Actual Output – Actual Cost
= 1,08,000 – 1,04,800 = Rs. 3200 (F)
Variable Overhead Variances
Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance = (Standard hours for actual output – Actual hours) × Standard
Variable OH per hour
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.19
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
= (72,000 – 70,400) × 0.50 = Rs. 800 (F)
Variable Overhead Expenditure Variance = (Standard Rate – Actual Rate) × Actual hours
= (0.50 – 0.53409) × 70,400 = Rs. 2,400 (A)
Variable Overhead Cost Variance = Standard Cost – Actual Cost
= (36,000 – 37,600) = Rs. 1,600 (A)
Fixed Overhead Variances:
Fixed Overhead Volume Variance = (Actual output × Standard Rate) – Budgeted Overhead
= (72,000 × 0.50) – 40,000 = Rs. 4,000 (A)
Fixed Overhead Expenditure Variance = Budgeted Overhead – Actual Overhead
= (40,000 – 39,200) = Rs. 800 (F)
Fixed Overhead Cost Variance = (Standard Cost) – Actual Cost
= (36,000 – 39,200) = Rs. 3,200 (A)
Sales Variance
Sales Volume Variance = (Actual Quantity – Budgeted Quantity) × Budgeted Profit
= (72,000 – 80,000) × 0.50 = Rs. 4,000 (A)
Working Notes:
Budgeted Margin = Price – Standard Cost
= 4.00 – 3.50 = Rs.0.50 per unit
Solution 32:
(i) Material Cost , price and usage variance
Material cost variance ( on the basis of consumed quantity)
= SQ × SP – AQ Consumed × AP
= (5 kg. × 62,000 units × ₹ 15) - (3,20,000 kg. × ₹ 14)
= ₹ 46,50,000 - ₹ 44,80,000
= ₹ 1,70,000 (F)
Alternatively,
Material Cost Variance (on the basis of purchased quantity)
= SQ × SP – AQ Purchase × AP
= 3,10,000 × ₹ 15 – 3,50,000 × ₹ 14
= ₹ 2,50,000 (A)
Material Price Variance (on the basis of consumed quantity)
= AQ Consumed × SP – AQ Consumed × AP
= (3,20,000 kg. × ₹ 15) - (3,20,000 kg. × ₹ 14)
= ₹ 3,20,000 (F)
Alternatively,
Material Price Variance (on the basis of purchased quantity)
= (SP – AP) × AQPurchase
= (₹ 15 - ₹ 14) × 3,50,000 = ₹ 3,50,000 (F)
Material Usage Variance = SP × SQ – SP × AQ Consumed
= (₹ 15 × 5 kg. × 62,000 units) – (₹ 15 × 3,20,000 kg.)
= ₹ 46,50,000 – ₹ 48,00,000
= ₹ 1,50,000 (A)
(ii) Labour cost Variance = SH × SR – AH × AR
= 2,48,000 hours × ₹ 20 – 2,20,000 hours × ₹ 21
= ₹ 49,60,000 – ₹ 46,20,000
= ₹ 3,40,000 (F)
Rate Variance = (SR – AR) × AH
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.20
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
= (₹ 20 – ₹ 21) × 2,20,000 = 2,20,000 (A)
Efficiency Variance = (SH – AH) × SR
= (2,48,000 – 2,20,000) × ₹ 20
= 5,60,000 (F)
(iii) Hours Saved = 2,48,000 – 2,20,000 = 28000 hrs.
Bonus Rate = ₹ 20 × 50% = ₹ 10
Bonus = 28,000 × ₹ 10 = ₹ 2,80,000
Solution 33:
SR – Standard Labour Rate per hour
AR – Actual Labour rate per hour
SH – Standard Hours
AH – Actual Hours
(i) Labour rate variance = AH (SR – AR)
-1,53,846 = 25,641 (12 – AR)
- 6 = 12 – AR
AR = ₹ 18
(ii) Labour Efficiency = SH/AH x 100 = 105.3
SH = AH x 105.3/100 = 25,641 x 105.3/100
SH = 26,999.973
SH = 27,000 hours
(iii) Labour Efficiency variance = SR (SH – AH)
= 12 (27,000 – 25,641)
= ₹ 16,308 (F)
(iv) Standard Labour Cost per unit = 27,000 x 12/9,000 = ₹ 36
(v) Actual Labour Cost per unit = 25,641 x 18/9,000 = ₹ 51.282
Solution 34:
Basic Calculations:
Standard for 20,000 kg. Actual for 20,000 kg.
Qty. Rate Amount Qty. Rate Amount
Kg. (₹) (₹) Kg. (₹) (₹)
A 10,000 25 2,50,000 11,000 23 2,53,000
B 7,000 45 3,15,000 7,500 48 3,60,000
C 5,000 55 2,75,000 4,500 60 2,70,000
Total 22,000 8,40,000 23,000 8,83,000
Calculation of Variances:
(i) Material Cost Variance = Std. Cost for actual output–Actual cost
MCV=8,40,000– 8,83,000 = ₹ 43,000(A)
(ii) Material Price Variance = (SP–AP) × AQ
A = (25 - 23) x 11,000 = 22,000 (F)
B = (45 – 48) x 7,500 = 22,500 (A)
C = (55 – 60) x 4,500 = 22,500 (A)
23000 (A)
(iii) Material Usages Variance = (SQ–AQ) × SP
A = (10,000 – 11,000) x 25 = 25,000 (A)
B = (7,000 – 7,500) x 45 = 22,500 (A)
C = (5,000 – 4,500) x 55 = 27,500 (F)
20,000 (A)
(iv) Material Yield Variance = (SQ–RSQ*) × SP
A = (10,000 – 10,454.54) x 25 = 11,363.5(A)
B = (7,000 – 7,318.18) x 45 = 14,318.1(A)
C = (5,000 – 5,227.27) x 55 = 12,500(A)
38,181.6(A)
*Revised Standard Quantity (RSQ)
10,000
A = 22,000 × 23,000 = 10,454.54
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.21
STANDARD COSTING - SOLUTION FT
7,000
B = 22,000 × 23,000 = 7,318.18
5,000
C= 22,000
× 23,000 = 5,227.27
Material Yield Variance can also be Calculated as below
Material yield variance = Standard cost per unit (Actual yield – Standard yield)
₹8,40,000
Standard cost per unit = 20,000 = ₹ 42
20,000
New Standard Yield = 22,000
× 23,000 = 20,909
Material yield variance = ₹ 42 (20,000 – 20,909)
= ₹ 38,178 (A)
CA Nitin Guru | www.edu91.org 12.22
You might also like
- 7166materials Problems-Standard CostingDocument14 pages7166materials Problems-Standard CostingLumina JulieNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing & Variance AnalysisDocument19 pagesStandard Costing & Variance AnalysisFUNTV5No ratings yet
- 18-10-SA-V1-S1 Solved Problems SC PDFDocument14 pages18-10-SA-V1-S1 Solved Problems SC PDFAlbsNo ratings yet
- Sub-Usage Variance: MaterialDocument1 pageSub-Usage Variance: Materialpatleashish3No ratings yet
- PROBLEMSChap 7 SMDocument27 pagesPROBLEMSChap 7 SMVillena Divina VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsAlbsNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsyanbladeNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsShruti BannerjeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsAfsahNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsShubham NamdevNo ratings yet
- 18 10 SA V1 S1 Solved Problems SC PDFDocument14 pages18 10 SA V1 S1 Solved Problems SC PDFTheVagabond HarshalNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDerrick de los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical Problemskiran shettyNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical Problemsyousuf AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsRuchi pariharNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsNeelima Varma NadimpalliNo ratings yet
- Determination: IntroductionDocument1 pageDetermination: Introductionpatleashish3No ratings yet
- Standard Costing Example SolutionDocument2 pagesStandard Costing Example SolutionVikas KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing With Solutions: SolutionDocument3 pagesStandard Costing With Solutions: Solution777priyankaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial Accounting Canadian 5th Edition Brewer Solutions Manual DownloadDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Managerial Accounting Canadian 5th Edition Brewer Solutions Manual DownloadWm Mcgranahan100% (28)
- Silo - Tips Standard Costing With SolutionsDocument65 pagesSilo - Tips Standard Costing With SolutionsAlbert MuzitiNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing & Variance AnalysisDocument18 pagesStandard Costing & Variance AnalysisMahesh G VNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing 2Document69 pagesStandard Costing 2Jash SanghviNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 AnswerDocument7 pagesTutorial 4 AnswernajihahNo ratings yet
- MCV MPVDocument8 pagesMCV MPVHarsh MittalNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing: 1. Single MaterialDocument7 pagesStandard Costing: 1. Single MaterialManisha KhatriNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting and Decision Making: Submitted ByDocument12 pagesManagement Accounting and Decision Making: Submitted ByKavisha singhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Solutions - Inclass ExercisesDocument12 pagesChapter 10 Solutions - Inclass ExercisesSummerNo ratings yet
- It Will Be Recalled From The Previous Section That A Variance Is The Difference Between Standard Cost and Actual CostDocument4 pagesIt Will Be Recalled From The Previous Section That A Variance Is The Difference Between Standard Cost and Actual CostBisag AsaNo ratings yet
- 1920-1-ACCO 20073 - Solutions To STD Cost ProblemsDocument4 pages1920-1-ACCO 20073 - Solutions To STD Cost ProblemsRaegharp Constantioul100% (1)
- STANDARD COSTING With GP VARIANCE ANALYSIS KEY ANSWERSDocument19 pagesSTANDARD COSTING With GP VARIANCE ANALYSIS KEY ANSWERSaziel caith florentinNo ratings yet
- ItunganDocument8 pagesItunganIjal dhiaulhaqNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing: Cost AccountingDocument15 pagesStandard Costing: Cost Accountingwilson pribadiNo ratings yet
- Board of Studies Academic Chapter 13 Standard Costing Practice Question File 3 1649748588Document29 pagesBoard of Studies Academic Chapter 13 Standard Costing Practice Question File 3 1649748588samueladino876No ratings yet
- Standard Costing (I) - SolutionsDocument3 pagesStandard Costing (I) - Solutions行歌No ratings yet
- Standard Costing With Solution-1Document11 pagesStandard Costing With Solution-1jikuenterprise789No ratings yet
- Ch05 Traditional Overheads Versus Activity-Based CostingDocument15 pagesCh05 Traditional Overheads Versus Activity-Based CostingAndrew ChongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Variance Analysis)Document57 pagesChapter 6 (Variance Analysis)annur azalillahNo ratings yet
- MAF Mixed and Yield Variances (Eng)Document8 pagesMAF Mixed and Yield Variances (Eng)BirukNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 (Individu)Document13 pagesChapter 12 (Individu)Rahmatul MaghfirohNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument16 pagesStandard CostingJash SanghviNo ratings yet
- Soal 1: 1. Computed Equivalent Unit For Production CostDocument10 pagesSoal 1: 1. Computed Equivalent Unit For Production CostRaihan Rohadatul 'AisyNo ratings yet
- HbjhjhjhujuhjDocument14 pagesHbjhjhjhujuhjnjkjhNo ratings yet
- FOH Rate Rp.180.000.000: Jawaban Soal 1: 1. PT. Kopindo Persada RP 6.000 / DLH 30.000 Traditional CostingDocument4 pagesFOH Rate Rp.180.000.000: Jawaban Soal 1: 1. PT. Kopindo Persada RP 6.000 / DLH 30.000 Traditional Costingabd storeNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument11 pagesStandard CostinganishaNo ratings yet
- Item To Classify Standard Actual Type of VarianceDocument7 pagesItem To Classify Standard Actual Type of Variancedavid johnsonNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Personnel and DivisionsDocument37 pagesEvaluating Personnel and DivisionsGaluh Boga KuswaraNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document22 pagesCH 14Rizza Mae EudNo ratings yet
- M11 CHP 10 1 Standard Costs 2011 0524Document58 pagesM11 CHP 10 1 Standard Costs 2011 0524Rose Ann De Guzman67% (3)
- © The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2015. All Rights Reserved. Solutions Manual, Chapter 10 21Document3 pages© The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2015. All Rights Reserved. Solutions Manual, Chapter 10 21RanaNo ratings yet
- Fact Pattern: Example 10.5 (Direct Material Cost Variances)Document9 pagesFact Pattern: Example 10.5 (Direct Material Cost Variances)Saiyed KosinNo ratings yet
- Problem10 18 and 10 20Document9 pagesProblem10 18 and 10 20DhanushaNo ratings yet
- Problem 2 of STD CostingDocument3 pagesProblem 2 of STD CostingBiswajit BNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting Asia Pacific 1st Edition Mowen Solutions ManualDocument29 pagesManagerial Accounting Asia Pacific 1st Edition Mowen Solutions Manualdonaldvioleti7o100% (21)
- Chapter 12Document13 pagesChapter 12mikeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Standard Costing Nov 2020 2Document112 pagesChapter 12 Standard Costing Nov 2020 2Kunal KuvadiaNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance Analysis: 22. A. Total Purchases AP × AQDocument7 pagesStandard Costing and Variance Analysis: 22. A. Total Purchases AP × AQShaira UnggadNo ratings yet
- Analisa Usahatani Produksi Buah Melon Luas 1000 M : Jumlah RP 3.471.500Document6 pagesAnalisa Usahatani Produksi Buah Melon Luas 1000 M : Jumlah RP 3.471.500Agung Dwi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument2 pagesRRLMary Joyce CacoNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Dan StatistikaDocument11 pagesEvaluasi Dan StatistikaAmrita Oza NabillaNo ratings yet
- Downstream Petroleum Sector and Fuel Quality: The Quality of Transport FuelsDocument7 pagesDownstream Petroleum Sector and Fuel Quality: The Quality of Transport Fuelssanjayshah99No ratings yet
- Bid Evaluation GuidelineDocument11 pagesBid Evaluation GuidelineJanith Saumya BandaraNo ratings yet
- Resale Rights - The Alternative: A Must Have Guide For All Resellers and Those in The Making!Document18 pagesResale Rights - The Alternative: A Must Have Guide For All Resellers and Those in The Making!CarlosNo ratings yet
- ExxonMobil Aptitude Test 1Document21 pagesExxonMobil Aptitude Test 1Michael WestNo ratings yet
- Nabus Vs PacsonDocument8 pagesNabus Vs PacsonGladys BantilanNo ratings yet
- Business Plan ENT300 SlaynitizerDocument47 pagesBusiness Plan ENT300 Slaynitizerimran roslan100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Index NumberDocument6 pagesChapter 11 Index Numbersharkfin1403100% (1)
- Holy Family Tender For Lab Items Due On 19-04-2022Document27 pagesHoly Family Tender For Lab Items Due On 19-04-2022Naveed ShahNo ratings yet
- PROCESS COSTING - CW - ExamplesDocument12 pagesPROCESS COSTING - CW - Exampleskushgarg627100% (1)
- Man TparDocument10 pagesMan TparFrederick GbliNo ratings yet
- European Purchase Terms - EnglishDocument21 pagesEuropean Purchase Terms - EnglishgheNo ratings yet
- Ford's Marketing PlanDocument12 pagesFord's Marketing PlanHanna Vanya100% (2)
- Aptitude Shortcuts and General FormulaeDocument6 pagesAptitude Shortcuts and General FormulaeNive AdmiresNo ratings yet
- Fin 121 Answer KeyDocument21 pagesFin 121 Answer KeyDC AranetaNo ratings yet
- Business Understanding of Flower ShopDocument42 pagesBusiness Understanding of Flower ShopMariana Melo RobertoNo ratings yet
- Tesco PLC: A Critical Review On It'S Key Practices People, Marketing, Operations and FinanceDocument21 pagesTesco PLC: A Critical Review On It'S Key Practices People, Marketing, Operations and FinanceNick1No ratings yet
- đề cương thi KTQTDocument51 pagesđề cương thi KTQTHoàng LâmNo ratings yet
- ECONOMICS P1 M18 To J22 C.VDocument428 pagesECONOMICS P1 M18 To J22 C.VsukaNo ratings yet
- Materials Management Business Blueprint V1.0Document27 pagesMaterials Management Business Blueprint V1.0shailNo ratings yet
- Indian Economy Indian Economy: (General Studies)Document152 pagesIndian Economy Indian Economy: (General Studies)LovyNo ratings yet
- MKT 571 Final Exam Answers UpdatedDocument5 pagesMKT 571 Final Exam Answers UpdatedRogue Phoenix100% (4)
- Paper-2 The Government and The Economy (Macroeconomics) Book Chapter (25 To 34) Macroeconomics ObjectiveDocument39 pagesPaper-2 The Government and The Economy (Macroeconomics) Book Chapter (25 To 34) Macroeconomics ObjectiveSharif HossainNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument43 pagesEconomicsAbhishek D. KumarNo ratings yet
- Industrial-Marketing MBADocument111 pagesIndustrial-Marketing MBAGaurav S Jadhav100% (1)
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument62 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysishanaNo ratings yet
- Economical EnvironmentDocument10 pagesEconomical EnvironmentHedayat Ullah100% (1)
- EbayDocument81 pagesEbayJohnny ChanNo ratings yet
- Fashion CycleDocument26 pagesFashion CycleAjinder Deol100% (1)